Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
QB EEE-5th Communication Theory RAVEEN YADAV
Hochgeladen von
Praveen YadavOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
QB EEE-5th Communication Theory RAVEEN YADAV
Hochgeladen von
Praveen YadavCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Shri Santosh Rungta Group of Institutions
Question Bank
Branch ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS
ENGG.
Semester V
Subject Communication Theory
Subject Code 324556(24)
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
http://www.rungta.ac.in
Session 2017-18
Shri Santosh Rungta Group of Institutions
Unit -I
(a) Write any two properties of Fourier transform. 2
(b) A signal m(t) is multiplied by a sinusoidal waveform of frequency fc . The product signal 6
is 𝑣(𝑡) = 𝑚(𝑡) 𝑐𝑜𝑠2𝜋𝑓𝑐 𝑡. if the fourier transform of m(t) is M(f) i.e.
1 ∞
𝑀(𝑓) = ∫ 𝑚(𝑡) 𝑒 −𝑗2𝜋𝑓𝑡 𝑑𝑡
−∞
Find the fourier transform of v(t).
(a) Define modulating signal, carrier signal and modulated signal. 2
2 (b) Determine the percentage power saving when the carrier wave and one of the sidebands are 6
suppressed in an AM wave modulated to a depth of (i) 100% (ii) 50%.
(a) How many AM broadcast can be accommodated in 100 KHz bandwidth if highest frequency 2
3 modulating carrier is 5 KHz.
(b) Explain demodulation of AM wave by using envelope detector. 6
(a) Why amplitude modulation is considered to be inefficient system? 2
4
(b) Explain square law modulator method for generation of AM wave. 6
(a)What is the need of modulation? 2
(b) The power transmitted by a SSB transmitter is 10kW. It is required to be replaced by standard 6
5
AM transmission having modulation index of 0.8 and same power. Determine the power contents
of the carrier and each of the sidebands. Also compute the transmission efficiency.
6 Explain the generation of SSB signal using (i) filter method (ii) phase shift method. 8
7 Explain the feedback arrangement for local oscillator synchronization in synchronous detector. 8
An AM signal is represented in time domain as: 𝑠(𝑡) = 20 [1 + 0.9 cos 2𝜋 × 104 𝑡] cos 2𝜋 × 8
106 𝑡. The signal is radiated in to free space. Sketch the spectrum and calculate the bandwidth
8
required to transmit, power radiated, transmission efficiency. Given antenna resistance (50 +
j0)Ω load.
Explain the generation of SSB signals using filter method with the help of example. Consider the 8
9 message is band limited to 50 Hz-5 KHz, lower carrier frequency is 200 KHz and higher carrier
frequency is 11MHz.
10 Explain the generation of DSB-SC signal using balanced modulator. 8
Draw the frequency domain diagram of SSB-SC modulated signal for periodic and non-periodic 8
11
modulating signal.
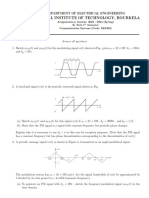
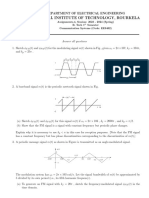
The waveform 𝑣(𝑡) = (1 + 𝑚 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜔𝑚 𝑡)𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜔𝑐 𝑡, with m a constant (𝑚 ≤ 1), is applied to the 8
diode demodulator of fig-1. Show that, if the demodulator output is to follow the envelop of v(t),
12 it is required that any time t0 :
1 𝑚 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜔𝑚 𝑡0
≥ 𝜔𝑚 ( )
𝑅𝐶 1 + 𝑚 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜔𝑚 𝑡0
Shri Santosh Rungta Group of Institutions
Fig-1
Obtain the expression for the signal V3(t) in block diagram shown in fig. Where 𝑉1 (𝑡) = 8
10𝑐𝑜𝑠2000𝜋𝑡 + 4𝑐𝑜𝑠200𝜋𝑡 & 𝑉2 (𝑡) = 𝑉1 (𝑡) + 𝑉12 (𝑡). BPF filter is an ideal filter with
passband 800Hz to 1200Hz.
13
Unit -II
(a) Define frequency deviation. 2
14 (b) An FM wave modulated to depth of 8 generates a bandwidth of 180 KHz. Find the frequency 6
deviation
(a) Define Carson’s rule. 2
15
(b) Explain any one method of FM generation in detail. 6
(a) What is the bandwidth of NBFM and WBFM. 2
16 (b) Find the bandwidth of commercial FM transmission assuming frequency deviation 75 KHz 6
and bandwidth of modulating signal X(t), fm= 15 KHz.
(a) Draw the frequency spectrum of NBFM. 2
17
(b) Discuss reactance modulator method for generation of FM wave. 6
(a) Define instantaneous frequency in FM. 2
(b) An angle modulated signal with carrier frequency 𝜔𝑐 = 2𝜋105 is described by equation 6
𝑣(𝑡) = 10 cos(𝜔𝑐 𝑡 + 5 sin(3 × 103 𝑡) + 10 sin(2𝜋 × 103 𝑡)).Calculate
18 i. Power of modulated signal
ii. Find the frequency deviation Δf.
iii. Find the deviation ratio β .
iv. Find the phase deviation Δф.
v. Estimate the bandwidth of v(t).
19 What is WBFM? Derive its general expression. 8
Shri Santosh Rungta Group of Institutions
20 Explain Armstrong method of generating phase modulated signal. 8
21 Derive the mathematical equation of FM and also give the relationship between FM and PM. 8
Write short notes on (i) pre-emphasis network (ii) de-emphasis network. 𝑉(𝑡) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑤𝑐 𝑡 + 8
22 0.2 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑤𝑚 𝑡. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑤𝑐 𝑡 (i) show that V(t) is a combination of AM and FM signal. (ii) sketch the
phasor diagram at t=0.
23 Explain pre-emphasis and de-emphasis process. 8
A single tone Modulating signal cos(15𝜋 × 103 𝑡) frequency modulate a carrier of 10MHz and 8
produces a frequency deviation of 75KHz. Find
1. Modulation Index
24 2. Phase deviation produced in FM Waves
3. If other modulating signal produces a modulation index of 100 while maintaining the
same deviation. Find Amplitude and Phase of the modulating signal. Assume the
frequency Sensitivity kf =15KHz per volts.
Unit –III
(a) What is aperture effect? 2
25
(b) Explain natural and flat top sampling. Compare the two. 6
(a) What is aliasing? 2
26 (b) A Bandpass signal has spectral range that extends from 20-82KHz. Find the acceptable range
of sampling frequency fs. 6
(a) An analog signal is expressed by the equation 𝑥(𝑡) = 3𝑐𝑜𝑠50𝜋𝑡 + 10𝑠𝑖𝑛300𝜋𝑡 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠100𝜋𝑡.
Calculate the Nyquist rate for this signal. 2
27
(b) Explain PAM with the help of flat top sampling. 6
(a) Define Nyquist rate and Nyquist interval. 2
(b) A TDM system used is used to multiplex the 4 signals 𝑚1 (𝑡) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜔0 𝑡, 𝑚2 (𝑡) =
28 0.5𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜔0 𝑡, 𝑚3 (𝑡) = 2𝑐𝑜𝑠2𝜔0 𝑡, 𝑚4 (𝑡) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠4𝜔0 𝑡. (a) If each signal is sampled at the same
sampling rate calculate the minimum sampling rate fs . (b) What is the commutator speed in 6
revolutions per second?
(a) What is guard band? 2
29 (b) Explain FDM technique with a proper block diagram.
6
30 Explain the generation and detection of PPM with suitable time diagram. 8
31 State and prove sampling theorem for low pass signal. 8
32 Compare TDM and FDM. 8
Shri Santosh Rungta Group of Institutions
33 Compare the various pulse analog modulation methods. 8
34 Explain the generation and detection of PWM with suitable time diagram. 8
Unit –IV
(a) What is sampling? 2
(b) 24 telephone channels each bandlimited to 3.4 KHz are to be time division multiplexed by 6
35
using PCM. Calculate the bandwidth of the PCM system for 128 quantization levels and 8KHz
sampling frequency.
(a) What is the purpose of sample-and-hold circuit? 2
36 (b) A massage signal 𝑚(𝑡) = 10𝑐𝑜𝑠8𝜋103 𝑡 is transmitted through a channel using 4bit PCM. The 6
sampling rate is 15% of the nyquist rate. Calculate the all parameters of PCM system.
(a) What does quantizer do? 2
37
(b) Explain uniform quantization of signals with the help of uniform quantizer. 6
(a) Give the number of quantization level if massage signal 𝑚(𝑡) = 10 sin 10𝜋𝑡 and 5 bit PCM 2
38 system is used.
(b) What is quantization? Derive expression for quantization error. 6
(a) Define Step size for quantization process. 2
39
(b) Write a short note on slope overload distortion and granular noise. 6
40 Describe PCM generation system. 8
41 Explain adaptive delta modulation. 8
42 Explain BPSK transmitter and receiver. 8
43 Explain delta modulation. What are the drawbacks of this system and how it can be eliminated? 8
44 Explain PSK and DPSK. Compare the two. 8
45 Explain FSK with the help of block diagram. 8
46 Explain Differential phase shift keying. 8
Unit –V
47 (a) Define source coding. 2
(b) A source emits seven symbols 𝑥1 , 𝑥2 , … … . , 𝑥7 with respective probabilities 0.35, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1, 6
0.04, 0.005 and 0.005. Give Huffman coding for these symbols and find the average length of the
code word.
48 (a) Define entropy. 2
(b) A continuous signal is band limited to 5KHz. The signal is quantized in 8 levels of a PCM 6
system with the probabilities 0.25, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1, 0.05, 0.05 and 0.05. Calculate the entropy and the
rate of information.
49 (a) What is mutual information? 2
Shri Santosh Rungta Group of Institutions
(b) Find the mutual information and channel capacity of the channel. Given 𝑝(𝑥1 ) = 0.6, 𝑝(𝑥2 ) = 6
0.4.
50 (a) State the Shannon’s theorem. 2
(b) Explain entropy and information rate. 6
51 (a) What is channel capacity. 2
(b) Prove that C=W Log[1+S/N] bits/sec 6
52 Discuss the various aspects of discrete memory less channels (DMC). 8
53 Consider a binary memory less source X with two symbols X1 and X2. Show that H(x) is maximum 8
when both X1 and X2 are equiprobable.
54 Explain SHANNON’S theorem. 8
55 Give short notes on mutual information. 8
56 Explain coding efficiency. Show that the coding efficiency is maximum when P(0) =P(1). 8
57 Find the mutual information for the channel shown in Fig. 8
58 Apply the Shannon-Fano coding procedure for the following message ensemble: 8
[𝑋] = [𝑥1 , 𝑥2 , 𝑥3 , 𝑥4 , 𝑥5 , 𝑥6 , 𝑥7 , 𝑥8 ]
[𝑃] = [1⁄4 , 1⁄8 , 1⁄16 , 1⁄16 , 1⁄16 , 1⁄4 , 1⁄16 , 1⁄8]
Take no of symbols are 2. Calculate efficiency of the code.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Question BankDokument6 SeitenQuestion Banksweetkhushboo786_592Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Radio Sony Xplod PDFDokument52 SeitenManual Radio Sony Xplod PDFSara PozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massive MIMO KPIsDokument2 SeitenMassive MIMO KPIsSharique IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRU3971 HuaweiDokument16 SeitenRRU3971 Huaweiercanaktas73% (11)
- 35 Lte Eran7.0 Ul Comp FeatureDokument36 Seiten35 Lte Eran7.0 Ul Comp FeaturePhan An100% (1)
- Ect305 Analog and Digital Communication, December 2022Dokument3 SeitenEct305 Analog and Digital Communication, December 2022Dinil DhananjayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet IIDokument3 SeitenWorksheet IIBirhanu MelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acs UniversityqpDokument20 SeitenAcs Universityqpgkk001Noch keine Bewertungen
- rr221702 Analog CommunicationsDokument8 Seitenrr221702 Analog CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University CTDokument3 SeitenAnna University CTprayog8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog CommunicationsDokument4 SeitenAnalog CommunicationsJagadeesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice SetDokument5 SeitenPractice Setrishavkumarsingh088Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communication (ECE - 3103) PDFDokument2 SeitenAnalog Communication (ECE - 3103) PDFDevender DuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr322205 Communication SystemsDokument7 Seitenrr322205 Communication SystemsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Dec. ECT305-ADokument3 Seiten2021 Dec. ECT305-ADinil DhananjayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 PDFDokument5 SeitenAssignment 2 PDFSourav kumar MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Dokument5 Seiten07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Anonymous BHcPexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog CommunicationsDokument6 SeitenAnalog CommunicationsSri KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rr220401 Communication TheoryDokument8 SeitenRr220401 Communication TheorySrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICS Worksheet1Dokument5 SeitenICS Worksheet1agergizat girmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05220405 Analog CommunicationsDokument8 Seitenr05220405 Analog CommunicationsandhracollegesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument5 SeitenAssignmentpaper.2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communications (DCOM)Dokument4 SeitenDigital Communications (DCOM)Mamotete MohohloNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05220405 Analog CommunicationsDokument7 Seitenr05220405 Analog CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Sourav kumar MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ra Ec 05032 Analog CommunicationsDokument1 SeiteRa Ec 05032 Analog CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Model Question Paper: V SemesterDokument3 SeitenAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Model Question Paper: V SemesterChandra SekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved ProblemsDokument10 SeitenSolved ProblemsAhmed AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved ProblemsDokument10 SeitenSolved ProblemsRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude ModulationDokument3 SeitenAmplitude ModulationArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr310405 Digital CommunicationsDokument8 Seitenrr310405 Digital CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDokument4 SeitenPractice Questionspratik shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.vijaikirubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr321001 Communication EngineeringDokument8 Seitenrr321001 Communication EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- NovemberDecember 2020Dokument1 SeiteNovemberDecember 2020PoongodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Theory Overall Question BankDokument7 SeitenCommunication Theory Overall Question BankECEOCETNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code: E3077Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper Code: E3077tamil09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adc 1Dokument2 SeitenAdc 1nithyajothiNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr220401 Communication TheoryDokument8 Seitenrr220401 Communication TheorySRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsDokument3 SeitenBEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsSiam hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4-SolutionDokument11 SeitenTutorial 4-SolutionZaidi Mat ZainuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument11 SeitenAssignment 2secidih495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationDokument3 SeitenAssignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationRhelf Mae ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 3Alok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment3 SolutionsDokument12 SeitenAssignment3 SolutionsabaalharthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- T) V. The Total SidebandDokument19 SeitenT) V. The Total SidebandPramiti ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Questions Bank EC CommunicationDokument10 SeitenGate Questions Bank EC CommunicationfreefreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec332 - Communication Theory and SystemDokument3 SeitenEc332 - Communication Theory and SystemsubhazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 4Alok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)krithikgokul selvam100% (1)
- EEE302 SampQs MergedDokument78 SeitenEEE302 SampQs Mergedc gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aptitutude QuestionsDokument10 SeitenAptitutude QuestionsKalirajan KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiDokument8 SeitenCentral College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiqweweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment#1ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Extra BENT3753Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Extra BENT3753Muhammad AimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Following Paper ID and Roll No. To Be Filled in Your Answer BookDokument4 SeitenFollowing Paper ID and Roll No. To Be Filled in Your Answer BookNivedita BasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Dokument2 SeitenSchool of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Dinesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Communication CSP-310 Homework Assignment 2: (Submission Deadline: October 28, 2017)Dokument1 SeiteWireless Communication CSP-310 Homework Assignment 2: (Submission Deadline: October 28, 2017)Sachin AkhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pue 4114 Cat1-2022Dokument2 SeitenPue 4114 Cat1-2022Frankyz Oraekwe ObiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondVon EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 12Dokument15 SeitenLec 12Praveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) IDokument10 SeitenFHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) IPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 8Dokument8 SeitenLec 8Praveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antennas: Isotropic RadiatorDokument4 SeitenAntennas: Isotropic RadiatorPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medium Access Control: - MAC Belongs To Data Link Control LayerDokument7 SeitenMedium Access Control: - MAC Belongs To Data Link Control LayerPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Propagation Ranges: SenderDokument5 SeitenSignal Propagation Ranges: SenderPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3Dokument14 SeitenLec 3Praveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequencies For Mobile CommunicationDokument6 SeitenFrequencies For Mobile CommunicationPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1Dokument9 SeitenLec 1Praveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early History of Wireless CommunicationDokument7 SeitenEarly History of Wireless CommunicationPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spread Spectrum Technology: Interference Spread Signal Signal Spread Interference Power PowerDokument5 SeitenSpread Spectrum Technology: Interference Spread Signal Signal Spread Interference Power PowerPraveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- A High Gain Microstrip Patch Array For 5 GHZ Wlan ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenA High Gain Microstrip Patch Array For 5 GHZ Wlan ApplicationsYossef ARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tbs Tango ManualDokument29 SeitenTbs Tango ManualGaluh PrambananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four: Angle ModulationDokument20 SeitenChapter Four: Angle Modulationhayumbe08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mettler Toledo 8442 Operation User S Manual 29Dokument29 SeitenMettler Toledo 8442 Operation User S Manual 29anasalawayNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioSonic US100RDokument108 SeitenBioSonic US100RSomars AvendañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aal 233 Kmia..SbgrDokument62 SeitenAal 233 Kmia..SbgrDiego GomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume For Broadcasting InternshipDokument7 SeitenResume For Broadcasting Internshipbcrqs9hr100% (2)
- Fresnel ZoneDokument4 SeitenFresnel ZoneMuhammad NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Encoding Techniques (Part 2)Dokument31 SeitenSignal Encoding Techniques (Part 2)Arslan AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrugadas GranetDokument9 SeitenCorrugadas GranetKevs SsmNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRU3939 DescriptionDokument12 SeitenRRU3939 DescriptionrimouchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quinstar 2009 CatalogDokument216 SeitenQuinstar 2009 Catalog9999igiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELWAVE DuplexersDokument4 SeitenCELWAVE Duplexersdavidkumul02Noch keine Bewertungen
- A68 RF Hardware Trouble Shooting Guide - WO - SA - A8960 - 1001 PDFDokument56 SeitenA68 RF Hardware Trouble Shooting Guide - WO - SA - A8960 - 1001 PDFDnw DigitalprintingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sony CCD-TR67 PDFDokument80 SeitenSony CCD-TR67 PDFClemente GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voice Solution in 4G - VoLTEDokument10 SeitenVoice Solution in 4G - VoLTEMuntadher KamelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors 17 00341 v2Dokument36 SeitenSensors 17 00341 v2rubertussNoch keine Bewertungen
- TBA120 Demodulator Circuit IcDokument3 SeitenTBA120 Demodulator Circuit IcEleonor CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardo's Scala Rider Q3/Q3 MultiSet - User ManualDokument16 SeitenCardo's Scala Rider Q3/Q3 MultiSet - User ManualgogglespiezonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: 90 Series Open Frame TouchscreenDokument24 SeitenUser Manual: 90 Series Open Frame Touchscreenchristian.kojiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toaz - Info Planning Amp Design PRDokument4 SeitenToaz - Info Planning Amp Design PRSamuel FredrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final - Exam of An Antenna - 2020 - IDokument2 SeitenFinal - Exam of An Antenna - 2020 - Iمهيمن الابراهيميNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-14 Batch Vi Sem Grade AnalysisDokument4 Seiten10-14 Batch Vi Sem Grade AnalysisPrabha Karan MurugadossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume For Radio InternshipDokument7 SeitenResume For Radio Internshipafdnarfmi100% (1)
- Heron HD3430 Regulatory Addendum (ENG)Dokument2 SeitenHeron HD3430 Regulatory Addendum (ENG)Abidi CharfeddineNoch keine Bewertungen
- AM Demodulation (Summary)Dokument18 SeitenAM Demodulation (Summary)ljjbNoch keine Bewertungen