Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Medical and Nursing Management Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
Pau-pau Basi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten7 SeitenThe document summarizes the nursing care plan for a child with chronic lung disease. It assesses the child's respiratory status and provides interventions to improve breathing patterns and maintain clear airways. The plan aims to establish normal breathing over time through positioning, fluid intake, monitoring for distress signs, and keeping the environment allergen-free. The overall goal is to effectively manage respiratory issues related to immature lung development in premature infants.
Originalbeschreibung:
ncp for risk for infection
Originaltitel
Assessment 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document summarizes the nursing care plan for a child with chronic lung disease. It assesses the child's respiratory status and provides interventions to improve breathing patterns and maintain clear airways. The plan aims to establish normal breathing over time through positioning, fluid intake, monitoring for distress signs, and keeping the environment allergen-free. The overall goal is to effectively manage respiratory issues related to immature lung development in premature infants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten7 SeitenMedical and Nursing Management Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
Pau-pau BasiThe document summarizes the nursing care plan for a child with chronic lung disease. It assesses the child's respiratory status and provides interventions to improve breathing patterns and maintain clear airways. The plan aims to establish normal breathing over time through positioning, fluid intake, monitoring for distress signs, and keeping the environment allergen-free. The overall goal is to effectively manage respiratory issues related to immature lung development in premature infants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 7
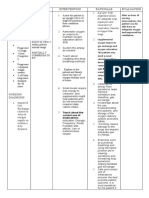
CHAPTER VII
MEDICAL AND NURSING MANAGEMENT
Nursing Care Plan
ASSEESSMENT EXPLANATION OF PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM
SUBJECTIVE: Chronic lung STO: ➢ Assessed ➢ Tachypnea After 8 hours of
“Nahihirapan disease is a ➢ After 8 hours respiratory indicates nursing
huminga si baby general term for of nursing status, noting respiratory intervention,
kaya naka-oxygen long-term intervention, signs of distress the client
at hindi normal respiratory the child will respiratory especially when maintained
yung sounds ng problem in be able to have distress such RR is airway passing,
paghinga niya” premature clear breath as tachypnea, >75breaths/min; clear breath
as verbalized by babies. It Is sounds and nasal flaring, expiratory sounds and
the mother of also known as regular grunting, grunting regular
the child. Bronchopulmonary breathing retractions or represents breathing
Dysplasia (BPD). pattern. crackles. attempt to pattern.
OBJECTIVE: CLD in infant’s maintain
➢ Oxygen in use VEINS that LTO: alveolar
via nasal damaged tissue ➢ After 2 days of expansion;
cannula in the newborn’s nursing nasal flaring
➢ Use of lungs is intervention, is a
accessory breathing and the child will compensatory
muscle noted health problems be able to mechanism to
it occurs when a establish a increase
normal diameter of
➢ Irregular newborn have respiratory nares and
breathing been injured. pattern and increase oxygen
pattern normal skin intake.
➢ O2 saturation color. ➢ Assessed skin ➢ Lack of oxygen
is 90% color for will result in
development of cyanosis.
NURSING cyanosis.
DIAGNOSIS: ➢ Positioned the ➢ To enable the
Ineffective patient in semi body to
airway clearance fowler’s recuperate and
related to position. repair.
chronic lung
disease as ➢ Instructed the ➢ To decrease the
evidenced by mother to let metabolic rate
cyanosis her baby rest, and oxygen
minimize consumption.
stimulation and
energy
expenditure.
➢ Instructed the ➢ Increased mucus
mother to and sputum
increase fluid secretions can
intake. lead to
dehydration;
increased water
intake can help
dissolve
secretions.
➢ Kept ➢ Presence may
environment trigger
allergen-free allergic
such as dust, response that
feather may cause
pillows, smoke further
or pollen. increase in
mucus
secretion.
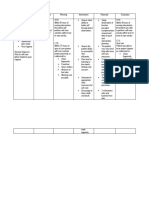
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM
Objective: Lungs that are STO: After 4 ➢ Assessed ➢ Manifestations After 2 days of
➢ Preterm birth lacking in hours of nursing respiratory of respiratory nursing
➢ With oxygen via surfactant (a intervention, rate, depth distress is intervention,
nasal cannula solution that the infant will and ease. dependent on the patient
regulated at 5 prevents the experience an indicative of shows normal and
liters per lungs from effective the degree of effective
minute sticking breathing lung respiratory
➢ RR: 37 together during pattern as involvement pattern
breaths/min breathing), are evidenced by no and underlying
➢ O2 saturation considered episodes of general
of 90% premature. Any apnea. status.
➢ With episodes premature baby ➢ Position head ➢ To promotes
of apnea (5-10 born before 37 appropriate expectoration,
seconds) weeks age of LTO: After 2 for age and clearing or
gestation can be days of nursing condition to infection.
NURSING diagnosed with a intervention, open or
DIAGNOSIS: premature lung. the patient will maintain open
Ineffective Breathing establish a airway to
breathing problems in normal, determine
pattern related premature babies effective ability to
to immature may be due to an respiratory protect own
pulmonary immature lung pattern as airway.
development rather than a evidenced by ➢ Instructed the ➢ To prevent
specific disease absence of mother to drying of
or complication. cyanosis and increase oral secretions.
apnea. fluid intake
of the
patient.
➢ Humidifier at ➢ To loosen
bedside. secretions.
➢ Instructed the ➢ To help
mother to maintain
positioned the adequate lung
patient in expansion thus
semi fowler’s preventing
position. buildup of
secretions.
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM
Subjective: Respiratory STO: After 8 ➢ Assessed for ➢ Abnormality After nursing
n/a distress results hours of nursing respiration indicates intervention,
from surfactant intervention, noting for respiratory the patient was
Objective: deficiency, the patient will rate, rhythm compromise. able to maintain
➢ With oxygen via usually seen in be able to and pattern. airway patency
nasal cannula premature maintain airway ➢ Assessed airway ➢ Maintaining the and free from
regulated at 5 infants, but can patency and the for patency. airway is respiratory
liters per occur with mother will always the distress.
minute decreased report first priority,
➢ Episodes of frequency in improvement if especially in
apnea term infants. oxygen exchange case of trauma,
➢ V/S taken as Incidence rates acute
follows: range from 86% neurological
RR: 37 at 24 weeks to LTO: After 3 decompensation,
breaths/min less than 1% at days of nursing or cardiac
O2 Saturation of 39 weeks. intervention, arrest.
90% Respiratory mother will
distress should report the ➢ Auscultated ➢ Adventitious
NURSING be anticipated reduction of lungs for breath sounds
DIAGNOSIS: in the setting congestion with presence of may indicate
of any preterm breath sounds adventitious presence of
Risk for delivery, clear and breath sounds. mucous plug,
respiratory delivery where noiseless increasing
distress amniotic fluid respiration. airway
indices indicate resistance or
pulmonary presence of
immaturity and fluid along
in any infant larger airways.
born to a ➢ Assessed ➢ Increasing
diabetic mother. changes in lethargy,
mental status. confusion,
restlessness or
irritability
can be early
signs of
cerebral
hypoxia.
➢ Assessed cough ➢ Consider
for possible causes
effectiveness for ineffective
and cough:
productivity. respiratory
muscle fatigue,
severe
bronchospasm,
thick tenacious
secretions and
others.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudySheryl Anne GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 2201 Final Exam ReviewDokument24 SeitenBiology 2201 Final Exam ReviewSarah Crowe100% (5)
- Chapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract DisordersDokument17 SeitenChapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract DisordersMary SingletonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emphysema Case Study E3Dokument28 SeitenEmphysema Case Study E3scarletsky1975% (8)
- Drug Study Adn Ncp-Case Pres.Dokument22 SeitenDrug Study Adn Ncp-Case Pres.MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Nursing-Process-in-the-care-of-the-Community - FGBDokument41 Seiten2 Nursing-Process-in-the-care-of-the-Community - FGBKim Bok JooNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument10 SeitenNCPJose CousinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 112 Fluid and ElectrolytesDokument2 SeitenNCM 112 Fluid and ElectrolytesAngeline NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIrish Jane GalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - JaundiceDokument5 SeitenNCP - JaundiceQueen Shine0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Dokument3 SeitenElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Case 3 and 4Dokument12 SeitenNCP Case 3 and 4boomer SeargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameDokument3 SeitenDrug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaster Nursing SAS Session 8Dokument5 SeitenDisaster Nursing SAS Session 8Niceniadas CaraballeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan #1: IndependentDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan #1: IndependentMaria ThereseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ordonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleDokument4 SeitenOrdonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleKyla OrdonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- RabiesDokument12 SeitenRabieszenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ko BabyDokument3 SeitenNCP Ko BabyDaniel ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Schools of Thought - Part TwoDokument56 SeitenEthical Schools of Thought - Part TwoFille_Anne_Lay_1019100% (1)
- Document 32Dokument3 SeitenDocument 32Grace CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Diagnostic ProceduresDokument41 SeitenRespiratory Diagnostic Proceduresseigelystic100% (23)
- Involving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialDokument10 SeitenInvolving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialAngel MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP ProperDokument9 SeitenNCP Properstephanie eduarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- CHN Lecture Module 7 Doh Programs Related To Family HealthDokument42 SeitenCHN Lecture Module 7 Doh Programs Related To Family HealthMhianne SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDokument7 SeitenNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws Affecting Public Health and Practice of CHNDokument4 SeitenLaws Affecting Public Health and Practice of CHNheide25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Angina PectorisDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Angina PectorisLeroy LoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument9 SeitenNCPHendy Hency YunusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gregorio, Forgive Us All: Community Health Nursing 1 Activity #1Dokument2 SeitenGregorio, Forgive Us All: Community Health Nursing 1 Activity #1Cacamo Rexell-anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan DMDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan DMnikaaraaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For HYPERTHERMIADokument3 SeitenNCP For HYPERTHERMIAGil Ganiban0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationFebee GeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenCollege of Nursing Nursing Care PlanteuuuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter61 Management of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionDokument49 SeitenChapter61 Management of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionAhmed 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1. Assessing Your Understanding: Ethical Principle Example in Nursing PracticeDokument4 SeitenTask 1. Assessing Your Understanding: Ethical Principle Example in Nursing PracticeRanz Kenneth G. FrandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenPathophysiologyDimple BlancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP On Nerborn CareDokument7 SeitenNCP On Nerborn CareMandeep KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImciDokument3 SeitenImciJohn Benzon0% (1)
- Hyogo FrameworkDokument6 SeitenHyogo FrameworkPaul AriolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEDokument2 SeitenCourse Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEKhate BartolomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nebu&CPTDokument32 SeitenNebu&CPTAbigail Bantayan100% (1)
- Hildegard Peplau Theory of Interpersonal RelationsDokument1 SeiteHildegard Peplau Theory of Interpersonal RelationsTADZMALYN JINANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence-Based Nursing Feu NRMFDokument3 SeitenEvidence-Based Nursing Feu NRMFreformamrNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP RiskDokument2 SeitenNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IbuprofenDokument2 SeitenIbuprofenKate AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Risk InfectionDokument1 SeiteNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDokument9 SeitenNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Last NCP in InfantDokument1 SeiteLast NCP in Infantmitsuki_sylphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moira Mae B. Balite BSN 2A: Post Partum Care DefinitionDokument5 SeitenMoira Mae B. Balite BSN 2A: Post Partum Care DefinitionMoiraMaeBeridoBaliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Teaching PlanDokument3 SeitenHealth Teaching PlanSonia MambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Respiratory Tract ProblemsDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Respiratory Tract ProblemsDianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDokument6 SeitenNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- NCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionDokument1 SeiteNCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionGale DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenDate Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkimglaidyl bontuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments, Chapter 15, Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthDokument8 SeitenAssignments, Chapter 15, Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Fears Related To Pregnancy, Labor, and Delivery and Coping Mechanisms Among Primigravida MothersDokument70 SeitenCommon Fears Related To Pregnancy, Labor, and Delivery and Coping Mechanisms Among Primigravida MothersSmile Tambanillo0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance NCPDokument1 SeiteIneffective Airway Clearance NCPBenz ParCoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs and NCPDokument4 SeitenDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 NCM 112Dokument4 SeitenTopic 3 NCM 112Marielle ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Bronchiolitis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDokument14 Seiten5 Bronchiolitis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsAnnapoorna SHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan FinalJny SthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basi, Pauline R. NDA-1 March 18, 2020: Function of BandagingDokument9 SeitenBasi, Pauline R. NDA-1 March 18, 2020: Function of BandagingPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study in PharmaDokument69 SeitenDrug Study in PharmaPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Bengbeng'S Special Pancit": Thank You For Supporting Our Small BusinessDokument1 Seite"Bengbeng'S Special Pancit": Thank You For Supporting Our Small BusinessPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 2Dokument20 SeitenDrug Study 2Pau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMC Nursing ServiceDokument1 SeiteBMC Nursing ServicePau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delayed Growth NCPDokument3 SeitenDelayed Growth NCPPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study NurseryDokument6 SeitenDrug Study NurseryPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Like Sitting at The Headquarters Desk and Writing Up Reports, Police Officers Have A Hard Time in Maintaining Their FitnessDokument2 SeitenLike Sitting at The Headquarters Desk and Writing Up Reports, Police Officers Have A Hard Time in Maintaining Their FitnessPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrlytes 1Dokument14 SeitenFluids and Electrlytes 1Pau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Blood Count Result Form Test Name Result Reference RangeDokument4 SeitenComplete Blood Count Result Form Test Name Result Reference RangePau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired SocialDokument5 SeitenNCP Impaired SocialPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PsychopathDokument1 SeitePsychopathPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument2 SeitenAssessmentPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethnicityrefers To The Shared SocialDokument1 SeiteEthnicityrefers To The Shared SocialPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Project Management To Reduce The Operating Room InfectionDokument8 SeitenNursing Project Management To Reduce The Operating Room InfectionPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harvard T.H. Chan School Such As Diabetes and Heart Diseases Are Significantly Higher in Some Ethnic Groups (Dokument1 SeiteHarvard T.H. Chan School Such As Diabetes and Heart Diseases Are Significantly Higher in Some Ethnic Groups (Pau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenNCP Pneumoniakaiserdominick100% (2)
- AWFA+First+Aid+E-Manual+Vs5.3 Aug+2019Dokument88 SeitenAWFA+First+Aid+E-Manual+Vs5.3 Aug+2019Tomas BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sputum Analysis and BalDokument41 SeitenSputum Analysis and BalClaire GonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Biology 11Dokument36 SeitenChapter 11 Biology 11ax1leNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innervation of Respiratory SystemDokument21 SeitenInnervation of Respiratory SystemYusuf MusthafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5fa52afab023b500180cf452 - ## - Respiration Dpp-1 (Tina Mam)Dokument4 Seiten5fa52afab023b500180cf452 - ## - Respiration Dpp-1 (Tina Mam)NEW SOLUTION POINTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjuncts To Mechanical Ventilation: Tantani SugimanDokument36 SeitenAdjuncts To Mechanical Ventilation: Tantani SugimanAndi Upik FathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of AsthmaDokument29 SeitenManagement of AsthmaAbdullah Al ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemDokument7 SeitenActivity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemFheby ValerieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 18 Respiratory FinalDokument15 SeitenModule 18 Respiratory FinalJayR MendonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANATOMY of PneumoniaDokument7 SeitenANATOMY of PneumoniaJanika Rivera HartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Short TermDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Short TermKristine Young100% (1)
- Zab Mohsenifar, Guy W. Soo Hoo Lung Biology in Health & Disease Volume 213 Practical Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Respiratory Failure PDFDokument444 SeitenZab Mohsenifar, Guy W. Soo Hoo Lung Biology in Health & Disease Volume 213 Practical Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Respiratory Failure PDFAnca Dumitru50% (2)
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- AtelektasisDokument10 SeitenAtelektasisSaputri AnggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wirksam Pharma Private Limited CataloguDokument22 SeitenWirksam Pharma Private Limited Catalogusanjay_gawaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demo LPDokument3 SeitenDemo LPNikki Anne BerlanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 107A Pedia Week 5-7 Growth and DevelopmentDokument30 SeitenNCM 107A Pedia Week 5-7 Growth and DevelopmentInsatiable CleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument28 SeitenDrug StudyJo Honey TimosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchodilators: Uses ActionDokument4 SeitenBronchodilators: Uses Actionammar amerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosa Gagal NafasDokument34 SeitenDiagnosa Gagal NafasFariz Auliadi KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System - Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenRespiratory System - Answer Keyapi-25002257750% (2)
- Melc 2 Healthy LifestyleDokument39 SeitenMelc 2 Healthy LifestyleJENNIFER DAVIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 NAT Mock Test Science Grade 6 2013Dokument8 Seiten2013 NAT Mock Test Science Grade 6 2013mjae18100% (1)
- Physiological Changes in PregnancyDokument40 SeitenPhysiological Changes in PregnancyArhum SiddiqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Cancer - Symptoms and Causes - Mayo ClinicDokument9 SeitenLung Cancer - Symptoms and Causes - Mayo ClinicTakuranashe DebweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDokument4 SeitenAssessment of Respiratory FunctionCristine Dominique E. DonaireNoch keine Bewertungen