Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
New DOCX Document
Hochgeladen von
Punjabi Football0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten2 Seitennxnxxxx
Originaltitel
New DOCX Document (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldennxnxxxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten2 SeitenNew DOCX Document
Hochgeladen von
Punjabi Footballnxnxxxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Abstract:
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is an important
prognostic indicator of cardiovascular outcomes. It is
used clinically to determine the indication for several
therapeutic interventions. LVEF is most commonly
derived using in-line tools and some manual assessment
by cardiologists from standardized echocardiographic
views. LVEF is typically documented in free-text reports,
and variation in LVEF documentation pose a challenge
for the extraction and utilization of LVEF in
computer-based clinical workflows. To address this
problem, we developed a computerized algorithm to
extract LVEF from echocardiography reports for the
identification of patients having heart failure with
reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) for therapeutic
intervention at a large healthcare system. We processed
echocardiogram reports for 57,158 patients with coded
diagnosis of Heart Failure that visited the healthcare
system over a two-year period. Our algorithm identified
a total of 3910 patients with reduced ejection fraction. Of
the 46,634 echocardiography reports processed, 97%
included a mention of LVEF. Of these reports, 85%
contained numerical ejection fraction values, 9%
contained ranges, and the remaining 6% contained
qualitative descriptions. Overall, 18% of extracted
numerical LVEFs were ≤ 40%. Furthermore, manual
validation for a sample of 339 reports yielded an
accuracy of 1.0. Our study demonstrates that a regular
expression-based approach can accurately extract LVEF
from echocardiograms, and is useful for delineating
heart-failure patients with reduced ejection fraction.
Introduction:
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is an important
prognostic indicator of cardiovascular outcomes [1, 2].
Clinically, it is used to guide the therapeutic pathways
for patients having heart failure [3]. LVEF is estimated
manually by cardiologists during echocardiographic
examinations, and is typically documented in free-text
reports [4]. Variation in LVEF documentation from the
echocardiograms pose a challenge for the extraction and
utilization of LVEF in computer-based clinical
workflows.
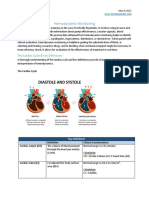
Significance of left ventricle ejection fraction:
During each heartbeat, when the heart contracts, it ejects
blood from the two pumping chambers called ventricles,
and the ventricles refill with blood when the heart relaxes.
The term “ejection fraction” (EF) refers to the percentage
of blood that is pumped out of a filled ventricle with each
heartbeat. A LVEF of 55% or higher is considered
normal under physiologic loading conditions, with an EF
of 50% or lower being considered reduced. Notably, EFs
between 50 and 55% are considered “borderline”
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2018 Article 1066Dokument12 Seiten2018 Article 1066Saif HadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ehf2 13519Dokument10 SeitenEhf2 13519Defriyan RamziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Right Ventricular Function and Pulmonary Pressures On Heart Failure PrognosisDokument7 SeitenEffect of Right Ventricular Function and Pulmonary Pressures On Heart Failure PrognosisMatthew MckenzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mala Goli 2018Dokument9 SeitenMala Goli 2018ErtanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal OmiDokument14 SeitenJurnal OmiYogie YahuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0256 Version 2019Dokument66 Seiten0256 Version 2019vanessa armeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LV Systolic FunctionDokument36 SeitenLV Systolic Functionsruthimeena6891Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument13 SeitenUntitledAnjali G SNoch keine Bewertungen
- English JournalDokument8 SeitenEnglish JournalDebby CinthyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeac123 PDFDokument3 SeitenJeac123 PDFRaquel AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atwater 2020Dokument6 SeitenAtwater 2020Vlada SiricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artigo 16Dokument8 SeitenArtigo 16Gavin TexeirraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Left Atrial Strain As A Predictor of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Heart FailureDokument11 SeitenLeft Atrial Strain As A Predictor of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Heart FailureWirawan PrabowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Cases in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionVon EverandClinical Cases in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionWilliam R. AugerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christersson2022 Article ScreeningForBiomarkersAssociatDokument11 SeitenChristersson2022 Article ScreeningForBiomarkersAssociatS FznsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLMF - ResumenDokument5 SeitenSLMF - ResumenMaría F SLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sepsis Parte 2Dokument12 SeitenSepsis Parte 2Maria AlejandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco DopplerDokument8 SeitenEco DopplerClaudia IsabelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE and CHFDokument9 SeitenPE and CHFKu Li ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejection FractionDokument3 SeitenEjection FractionKhristy AbrielleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jourding VMT Score FixDokument35 SeitenJourding VMT Score FixCarnageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) - Associated Acute Cor Pulmonale and Patent Foramen Ovale: A Multicenter Noninvasive Hemodynamic StudyDokument6 SeitenAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) - Associated Acute Cor Pulmonale and Patent Foramen Ovale: A Multicenter Noninvasive Hemodynamic StudyminiypuntoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0002914922005355 MainDokument11 Seiten1 s2.0 S0002914922005355 MainRamona GhengheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Operative Assessment/ Monitoring: Arif Hussain Demonstrator Anesthesia Ipms-KmuDokument20 SeitenPre-Operative Assessment/ Monitoring: Arif Hussain Demonstrator Anesthesia Ipms-Kmuayub khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrients 14 04051 PDFDokument17 SeitenNutrients 14 04051 PDFArchita AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Critical Care Echocardiography-Driven Approach To Undifferentiated ShockDokument7 SeitenA Critical Care Echocardiography-Driven Approach To Undifferentiated ShockNoel Saúl Argüello SánchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Dan CBFDokument5 SeitenCHF Dan CBFRisky Ilona SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICRJ-Validation of Cornell Product As A Method of Assessing Left Ventricular HypertrophyDokument5 SeitenICRJ-Validation of Cornell Product As A Method of Assessing Left Ventricular Hypertrophysamir raflaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FuDokument10 SeitenDifferences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FueugeniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1414 431X BJMBR 53 7 E9646Dokument16 Seiten1414 431X BJMBR 53 7 E9646leidyalexserraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument52 Seiten2016 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and TreatmentDedy KristoferNoch keine Bewertungen
- CardiovascularDokument37 SeitenCardiovascularapi-19916399Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal HFimpEF - PrediktorDokument9 SeitenJurnal HFimpEF - PrediktorPrana JagannathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article2017ICMBoissier DysfonctionVGSepticshockDokument10 SeitenArticle2017ICMBoissier DysfonctionVGSepticshockenriquegarciagalianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New-Onset Supraventricular Arrhythmia During Septic Shock: Prevalence, Risk Factors and PrognosisDokument8 SeitenNew-Onset Supraventricular Arrhythmia During Septic Shock: Prevalence, Risk Factors and PrognosisAhmad FahroziNoch keine Bewertungen
- uCQiPF SdarticleDokument7 SeitenuCQiPF Sdarticlequijybo42Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atm 09 20 1587Dokument14 SeitenAtm 09 20 1587Wina Pertiwi 2003113414Noch keine Bewertungen
- s13089 022 00286 2Dokument11 Seitens13089 022 00286 2Maudiel BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eacvi Recommendations Valvular Regurgitation SummaryDokument34 SeitenEacvi Recommendations Valvular Regurgitation SummaryWilli SotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myocardial Work in Nonobstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Implications For OutcomeDokument8 SeitenMyocardial Work in Nonobstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Implications For Outcomeme1921Noch keine Bewertungen
- 67-Article Text-115-1-10-20171026Dokument5 Seiten67-Article Text-115-1-10-20171026Maria MiripNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jcu 17 127 PDFDokument8 SeitenJcu 17 127 PDFRezkyFYNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1936878X17306174 MainDokument9 Seiten1 s2.0 S1936878X17306174 MainSalma Noor AlmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haemodynamic MonitoringDokument6 SeitenHaemodynamic MonitoringAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Prevalence and Prognosis of Respiratory Muscle WeaDokument7 SeitenPrevalence and Prognosis of Respiratory Muscle WealalopotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Monitoring Pocket CardDokument5 SeitenHemodynamic Monitoring Pocket CardFitz JaminitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain-2010-Eyre-59-62Dokument4 SeitenContin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain-2010-Eyre-59-62deadbysunriseeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Value of A New Speckle Tracking Index Including Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain and Torsion in Patients With Dilated CardiomyopathyDokument8 SeitenThe Value of A New Speckle Tracking Index Including Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain and Torsion in Patients With Dilated Cardiomyopathymarsim92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Decoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonVon EverandDecoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonAfzal SohaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring XXXDokument14 SeitenPrinciples of Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring XXXmarelnozakanitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insufficienze Valvolari ESCDokument34 SeitenInsufficienze Valvolari ESCAFA.BLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Falla Cardiaca Con Fevi Mejorada Es Posible Escapar Del PasadoDokument9 SeitenFalla Cardiaca Con Fevi Mejorada Es Posible Escapar Del PasadoRenzo RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Andrew C. Y. To MBCHB, Allan L. Klein MDDokument14 SeitenRole of Echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Andrew C. Y. To MBCHB, Allan L. Klein MDsarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eacvi Recommendations Valvular Regurgitation Summary PDFDokument34 SeitenEacvi Recommendations Valvular Regurgitation Summary PDFstoicea_katalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey of Shaped-Based Registration and Segmentation Techniques For Cardiac ImagesDokument24 SeitenA Survey of Shaped-Based Registration and Segmentation Techniques For Cardiac ImagesFaiz Zeo XiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Valuable Echocardiographic Indicator For The Optimal Tightness of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery BandingDokument8 SeitenA Valuable Echocardiographic Indicator For The Optimal Tightness of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery BandingRafailiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Strain and Other Echocardiographic Parameters in The Evaluation of Early and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery RevascularizationDokument8 SeitenApplication of Strain and Other Echocardiographic Parameters in The Evaluation of Early and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery RevascularizationSondang JasmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smith 2013 SMIIDokument9 SeitenSmith 2013 SMIIGryseldaGryGryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ehr 254Dokument8 SeitenEhr 254Virginia ZagorniiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bragg Waveguide and Its DescriptionDokument22 SeitenBragg Waveguide and Its DescriptionPratibha Karki RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument16 SeitenChapter 1MulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B2 First Unit 11 Test: Section 1: Vocabulary Section 2: GrammarDokument1 SeiteB2 First Unit 11 Test: Section 1: Vocabulary Section 2: GrammarNatalia KhaletskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocr Graphics Gcse CourseworkDokument6 SeitenOcr Graphics Gcse Courseworkzys0vemap0m3100% (2)
- Persona Core Poster - Creative Companion1 PDFDokument1 SeitePersona Core Poster - Creative Companion1 PDFAdemola OgunlaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Digest: Pedro Elcano and Patricia Elcano Vs - Reginald Hill and Marvin HillDokument5 SeitenCase Digest: Pedro Elcano and Patricia Elcano Vs - Reginald Hill and Marvin Hillshirlyn cuyongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ais Activiy Chapter 5 PDFDokument4 SeitenAis Activiy Chapter 5 PDFAB CloydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Literacy Skills and Self-Efficacy Among Grade-12 - Computer System Servicing (CSS) StudentsDokument25 SeitenComputer Literacy Skills and Self-Efficacy Among Grade-12 - Computer System Servicing (CSS) StudentsNiwre Gumangan AguiwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 - Simulation of HVDC SystemDokument24 SeitenUnit 5 - Simulation of HVDC Systemkarthik60% (10)
- Teaching Philosophy StatementDokument25 SeitenTeaching Philosophy Statementtchrdale27Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of Least Learned Competencies MAPEH7 1st To 3rd QuarterDokument3 SeitenList of Least Learned Competencies MAPEH7 1st To 3rd QuarterMark Dexter MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art 3-6BDokument146 SeitenArt 3-6BCJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Present Simple and Present Continuous Part 2Dokument2 SeitenLesson 4 Present Simple and Present Continuous Part 2DeniseVuoto100% (1)
- Persephone by Julia Donaldson: (A Meadow. Enters Persephone, Picking The Petals of A Daisy.)Dokument10 SeitenPersephone by Julia Donaldson: (A Meadow. Enters Persephone, Picking The Petals of A Daisy.)Dobler Liliana100% (1)
- Chanakya National Law UniversityDokument23 SeitenChanakya National Law Universityshubham kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme Big Cat FactsDokument3 SeitenMark Scheme Big Cat FactsHuyền MyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asher - Bacteria, Inc.Dokument48 SeitenAsher - Bacteria, Inc.Iyemhetep100% (1)
- CH 13 ArqDokument6 SeitenCH 13 Arqneha.senthilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travel Smart: Assignment 1: Project ProposalDokument14 SeitenTravel Smart: Assignment 1: Project ProposalcattytomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Service: P2245m-PorkDokument3 SeitenPublic Service: P2245m-PorkDaniela Ellang ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Bones and Buddhas Contemplation of TH PDFDokument215 SeitenOf Bones and Buddhas Contemplation of TH PDFCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation Research Part F: Andreas Lieberoth, Niels Holm Jensen, Thomas BredahlDokument16 SeitenTransportation Research Part F: Andreas Lieberoth, Niels Holm Jensen, Thomas BredahlSayani MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Psychomotor Profile of Pupils in Early Childhood EducationDokument11 SeitenThe Psychomotor Profile of Pupils in Early Childhood EducationLEINHARTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ryan Brown: Michigan State UniversityDokument2 SeitenRyan Brown: Michigan State UniversitybrownteachesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFDokument2 SeitenExamination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFAntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write An Argumented EssayDokument35 SeitenHow To Write An Argumented EssayFarhad UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenCheat SheetFrancis TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Making and Problem Solving & Managing - Gashaw PDFDokument69 SeitenDecision Making and Problem Solving & Managing - Gashaw PDFKokebu MekonnenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endless Pursuit of Truth: Subalternity and Marginalization in Post-Neorealist Italian FilmDokument206 SeitenThe Endless Pursuit of Truth: Subalternity and Marginalization in Post-Neorealist Italian FilmPaul MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Internet Goldman SachsDokument86 SeitenIndia Internet Goldman SachsTaranjeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen