Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Antibiotics - Classification & Mode of Action PDF
Hochgeladen von
tarun paulOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Antibiotics - Classification & Mode of Action PDF
Hochgeladen von
tarun paulCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
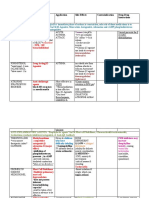
INFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICS
Following is the list of antibiotics, sorted by class. The highest division is between bactericidal antibiotics and bacteriostatic antibiotics.
Bactericidals kill bacteria directly where bacteriostatics prevent them from dividing. However, these classifications are based on laboratory
behavior; in practice, both of these are capable of ending a bacterial infection.
Antibiotics by class
Mechanism of
Generic name Brand names Common uses[2] Possible side effects[2]
action
Aminoglycosides
Amikacin Amikin Binding to the
Gentamicin Garamycin bacterial 30S
ribosomal subunit
Kanamycin Kantrex
Infections caused by Gram- (some work by
Neomycin Neo-Fradin[3] negative bacteria, such as binding to the 50S
Netilmicin Netromycin Escherichia coli and Hearing loss subunit), inhibiting
Tobramycin Nebcin Klebsiella particularly Vertigo the translocation of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. the peptidyl-tRNA
Effective against Aerobic
Kidney damage
from the A-site to the
bacteria (not P-site and also
obligate/facultative causing misreading
Paromomycin Humatin anaerobes) and tularemia. of mRNA, leaving the
bacterium unable to
synthesize proteins
vital to its growth.
Spectinomycin Trobicin Gonorrhea
Ansamycins
Geldanamycin Experimental, as antitumor
Herbimycin antibiotics
Traveler's diarrhea caused
Rifaximin Xifaxan
by E. coli
Carbacephem
prevents bacterial
cell division by
Loracarbef Lorabid Discontinued
inhibiting cell wall
synthesis.
Carbapenems
Ertapenem Invanz Bactericidal for both Gram- Gastrointestinal upset and
Doripenem Doribax positive and Gram-negative diarrhea
organisms and therefore Nausea
Imipenem/Cilastatin Primaxin
useful for empiric broad- Seizures Inhibition of cell wall
spectrum antibacterial synthesis
coverage. (Note MRSA
Headache
Meropenem Merrem Rash and allergic reactions
resistance to this class.)
Cephalosporins (First generation)
Cefadroxil Duricef Gastrointestinal upset and Same mode of action
Cefazolin Ancef diarrhea as other beta-lactam
Keflin Good coverage against Gram Nausea (if alcohol taken antibiotics: disrupt
Cefalotin or Cefalothin positive infections. concurrently) the synthesis of the
(discontinued)
Allergic reactions peptidoglycan layer
Cefalexin Keflex of bacterial cell walls.
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 1
Cephalosporins (Second generation)
Cefaclor Distaclor
Cefamandole
Mandol Gastrointestinal upset and Same mode of action
(discontinued) diarrhea as other beta-lactam
Less gram positive cover, Nausea (if alcohol taken
Mefoxin antibiotics: disrupt
Cefoxitin improved gram negative concurrently)
(discontinued) the synthesis of the
cover.
Cefprozil Cefzil Allergic reactions peptidoglycan layer
of bacterial cell walls.
Ceftin, Zinnat
Cefuroxime
(UK)
Cephalosporins (Third generation)
Cefixime Suprax
Cefdinir Omnicef, Cefdiel
Cefditoren Spectracef
Cefobid Gastrointestinal upset and Same mode of action
Cefoperazone
(discontinued) Improved coverage of Gram diarrhea as other beta-lactam
Cefotaxime Claforan negative organisms, except Nausea (if alcohol taken antibiotics: disrupt
Cefpodoxime Vantin Pseudomonas. Reduced concurrently) the synthesis of the
Ceftazidime Fortaz Gram positive cover. Allergic reactions peptidoglycan layer
of bacterial cell walls.
Ceftibuten Cedax
Cefizox
Ceftizoxime
(discontinued)
Ceftriaxone Rocephin
Cephalosporins (Fourth generation)
Gastrointestinal upset and Same mode of action
diarrhea as other beta-lactam
Covers pseudomonal Nausea (if alcohol taken antibiotics: disrupt
Cefepime Maxipime concurrently)
infections. the synthesis of the
Allergic reactions peptidoglycan layer
of bacterial cell walls.
Cephalosporins (Fifth generation)
Same mode of action
Gastrointestinal upset and as other beta-lactam
diarrhea antibiotics: disrupt
Ceftaroline fosamil Teflaro Used to treat MRSA
Allergic reaction the synthesis of the
peptidoglycan layer
of bacterial cell walls.
Gastrointestinal upset and Same mode of action
diarrhea as other beta-lactam
Nausea (if alcohol taken antibiotics: disrupt
Ceftobiprole Zeftera Used to treat MRSA concurrently) the synthesis of the
Allergic reactions peptidoglycan layer
of bacterial cell walls.
Glycopeptides
Teicoplanin Targocid (UK) Active against aerobic and inhibiting
Vancomycin Vancocin anaerobic Gram positive peptidoglycan
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 2
bacteria including MRSA; synthesis
Vancomycin is used orally
Telavancin Vibativ
for the treatment of C.
difficile
Lincosamides
Clindamycin Cleocin Serious staph-, pneumo-,
Bind to 50S subunit
and streptococcal infections
of bacterial
in penicillin-allergic Possible C. difficile-related
ribosomal RNA
Lincomycin Lincocin patients, also anaerobic pseudomembranous enterocolitis
thereby inhibiting
infections; clindamycin
protein synthesis
topically for acne
Lipopeptide
Bind to the
membrane and cause
rapid depolarization,
resulting in a loss of
Daptomycin Cubicin Gram-positive organisms
membrane potential
leading to inhibition
of protein, DNA and
RNA synthesis
Macrolides
Zithromax,
Azithromycin Sumamed,
Xithrone
Nausea, vomiting, and
Clarithromycin Biaxin Streptococcal infections, inhibition of bacterial
diarrhea (especially at
syphilis, upper respiratory protein biosynthesis
Dynabac higher doses)
Dirithromycin tract infections, lower by binding reversibly
(discontinued) Prolonged QT interval to the subunit 50S of
respiratory tract infections, (especially erythromycin)
Erythocin, mycoplasmal infections, the bacterial
Erythromycin Jaundice
Erythroped Lyme disease ribosome, thereby
Roxithromycin inhibiting
translocation of
Tao
Troleandomycin peptidyl tRNA.
(discontinued)
Telithromycin Ketek Pneumonia Visual Disturbance, Liver Toxicity.[4]
Spiramycin Rovamycine Mouth infections
Monobactams
Same mode of action
as other beta-lactam
antibiotics: disrupt
Aztreonam Azactam
the synthesis of the
peptidoglycan layer
of bacterial cell walls.
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 3
Nitrofurans
Bacterial or protozoal
Furazolidone Furoxone
diarrhea or enteritis
Macrodantin,
Nitrofurantoin Urinary tract infections
Macrobid
Oxazolidonones
Thrombocytopenia
Linezolid Zyvox VRSA Peripheral neuropathy
Phase II clinical Protein synthesis
Posizolid inhibitor; prevents
trials
the initiation step
Phase II clinical
Radezolid
trials
Phase II clinical
Torezolid
trials
Penicillins
Amoxicillin Novamox, Amoxil
Principen
Ampicillin
(discontinued)
Azlocillin
Geocillin
Carbenicillin
(discontinued)
Tegopen
Cloxacillin
(discontinued)
Dynapen
Dicloxacillin
(discontinued)
Floxapen (Sold to
European
Flucloxacillin
generics Actavis Gastrointestinal upset and
Group) diarrhea Same mode of action
Mezlin Wide range of infections; Allergy with serious as other beta-lactam
Mezlocillin penicillin used for antibiotics: disrupt
(discontinued) anaphylactic reactions
streptococcal infections, the synthesis of the
Staphcillin syphilis, and Lyme disease
Brain and kidney damage
peptidoglycan layer
Methicillin (rare)
(discontinued) of bacterial cell walls.
Unipen
Nafcillin
(discontinued)
Prostaphlin
Oxacillin
(discontinued)
Pentids
Penicillin G
(discontinued)
Veetids (Pen-Vee-
Penicillin V
K) (discontinued)
Pipracil
Piperacillin
(discontinued)
Penicillin G Pfizerpen
Negaban (UK)
Temocillin
(discontinued)
Ticar
Ticarcillin
(discontinued)
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 4
Penicillin combinations
Amoxicillin/clavulanate Augmentin The second
Ampicillin/sulbactam Unasyn component prevents
bacterial resistance
Piperacillin/tazobactam Zosyn
to the first
Ticarcillin/clavulanate Timentin component
Polypeptides
Inhibits isoprenyl
pyrophosphate, a
molecule that carries
the building blocks of
Bacitracin
the peptidoglycan
bacterial cell wall
outside of the inner
membrane [5]
Colistin Coly-Mycin-S Eye, ear or bladder Interact with the
infections; usually applied gram negative
directly to the eye or bacterial outer
inhaled into the lungs; membrane and
rarely given by injection, cytoplasmic
Kidney and nerve damage (when membrane. It
although the use of
given by injection) displaces bacterial
intravenous colistin is
experiencing a resurgence counter ions, which
due to the emergence of destabilizes the outer
multi drug resistant membrane. They act
Polymyxin B organisms. like a detergent
against the
cytoplasmic
membrane, which
alters its
permeability.
Polymyxin B and E
are bactericidal even
in an isosmotic
solution.
Quinolones
Cipro, Ciproxin,
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprobay
Enoxacin Penetrex
Urinary tract infections,
Gatifloxacin Tequin
bacterial prostatitis, inhibit the bacterial
Levofloxacin Levaquin community-acquired DNA gyrase or the
Lomefloxacin Maxaquin pneumonia, bacterial Nausea (rare), irreversible damage topoisomerase IV
Moxifloxacin Avelox diarrhea, mycoplasmal to central nervous system enzyme, thereby
infections, gonorrhea (uncommon), tendinosis (rare) inhibiting DNA
Nalidixic acid NegGram
Norfloxacin Noroxin replication and
transcription.
Ofloxacin Floxin, Ocuflox
Trovafloxacin Trovan Withdrawn
Grepafloxacin Raxar Withdrawn
Sparfloxacin Zagam Withdrawn
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 5
Temafloxacin Omniflox Withdrawn
Sulfonamides
Mafenide Sulfamylon Folate synthesis
Sulfonamidochrysoidine inhibition. They are
Prontosil competitive
(archaic)
inhibitors of the
Sulamyd, Bleph-
Sulfacetamide enzyme
10
dihydropteroate
Sulfadiazine Micro-Sulfon Nausea, vomiting, and
synthetase, DHPS.
diarrhea
Silver sulfadiazine Silvadene DHPS catalyses the
Urinary tract infections Allergy (including skin conversion of PABA
Sulfamethizole Thiosulfil Forte rashes)
(except sulfacetamide, used (para-
Sulfamethoxazole Gantanol for eye infections, and Crystals in urine aminobenzoate) to
Sulfanilimide (archaic) mafenide and silver Kidney failure dihydropteroate, a
Sulfasalazine Azulfidine sulfadiazine, used topically Decrease in white blood key step in folate
for burns) cell count synthesis. Folate is
Sulfisoxazole Gantrisin
Sensitivity to sunlight necessary for the cell
to synthesize nucleic
acids (nucleic acids
Trimethoprim- are essential building
Sulfamethoxazole (Co- Bactrim, Septra blocks of DNA and
trimoxazole) (TMP-SMX) RNA), and in its
absence cells will be
unable to divide.
Tetracyclines
Demeclocycline Declomycin Gastrointestinal upset
Doxycycline Vibramycin Sensitivity to sunlight inhibiting the binding
Syphilis, chlamydial Potential toxicity to mother
Minocycline Minocin of aminoacyl-tRNA to
infections, Lyme disease, and fetus during pregnancy
Oxytetracycline Terramycin the mRNA-ribosome
mycoplasmal infections,
acne rickettsial infections,
Enamel hypoplasia complex. They do so
(staining of teeth; mainly by binding to
*malaria *Note: Malaria is
Sumycin, potentially permanent) the 30S ribosomal
caused by a protist and not
Tetracycline Achromycin V, transient depression of subunit in the mRNA
a bacterium.
Steclin bone growth translation complex.
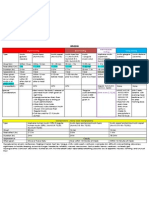
Drugs against mycobacteria
Clofazimine Lamprene Antileprotic
Dapsone Avlosulfon Antileprotic
Capreomycin Capastat Antituberculosis
Antituberculosis, urinary
Cycloserine Seromycin
tract infections
Ethambutol Myambutol Antituberculosis
Inhibits peptide
Ethionamide Trecator Antituberculosis
synthesis
Isoniazid I.N.H. Antituberculosis
Pyrazinamide Aldinamide Antituberculosis
Binds to the β
Rifadin, mostly Gram-positive and Reddish-orange sweat, tears, and subunit of RNA
Rifampicin (Rifampin in US)
Rimactane mycobacteria urine polymerase to inhibit
transcription
Mycobacterium avium
Rifabutin Mycobutin rash, discolored urine, GI symptoms
complex
Rifapentine Priftin Antituberculosis
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 6
As other
Streptomycin Antituberculosis Neurotoxicity, ototoxicity
aminoglycosides
Others
Spirochaetal infections
Arsphenamine Salvarsan
(obsolete)
meningitis, MRSA, topical Inhibits bacterial
use, or for low cost internal protein synthesis by
Chloramphenicol Chloromycetin treatment. Historic: typhus, Rarely: aplastic anemia. binding to the 50S
cholera. gram negative, subunit of the
gram positive, anaerobes ribosome
Inactivates
enolpyruvyl
Fosfomycin Monurol Acute cystitis in women transferase, thereby
blocking cell wall
synthesis
Fusidic acid Fucidin
Produces toxic free
radicals which
disrupt DNA and
Infections caused by proteins. This non-
Discolored urine, headache, metallic
anaerobic bacteria; also specific mechanism
Metronidazole Flagyl taste, nausea ; alcohol is
amoebiasis, trichomoniasis, is responsible for its
contraindicated
Giardiasis activity against a
variety of bacteria,
amoebae, and
protozoa.
Inhibits isoleucine t-
RNA synthetase
Ointment for impetigo,
Mupirocin Bactroban (IleRS) causing
cream for infected cuts
inhibition of protein
synthesis
Platensimycin
Quinupristin/Dalfopristin Synercid
A chloramphenicol
analog. May inhibit
Gram-negative, Gram-
bacterial protein
Thiamphenicol positive, anaerobes. widely Lacks known anemic side-effects.
synthesis by binding
used in veterinary medicine.
to the 50S subunit of
the ribosome
Tigecycline Tigacyl
upset stomach, bitter taste, and
Tinidazole Tindamax Fasigyn protozoan infections
itchiness
Proloprim,
Trimethoprim Urinary Tract Infections
Trimpex
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 7
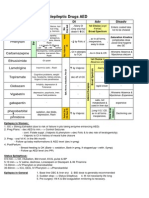
1st generation ( Quinolones)
cinoxacin (Cinobac) (Removed from clinical use) [61]
flumequine (Flubactin) (Genotoxic carcinogen)(Veterinary use)
nalidixic acid (NegGam, Wintomylon)[61] (Genotoxic carcinogen)
oxolinic acid (Uroxin) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
piromidic acid (Panacid) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
pipemidic acid (Dolcol) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
rosoxacin (Eradacil) (Restricted use, currently unavailable in the United States)
2nd generation ( Quinolones)
The 2nd generation class is sometimes subdivided into "Class 1" and "Class 2".[62]
ciprofloxacin (Ciprobay, Cipro, Ciproxin)[61][63]
enoxacin (Enroxil, Penetrex)[61] (Removed from clinical use)
fleroxacin (Megalone, Roquinol) (Removed from clinical use)
lomefloxacin (Maxaquin)[61](Discontinued in the United States)
nadifloxacin (Acuatim, Nadoxin, Nadixa) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
norfloxacin (Lexinor, Noroxin, Quinabic, Janacin)[61](restricted use)[64]
ofloxacin (Floxin, Oxaldin, Tarivid)[61] (Discontinued in the United States)
pefloxacin (Peflacine) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
rufloxacin (Uroflox) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
3rd generation ( Quinolones)
Unlike the first and second generation, the third generation is active against streptococci. [62]
balofloxacin (Baloxin) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
gatifloxacin (Tequin) (Zymar) (removed from clinical use)[65] Sometimes reported as 4th generation.[63][66]
grepafloxacin (Raxar) (Removed from clinical use)
levofloxacin (Cravit, Levaquin)[61][63]
moxifloxacin (Avelox,Vigamox)[61](restricted use).[67] Sometimes reported as 4th generation.[63][68]
pazufloxacin (Pasil, Pazucross) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
sparfloxacin (Zagam)[61](restricted use),[69]
temafloxacin (Omniflox) (Removed from clinical use)[70]
tosufloxacin (Ozex, Tosacin) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
4th generation ( Quinolones)
clinafloxacin [63](Currently unavailable in the United States)
gemifloxacin (Factive)
sitafloxacin (Gracevit) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
trovafloxacin (Trovan) (Removed from clinical use)[61][63]
prulifloxacin (Quisnon) (Currently unavailable in the United States)
In development ( Quinolones)
garenoxacin (Geninax)(Application withdrawn due to toxicity issues)
ecinofloxacin[71]
delafloxacin
List of sulfonamides
Antibiotics / Dihydropteroate synthetase inhibitors
Short-acting
Sulfaisodimidine
Sulfanilamides
Intermediate-acting
Sulfadiazine
Sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
Long-acting
Sulfadimethoxine
Sulfamethoxypyridazine (SMP)
Ungrouped
Sulfacetamide
Sulfadoxine
Dr. Jaydip Mulik ( M.V.Sc. DCT, MBA) Page 8
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mu 002Dokument10 SeitenMu 002chandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Body Receptors PDFDokument1 SeiteDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- (OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Dokument16 Seiten(OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Yavuz DanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Meningitis TheoryDokument3 SeitenConcept Map Meningitis TheoryMia AuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDokument6 SeitenMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Codiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Dokument1 SeiteCodiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Kristi WrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsDokument3 SeitenDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Dokument40 SeitenAntibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Moses MberwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onco PharmacologyDokument9 SeitenOnco Pharmacologyarn0ld21Noch keine Bewertungen
- SARP (Skin Anesthesia Radiology Psychiatry) Review 2010Dokument4 SeitenSARP (Skin Anesthesia Radiology Psychiatry) Review 2010QworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtropineDokument4 SeitenAtropinePark EyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Calorie MalnutritionDokument6 SeitenProtein Calorie MalnutritionfirdakusumaputriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Drugs Used in O.S. Common Drug Interactions in O.S. Practice Oral SurgeryDokument52 SeitenEmergency Drugs Used in O.S. Common Drug Interactions in O.S. Practice Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetDokument1 SeitePharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetPattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary AntibioticsDokument2 SeitenAntibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary Antibioticsgalihja100% (1)
- Pharma GI CardsDokument16 SeitenPharma GI CardsDoctorsHangout.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDokument1 SeiteCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Dokument1 SeiteLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Adrianne BazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famotidine (Pepcid)Dokument1 SeiteFamotidine (Pepcid)Adrianne BazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Dosage of Antimicrobial Agents in Veterinary MedicineDokument24 SeitenClassification and Dosage of Antimicrobial Agents in Veterinary MedicineSunil0% (1)
- Toxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiDokument59 SeitenToxicology: by Group 4 2018/2019 Tan Geok Eng Reena DewiTan Geok EngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study GuideDokument3 SeitenDrug Study GuideNicole CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDokument14 SeitenPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med CardsDokument4 SeitenMed CardsSonia FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Medications UsedDokument3 SeitenCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardDokument2 SeitenDrug CardHannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AdvilDokument1 SeiteDrug AdvilDiana Laura LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System: Antiasthmatic Drugs Cardiac GlycosidesDokument4 SeitenRespiratory System: Antiasthmatic Drugs Cardiac GlycosidesNurse HoomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Dokument16 SeitenOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- Opioids PDFDokument2 SeitenOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinDokument1 SeiteGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinChristopher LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Animal BitesDokument39 SeitenApproach To Animal BitesNetii FarhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracranial Hypertension or Increased ICPDokument11 SeitenIntracranial Hypertension or Increased ICPRomina Irish MatutinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abx FinalDokument3 SeitenAbx Finalyanks1120Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDokument1 SeiteAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Noch keine Bewertungen
- ClindamycinDokument3 SeitenClindamycinShaira TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDokument16 SeitenRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- V V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageDokument1 SeiteV V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageCyndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Questionnaire CandidateDokument5 SeitenHealth Questionnaire CandidateSaudia Arabia JobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsDokument3 SeitenLecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NERVOUS MnemonicsDokument4 SeitenNERVOUS MnemonicsHimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardsDokument3 SeitenDrug CardsDave HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobic Drug CardDokument1 SeiteMobic Drug CardSheri490Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1onDokument4 SeitenDysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1ontantalizin marieNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Study Pharmacology Checklist Cheat SheetDokument4 SeitenHow To Study Pharmacology Checklist Cheat SheetJOSHUA DICHOSONoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulin Chart 05032012 PDFDokument1 SeiteInsulin Chart 05032012 PDFTiffany CrittendenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardsDokument11 SeitenDrug CardsLizShermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncology Lectures 1 7 DR - FerrolinoDokument24 SeitenOncology Lectures 1 7 DR - FerrolinoMiguel Cuevas DolotNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Dokument5 SeitenSNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Whitney Krabbenhoft100% (1)
- Drug KenalogDokument1 SeiteDrug KenalogSrkocherNoch keine Bewertungen
- VasopressinDokument2 SeitenVasopressinKim LompotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sepsis and Septic Shock: Elise Mittleman Boller, - Cynthia M. OttoDokument9 SeitenSepsis and Septic Shock: Elise Mittleman Boller, - Cynthia M. OttoIan SabogalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport of Critically Ill Adults 2011Dokument1 SeiteTransport of Critically Ill Adults 2011velocity25Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Kids Are Alright Pediatric Trauma PearlsDokument21 SeitenThe Kids Are Alright Pediatric Trauma PearlsDaniel Torres CutivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunomodulation in Domestic Food Animals: Advances in Veterinary Science and Comparative MedicineVon EverandImmunomodulation in Domestic Food Animals: Advances in Veterinary Science and Comparative MedicineBernald CharleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Dokument2 SeitenAntiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Linlin100% (1)
- Mishba +pharmacology + Tapan ShahDokument232 SeitenMishba +pharmacology + Tapan ShahRaushan BlakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyVon EverandThe Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyLawrence ChakrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics by Class: Escherichia ColiDokument8 SeitenAntibiotics by Class: Escherichia ColiCremona ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics ListDokument14 SeitenAntibiotics ListBrenda LiawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Livestock MapsDokument6 SeitenLivestock Mapstarun paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- State / U.T. Wise Cross Bred Cattle DensityDokument12 SeitenState / U.T. Wise Cross Bred Cattle Densitytarun paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brill Formulation Manual 1Dokument5 SeitenBrill Formulation Manual 1tarun paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hy-Line Brown Layer Management Guide PDFDokument32 SeitenHy-Line Brown Layer Management Guide PDFtarun paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- AchalasiaDokument40 SeitenAchalasiaedo andriyanto100% (1)
- Panic StationsDokument9 SeitenPanic Stationsdaneen naqviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Module 1Dokument60 SeitenLecture Notes Module 1Bommineni Lohitha Chowdary 22213957101Noch keine Bewertungen
- ScoliosisDokument9 SeitenScoliosisCristina CarterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy: Original ArticleDokument7 SeitenJournal of Infection and Chemotherapy: Original ArticleNoNWONoch keine Bewertungen
- Act For Insomnia Act I by DR Guy Meadows The Sleep SchoolDokument7 SeitenAct For Insomnia Act I by DR Guy Meadows The Sleep SchoolDharmendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study of Bronchial Asthma in Acute ExacerbationDokument16 SeitenCase Study of Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbationdextroid1290% (29)
- 50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know NowDokument29 Seiten50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know Nowtandz100% (19)
- Memory and HypnosisDokument7 SeitenMemory and HypnosisshadowraithsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trephination For AcuteDokument3 SeitenTrephination For AcuteDr.Ibrahim Al-QwizanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNB-Minimal Access Surgery: Competency Based Training ProgrammeDokument31 SeitenFNB-Minimal Access Surgery: Competency Based Training ProgrammeAMBUJ KUMAR SONINoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma ProteinsDokument18 SeitenPlasma ProteinsTARIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desigen of Wastewater Treatment PlantDokument68 SeitenDesigen of Wastewater Treatment PlantNeeraj kabirpanthi100% (5)
- The Learning Curve For Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy PDFDokument5 SeitenThe Learning Curve For Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy PDFIgor CemortanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument16 SeitenEnglishEugenius Divine LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Episiotomy and SuturingDokument5 SeitenEpisiotomy and SuturingAnila SajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Massage ContractDokument2 SeitenCorporate Massage ContractCiorîcă Denisa TerapeutNoch keine Bewertungen
- FlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...Dokument12 SeitenFlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...andrelbportoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline and Treatment Algorithm For Burn InjuriesDokument12 SeitenGuideline and Treatment Algorithm For Burn InjuriesGrnitrv 22Noch keine Bewertungen
- DR Mahdavi - Mechanical VentilationDokument28 SeitenDR Mahdavi - Mechanical VentilationHimanshu ShrimaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Curriculum For Hemodialysis Technician Forth EditionDokument612 SeitenCore Curriculum For Hemodialysis Technician Forth EditionRajiv Medanki60% (5)
- Effect of Pharmacist Intervention and Initiation of Home Blood Pressure Monitoring in Patients With Uncontrolled HypertensionDokument6 SeitenEffect of Pharmacist Intervention and Initiation of Home Blood Pressure Monitoring in Patients With Uncontrolled HypertensionPathiwat M ChantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buku BacaanDokument329 SeitenBuku BacaanNurhasni FebrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialysis Nurse Responsibilities and DutiesDokument22 SeitenDialysis Nurse Responsibilities and DutiesWyn Agustin0% (1)
- Automated Drain CleanerDokument43 SeitenAutomated Drain Cleanervrinda hebbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obsessive Compulsive DisorderDokument14 SeitenObsessive Compulsive Disorderfrancis00090100% (1)
- SC Writ of Continuing Mandamus Case MMDA Et Al. vs. Concerned Residents of Manila Bay Et Al. GR Nos. 171947 48 2 15 2011Dokument25 SeitenSC Writ of Continuing Mandamus Case MMDA Et Al. vs. Concerned Residents of Manila Bay Et Al. GR Nos. 171947 48 2 15 2011Mary Grace Dionisio-RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical AbbreviationsDokument2 SeitenSurgical AbbreviationsRona PieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapy ProblemDokument19 SeitenDrug Therapy ProblemAulia NorfiantikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dentine HypersensitivityDokument32 SeitenDentine Hypersensitivityitdoc100% (1)