Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
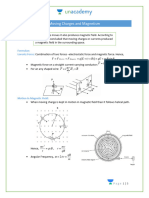
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Hochgeladen von
Sai PrajitCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Hochgeladen von
Sai PrajitCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
u
Formulae For 1 11
MOVING CHARGES & MAGNETISM
1
1
By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A'
CHAPTER FORMULAS
& NOTES
Important Terms, Definitions & Formulae
Top Formulae
1. Lorentz Force :Force on a charge q moving with velocity v in the
presence of magnetic and electric fields B and E.
F q(vxB E)
The magnetic force FB q(vxB) is normal to v and work done by it is
zero.
2. Force F on a straight conductor of length and carrying a steady
current I placed in a uniform external magnetic field B,
F IxB
3. A charge q executes a circular orbit in a plane normal with frequency
called the cyclotron frequency given by:
qB
c
2 m
This cyclotron frequency is independent of the particle’s speed and
radius.
4. Biot – Savart law asserts that the magnetic field dB due to an element
d carrying a steady current I at a point P at a distance r from the
current element is:
μ d r
0
dB I 3
4π r
5. Magnetic field due to circular coil of radius R carrying a current I at an
axial distance x from the centre is
μ0IR2
B
3 /2
2 x2 R2
At the centre of the coil,
CHAPTER FORMULAS & NOTES
2
μ0I
B
2R
6. Ampere’s Circuital Law: For an open surface S bounded by a loop C,
μ0I where I refers o the
then the Ampere’s law states that B.d
c
current passing through S.
If B is directed along the tangent to every point on the perimeter them
BL μ0Ie
where Ie is the net current enclosed by the closed circuit.
7. Magnetic field at a distance R from a long, straight wire carrying a
current I is given by:
μ0I
B
2R
The field lines are circles concentric with the wire.
8. Magnetic field B inside a long Solenoid carrying a current I is
B = µ0 nI
where n is the number of turns per unit length.
For a toriod,
μ0NI
B
2πr
where N is the total numbers of turns and r is the average radius.
9. Magnetic moment m of a planar loop carrying a current I, having N
closely wound turns, and an area A, is
m NIA
Direction of m is given by the right – hand thumb rule: curl and palm
of your right hand along the loop with the fingers pointing in the
direction of the current. The thumb sticking out gives the direction of
m (and A ).
When this loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field B, the force F on it
is: F = 0
And the torque on it is,
mxB
CHAPTER FORMULAS & NOTES 3
In a moving coil galvanometer, this torque is balanced by a counter
torque due to a spring, yielding.
kΦ = NI AB
where Φ is the equilibrium deflection and k the torsion constant of the
spring.
10. An electron moving around the central nucleus has a magnetic
moment μ , given by
e
μ
2m
where is the magnitude of the angular momentum of the circulating
electron about the central nucleus. The smallest value of μ is called
the Bohr magneton µB and it is µB = 9.27 x 10–24 J/T
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- RCE World Rallycross Championship 2014 New PDFDokument40 SeitenRCE World Rallycross Championship 2014 New PDFAnita DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic and Compressible Flow TurbomachinesDokument146 SeitenHydraulic and Compressible Flow TurbomachinesPaul Healy100% (3)
- Hughes 500 C IpcDokument479 SeitenHughes 500 C IpcRodolfo Rol100% (1)
- SHC 302 FinalDokument285 SeitenSHC 302 FinalAmr HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plumbing & Fire Fighting Design & Construction - IPC & NFPA - Online Training CourseDokument10 SeitenPlumbing & Fire Fighting Design & Construction - IPC & NFPA - Online Training CourseNexus Inspectorate Private LimitedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 Hydraulic Subsurface Pumps 1987 Developments in Petroleum ScienceDokument102 SeitenChapter 15 Hydraulic Subsurface Pumps 1987 Developments in Petroleum ScienceFalokid RaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument3 SeitenMoving Charges and MagnetismGoogle AnvekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charge and MagnetismDokument3 SeitenMoving Charge and Magnetismdevgamer749Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes Ch04 Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes Ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism8D Audio TuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 NotesDokument2 SeitenChapter 4 NotesMohit GurjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes Ch04 Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes Ch04 Moving Charges and MagnetismMehul PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 NotesDokument2 SeitenChapter 4 NotesprithiksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism: SyllabusDokument18 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism: Syllabusaabid ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic and Mechanic Effect of Electric CurrentDokument135 SeitenMagnetic and Mechanic Effect of Electric Currentroydenmiranda62Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism and Magnetic Effects of CurrentDokument3 SeitenMagnetism and Magnetic Effects of CurrentKartikNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-04: Moving Charges and Magnetism Force On A Straight ConductorDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-04: Moving Charges and Magnetism Force On A Straight ConductorsumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Снимок экрана 2023-05-17 в 21.56.17Dokument24 SeitenСнимок экрана 2023-05-17 в 21.56.17niabmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field (Electromagnets)Dokument22 SeitenMagnetic Field (Electromagnets)allfanaccNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edited Formula Sheet Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument5 SeitenEdited Formula Sheet Moving Charges and Magnetismsugumarharini145Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 22 - ElectromagnetismDokument5 SeitenTopic 22 - ElectromagnetismMauriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Magnetic Field (EMF)Dokument42 SeitenElectro Magnetic Field (EMF)d anjilappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vii (Moving Charges and Magnetism)Dokument16 SeitenSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vii (Moving Charges and Magnetism)sojakoj867Noch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROMAGNETISM (Short Inside Book)Dokument17 SeitenELECTROMAGNETISM (Short Inside Book)daniyal.king55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDokument15 SeitenChapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionKELLY NGU SHU YI MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Formula SheetDokument8 SeitenMoving Charges and Magnetism Formula SheetBhushan soriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Magnetic Field: General Physics Phys. 106Dokument127 SeitenSources of Magnetic Field: General Physics Phys. 106hwuhwuheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charges and Magnetism: Chapter - 4Dokument52 SeitenMoving Charges and Magnetism: Chapter - 4hlloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Magnetic Induction: SynopsisDokument35 SeitenElectro Magnetic Induction: SynopsisKeertanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Marks Questions & Answers: 4. Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument12 SeitenOne Marks Questions & Answers: 4. Moving Charges and MagnetismSachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biot 200601154800Dokument26 SeitenBiot 200601154800UMAIR ASHFAQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current & Mechanical Effct of Electric CurrentDokument41 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Electric Current & Mechanical Effct of Electric CurrentShweta Y KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument27 SeitenMoving Charges and MagnetismAkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 PhyDokument32 SeitenChapter 5 Phyatintasya18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revised SR PhyDokument29 SeitenRevised SR PhytattikotasatishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effects of Currents and MagnetostaticsDokument23 SeitenMagnetic Effects of Currents and MagnetostaticsMunish Dogra100% (1)
- 19 Magnetism Formula Sheets QuizrrDokument7 Seiten19 Magnetism Formula Sheets QuizrrDhairya SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsDokument8 SeitenMagnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsTshiamo MotaungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19 Magnetism Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFDokument6 Seiten19 Magnetism Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFchucha kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism and MatterDokument4 SeitenMagnetism and MatterPranshu PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY71-Topic 9-Electromagnetic Induction-AK Removed QuestionsDokument20 SeitenPHY71-Topic 9-Electromagnetic Induction-AK Removed QuestionsnadalmzrNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR PHY VsaqDokument4 SeitenSR PHY VsaqtattikotasatishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap28 PaginePDF AmaldiBluDokument6 SeitenCap28 PaginePDF AmaldiBluCaterina ZaninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction: Theory and Exercise BookletDokument62 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction: Theory and Exercise Bookletabc9999999999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field Circular Coil 01-30-2017Dokument10 SeitenMagnetic Field Circular Coil 01-30-2017Michael GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Ch21 SolutionDokument7 SeitenTutorial Ch21 SolutiontonyformedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charge & Magnetism 26.1Dokument2 SeitenMoving Charge & Magnetism 26.1EbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RtreterterDokument419 SeitenRtreterterMohammedNasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9 Magnetic InteractionsDokument11 SeitenLab 9 Magnetic InteractionsUyên NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMTL ProblemsDokument6 SeitenEMTL ProblemsPhani KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1233140-Motion of Charge and Magnetic FieldDokument22 Seiten1233140-Motion of Charge and Magnetic FieldMohit SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Fields and Magnetic Forces: Properties of MagnetDokument54 SeitenMagnetic Fields and Magnetic Forces: Properties of Magnetمارتن بولسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Chapter - 14 (Lecture-18)Dokument17 SeitenPhysics Chapter - 14 (Lecture-18)Adeela UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC Chapter 30Dokument98 SeitenPC Chapter 30ultimu100% (1)
- (Jiha) Chapter 4 - MagnetismDokument96 Seiten(Jiha) Chapter 4 - Magnetismnaderaqistina23Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physc em Electromagnetic Problem Solving Techniques 2020-03-20Dokument64 SeitenAP Physc em Electromagnetic Problem Solving Techniques 2020-03-20Armored SumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alt F4Dokument4 SeitenAlt F4John Rhey ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument16 SeitenElectromagnetic InductionPRIYAA A/P JAYASANKAR / UPMNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Ix (Electromagnetic Induction)Dokument4 SeitenSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Ix (Electromagnetic Induction)sojakoj867Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charges and Magnetism: Right-Hand Thumb RuleDokument6 SeitenMoving Charges and Magnetism: Right-Hand Thumb RuleSahil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emi TheoryDokument12 SeitenEmi TheoryYash MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFViji GowriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes Ch04 Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes Ch04 Moving Charges and MagnetismTanmayGairolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFTushar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFKOMAL NAVARIYANoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFDokument2 Seiten12 Physics Notes ch04 Moving Charges and Magnetism PDFNaveen RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IVon EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Iii Digital Circuits: Decimal Number SystemDokument135 SeitenUnit Iii Digital Circuits: Decimal Number SystemSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyderabad Institute of Technology and Management Faculty PresentationDokument19 SeitenHyderabad Institute of Technology and Management Faculty PresentationSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I PN Junction Diode: 1.0 IntroductonDokument24 SeitenUnit-I PN Junction Diode: 1.0 IntroductonSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyderabad Institute of Technology and Management Faculty PresentationDokument54 SeitenHyderabad Institute of Technology and Management Faculty PresentationSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eg Question Bank For Mid ExamsDokument2 SeitenEg Question Bank For Mid ExamsSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I: Differential Equations ofDokument24 SeitenUnit-I: Differential Equations ofSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I: Differential Equations ofDokument9 SeitenUnit-I: Differential Equations ofSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reality TV Student Worksheet PDFDokument5 SeitenReality TV Student Worksheet PDFSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyderabad Institute of Technology and Management Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument2 SeitenHyderabad Institute of Technology and Management Department of Mechanical EngineeringSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salient Features of Kurnool District: Location and CompositionDokument6 SeitenSalient Features of Kurnool District: Location and CompositionSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guntur District DHB - 2013Dokument287 SeitenGuntur District DHB - 2013Sai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ananta PurDokument11 SeitenAnanta PurSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conic Sections VedantuDokument43 SeitenConic Sections VedantuSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Important QuestionDokument16 SeitenMaths Important QuestionSai PrajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOXE B5i - ENG PDFDokument7 SeitenDOXE B5i - ENG PDFRiswanda HimawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corr BHELDokument32 SeitenCorr BHELDGM BoilerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH6 - NDE SymbolsDokument32 SeitenCH6 - NDE SymbolsEdgar SerafinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE WeldstarDokument6 SeitenGE WeldstarJamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flecha CardanDokument6 SeitenFlecha CardanCarlos roberto Aguiirre rosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Flow Experiment System Specification GenericDokument2 SeitenHeat Flow Experiment System Specification GenericpinkpanterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroflo SelectionDokument1 SeiteHydroflo SelectionJosh SorensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Da8: (Formerly DA8/9) Direct-Acting, Positive Bias Differential Back Pressure RegulatorDokument18 SeitenModel Da8: (Formerly DA8/9) Direct-Acting, Positive Bias Differential Back Pressure RegulatorBoubekeur HamegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen - Importance of Welding in L & T PDFDokument30 SeitenGen - Importance of Welding in L & T PDFSivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SINOPEC Industrial CatalogueDokument12 SeitenSINOPEC Industrial CatalogueSumaya Akter0% (1)
- Manual Compresor Water FurnaceDokument50 SeitenManual Compresor Water FurnaceFred GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear OilsDokument3 SeitenGear OilsPurchase ZenoilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolt Capacities: Grade 4.6 Bolts in S355Dokument3 SeitenBolt Capacities: Grade 4.6 Bolts in S355Ah ChiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banda Lido Datasheet - uni-OWLDokument2 SeitenBanda Lido Datasheet - uni-OWLVilma sagresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07-Eixo Dianteiro 2Dokument18 Seiten07-Eixo Dianteiro 2Renato AssisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machining and Machine Tool Operation PI GATE 2020 Previous Year With Ans KeyDokument21 SeitenMachining and Machine Tool Operation PI GATE 2020 Previous Year With Ans Keyhyper meshNoch keine Bewertungen
- A320-Mel-Cdl-Cdd StatusDokument18 SeitenA320-Mel-Cdl-Cdd StatusvproNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Writing Differential EquationDokument9 SeitenMethods of Writing Differential EquationDillah UtamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homelite String Trimmer Parts Manual HBC30 String Trimmer UT 15085Dokument12 SeitenHomelite String Trimmer Parts Manual HBC30 String Trimmer UT 15085marcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manitou MHT 10120 enDokument16 SeitenManitou MHT 10120 enElardus EngelbrechtNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementDokument35 SeitenNPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume: Professional ExperienceDokument3 SeitenResume: Professional ExperienceShankker KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Catalogue - Waterfalls Manufacturing - 2022 EditionDokument16 SeitenGeneral Catalogue - Waterfalls Manufacturing - 2022 Editionmuhammad nurochmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeatDokument54 SeitenHeatARNAV GOELNoch keine Bewertungen