Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Hochgeladen von
Clemo 2Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Hochgeladen von
Clemo 2Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
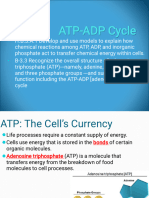
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in
living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of
life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed
in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate
(AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP so that the human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP
each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme.
From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it
consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Is An Organic Compound That Provides Energy To DriveDokument1 SeiteAdenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Is An Organic Compound That Provides Energy To DriveANoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP: The Cell's Energy CurrencyDokument4 SeitenATP: The Cell's Energy CurrencyVignesh100% (1)
- Gen Bio Cycles - FermentationDokument13 SeitenGen Bio Cycles - Fermentationyxcz.rzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atp-Adp Cycle: Presentation By: Miranda, Morales, Morando, NietesDokument7 SeitenAtp-Adp Cycle: Presentation By: Miranda, Morales, Morando, NietesYOSEF AZRIEL CONCEPCION MORALESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atp EssayDokument3 SeitenAtp EssayValeria PunzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19 AtpDokument34 Seiten19 AtpSheena BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADP ATP Cycle Photo IntroDokument16 SeitenADP ATP Cycle Photo IntronyxhelexiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP Energy Currency of the CellDokument28 SeitenATP Energy Currency of the CellDbez JonniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP & ADP Cycle ExplainedDokument15 SeitenATP & ADP Cycle ExplainedMay PaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Complete Reaction For The Hydrolysis of Adenosine Triphosphat1Dokument15 SeitenExplain The Complete Reaction For The Hydrolysis of Adenosine Triphosphat1NURAIHAN BINTI HASHIM MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtpDokument10 SeitenAtpSheba HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atp Adp CycleDokument13 SeitenAtp Adp Cycleelladomingo54Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointDokument18 SeitenATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointJohn Iderf LagardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenosine TriphosphateDokument2 SeitenAdenosine TriphosphateThanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsDokument2 SeitenATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsHayze Jones50% (2)
- PE Report - Output - Villanueva 1Dokument3 SeitenPE Report - Output - Villanueva 1Rico Yan CanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of ATPDokument2 SeitenRole of ATPWilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy MetabolismDokument12 SeitenKarl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy Metabolismمحمد جانNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP - ADP Cycle: Module 1 - Energy TransformationDokument10 SeitenATP - ADP Cycle: Module 1 - Energy TransformationNoreen AlipioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coenzyme Cells Nucleotides Phosphate: Clark Hailie Wayne Estrella 9-MendeleevDokument1 SeiteCoenzyme Cells Nucleotides Phosphate: Clark Hailie Wayne Estrella 9-MendeleevClark Hailie Wayne EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions That Produce and Consume ATPDokument7 SeitenReactions That Produce and Consume ATPsittinginthecorner1Noch keine Bewertungen
- AtpDokument2 SeitenAtpArvinderSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy TransformationDokument1 SeiteEnergy TransformationRense Jun PunsalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsDokument38 SeitenHydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsSHIFA ALTAFNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP ADP CycleDokument20 SeitenATP ADP CycleButz AnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-editDokument30 SeitenADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-editSiti Ayu MegawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role and ApplicationDokument12 SeitenThe Role and ApplicationÂn NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP PPTDokument13 SeitenATP PPTMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Atp-Adp CycleDokument20 SeitenAtp-Adp Cyclekim cchlNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP ADP SlidesDokument14 SeitenATP ADP SlidesNorsaifah AbduljalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsDokument38 SeitenHydrolysis of Nucleic AcidsSHIFA ALTAFNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP - The Energy Currency of CellsDokument12 SeitenATP - The Energy Currency of CellsJohn OsborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument2 SeitenEnergydR SHAMMIR AHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function in CellsDokument5 Seiten1 Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function in CellspNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atp and Coupled ReactionDokument3 SeitenAtp and Coupled ReactionBhea Mariel CaipangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATPDokument3 SeitenATPshekinah656Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atp STR FinDokument16 SeitenAtp STR FinNimsha KamalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Atp In-Wps OfficeDokument14 SeitenRole of Atp In-Wps OfficeElsa Barrientos BatasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amoeba SistersDokument1 SeiteAmoeba SistersrebekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Dokument10 SeitenAtp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Aditya Sunil NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- WordDokument6 SeitenWordJonel SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP ADP CycleDokument14 SeitenATP ADP CycleLalchan MiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP: The Energy Currency of the CellDokument12 SeitenATP: The Energy Currency of the CellCielo PepitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 2 Learning Activity Sheet 1 (Flow of Energy)Dokument3 SeitenQuarter 2 Learning Activity Sheet 1 (Flow of Energy)Lorman MaylasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 Q2 Wk2 QADokument32 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 Q2 Wk2 QAEdreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP-ADP Cycle: The Cellular Energy TransformationDokument33 SeitenATP-ADP Cycle: The Cellular Energy TransformationPrincess EscandalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologicalReview29 4 ATP PresentationDokument21 SeitenBiologicalReview29 4 ATP Presentationsmithsashay74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Role of ATP in Energy Coupling and TransferDokument1 SeiteRole of ATP in Energy Coupling and TransferOmbrog JustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coupled Reactions: ATP-ADP CycleDokument2 SeitenCoupled Reactions: ATP-ADP CycleJasmin MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy CouplingDokument3 SeitenEnergy CouplingHannah VillocenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Blocks of Life: The Structure and Function of NucleotidesDokument12 SeitenBuilding Blocks of Life: The Structure and Function of NucleotidesIlac Tristan BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QTR 2 MOD 1 - ATP ProductionDokument43 SeitenQTR 2 MOD 1 - ATP ProductionCasey PedrayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenosine TriphosphateDokument11 SeitenAdenosine TriphosphateAyush LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria ATPDokument5 SeitenAerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria ATPjatsugbNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenbioDokument5 SeitenGenbioYkhay ElfanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- STUDY GUIDE 1 NotesDokument4 SeitenSTUDY GUIDE 1 NotesBae SeujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Wasla Bashir) (26) (Z 1802) (Assignment 3)Dokument8 Seiten(Wasla Bashir) (26) (Z 1802) (Assignment 3)Rafia NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP: Adenosine TriphosphateDokument3 SeitenATP: Adenosine TriphosphateClaire ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NucleotideDokument56 SeitenNucleotideDhara NPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phyto ChemistryDokument1 SeitePhyto ChemistryClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Glomerular Basement MembraneDokument1 SeiteGlomerular Basement MembraneClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Molar Attenuation CoefficientDokument1 SeiteThe Molar Attenuation CoefficientClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared SpecDokument1 SeiteInfrared SpecClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electron PairDokument1 SeiteElectron PairClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isobestic PointDokument1 SeiteIsobestic PointClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Partial DerivativeDokument1 SeitePartial DerivativeClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- InfraredDokument1 SeiteInfraredClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radiant PowerDokument1 SeiteRadiant PowerClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- AbsorbanceDokument1 SeiteAbsorbanceClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Composite BosonDokument1 SeiteComposite BosonClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transition MetalsDokument1 SeiteTransition MetalsClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric FieldDokument1 SeiteElectric FieldClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooper PairDokument1 SeiteCooper PairClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- LigandDokument1 SeiteLigandClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Chemistry PDFDokument855 SeitenIntroductory Chemistry PDFOvaizOwaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination ComplexDokument2 SeitenCoordination ComplexClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CisplatinDokument1 SeiteCisplatinClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- TH Social and Economic Impact of NaturalDokument5 SeitenTH Social and Economic Impact of NaturalClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Krebs CycleDokument1 SeiteKrebs CycleClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- PhotosynthesisDokument1 SeitePhotosynthesispoint013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marxism: A Theory of Working-Class Self-EmancipationDokument1 SeiteMarxism: A Theory of Working-Class Self-EmancipationClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trade UnionDokument1 SeiteTrade UnionClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- TH Social and Economic Impact of NaturalDokument5 SeitenTH Social and Economic Impact of NaturalClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Production: Aluminium Hydroxide Minerals Are The Main Component of Bauxite, The Principal Ore of Aluminium. A MixtureDokument1 SeiteProduction: Aluminium Hydroxide Minerals Are The Main Component of Bauxite, The Principal Ore of Aluminium. A MixtureClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Chromatography Separates Colored InksDokument5 SeitenPaper Chromatography Separates Colored InksClemo 20% (1)
- Techniques PDFDokument116 SeitenTechniques PDFClemo 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Chromatography Separates Colored InksDokument5 SeitenPaper Chromatography Separates Colored InksClemo 20% (1)
- NVIDIA Control Panel and System Monitor With ESA User GuideDokument45 SeitenNVIDIA Control Panel and System Monitor With ESA User GuidePivaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonDokument6 SeitenDNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonRomalyn MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosynthesis of MacromoleculessDokument12 SeitenBiosynthesis of MacromoleculessTemidayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rna PDFDokument49 SeitenRna PDFbangbro93_30900715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0685-0755)Dokument71 SeitenLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0685-0755)Ricky HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19 - Gluconeogenesis & Amp The Control of Blood GlucoseDokument14 SeitenChapter 19 - Gluconeogenesis & Amp The Control of Blood Glucoserenzo041199Noch keine Bewertungen
- B Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IDokument89 SeitenB Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IRishab GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1-Lipids-Qp Alevel-Edexcel-Biology UpdatedDokument12 Seiten2.1-Lipids-Qp Alevel-Edexcel-Biology UpdatedAbdala AbdulrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Enzymes Grade 11Dokument20 SeitenBiology - Enzymes Grade 11Azad RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioc 470 Notes Lecture 1Dokument3 SeitenBioc 470 Notes Lecture 1anon_900161280Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 12 ExamDokument139 SeitenBio 12 ExamAndrew AbdelmalekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zymography Methods For Visualizing Hydrolytic EnzymesDokument11 SeitenZymography Methods For Visualizing Hydrolytic EnzymesIonescu AlexandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eclat Cosmetic skincare shipment to NetherlandsDokument7 SeitenEclat Cosmetic skincare shipment to NetherlandsMuhammad Ameer Hamza KayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription Sample Old Essay PDFDokument7 SeitenTranscription Sample Old Essay PDFOccamsRazorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docking and Molecular Dynamics Calculations of PyrDokument15 SeitenDocking and Molecular Dynamics Calculations of PyrVeliyana Londong AlloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antipurinergic Therapy For Autism-An In-Depth Review.Dokument15 SeitenAntipurinergic Therapy For Autism-An In-Depth Review.Miguel Romero100% (1)
- DownloadDokument8 SeitenDownloadDado MottaNoch keine Bewertungen
- H. Pylory Sec. GenomicaDokument15 SeitenH. Pylory Sec. GenomicaJonatan Jsb100% (1)
- Acetate PathwayDokument25 SeitenAcetate PathwaySangga Buana KomaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and TranslationDokument45 SeitenTranscription and TranslationDev AshwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Peroxisome Metabolism 20760414Dokument56 Seiten2nd Peroxisome Metabolism 20760414Rawbeena RamtelNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Scholastica's College Tacloban: Biochemistry For Nursing' Course PlanDokument2 SeitenSt. Scholastica's College Tacloban: Biochemistry For Nursing' Course PlanTheresia RellesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenBio Assignment 1hooriya bilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes PowerpointDokument39 SeitenEnzymes PowerpointRizky Yudha IrawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNAmazing Challenge (Protein Synthesis)Dokument6 SeitenDNAmazing Challenge (Protein Synthesis)DivineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 10Dokument141 SeitenBiology 10mattran100% (2)
- Transcription PPTDokument69 SeitenTranscription PPTEllieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 4. Assignment. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyDokument2 SeitenDay 4. Assignment. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyRaul Ramirez RangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramji 2015Dokument13 SeitenRamji 2015AlexandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4 (Biochemistry) Tca HMP and Uronic Acid PathwayDokument15 Seiten2.4 (Biochemistry) Tca HMP and Uronic Acid Pathwaylovelots1234100% (1)
- Coagulation Made EasyDokument27 SeitenCoagulation Made EasyHaris TanNoch keine Bewertungen