Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
General Mathematics
Hochgeladen von
Cyril Kate Basilan TabinasCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
General Mathematics
Hochgeladen von
Cyril Kate Basilan TabinasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
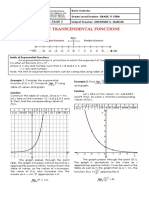
INVERSE FUNCTION LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
- If f is a one-to-one function, then the inverse of f is For x>0, a>1 and a not equal to 1.
denoted by f -1, is the function formed by reversing
logax if and only if x=ay
all the ordered pairs in f thus, f -1 = {y,x} / {x,y} is in f.
The function f(x)=logax is called the logarithmic function
PROPERTIES OF AN INVERSE FUNCTION
with base a.
If the f -1 inverse function exist:
PROPERTIES OF A LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION
-1
1. f is a one-to-one function also f is one-to-one.
Let f(x)=logax; a>0 and a not equal to 1.
2. The domain of f -1 is the range of f
1. The domain is the set of positive real numbers.
-1
3. The range of f is the domain of f.
2. The range is the set of real numbers.
PROPERTIES OF AN INVERSE FUNCTION
3. The x-intercept is at point (1,0) where f(1)=0
The functions f and g are inverse of each other if
4. f(a)=1
f(g(x))=x, for every x is the domain of g and,
5. If 0<a<1, as the value of x increases, the value of y
g(f(x))=x, for every x is the domain of f. decreases.
EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION 6. If a>1, as the value of x decreases, the value of y
increases.
The exponential function f with base a is denoted as
7. The function f is one-to-one, that logax=logay if and
f(x) = ax where a<0, a not equal to 1 and x as any
only if x=y.
real number.
8. The graph of f has vertical asymptote x=0 or the x-axis.
PROPERTIES OF AN EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION
LAWS OF LOGARITHMS
Let f(x) = bx, b>0 & b not equal to 1
logaxy = logax + logay
1. The domain is the set of real numbers (-∞,∞)
loga(x/y) = logax - logay
2. The range is the set of positive real numbers.
logaxr = rlogax
3. If b>0, f is an increasing exponential function, if
0<b<1, f is a decreasing exponential function.
4. The function f passes through the point (0,1) where
f(0)=b0=1
5. The graph approaches but does not reach the axis.
The x-axis is the horizontal asymptote.
LAWS OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION
Let a and b be positive real number where a and b are
not equal to one and x and y be real numbers.
axay = ax+y (a/b)x = ax/bx ax/bx
(ax)y = axy (ax/by) = ax-y
(ab)x = axbx
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grade 11 General MathematicsDokument5 SeitenGrade 11 General Mathematicsjun del rosario78% (9)
- General Mathematics Chapter 1: FunctionsDokument24 SeitenGeneral Mathematics Chapter 1: FunctionsJN Ris100% (4)
- Holy Rosary College of Santa Rosa Laguna, Inc.: Lesson 3 Simple AnnuityDokument5 SeitenHoly Rosary College of Santa Rosa Laguna, Inc.: Lesson 3 Simple AnnuityJohn ClarenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics Chapter 3: One-to-One FunctionsDokument21 SeitenGeneral Mathematics Chapter 3: One-to-One FunctionsJN Ris100% (2)
- General Mathematics Grade 11 First Grading ExamDokument2 SeitenGeneral Mathematics Grade 11 First Grading ExamJeffren P. Miguel100% (3)
- Gen Math Q1 Mod 2Dokument49 SeitenGen Math Q1 Mod 2Joselito Ubaldo100% (1)
- Gen Math Q1 Mod 3Dokument16 SeitenGen Math Q1 Mod 3Joselito Ubaldo100% (2)
- Clmd4ageneralmathematicsshs PDFDokument736 SeitenClmd4ageneralmathematicsshs PDFJermer Tabones89% (9)
- Q1 SHS General Mathematics 11 Module 4Dokument35 SeitenQ1 SHS General Mathematics 11 Module 4Jasmine A. Afinidad75% (4)
- 2nd Quarter Week 3-4Dokument7 Seiten2nd Quarter Week 3-4John Clarence89% (9)
- Exam in Pre-CalculusDokument1 SeiteExam in Pre-CalculusmarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Math - Grade 11 - Q2 Module 9 Stocks and BondsDokument27 SeitenGen Math - Grade 11 - Q2 Module 9 Stocks and BondsErin Bernardino100% (1)
- Grade 11 General Math - TeacherDokument508 SeitenGrade 11 General Math - TeacherA.M.A100% (2)
- Module 3 Gen MathDokument15 SeitenModule 3 Gen MathGrant Hill AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Math First QuarterDokument199 SeitenGen Math First QuarterRolly Dominguez Balo100% (1)
- GenMath Q1-Mod4-EXPONENTIAL-FUNCTIONS-v5Dokument43 SeitenGenMath Q1-Mod4-EXPONENTIAL-FUNCTIONS-v5MIRAFLOR ABREGANA100% (1)
- General Mathematics Module 2021-2022Dokument61 SeitenGeneral Mathematics Module 2021-2022Gianina De Leon100% (3)
- GenMath11 Q1 Mod7 ExponentialFunctions Week7 (Revised)Dokument15 SeitenGenMath11 Q1 Mod7 ExponentialFunctions Week7 (Revised)Jovic rullepaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 2 Module 3Dokument9 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 2 Module 3joebert agraviadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 25: Representations of Logarithmic FunctionsDokument27 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 25: Representations of Logarithmic FunctionsDaphneeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Calculus: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Determine The Standard Form of Equation of An EllipseDokument32 SeitenPre-Calculus: Quarter 1 - Module 7: Determine The Standard Form of Equation of An Ellipselucas scottNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 8.1 Representations of Logarithmic FunctionsDokument19 SeitenWEEK 8.1 Representations of Logarithmic FunctionsOreo ProductionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Representation of Rational FUNCTIONSDokument31 SeitenRepresentation of Rational FUNCTIONSNestor Liwagon Balansag100% (2)
- Gen Math11 - Q1 - Mod1 - Functions - v2Dokument28 SeitenGen Math11 - Q1 - Mod1 - Functions - v2Anonymous 6gthRen100% (1)
- MODULE 4-Basic Calculus PDFDokument10 SeitenMODULE 4-Basic Calculus PDFEzekiel0% (1)
- Q1 General Mathematics 11 - Module 1Dokument41 SeitenQ1 General Mathematics 11 - Module 1Prince Randy100% (2)
- Gen-Math11 Q1 Mod3 Operations-On-functions 08082020Dokument24 SeitenGen-Math11 Q1 Mod3 Operations-On-functions 08082020jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signed Off - General Mathematics11 - q1 - m4 - Exponential Functions - v3Dokument32 SeitenSigned Off - General Mathematics11 - q1 - m4 - Exponential Functions - v3rossie vim s. fernandez100% (2)
- STEM - PC11AG-If-1 (Systems of Nonlinear Equations-Illustrate System of Nonlinear Equation)Dokument10 SeitenSTEM - PC11AG-If-1 (Systems of Nonlinear Equations-Illustrate System of Nonlinear Equation)Chad Lowe Verdan Villarroya100% (3)
- Pre CalculusDokument70 SeitenPre Calculusveil clarizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen-Math11 Q1 Mod7 Presentions-Of-functions 08082020Dokument16 SeitenGen-Math11 Q1 Mod7 Presentions-Of-functions 08082020Ralph MapacpacNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 9Dokument20 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 9Aljhon A. MarajuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genmath q1 Mod8 TheDomainandRangeofRationalFunctions v2Dokument25 SeitenGenmath q1 Mod8 TheDomainandRangeofRationalFunctions v2Ateng Prin Cese100% (2)
- PreCalculus - Module 1Dokument11 SeitenPreCalculus - Module 1Alejandro Yadao Gonzales III89% (18)
- General Mathematics 2Dokument22 SeitenGeneral Mathematics 2gaile tabernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 3 - Module 6 Central Limit TheoremDokument20 SeitenStatistics and Probability: Quarter 3 - Module 6 Central Limit TheoremReign EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Calculus TG v4 102716Dokument346 SeitenBasic Calculus TG v4 102716Jessie TD100% (1)
- Pre-Calculus - Module 1-Conic SectionsDokument11 SeitenPre-Calculus - Module 1-Conic SectionsKharl Ace Asis50% (2)
- Daily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusDokument46 SeitenDaily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusLeah Mae France100% (2)
- GR 11 GenMath 02 Rational FunctionsDokument80 SeitenGR 11 GenMath 02 Rational FunctionsJeffrey Chan100% (7)
- LP Rational FunctionDokument10 SeitenLP Rational FunctionJaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 21: Intercepts, Zeroes and Asymptotes of Exponential FunctionsDokument27 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 21: Intercepts, Zeroes and Asymptotes of Exponential FunctionsDaphneeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Math First QuarterDokument194 SeitenGen Math First QuarterDindin Oromedlav Lorica100% (8)
- Quarter 1 - Module 4 Exponential Functions: General MathematicsDokument43 SeitenQuarter 1 - Module 4 Exponential Functions: General MathematicsJemar NamokNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Rational Functions, Equations and InequalitiesDokument35 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Rational Functions, Equations and InequalitiesDaphnee83% (6)
- Piecewise and Inverse Functions and Composition of FunctionsDokument35 SeitenPiecewise and Inverse Functions and Composition of FunctionsDCHKLian 17100% (1)
- Q1 Pre-Calculus 11 Module 5Dokument22 SeitenQ1 Pre-Calculus 11 Module 5Leanne Del Rosario100% (5)
- Genmath q1 Mod2 Evaluatingfunctions v2 PDFDokument29 SeitenGenmath q1 Mod2 Evaluatingfunctions v2 PDFJohnreyDelosSantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 2 (Week 2) Rational FunctionsDokument22 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 2 (Week 2) Rational FunctionsKimberly Trocio KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-2Dokument15 SeitenMath 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-2kenrick090% (1)
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 19: Representations of Exponential FunctionsDokument19 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 19: Representations of Exponential FunctionsDaphnee100% (1)
- Pre-Calculus: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Determine The Standard Form of Equation of A ParabolaDokument32 SeitenPre-Calculus: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Determine The Standard Form of Equation of A ParabolaMark Allen Labasan100% (2)
- Pre-Calculus ModuleDokument157 SeitenPre-Calculus ModuleDaniel Sigalat Loberiz100% (14)
- GRADE 11 General Mathematics Week 2 Quarter 1 ModuleDokument12 SeitenGRADE 11 General Mathematics Week 2 Quarter 1 ModuleCasey Erica Nicole CarranzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 BooksDokument23 Seiten0 BooksAjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Math Full Book PBDokument215 Seiten2nd Year Math Full Book PBFAizan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 G12 Math E PDFDokument215 Seiten2018 G12 Math E PDFhamza50% (2)
- FunctionDokument17 SeitenFunctionsuar90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDokument3 SeitenExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsManel KricheneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Von EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Noch keine Bewertungen
- SEAM-Maths1-1.2 SD-Trigonometric Functions 28-8-19 SPCEDokument13 SeitenSEAM-Maths1-1.2 SD-Trigonometric Functions 28-8-19 SPCESatish BarotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Exam Paper SolutionDokument18 SeitenSample Exam Paper SolutionDouglas CaiafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRPDokument15 SeitenIRPVamshi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- L26 Travelling Salesman Problem Using B and BDokument28 SeitenL26 Travelling Salesman Problem Using B and BShivansh RagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dijkstra AlgorithmDokument23 SeitenDijkstra AlgorithmJorgeCanoRamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA6566 (R-13) QB 2013 RegulationDokument19 SeitenMA6566 (R-13) QB 2013 RegulationSachin ManjunathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityShiv PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview PDFDokument100 SeitenInterview PDFDespicable ProgrammerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Trigonometric EquationsDokument13 Seiten06 Trigonometric EquationsRon HartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endsem Question Paper DSADokument18 SeitenEndsem Question Paper DSAayushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios: ObjectivesDokument10 SeitenTrigonometric Ratios: Objectivesneelann8902Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complementary Error Function Table: X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X)Dokument1 SeiteComplementary Error Function Table: X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X) X Erfc (X)Yadu KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic-Programming Algorithms For Shortest Path Prob - LemsDokument4 SeitenDynamic-Programming Algorithms For Shortest Path Prob - LemsYannis FertakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAA 2marks With AnswersDokument11 SeitenDAA 2marks With AnswersmiraclesureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory-Unit1Dokument38 SeitenGraph Theory-Unit1Kranthi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PDFDokument4 Seiten1 PDFAarti SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Left Leaning Red-Black TreeDokument78 SeitenLeft Leaning Red-Black TreeDanielAndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0 State Space Representation of ProblemsDokument18 Seiten3.0 State Space Representation of ProblemsnikwplayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021SEM2 CS3230 SolsDokument10 Seiten2021SEM2 CS3230 SolsNancy QNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem Notes PDFDokument9 SeitenClass 11 Maths Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem Notes PDFDevesh Kumar ElangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAA Worksheet-3.1 20BCS7611Dokument11 SeitenDAA Worksheet-3.1 20BCS7611AYUSH TIWARINoch keine Bewertungen
- 21MAT756Dokument3 Seiten21MAT756krithesh510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rapports Salle Des F TesDokument180 SeitenRapports Salle Des F TesMarcTimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument6 SeitenAssignment 2Jared BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHMM1014 Tutorial 1 Number and SetDokument8 SeitenFHMM1014 Tutorial 1 Number and SetCrKxiangKhorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Math Chapter 5Dokument14 SeitenDiscrete Math Chapter 5kumar_anup11Noch keine Bewertungen
- MA1301 Help SheetDokument3 SeitenMA1301 Help SheetChng Pei SzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSA SyllabusDokument2 SeitenDSA SyllabusAmrit AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument88 SeitenChapter 10RameeshPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMW Nature of Mathematics (Mathematics in Our World) PDFDokument246 SeitenMMW Nature of Mathematics (Mathematics in Our World) PDFjescy pauloNoch keine Bewertungen