Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hypoxia
Hochgeladen von
Muhammad Kasi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten1 SeiteThis document discusses the different types of hypoxia, which is a low level of oxygen in the tissues. It outlines four main types of hypoxia: pulmonary, anemic, circulatory, and histotoxic hypoxia. Pulmonary hypoxia is caused by issues in the lungs delivering oxygen to the bloodstream. Anemic hypoxia occurs when there is a lack of hemoglobin or viable hemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood. Circulatory hypoxia results from decreased blood circulation through the lungs. Histotoxic hypoxia is when tissues cannot utilize available oxygen, often due to poisoning.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Hypoxia.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document discusses the different types of hypoxia, which is a low level of oxygen in the tissues. It outlines four main types of hypoxia: pulmonary, anemic, circulatory, and histotoxic hypoxia. Pulmonary hypoxia is caused by issues in the lungs delivering oxygen to the bloodstream. Anemic hypoxia occurs when there is a lack of hemoglobin or viable hemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood. Circulatory hypoxia results from decreased blood circulation through the lungs. Histotoxic hypoxia is when tissues cannot utilize available oxygen, often due to poisoning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten1 SeiteHypoxia
Hochgeladen von
Muhammad KasiThis document discusses the different types of hypoxia, which is a low level of oxygen in the tissues. It outlines four main types of hypoxia: pulmonary, anemic, circulatory, and histotoxic hypoxia. Pulmonary hypoxia is caused by issues in the lungs delivering oxygen to the bloodstream. Anemic hypoxia occurs when there is a lack of hemoglobin or viable hemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood. Circulatory hypoxia results from decreased blood circulation through the lungs. Histotoxic hypoxia is when tissues cannot utilize available oxygen, often due to poisoning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Hypoxia low and high
Low oxygen content in the tissue the relationship of (V) to (Q)
Hypoxemia Pure hypoventilation
Low oxygen content in the blood Wasserman's number
How much oxygen does the body use per inadequate Ve without lung pathology
minute at rest? Shunt
250ml Physiologic and anatomic
How much oxygen does the body use ANEMIC HYPOXIA
under conditions of demand? a decreased level of viable (usable)
5.0 liters Hemoglobin (Hb) available for oxygen
Anaerobic metabolism transport
metabolism without the use of oxygen 2 types of anemic hypoxia
when does anaerobic metabolism occur? Lack of hemoglobin and loss of viable
when the body does not have enough hemoglobin
oxygen Lack of hemoglobin
oxygen demand is >supply reduced hemoglobin. blood loss,
what is produced during anaerobic decreased or faulty RBC production,
exercise? destruction of RBC
Lactic acid. affects PH and damages the Loss of Viable Hemoglobin
cells Carbon monoxide poisoning
symptoms of hypoxia CIRCULATORY HYPOXIA
increased RR, HR, cardiac output, BP, Decreased blood circulation through the
WOB pulmonary system
Dyspnea, nausea, irritability, anxiety, Types of circulatory hypoxia
fear poor cardiac output, shock, hemorrage
Extreme cases: cardiac arrhythmia's, poor cardiac output
cardiac arrest, Clubbing heart failure, valve or heart muscle
Treating Hypoxia disease. Heart muscle damage.
determine the source of the hypoxia to HISTOTOXIC HYPOXIA
properly treat. cell poisoning where body tissue cannot
Oxygen and hypoxia utilize available oxygen
oxygen is used to treat the symptoms of Types of Histotoxic hypoxia
hypoxia not the cause cyanide poisoning, profound electrolyte
4 types of hypoxia disorders
Pulmonary, anemic, circulatory,
histotoxic
PULMONARY HYPOXIA
caused by lung dysfunction, resulting in
lower oxygen being delivered to the
pulmonary capillary bed.
5 types of pulmonary hypoxia
V/Q mismatch, pure hypoventilation,
shunt, diffusion defect, decreased
inhaled oxygen level.
V/Q mismatch
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- University of Balochistan MA MSC International Relation Past Paper 2015 International LawDokument1 SeiteUniversity of Balochistan MA MSC International Relation Past Paper 2015 International LawMuhammad KasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Daily Imroz. 18-01-2020Dokument8 SeitenDaily Imroz. 18-01-2020Muhammad KasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Daily Talatum News 15 Jan 2020Dokument4 SeitenDaily Talatum News 15 Jan 2020Muhammad KasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Admission FormDokument11 SeitenAdmission FormMuhammad KasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- NTS TEST QuestionDokument50 SeitenNTS TEST QuestionMuhammad KasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1700 Mcqs AgricultureDokument96 Seiten1700 Mcqs AgricultureMuhammad KasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Pain Trigger Point Therapy For Exercise Professionals Exam Pack 0616Dokument42 SeitenAnatomy of Pain Trigger Point Therapy For Exercise Professionals Exam Pack 0616Dharmender Singh67% (3)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Braden PD12Dokument17 SeitenBraden PD12Juan Carlos SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Staff No Name Stat Station GradeDokument40 SeitenStaff No Name Stat Station Graderadhey shyam sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- AVSXX App - Jan2003Dokument52 SeitenAVSXX App - Jan2003Jonah RagleNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- En 1092 1 FlangeDokument60 SeitenEn 1092 1 FlangepindarelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Normality in Acid - Base - E-LifesDokument5 SeitenCalculation of Normality in Acid - Base - E-LifesMostafa FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Practice Exam Paper 3Dokument4 SeitenPractice Exam Paper 3Joshua Ong0% (1)
- Phed04020-Module 2 - BasketballDokument25 SeitenPhed04020-Module 2 - BasketballEdnalyn BalicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- 246584-Feats - Eberron FinalDokument4 Seiten246584-Feats - Eberron FinalCristóbal Contreras Chandía0% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Naked Chords - by James ArthurtabsDokument3 SeitenNaked Chords - by James ArthurtabsMaria Cecília PeçanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Mercedes Benz CLA 2019 PDFDokument16 SeitenMercedes Benz CLA 2019 PDFMiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Design Concepts For The Proposed New Cavan Monaghan Community CentreDokument23 SeitenDesign Concepts For The Proposed New Cavan Monaghan Community CentrePeterborough ExaminerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Sports: FootballDokument1 SeiteSports: FootballShirley DicksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- L5R Traps 5e (Donjon Translation)Dokument1 SeiteL5R Traps 5e (Donjon Translation)Jose Manuel Caeiro TopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Coaching Diversity: The Rooney Rule, Its Application and Ideas For ExpansionDokument10 SeitenCoaching Diversity: The Rooney Rule, Its Application and Ideas For Expansionbear clawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code Breaker 1Dokument14 SeitenCode Breaker 1Sutana_GdNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE 101 ManualDokument24 SeitenPE 101 ManualNicole VillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
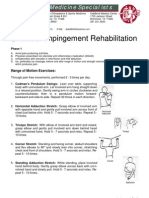
- Shoulder Impingement RehabilitationDokument3 SeitenShoulder Impingement RehabilitationHamzh Sallam100% (2)
- Legacy MC Version MatrixDokument45 SeitenLegacy MC Version MatrixLiam JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Nerves WikipediaDokument6 SeitenSpinal Nerves WikipediaMM NabeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colombiaf 1Dokument1 SeiteColombiaf 1Alonso Pahuacho PortellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Shoulder Performance - Cressey ReinoldDokument40 SeitenOptimal Shoulder Performance - Cressey ReinoldPricope Madalina93% (14)
- Delta GreenDokument310 SeitenDelta Greenpopscythe100% (14)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Fourth Quarterly Test in Mathematics 6Dokument4 SeitenFourth Quarterly Test in Mathematics 6Cher An JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Folklore Bestiary For 5E and OSE by Olivier Revenu - KickstarterDokument1 SeiteA Folklore Bestiary For 5E and OSE by Olivier Revenu - KickstarterTesting0% (3)
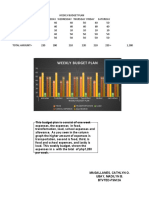
- Weekly Budget PlanDokument1 SeiteWeekly Budget PlanCathlyn MagallanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knight Endings Knight Has Restricted MobilityDokument33 SeitenKnight Endings Knight Has Restricted Mobilitygauchao100% (1)
- The Stand User - GM BinderDokument11 SeitenThe Stand User - GM BinderJeremiah HodgsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torque Converter Turbine Speed SensorDokument1 SeiteTorque Converter Turbine Speed SensorJuan Alberto MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diferencial 14XDokument38 SeitenDiferencial 14XPancho CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)