Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dom Lab Ivsem
Hochgeladen von
Sonu DasCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dom Lab Ivsem
Hochgeladen von
Sonu DasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
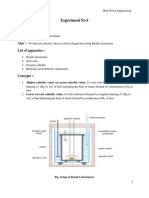
EXPERIMENT NO.
- 5
AIM: - To study various types of cam and follower arrangements.
APPARATUS USED: - Cam and follower arrangements.
THEORY: - 1. Definition of Cam & Follower.
2. Classification of Cam & Follower.
3. Diagrams of Cam & Follower.
4. Working & Construction of Cam & Follower.
5. Advantages & Disadvantages of Cam & Follower.
6. Applications of Cam & Follower. .
7. Examples of Cam & Follower.
CAM & FOLLOWER :- A cam is a mechanical member used to impart desired motion to a
follower by direct contact. The cam may be rotating or reciprocating whereas the follower
may be rotating, reciprocating or oscillating. A cam and the follower combination belongs to
the category of higher pairs.
• A driver member known as the cam.
• A driven member called the follower
Types of Cams :
A. According to shape
(i) wedge and flat Cams :- A wedge cam has a wedge W which, in general, has a
translational motion. The follower. The follower F can either translate or oscilate.
(ii) Radial or Disc Cams :- A cam in which the follower moves radially from the
centre of rotation of the cam is known as a radial or a disc cam.
(iii) Spiral cams :- A spiral cam is a face cam in which a groove is cut in the form of a
spiral as shown in fig. the spiral spiral groove consists of teeth which mesh with a
pin gear follower.
(iv) Cylindrical cams :- In a cylindrical cam, a cylinder which has a circumferential
contour cut in the surface, rotate about its axis.
(v) Conjugate cams :- A conjugate cam is a double – disc cam, the two discs being
keyed together and are in constant touch with the two rollers of a follower. It is
used for low noise, high speed and dynamic loads.
(vi) Globoidal cams :- A globoidal cam can have two types of surfaces, convex or
concave. A circumferential contour is cut on the surface of rotation of the cam to
impart motion to the follower which has an oscillatory motion.
(vii) Spherical cams :- In a spherical cam, the follower oscillates about an axis
perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the cam.
B. According to Follower Movement
(i) Rise-Return-Rise (R-R-R) :- In this, there is alternate rise and return of the
follower with no periods of dwells. Its use is very limited in the industry. The
follower has a linear or an angular displacement.
(ii) Dwell-Rise-Return-Dwell (D-R-R-D) :- In such a type of cam, there is rise and
return of the follower after a dwell. This type is used more frequently than the R-
R-R type of cam
(iii) Dwell-Rise-Dwell-Return (D-R-D-R) :- It is most widely used type of cam. The
dwelling of the cam is followed by rise and dwell and subsequently by return and
dwell as shown in fig.
C. According to Manner of Constraint of the Follower
(i) Pre-loaded Spring Cam
(ii) Positive-Drive Cam
(iii) Gravity Cam
Types of Followers :-
A. According to shape
(i) Knife-edge Follower
(ii) Roller Follower
(iii) Mushroom Follower
B. According to Movement
(i) Reciprocating Follower
(ii) Oscillating Follower
C. According to Locating of Line of Movement
(i) Radial Follower
(ii) Offset Foolower
OBSERVATION & CONCLUSION: - 1. Comparison between Cam & Follower.
2. Type of Motion to be named.
APPLICATIONS :-
(i) Cams are used in Automatic machines
(ii) In internal combustion engine
(iii) In machine tools
(iv) Printing Control mechanisms
VIVA-QUESTIONS :-
(i) Define about cam & follower, Classification of cam & follower, advantage &
disadvantage, Applications.
(ii) Define Disc cam nomenclature.
(iii) Define the cut off-set position of follower motion.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Mini Project Report: Differential Gear SystemDokument22 SeitenMini Project Report: Differential Gear SystemSonu DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Mini Project On Double Door Refrigerator: by Group B, ME 6Dokument12 SeitenMini Project On Double Door Refrigerator: by Group B, ME 6Sonu DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Experiment No 6: Title Aim: - List of ApparatusDokument3 SeitenExperiment No 6: Title Aim: - List of ApparatusSonu DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Fin Type Heat Exchanger: Presented by Shiv Kamal Upadhaya (21) Sonu Das (22) Nirmalya RoyDokument8 SeitenFin Type Heat Exchanger: Presented by Shiv Kamal Upadhaya (21) Sonu Das (22) Nirmalya RoySonu DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- 8 3ThingWorxInstallation 1 0 174675 PDFDokument157 Seiten8 3ThingWorxInstallation 1 0 174675 PDFAuditio MandhanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- PCNSE DemoDokument11 SeitenPCNSE DemodezaxxlNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The English We SpeakDokument2 SeitenThe English We Speakcaeronmustai100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Diagnostic Test - Tle8Dokument2 SeitenDiagnostic Test - Tle8rose mae marambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sword and The Exquisiteness PDFDokument1.437 SeitenThe Sword and The Exquisiteness PDFTaruna UnitaraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- To Word AkheebDokument31 SeitenTo Word AkheebDavid Raju GollapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- UVEX - Helmets & Eyewear 2009Dokument19 SeitenUVEX - Helmets & Eyewear 2009Ivica1977Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- High School Department PAASCU Accredited Academic Year 2017 - 2018Dokument6 SeitenHigh School Department PAASCU Accredited Academic Year 2017 - 2018Kevin T. OnaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Charging Station For E-Vehicle Using Solar With IOTDokument6 SeitenCharging Station For E-Vehicle Using Solar With IOTjakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- M14 PManualDokument382 SeitenM14 PManualnz104100% (2)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- AMC Middle Primary Years 3 and 4 - SolutionsDokument6 SeitenAMC Middle Primary Years 3 and 4 - SolutionsSherry JiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 Risk and InsuranceDokument4 Seiten30 Risk and InsuranceSiti Nur Ain RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Lay Planning TypesDokument1 SeiteLay Planning TypesGaurav Shakya100% (1)
- Marshall Mix Design (Nptel - ceTEI - L26 (1) )Dokument7 SeitenMarshall Mix Design (Nptel - ceTEI - L26 (1) )andrewcwng0% (1)
- Lesson 7Dokument6 SeitenLesson 7Jeya Plays YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Tracking System: Mentor - Yamini Ma'AmDokument10 SeitenApplication Tracking System: Mentor - Yamini Ma'AmBHuwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Chapter Mentor ProgramDokument13 SeitenGrand Chapter Mentor ProgramJulius Wright100% (1)
- Iso 27001 Requirementsandnetwrixfunctionalitymapping 1705578827995Dokument33 SeitenIso 27001 Requirementsandnetwrixfunctionalitymapping 1705578827995Tassnim Ben youssefNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTSDA2021 TSDBlack Belt ManualDokument160 SeitenWTSDA2021 TSDBlack Belt ManualJesus HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised LabDokument18 SeitenRevised LabAbu AyemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- 50 Interview Question Code Galatta - HandbookDokument16 Seiten50 Interview Question Code Galatta - HandbookSai DhanushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omega 900 InstructionsDokument27 SeitenOmega 900 InstructionsRA Dental LaboratoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal ComfortDokument50 SeitenThermal ComfortSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Technical Report ON Centre of Pressure ONA Plane Surface ExperimentDokument13 SeitenA Technical Report ON Centre of Pressure ONA Plane Surface ExperimentVictor OwolekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CrumpleZonesSE (Edit)Dokument12 SeitenCrumpleZonesSE (Edit)Dah Unknown MarksmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Practical Search Techniques in Path Planning For Autonomous DrivingDokument6 SeitenPractical Search Techniques in Path Planning For Autonomous DrivingGergely HornyakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultraviolet RadiationDokument3 SeitenUltraviolet RadiationbirlacementNoch keine Bewertungen
- TML IML DefinitionDokument2 SeitenTML IML DefinitionFicticious UserNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Staff OrderDokument2 SeitenHouse Staff OrderTarikNoch keine Bewertungen
- FacebookDokument2 SeitenFacebookAbhijeet SingareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)