Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
FSC Fmea Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
Hochgeladen von
VbaluyoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FSC Fmea Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
Hochgeladen von
VbaluyoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
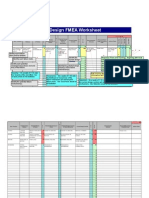
FSC FMEA
FAILURE MODE AND EFFECT ANALYSIS
Document FSC Site / Supplier / FMEA Team :
#: DFSILF-A Customer : FSCB C. Quiñones, C. Estacio, G. Baje, M.
Gestole, J. Matheu
Equipment Or Pkg FMEA Type:
Type : SO-8 Wireless DESIGN
Process Name Or Specification Number Originator:
BOTTOM FRAME SOIC, 8 LD, ETCHED
Or Parts: Clemens Quiñones
Reference Drawing: (CB)36-0001
Approvals:
Consuelo Tangpuz Noel Laylo Edwin Esperanza Cyrus dela Rama Roger Pineda
PTG Dept. Manager Engineering Dept. Maintenance Dept. Operations Manager QA & R Manager
Manager Manager
Rev # Date Originators Revision History Rev # Date Originators Revision History
A April Clemens Origination
23, Quiñones
1999
419671441.doc Page 1 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
419671441.doc Page 2 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Die Connect Intermitte RDSon 6 S Inconsistent DAP 6 DAP and fused 1 36 Change C. Estacio Actio 6 3 1 1
Attach s die ntly failure planarity which leads lie on the leadframe (lf) 10 Aug. n(s) 8
Pad back- provide will result to same plane thus design from ‘98 reflecte
(DAP) side to backside inconsistent reducing dual strand to d in
leadfram connection solder wire tendency of DAP single strand (CB)36-
e for (partial dispense height tilting during for better 0001
drain failure) resulting to upset process DAP planarity C. rev. B
connecti varying solder done by supplier Specify 2 mils Quiñones drawing
on quantity. Design maximum lf 11 Sept. Actio
Irregular DAP verification rail ‘98 n(s)
surface causing through etched parallelism to reflecte
poor soft solder leadframe tooling DAP in the d in
wetting during IQC visual drawing to (CB)
D/A sampling ensure 36-
inspection prior tolerable DAP C. Estacio 0001rev
to use planarity. 21 Aug. .D
Specify 0.5 ‘98
mil maximum
DAP surface Actio
flatness in n(s)
drawing. reflecte
d in
(CB)36-
0001
rev C
No Drain open 6 S Inconsistent DAP 3 (same as above) 1 18
connection planarity which
to die back can contribute to
(complete missing soft
failure) solder material
419671441.doc Page 3 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Isolates Complete Electrical 8 S DAP width too 9 Minimum 5 36 Reduce DAP C. Action(s) 8 2 1 1
drain failure to short wide causing clearance 0 width from 113 Quiñones Reflected 6
connecti isolation DAP-source or between DAP & mils 106 size, 5 Oct. ‘98 in
on from DAP-gate shorting source/ gate set thus increasing (CB)36-
source at 5.4 mils the minimum 0001
and gate Design clearance Rev. F
verification between DAP
through etched lf & source/ gate
tooling to 10.4 mils.
IQC dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
Over- Poor thermal 8 S DAP size too 4 DAP design rule: 2 64 Increase DAP C. Action(s) 8 4 2 6
isolation performance small to promote 7 mils longer than length from Quiñones reflected 4
(partial of device fast heat die in each side 155 to 160 to 1Feb ‘99 in
failure) dissipation DAP size = 113 compensate (CB)36-
mils x 155 mils metal volume 0001
IQC dimensional loss when DAP Rev. M
sampling width is
inspection prior reduced from
to use 113 mils to
SO-8 Package 106 mils.
thermal
simulation using
145 mils x 90
mils die size
419671441.doc Page 4 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
DAP Serve as Incorrect Wrong die 9 C DAP offset to 4 DAP x & y 1 36
(contin a die attach placement leadframe pilot/ dimensions with
ued) referenc reference Tilted die index hole (which respect to pilot
e or (partial resulting to will result to hole included in
guide for failure) poor gate & wrong D/A IQC dimensional
die source reference) inspection
attach contacts
placeme Electrical
nt fall-outs
(gate open
or short)
Mold dents
(due to die
overhangin
g the mold
outline)
419671441.doc Page 5 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Dissipat Inefficient Poor 9 C D/A voids due to 5 Material 4 18 Increase DAP C. Action(s) 9 5 2 9
es heat heatsinking thermal poor wetting as selection: 0 length from Quiñones reflected 0
during or heat device a result of Alloy194 with 155 to 160 to 1Feb ‘99 in
device dissipation performanc irregular DAP thermal compensate (CB)36-
applicati (partial e surface resistivity = metal volume 0001
on failure) Over- DAP size too 0.625 cal/cm- loss when Rev. M
stressed small to promote C-sec DAP width is
internal fast heat KFC with reduced from
package dissipation thermal 113 mils to C. Estacio
assembly resistivity = 106 mils. 21Aug.’98 Action(s)
resulting to 0.87 cal/cm-C- Specify 0.5 reflected
die cracks sec mil maximum in
and DAP design rule: DAP surface (CB)36-
possible 7 mils longer than flatness in 0001 rev.
mold die in each side drawing. C
compound DAP size = 113
burning mils x 155 mils
IQC dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
SO-8 Package
thermal
simulation using
145 mils x 90
mils die size
Design
verification
through etched
frame tooling
419671441.doc Page 6 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Die Suppress Soft solder Mold 8 S Location of D/A 6 Designed flow 1 48
Attach es on leads bleeding flow guide too guide center to
Flow outflow (total Mold tool far from fused fused lead
Guide( of D/A failure) dents (due leads distance = 7 mils
s) material to bulging [Ref: (CB)36-0001
(soft D/A Rev. M]
solder) material on Design
into leads verification
fused outside through etched lf
leads mold tooling
outline)
Mold
delaminatio
n
Spreads Die back RDSon 8 S Wrong flow 8 Designed star 2 12 Review star C.
out D/A voids failures guides location burst flow guide 8 burst flow Quiñones
material (partial & shape design at DAP guide design WW48-50
through- failure) center [Ref: for possible FY99
out die (CB)36-0001 Rev. redesigns
back M]
Design
verification
through etched lf
tooling
X-ray buy-off
during D/A
419671441.doc Page 7 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
DAP Holds Pad tilting Insufficient 9 C Width of tie bar 6 Designed total 1 54
Tie Bar DAP (partial amount of not be enough width of tie bar =
firmly to failure) dispensed to support the 12 mils
avoid solder as a DAP during Designed shape
twisting result of stamping of tie bar: two-
or tilting varying process pronged bridge
during dispense to Location of tie between DAP &
stampin DAP bar not able to mold clamping
g distance suppress area
/coining RDSon moments Tie bar is
(@ failures strategically
vendor minimal situated near the
side) drain DAP edge (no
contact fuse-lead side) for
Reliability a more rigid
failures due support
to cracks Design
induced by verification
thin solder through etched lf
layer tooling
Holds DAP Floating D/A voids 5 S Width of tie bar 6 (same as above) 3 90 Change C. Estacio/ Action(s) 5 5 1 2
firmly DAP during due to poor not be enough leadframe 10Aug. ‘98 reflected 5
during D/A scrubbing to support the design from in
D/A (partial @ D/A spring back dual strand to (CB)36-
failure) RDSon action of DAP single strand 0001 rev.
failures during D/A for stronger B
Wrong die Location of tie DAP support
position bar not able to
suppress
moments
419671441.doc Page 8 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
DAP Firmly Tie bar Index 8 S Width of tie bar 6 Designed total 1 48 Change C. Estacio Action(s) 8 3 1 2
Tie Bar supports premature jamming not be enough width of tie bar = leadframe 10Aug. ‘98 reflected 4
(contin the cut during during TNF to support the 12 mils design from in
ued) molded TNF package during Designed shape dual strand to (CB)36-
package (partial TNF of tie bar: two- single strand 0001 rev.
during failure) Location of tie pronged bridge for stronger B
trim & bar wrt molded between package package
form package not & mold clamping support
(TNF) able to suppress area during TNF
process moments Designed location
of tie bar: along
Y-axis of package
center
Design
verification
through etched lf
tooling
Too rigid Package 9 C Tie bar width too 5 Designed total 1 45
package delaminatio wide thus causing width of tie bar =
support n high mechanical 12 mils
(partial Package stress on the Designed shape
failure) crack package during of tie bar: two-
Reliability singulation pronged bridge
failures between package
& mold clamping
area
Design
verification
through etched lf
tooling
419671441.doc Page 9 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Mold Prevents Mold Visual 6 S Narrow clamping 1 Designed clamp 2 12 Increased mold C. Estacio Action(s) 6 5 1 3
Clampi mold flashing of reject width not able to 0 area width 0 clamping area 21Aug ‘98 reflected 0
ng flashing lower leads Solderabilit withstand mold outside package to from in
Area of leads (complete y problem transfer pressure is 12 mils approximately (CB)36-
below failure) High mold resulting to Testing of lf 30 mils to 50 0001 rev.
dambar compound flooding of mold prototypes during mils C
(via rail usage rate flashes into rail preliminary mold
downset downset channel tool set-up
channel) and into lower
leads
Holds DAP Flimsy tie Weakening 6 S Distance 4 Designed 1 24
tie bar bar support of tie bar between molded distance from
after mold Premature package and mold outline to
(partial breakage of mold clamping tie bar neck = 3.5
failure) tie bar area too wide mils
during Follow
dejunk & conventional SO-
TNF 8 design
Testing of lf
prototypes during
preliminary
dejunk & TNF
tools set-up
419671441.doc Page 10 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Damba Simplifies Mold Visual 6 S Narrow dambar 5 Designed dambar 1 30
r mold tool flashing of reject width not able to width = 10 mils
design & lower leads Solderabilit withstand mold Follow existing
prevents (complete y problem transfer pressure SO-8
flashing failure) High mold resulting to conventional
of mold compound flooding of mold dambar
compoun usage rate flashes into the specifications
d into lower leads
lower
leads
Allocate Incomplete External 8 S Dambar distance 5 Designed dambar 1 40
space for venting mold from package too to package
mold (partial package close obstructing distance = 10
venting failure) void – vented air during mils
visual reject mold packing Follow existing
Internal SO-8
mold conventional
package dambar
void – specifications
reliability
risk
Pools in Dejunking Package 9 C Dambar distance 5 Designed dambar 1 45 Increase lower C. Action(s) 9 3 1 2
mold errors crack (due too close to to package dambar Quiñones reflected 7
flashes (partial to dejunk package distance = 10 dimension of 29Sept. in
for dejunk failure) tool hitting mils outermost ‘98 (CB)36-
pkg edge) Follow existing leads (for 0001
Package SO-8 stronger Rev. E
delaminatio conventional dejunk tool)
n dambar
specifications
419671441.doc Page 11 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Leadfr Connects Flimsy Index 7 S Narrow leadframe 6 Designed 4 16 Change lf C. Estacio Action(s) 7 3 1 2
ame every unit leadframe jamming @ rails cannot resist leadframe rail 8 design from 10Aug. ‘98 reflected 1
Rail to make a (partial D/A mechanical width = 97mils/ dual strand to in
sturdy failure) Leadframe stresses causing side single strand, (CB)36-
leadframe bowing deformations Design thus 0001
strip Poor after several verification increasing Rev. B
(backbon alignment handling through etched lf the rail to lf C. Estacio
e of the to topframe tooling width ratio 21Aug. ‘98
leadframe resulting to from 27% to Action(s)
) poor source 41% reflected
& gate Increase rail in
contacts width to 126 (CB)36-
Electrical mils per side 0001
fall-outs Rev C
Leadfr Maintain Non-parallel Irregular 8 S Poor rail planarity 7 Design verification 6 33 Specify 2 mils C. Action(s) 8 6 2 9
ame parallelis bottomfram contact condition through etched lf 6 maximum Quiñones reflected 6
Rail m of e to between (irregular macro- tooling parallelism of 11Sept. in
(contin bottomfra topframe topframe & contours on rails rails wrt leads ‘98 (CB)36-
ued) me to assembly Si die surface) 0001 rev.
topframe (complete solder D
failure) bumps
Electrical
fall-outs
(gate/
source
open)
Low
process
yield
419671441.doc Page 12 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Maintain Non- No contact 8 S Poor surface 7 Design verification 6 33 Specify 0.5 C. Estacio Action(s) 8 6 2 9
lead coplanar between flatness of rail through etched lf 6 mils maximum 21Aug. ‘98 reflected 6
coplanarit topframe & topframe & tooling surface in
y of bottomfram solder balls/ flatness of rail (CB)36-
bottomfra e leads bumps in the drawing 0001 rev.
me to (complete Electrical C
topframe failure) fall-outs
(gate/
source
open)
Low
process
yield
419671441.doc Page 13 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Rail Connects Rail Floating 9 C Weak tie bar 6 Designed lead 1 54 Reduce leads C. Action(s) 9 6 1 5
Ti individual disconnects leads design tie bar width = 31 tie bar width Quiñones reflected 4
e units to (partial Intermittent Narrow tie bar mils from 31 mils 26Feb. ‘99 in
Ba leadframe failure) contact width Total to 28 mils (for (CB)36-
r rails & between horizontal rail strip cutting 0001
makes-up topframe & width (@downset purposes) Rev. P
width of solder balls/ area) = 202 mils
the bumps Design
leadframe Electrical verification
(Analogy: fall-outs through etched lf
ribs of the (gate/ tooling
human source
body') open)
Dejunk &
TNF index
jamming
Deflash
jamming
Low
process
yield
419671441.doc Page 14 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Rail Reduces Inconsistent No contact 8 S Rail tie bar 7 Designed slots 2 11 Increase total C. Action(s) 8 3 2 4
Tie Bar over-all downset between downset slots split rail tie bar 2 rail tie bar Quiñones reflected 8
Downs downset depth topframe & too small (its into three. Active downset slot 20Nov. ‘98 in
et rail tie bar (partial solder balls/ effect in tie bar locations length from (CB)36-
Slots volume failure) bumps reducing over-all along DAP tie bar, 115 mils to 0001
for Electrical upset rail dambar & leads 157 mils rev. J
improved fall-outs volume is tie bar
downset (gate/ insignificant) Designed rail tie
control of source bar downset slots
leadframe open) total length =
manufact Low 115 mils/ unit
uring process against 202 mils/
yield unit total rail
downset length
[Ref: (CB)36-0001
Rev H]
Design
verification
through etched lf
tooling
IQC dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
Rail Maintain Non-parallel No contact 8 S Poor planarity of 7 Designed rail tie 6 33 Specify 2 mils C. Action(s) 8 6 2 9
Tie Bar parallel & topframe & between rail wrt bar downset 6 maximum Quiñones reflected 6
Downs sufficient bottomfram topframe & bottomframe depth = 8 2 mils parallelism of 11Sept. in
et gap for e leads solder balls/ leads Design rails to ‘98 (CB)36-
topframe (partial bumps Inconsistent rail verification bottomframe 0001
failure) Electrical downset depth through etched lf leads rev. D
fall-outs tooling
(gate/
source
open)
Low
process
yield
419671441.doc Page 15 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Rail Maintains Leadframe Leadframe 5 S Varied rail tie 5 Specify 1 25
Tie Bar stacking offset deformatio bar downset downset angle
Downs ability of stacking ns angle dimension dimension and
et bottom- D/A input from leadframe practical angle
Angle frame jamming to leadframe location in
leadframe
drawing [Ref:
( CB)36-0001 Rev.
G]
Design
verification
through etched lf
tooling
Maintains Rail tie bar Floating 9 C Too much plastic 6 Designed 1 54
rail tie bar cracking leads deformation on downset angle
downset Intermittent rail tie bar dimension =
strength contact caused by too 1355 relative
between steep downset to rail surface
topframe & angle [Ref:( CB)36-0001
solder balls/ Rev. G]
bumps Design
Electrical verification
fall-outs through etched lf
(gate/ tooling
source
open)
Dejunk &
TNF index
jamming
Deflash
jamming
Low
process
yield
419671441.doc Page 16 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Square Facilitate Index Leadframe/ 7 S Irregular unit 9 Set index hole 1 63
Index leadframe jamming strip pitch (inter-index as pilot hole
Holes indexing (partial damage hole dimension) (leadframe
at failure) Package dimensional
various crack reference)
assembly High scrap Index/pilot
processes rate / low holes center
such as process dimensions
D/A, yield tolerance: 1 mil
dejunk & Set non-
TNF cumulative pilot
hole tolerance:
2 mils
IQC
dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
Aligns Misalign Vertical or 7 S Offset index hole 1 Set index hole 1 70
“internal internal horizontal wrt to location of 0 as reference to all
package” package to package DAP leadframe
of mold offsets dimensions
leadframe outline Leads including DAP
to mold (complete pinching Index/ pilot
tool failure) Leadform holes center
(square irregularitie dimension
shape tolerance: 1 mil
s
ensures
minimal IQC
contact dimensional
with or sampling
shape inspection prior
locating to use
pins of
mold)
419671441.doc Page 17 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Rail stress Leadframe Index 9 C Unequal 4 Leadframe is 1 36
relief camber jamming expansion of designed with nine
(complete Reflowed opposite rails pairs of index
failure) solder joint after soft solder holes at
cracks D/A or solder alternating
reflow process locations on
opposite rails
Circula Breaks Misfeeding Package 1 C Latitudinal & 6 Add circular 1 60
r symmetr @ Deflash cracking 0 longitudinal orientation holes
Leadfr y of Dejunk & Rough symmetry of adjacent to
ame leadfram TNF Package leadframe is square index
Orient e inorder Misloading Damaged perfect (except holes on one side
ation to @ mold tooling internal package of the rail [Ref:
Hole prevent High tooling design) (CB)36-0001 Rev.
misfeed- (complete maintenanc No immediate K)
ing @ failures) e cost visual distinction Circular
EOL Processing between top & orientation hole
processe delays bottom side of center dimension
s leadframe after tolerance wrt
package is index hole: 1 mil
molded IQC
dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
419671441.doc Page 18 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Circula Aligns Misalign Marginal or 1 C Offset alignment 8 Leadframe is 1 80
r bottom- leadframes no solder 0 stud wrt X & Y designed with
Leadfr frame and after contact to coordinates of nine pairs
ame topframe welding topframe square index alignment studs
Alignm assembly (complete Electrical holes. at alternating
ent prior to failure) fall-outs locations on
Studs welding (open/ opposite rails
shorts) [Ref: (CB)36-0001
Mold Rev L ]
package Alignment stud
offset center dimension
Leads tolerance wrt
pinching @ index hole: 1 mil
mold IQC dimensional
Leadform sampling
irregularitie inspection prior
s to use
Leads Connects Broken or Mechanical 6 S Leadwidth too 3 Designed lead 3 54
device missing reject narrow to resist width = 14 mils
(attached leads Low yield various EOL Follow
on DAP) (complete processing conventional SO-
to failure) stresses 8 design
external Material too Follow JEDEC
world brittle to specifica-tion for
withstand lead SOIC-8 package
stressing IQC dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
Cracking of Mechanical 6 S Material too 3 Specify Alloy194 3 54
leads reject brittle to Half-hard material
Solderabilit withstand lead in drawing
y failure stressing Follow
Material conventional SO-
elongation too 8 leadform
short relative to outline
projected Follow JEDEC
leadforming specifica-tion for
deformations SOIC-8 package
419671441.doc Page 19 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Leadfr Enhances Broken or Mechanical 6 S Lead thickness 3 Designed 3 54
ame lead missing reject too thin to resist leadframe
Thickn strength leads Low yield various EOL thickness = 8
ess (complete processing mils
failure) stresses Follow
Material too conventional SO-
brittle to 8 design
withstand lead Follow JEDEC
stressing specification for
SOIC-8 package
IQC dimensional
sampling
inspection prior
to use
Leadfr Ensures Mold Visual 6 S Unbalanced 3 Specify leadframe 2 36
ame good flashing of reject leadframe thickness
Thickn clamping lower leads Solderabilit thickness within tolerance of 0.3
ess at mold (complete y problem one strip mils in the
(contin failure) High mold drawing
ued)
compound IQC dimensional
usage rate sampling
inspection prior
to use
DAP Promotes Die back RDSon 8 S Porous Ag 7 Designed Ag 1 56
Plating wetting voids failures plating allowing plating thickness
(for and (partial Cu to migrate = 90u” min. [Ref:
soft spread of failure) towards Ag layer (CB)36-0001 Rev.
solder D/A M]
D/A
material Plating thickness
applicat
ion) on DAP measurements
included in IQC
sampling
inspection prior
to use
419671441.doc Page 20 of 21 29 April, 1999
Document # : DFSILF-A FSC FMEA
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
C Area/
Part/ Potential Potential S L Potential Cause O Design D R Recommended Individual Actions S O D R
Process Function Failure Effect(s) E A of Failure C Verification or E P Actions Responsibl Taken E C E P
Modes of Failure V S C Current Control T N e& V C T N
S Timeframe
Prevents Scattered RDSon 8 C Porous Ag 5 Added Ni flash 3 12 Improve Ag Leadfram
direct Cu-Sn IMC failures plating allowing (flood plating) 0 finish e vendor
intermetal formations Latent Cu to migrate underneath Ag compactness. –PBE
lic (IMC) on die back TMCL towards Ag layer layer to prevent WW50
formation (partial failures Too thin Ag layer Cu migration FY99-
of Cu & failure) such that Ag [Ref: (CB)36-0001 WW05-
Sn completely Rev. M] Specify type FY00
dissolves into Plating thickness of Ag finish
solder during measurements on leadframe C.
D/A, thus included in IQC drawing. Quiñones
rendering Cu sampling PD01
readily for IMC inspection prior FY00
formation to use
419671441.doc Page 21 of 21 29 April, 1999
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Design FMEA (DFMEA) TutorialDokument18 SeitenDesign FMEA (DFMEA) Tutorialpiero_rsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FmeaDokument31 SeitenFmeainder_sandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmea ProcessDokument25 SeitenFmea ProcessEmperor89100% (1)
- 5S Planned Activities and TimelineDokument1 Seite5S Planned Activities and TimelineVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 240-56062705 RTV Silicone Rubber Insulator Coating and Shed Extender Supplier StandardDokument10 Seiten240-56062705 RTV Silicone Rubber Insulator Coating and Shed Extender Supplier StandardJane ChatsiriphatthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRBFM WorksheetDokument1 SeiteDRBFM WorksheetHareth MRAIDINoch keine Bewertungen
- GR&R Training DraftDokument53 SeitenGR&R Training DraftLOGANATHAN VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement System Analysis LabDokument32 SeitenMeasurement System Analysis LabAnonymous 3tOWlL6L0U100% (1)
- Error Proofing For EMSDokument48 SeitenError Proofing For EMSsaleemanisaleemaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description of FMEA WorksheetDokument2 SeitenDescription of FMEA WorksheetIMV ACADEMYNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASQ - Design FMEADokument35 SeitenASQ - Design FMEABESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updates Dec09 AIAG FMEA-Ranking-TablesDokument3 SeitenUpdates Dec09 AIAG FMEA-Ranking-TablesSuresh Velu100% (1)
- Quality Management AnswersDokument42 SeitenQuality Management AnswersVrushali Nayak100% (1)
- SPC Basics: Presented By: Tariq KhurshidDokument50 SeitenSPC Basics: Presented By: Tariq Khurshidtkhurshid3997Noch keine Bewertungen
- The New Standard To Analyse Risks Within The Automotive Supply ChainDokument8 SeitenThe New Standard To Analyse Risks Within The Automotive Supply ChainYoga AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSA For AttributesDokument54 SeitenMSA For AttributesdesurkarbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Severity, Occurrence, and Detection Criteria For Design FMEADokument2 SeitenSeverity, Occurrence, and Detection Criteria For Design FMEAtejashraj93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shain in TaguchiDokument8 SeitenShain in TaguchisdvikkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Diagram ExamplesDokument8 SeitenStrategy Diagram ExamplesmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 FMEA Training - How To DoDokument45 Seiten02 FMEA Training - How To DoRamkumar PerumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 203 LSS Gbo - FmeaDokument47 Seiten203 LSS Gbo - FmeaRocker byNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Verification Process Project III Samudra Indonesia 20/11/2019 Samudra Indonesia 21/12/2019 See Project III R1 ReportDokument6 SeitenDesign Verification Process Project III Samudra Indonesia 20/11/2019 Samudra Indonesia 21/12/2019 See Project III R1 ReportAufa Jaya Perkasa LegalityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction PlanDokument14 SeitenReaction PlanMariaNilaZaragozaPalacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSA (Measurement System Analys)Dokument19 SeitenMSA (Measurement System Analys)Dazslam New VersionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setco Automotive LTD.: NP ChartDokument4 SeitenSetco Automotive LTD.: NP ChartDisha ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CorrectSPC PresentationDokument90 SeitenCorrectSPC Presentationpkj009Noch keine Bewertungen
- FMEA For DesignDokument7 SeitenFMEA For DesignPavan Kumar100% (1)
- AP QP ChecklistDokument6 SeitenAP QP ChecklistMartin BoianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Tools and MeasurementsDokument5 SeitenQuality Tools and MeasurementsYieli wal ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msa PresentationsDokument17 SeitenMsa PresentationsNarasimharaghavanPuliyurKrishnaswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 5 Core ToolDokument17 SeitenThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attribute Gage R&RDokument10 SeitenAttribute Gage R&RCésar MezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shainin Vs Six SigmaDokument4 SeitenShainin Vs Six Sigmabaro4518Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Case Against The AIAG-VDA DFMEADokument22 SeitenThe Case Against The AIAG-VDA DFMEA57641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample DFMEA - Full PackageDokument7 SeitenSample DFMEA - Full Packageabhisheksen.asindNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAMPLE - Process FlowDokument2 SeitenSAMPLE - Process Flowakav123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xfmea Pfmea PDFDokument8 SeitenXfmea Pfmea PDFvinidesoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dfmea TemplateDokument5 SeitenDfmea TemplateHerbert WeigeltNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFMEA Reference Card PDFDokument2 SeitenPFMEA Reference Card PDFRajesh Yadav100% (5)
- ATTRIBUTE MSADokument2 SeitenATTRIBUTE MSADINESHCHOUDHARY880% (1)
- Process Control PlanDokument10 SeitenProcess Control Planapi-3701688Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apqp MiniDokument14 SeitenApqp MiniSudhagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMEA Guide-Q1Dokument161 SeitenFMEA Guide-Q1Vikas SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Potentail Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisDokument1 SeiteProcess Potentail Failure Mode and Effects Analysiscong daNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Defining ProcessesDokument18 SeitenBasics of Defining ProcessesFaried Putra SandiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmea Analysis of Turret LatheDokument3 SeitenFmea Analysis of Turret LatheSathriyan SathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process and Measurement System Capability AnalysisDokument18 SeitenProcess and Measurement System Capability AnalysisUtkarsh MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMEA TemplateDokument6 SeitenFMEA TemplateHiếu Trần100% (1)
- 4 Measure - Measurement System AnalysisDokument63 Seiten4 Measure - Measurement System AnalysisSudhagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Review Based On Failure Mode 1-Day Workshop by TetrahedronDokument2 SeitenDesign Review Based On Failure Mode 1-Day Workshop by TetrahedrontetrahedronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peration Anagement: Concept of Quality Juran's PrincipleDokument24 SeitenPeration Anagement: Concept of Quality Juran's PrincipleAyushi BisenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlling The Assembly Process With The Use of SPCDokument6 SeitenControlling The Assembly Process With The Use of SPCSRIDHAREEE61Noch keine Bewertungen
- Root Cause Analysis - ShaininapproachDokument6 SeitenRoot Cause Analysis - ShaininapproachRaghavendra KalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Control Plan - DCPDokument2 SeitenDynamic Control Plan - DCPGabriel Caicedo RussyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Mistake ProofingDokument4 Seiten15 Mistake ProofingSteven Bonacorsi100% (2)
- 5 WhyDokument13 Seiten5 WhyPeter SzógaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmea Alignment Aiag and VdaDokument14 SeitenFmea Alignment Aiag and Vdahaitem100% (1)
- Manufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandManufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management System Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandQuality Management System Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chip OutPSM TemplateDokument20 SeitenChip OutPSM TemplateVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Wrist Strap Implementation at p1-2 Eol Rev2Dokument13 SeitenNon Wrist Strap Implementation at p1-2 Eol Rev2VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmel DB10 Failures ESR WW10'06Dokument13 SeitenAtmel DB10 Failures ESR WW10'06VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaflet For TS16949 AwarenessDokument3 SeitenLeaflet For TS16949 AwarenessVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOC - 6 Big Losses TrainingDokument46 SeitenTOC - 6 Big Losses TrainingVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step 1. Problem Definition/Objective: Step 2. Trend Chart / GoalDokument32 SeitenStep 1. Problem Definition/Objective: Step 2. Trend Chart / GoalVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Calendar Based On TGF and Idp - Rev.01 Ao 2.24.06Dokument11 SeitenTraining Calendar Based On TGF and Idp - Rev.01 Ao 2.24.06VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larry Miles and Value Engineering.Dokument3 SeitenLarry Miles and Value Engineering.VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal: Foresight 2020: The Future of Quality in The Age of TechnologyDokument14 SeitenJournal: Foresight 2020: The Future of Quality in The Age of TechnologyVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. W. Edwards Deming - The Father of The Quality EvolutionDokument3 SeitenDr. W. Edwards Deming - The Father of The Quality EvolutionVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurt Lewin - The Forces Are With You.Dokument1 SeiteKurt Lewin - The Forces Are With You.VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Sigma Case Studies - Vytra Call Center PDFDokument2 SeitenSix Sigma Case Studies - Vytra Call Center PDFVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- J. Edgar Thomson - Management and Railroad Pioneer.Dokument1 SeiteJ. Edgar Thomson - Management and Railroad Pioneer.VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Improvement - Fix The System, Not The WorkersDokument2 SeitenSafety Improvement - Fix The System, Not The WorkersVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scatter Plots: Management ResourcesDokument2 SeitenScatter Plots: Management ResourcesVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walter Shewhart - The Grandfather of Total Quality Management.Dokument1 SeiteWalter Shewhart - The Grandfather of Total Quality Management.VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaoru Ishikawa - The Man Behind The Fishbone Diagram.Dokument2 SeitenKaoru Ishikawa - The Man Behind The Fishbone Diagram.VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team Motivation: Management ResourcesDokument4 SeitenTeam Motivation: Management ResourcesVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is-Is Not Analysis: Company Confidential Company ConfidentialDokument12 SeitenIs-Is Not Analysis: Company Confidential Company ConfidentialVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philip Crosby - The Fun Uncle of The Quality RevolutionDokument1 SeitePhilip Crosby - The Fun Uncle of The Quality RevolutionVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 EdaDokument822 Seiten1 EdaMarielis Garcia Garcia100% (2)
- Is & Is Not Analysis of Subcon H Die Shear IssueDokument9 SeitenIs & Is Not Analysis of Subcon H Die Shear IssueVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Dewey - Philosophies On Management PDFDokument1 SeiteJohn Dewey - Philosophies On Management PDFVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is & Is Not Analysis of Subcon H Die Shear IssueDokument9 SeitenIs & Is Not Analysis of Subcon H Die Shear IssueVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursery Management and OperationDokument16 SeitenNursery Management and OperationVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8d HandoutsDokument16 Seiten8d HandoutsVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benefits of SexDokument16 SeitenBenefits of SexPhilomena NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seven WondersDokument17 SeitenSeven WondersVbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Do You See ? Can You See My Grandmother? Can You See My Daughter? Can You See Two People at The Same Time?Dokument14 SeitenWhat Do You See ? Can You See My Grandmother? Can You See My Daughter? Can You See Two People at The Same Time?VbaluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC 672772 RBRS Service TraningDokument385 SeitenBC 672772 RBRS Service TraningTeknik Makina100% (2)
- DC Motor: F Bli NewtonDokument35 SeitenDC Motor: F Bli NewtonMuhammad TausiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yz125 2005Dokument58 SeitenYz125 2005Ignacio Sanchez100% (1)
- ZH210LC 5BDokument24 SeitenZH210LC 5BPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ0% (1)
- Swanand 2009Dokument3 SeitenSwanand 2009maverick2929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quemador BrahmaDokument4 SeitenQuemador BrahmaClaudio VerdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPHPDokument4 SeitenIPHPAliah CasilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVSDokument3 SeitenEVSSuyash AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planetary Yogas in Astrology: O.P.Verma, IndiaDokument7 SeitenPlanetary Yogas in Astrology: O.P.Verma, IndiaSaptarishisAstrology50% (2)
- Graduate Macro Theory II: The Real Business Cycle Model: Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2017Dokument25 SeitenGraduate Macro Theory II: The Real Business Cycle Model: Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2017Joab Dan Valdivia CoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Science PedagogyDokument4 SeitenSocial Science PedagogyrajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerDokument4 SeitenDesign of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerabfstbmsodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design REE 302: CH 1: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering DesignDokument26 SeitenMachine Design REE 302: CH 1: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering DesignDull PersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL 4001Dokument2 SeitenSL 4001ardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsDokument57 SeitenChapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsAhmad FaidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.1 Essential Concepts: 1.1 What and How? What Is Heat Transfer?Dokument151 SeitenCh.1 Essential Concepts: 1.1 What and How? What Is Heat Transfer?samuel KwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Mathematics Content Through Explicit TeachingDokument39 SeitenTeaching Mathematics Content Through Explicit Teachingronna drio100% (1)
- History Homework Help Ks3Dokument8 SeitenHistory Homework Help Ks3afetnjvog100% (1)
- Form No. 1 Gangtok Municipal Corporation Deorali, SikkimDokument2 SeitenForm No. 1 Gangtok Municipal Corporation Deorali, SikkimMUSKAANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focal Length of Convex LensDokument5 SeitenFocal Length of Convex LensHey AnuragNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOA Project Presentation (GROUP 5)Dokument22 SeitenTOA Project Presentation (GROUP 5)Khadija ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 SK Kader Pendamping PGSDokument61 Seiten13 SK Kader Pendamping PGSrachman ramadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHAW Superdew 3 Specification SheetDokument3 SeitenSHAW Superdew 3 Specification SheetGeetha ManoharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 5 WarehousingDokument4 SeitenAssignment 5 WarehousingabbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation Column DesignDokument42 SeitenDistillation Column DesignAakanksha Raul100% (1)
- Aspen Plus User ModelsDokument339 SeitenAspen Plus User Modelskiny81100% (1)
- Student Workbook: Advance 3Dokument31 SeitenStudent Workbook: Advance 3Damaris VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile Strength of Ferro Cement With Respect To Specific SurfaceDokument3 SeitenTensile Strength of Ferro Cement With Respect To Specific SurfaceheminNoch keine Bewertungen
- R67068.0002 2 HB Profibus-Schnittstelle en KueblerDokument42 SeitenR67068.0002 2 HB Profibus-Schnittstelle en KueblerSabari StunnerNoch keine Bewertungen