Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Kode Transistor: Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) Pro-Electron Code
Hochgeladen von
Padim Nugraha0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
78 Ansichten1 SeiteKode Transistor
Originaltitel
Kode Transistor
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenKode Transistor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
78 Ansichten1 SeiteKode Transistor: Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) Pro-Electron Code
Hochgeladen von
Padim NugrahaKode Transistor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Kode Transistor
April 3rd, 2009 Info Servis TV 8 comments
< ![endif]-->< ![endif]-->
< ! /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-
tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-
parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0cm 5.4pt 0cm 5.4pt; mso-para-margin:0cm; mso-para-
margin-bottom:.0001pt; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:10.0pt; font-
family:"Times New Roman"; mso-ansi-language:#0400; mso-fareast-language:#0400;
mso-bidi-language:#0400;} -->
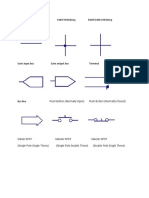
Japanese Industrial Standard
Pro-electron code
(JIS)
The first letter indicates the material:
A = Ge
SA: PNP HF transistor
B = Si
SB: PNP AF transistor
C = GaAs
SC: NPN HF transistor
R = compound materials.
SD: NPN AF transistor
(Most common type is B.)
SE: Diodes
SF: Thyristors
The second letter indicates the device
SG: Gunn devices
application:
SH: UJT
A: Diode RF
SJ: P-channel FET/MOSFET
B: Variac
SK: N-channel FET/MOSFET
C: transistor, AF, small signal
SM: Triac
D: transistor, AF, power
SQ: LED
E: Tunnel diode
SR: Rectifier
F: transistor, HF, small signal
SS: Signal diodes
K: Hall effect device
ST: Avalanche diodes
L: Transistor, HF, power
SV: Varicaps
N: Optocoupler
SZ: Zener diodes
P: Radiation sensitive device
Q: Radiation producing device
A = low gain
R: Thyristor, Low power
B = medium gain
T: Thyristor, Power
C = high gain
U: Transistor, power, switching
No suffix = ungrouped (any gain)
Y: Rectifier
Z: Zener, or voltage regulator diode
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Transistor and Diode DataDokument3 SeitenTransistor and Diode Datajohn mesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor InfoDokument3 SeitenTransistor InfoErantha SampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Symbols PDFDokument8 SeitenElectronics Symbols PDFDayanand Gowda KrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic MaterialsDokument14 SeitenElectronic MaterialsYzle Marie BalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode and Transistor NumberingDokument3 SeitenDiode and Transistor NumberingMohamedQassemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Profile - Electrotrack Electronics Solutions Private LimitedDokument4 SeitenCompany Profile - Electrotrack Electronics Solutions Private Limitedbdm.mumbaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics ComponentsDokument51 SeitenElectronics ComponentsMarlon AranasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kabel Kabel Terhubung Kabel Tidak TerhubungDokument9 SeitenKabel Kabel Terhubung Kabel Tidak Terhubungrohadi adiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEDEC Coding System Table For Diodes and TransistorsDokument3 SeitenJEDEC Coding System Table For Diodes and TransistorsSynworks Development Group100% (1)
- Color Codes and Irregular Marking-SampleDokument23 SeitenColor Codes and Irregular Marking-Samplemahrez laabidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color Codes and Irregular MarkingDokument354 SeitenColor Codes and Irregular MarkingOscarGonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical SymbolsDokument18 SeitenElectrical SymbolsIdzard Morais100% (1)
- EE 391 PSpiceDokument13 SeitenEE 391 PSpicePinaki BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCHEMATIC CodesDokument5 SeitenSCHEMATIC CodesNOFAL OgluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode ChartDokument1 SeiteDiode ChartCesar Vargas BenitezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing TransistorDokument15 SeitenTesting TransistorElarrio Arel Perez ToribioNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJT Mosfet IgbtDokument48 SeitenBJT Mosfet IgbtJeanmark NeilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elektronika Daya Dan PenerapannyaDokument30 SeitenElektronika Daya Dan PenerapannyaMuhammad AfdalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Transistor MarkingsDokument2 SeitenReading Transistor Markingsthomas.vivet6396Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolytic Capacitor - C: FunctionDokument9 SeitenElectrolytic Capacitor - C: FunctionekumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xpo CTDokument9 SeitenXpo CTBambang GastomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensor Turck TapaDokument2 SeitenSensor Turck Tapaluizbuche33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 MidDokument49 SeitenModule 1 MidZylah NorberteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Basic Circuit Theory: Graphics Used With Permission From AspencoreDokument47 SeitenIntroduction and Basic Circuit Theory: Graphics Used With Permission From AspencoreManigandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistors Sources Batteries Capacitors: CrystalsDokument8 SeitenResistors Sources Batteries Capacitors: CrystalsXu Binh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diodes and Applications - AnsDokument167 SeitenDiodes and Applications - AnsFrances RaphaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Assignment 7Dokument3 SeitenLab Assignment 7sraavanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year PspiceDokument28 Seiten2nd Year PspiceEsayas AfewerkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillators, Rev ADokument20 SeitenOscillators, Rev ASATVIK AGARWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Effect TransistorDokument11 SeitenField Effect TransistorAnurag YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Communication: ResearchDokument7 SeitenPrinciple of Communication: ResearchJony SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Transistors Data Book 1997Dokument23 SeitenRF Transistors Data Book 1997Marcos QuequeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistors and AmplifiersDokument285 SeitenTransistors and AmplifiersCris Diane G. DatingginooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Lab 2019Dokument37 SeitenElectronics Lab 2019Noor HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ham Cram: Amateur Radio Technician License Review CourseDokument120 SeitenHam Cram: Amateur Radio Technician License Review CourseNew UserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbols in Edc LabDokument13 SeitenSymbols in Edc LabmkrishnadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMD CatalogDokument80 SeitenSMD Catalogpbradaric91% (11)
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsVon EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Von EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Von EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualVon EverandInstrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Newnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket Book: Revised by the Editorial Staff of Electronics Today InternationalVon EverandNewnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket Book: Revised by the Editorial Staff of Electronics Today InternationalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Von EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Von EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesVon EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsVon EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alarm ListaDokument4 SeitenAlarm ListaNhím BiểnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELS ONE39 EL+Retarder-Prover 208-60 US1 GIACDokument11 SeitenELS ONE39 EL+Retarder-Prover 208-60 US1 GIACFreddy MayorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Traffic Light Control SystemDokument4 SeitenAutomatic Traffic Light Control SystemRajaMandapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delta M30A / M50ADokument4 SeitenDelta M30A / M50ASunil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Habilis 8Dokument6 SeitenTechnical Habilis 8Arturo TuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Mach 380, 400, 500, 700 - Mounting ManualDokument30 SeitenDr. Mach 380, 400, 500, 700 - Mounting ManualOmer KurtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robonic II Transfer SwitchDokument14 SeitenRobonic II Transfer SwitchJod CadieuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 555 Delay OFF Timer Circuit For Delay Before Turn OFF Circuit PDFDokument11 Seiten555 Delay OFF Timer Circuit For Delay Before Turn OFF Circuit PDFdhanysiregar100% (1)
- 1897 Edition of The National Electrical CodeDokument58 Seiten1897 Edition of The National Electrical CodevytoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phu Kien Khuon Song Ngu - 20190921Dokument3 SeitenPhu Kien Khuon Song Ngu - 20190921Loc NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation Sheets NZS 3604Dokument5 SeitenCalculation Sheets NZS 3604TuroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 314 Conduit Layout Lecture 1 PDFDokument18 SeitenEEE 314 Conduit Layout Lecture 1 PDFAnonymous YGLKp0kK100% (1)
- ANSI C82.4-2002 For Lamp Ballasts. Ballasts High-Intensity-Discharge and Low-Pressure Sodium Lamps (Multiple-Supply Type)Dokument20 SeitenANSI C82.4-2002 For Lamp Ballasts. Ballasts High-Intensity-Discharge and Low-Pressure Sodium Lamps (Multiple-Supply Type)Jose Luis Perez RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Engr. Jimmy Carter B. Nilo, RECE August 2018Dokument17 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits: Engr. Jimmy Carter B. Nilo, RECE August 2018jimmyboyjrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Phase Control of TriacDokument4 SeitenAc Phase Control of Triacjassisc0% (1)
- Teacher Class Group Subject Length Lessons/weekDokument15 SeitenTeacher Class Group Subject Length Lessons/weekNor Rahiyah ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massey FergusonDokument474 SeitenMassey FergusonroadpartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close Exam 8Dokument4 SeitenClose Exam 8sieged_rj3165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protection Relay Inspection ReportDokument37 SeitenProtection Relay Inspection ReportteferayirgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level Gauges & Switches PDFDokument6 SeitenLevel Gauges & Switches PDFsandesh sawateNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument433 SeitenUntitledДмитрий АндрюшкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- 132 Circuit BreakeDokument33 Seiten132 Circuit BreakeSami Ulhaq100% (1)
- Technical Data For Libra Metal Furring Runner PDFDokument2 SeitenTechnical Data For Libra Metal Furring Runner PDForc19Noch keine Bewertungen
- VULKAN Technologies PVT - LTD, PuneDokument7 SeitenVULKAN Technologies PVT - LTD, PuneDattatray GosaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selectable Output Horns, Strobes, and Horn/StrobesDokument4 SeitenSelectable Output Horns, Strobes, and Horn/StrobesCristian ManzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C200 D5e Spec Sheet Open Diesel GeneratorDokument4 SeitenC200 D5e Spec Sheet Open Diesel GeneratorDaniel KrismantoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- FGWilson 400KVA - TGDF7023 PERKINS ENGINEDokument391 SeitenFGWilson 400KVA - TGDF7023 PERKINS ENGINEKornelius David Pattiselanno100% (1)
- 000 P PQP 50001 001 R0aDokument40 Seiten000 P PQP 50001 001 R0aHerwin MaghinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTr3 2000 - 3000 1beDokument4 SeitenFTr3 2000 - 3000 1beAbdellah abdouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfalux High Bay LeafletDokument4 SeitenAlfalux High Bay LeafletShadi AbdelsalamNoch keine Bewertungen