Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ATUM (Rhamnosa E.coli)
Hochgeladen von
Ruth MichelleeCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ATUM (Rhamnosa E.coli)
Hochgeladen von
Ruth MichelleeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
E.
coli Inducible Expression Vectors
E. coli expression vectors are available with the following promoters: T5 or T7 (IPTG-inducible), rhaBAD (rhamnose-inducible), ara (arabinose and
IPTG-inducible) and phoA (induced by phosphate starvation). These vectors express in any strain of E. coli, except T7 promoter vectors which
require a strain that expresses the T7 RNA polymerase and ara promoter vectors which require a strain that expresses the repressor AraC.
E. coli Expression Vectors with the Rhamnose-inducible rhaBAD Promoter
To vary expression levels, vectors with the rhaBAD promoter are available with different strength ribosome binding sites and a choice of high
or low copy origins of replication. These vectors are also available with affinity tag fusions and with secretion signals to guide periplasmic
expression. A choice of resistance markers is available.
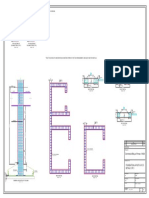
Plasmid Map
Your Gene
ATG GGT
strong RBS
Term_PhageT7
P_rhaBAD
2200 1
P_CmR 2100
100
200
2000
300
1900
400
1800
pD861 500
1700 Rham-ORF, Ecoli-Elec D
2230 bp
_pUC
600
1600
O ri
M_
700
Ka
1500
na
800
m
1400
yc
-r_ 900
in
1300
* 1200 1000
1100
Name Qty Storage
pD861 10Rx -20℃
rhaBAD Induction Protocol
The rhaBAD promoter is tightly regulated and tunable. Protein expression levels within each cell can be increased by using higher rhamnose
concentrations. This is in contrast to IPTG-inducible systems where a higher IPTG concentration increases the fraction of cells expressing
protein rather than the amount produced by each cell. The rhaBAD promoter is compatible with any E. coli strain or other Gram-negative
bacteria.
Grow cells overnight in LB plus antibiotic. Dilute into fresh LB with antibiotic, grow to mid-log (A600 0.6-0.8), induce by adding rhamnose to
a final concentration between 25 μM and 4 mM, and grow for an additional 4-8 hours. Titration of rhamnose concentrations allows optimal
conditions to be identified. This is particularly useful in the case of periplasmic expression because protein expression levels can be balanced
with the secretion system.
ATUM 1 877 362 8646 (Toll free)
37950 Central Court info@atum.bio
Newark, CA 94560 www.atum.bio
Rhamnose Vector Controls
Vectors expressing KringleYFP are available as controls. Any E. coli-optimized Protein Paintbox gene in an Electra MOTHER vector can also be
cloned into any Electra rhaBAD DAUGHTER vector.
ATUM 1 877 362 8646 (Toll free)
37950 Central Court info@atum.bio
Newark, CA 94560 www.atum.bio
Electra Cloning System
Electra is a simple one-tube universal cloning process that can be performed in a 5 minute bench-top reaction with the fidelity of a restriction-
based cloning system. A gene from one MOTHER vector is compatible with all DAUGHTER vectors, allowing rapid testing of many different
sequence contexts simultaneously.
Reagents
The Electra Reagents kit contains all necessary components to facilitate cloning a gene from a MOTHER into a DAUGHTER vector. The Electra
reaction can also be used to clone a PCR product into either a MOTHER or a DAUGHTER vector.
Electra Buffer Mix is supplied at 10X final concentration (use 2 µl in a 20 µl reaction)
Electra Enzyme Mix is supplied at 20X final concentration (use 1 µl in a 20 µl reaction)
Cloning Protocol
Component Volume (µl)
MOTHER DNA / Positive control (20 ng) 1
DAUGHTER Vector (20 ng) 1
Electra Buffer (10x) 2
Electra Enzyme (20x) 1
Water 15
Total 20
1. Combine components and incubate at 25-37°C for 5-20 minutes.
2. Transform 1-2 µl into chemically competent E. coli. (DH10B cells recommended)
3. Recover cells for 45 minutes and then plate on appropriate antibiotic for the DAUGHTER.
3a. Optionally include streptomycin at 100 µg/ml (for selection against pMOTHER with rpsL); or plate on YEG with antibiotic plus p-chloro
phenylalanine at 10mM (for selection against pMOTHER with pheS).
Positive Control
A positive control MOTHER vector carries a gene in which Ptet drives expression of green fluorescent protein (DasherGFP). A successful
Electra reaction will produce green fluorescent colonies from the DAUGHTER vector.
Electra DAUGHTER Vectors
Electra DAUGHTER vectors are supplied as linearized DNA, with overhangs compatible with an ATG (encoding methionine) at the 5' end and
GGT (encoding glycine) at the 3' end.
ATUM 1 877 362 8646 (Toll free)
37950 Central Court info@atum.bio
Newark, CA 94560 www.atum.bio
Electra MOTHER Vectors
Genes in MOTHER vectors have adjacent restriction sites that produce overhangs compatible with an ATG at the 5' end and GGT at the 3' end
upon digestion with SapI. Alternatively Electra ends can be added to any gene* by PCR. We recommend you add the following ends to your
PCR primers:
5'-TACACGTACTTAGTCGCTGAAGCTCTTCTATG....(ORF)....-3'
5'-TAGGTACGAACTCGATTGACGGCTCTTCTACC....(ORF Reverse Complement)....-3'
*Your gene must not contain any internal SapI recognition sites, since the Electra cloning process utilizes the typeIIs enzyme SapI.
MOTHER vectors also contain a counter-selection gene. This can be used to eliminate any residual gene propagating in the MOTHER.
Feature list descriptions
Kanamycin-r An effective bacteriocidal agent that inhibits ribosomal translocation thereby causing miscoding. The gene coding for kanamycin resistance is
Neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPT II/Neo). E.coli transformed with plasmid containing the kanamycin resistance gene can grow on media
containing 25 µg/ml kanamycin. Kanamycin is a white to off-white powder that is soluble in water (50mg/ml). (www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Kanamycin)
Ori_pUC The origin of replication is a sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. The pUC ori is a mutated form of origin derived from E. coli
plasmid pBR322 which allows production of greater than 500 copies of plasmid per cell. (www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Origin_of_replication)
P_rhaBAD The rhamnose-inducible promoter rhaBAD is capable of high level recombinant protein expression in the presence of L-rhamnose and is tightly
regulated by glucose in the absence of rhamnose. The rhaBAD promoter controls the genes rhaBAD organized in one operon. (www.wiley-vch.de/
books/sample/3527327290_c01.pdf)
strong RBS A ribosome binding site (RBS) is a sequence on mRNA that is bound by the ribosome during protein translation. It can be either the 5' cap
of a mRNA in eukaryotes, a region 6-7 nucleotides upstream of the start codon AUG in prokaryotes (called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence), or
an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) in viruses. Prokaryotic ribosomes recognize RBSs primarily via base-pairing between the RBS and an
unstructured end of the 16s rRNA molecule that forms part of the ribosome. Translation initiation rate of a particular mRNA can be regulated by
sequence of the RBS, leading to varying strengths - strong, medium or weak. (www.msb.embopress.org/content/7/1/481.abstract)
ATUM 1 877 362 8646 (Toll free)
37950 Central Court info@atum.bio
Newark, CA 94560 www.atum.bio
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aiting Shed: Floor Plan Front ElevationDokument4 SeitenAiting Shed: Floor Plan Front ElevationMary Jo Adamos75% (4)
- Silo 100 Ton Cement PDFDokument1 SeiteSilo 100 Ton Cement PDFMahmoud Taher El Khorzaty100% (3)
- Datasheet Aritco PublicLift Access 2021 en v1Dokument2 SeitenDatasheet Aritco PublicLift Access 2021 en v1Lê Văn HoạtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correct STS Final ExamDokument9 SeitenCorrect STS Final ExamJv OnaiPro100% (1)
- 155 - Flow Chart CV .8Dokument1 Seite155 - Flow Chart CV .8Mugywara luNoch keine Bewertungen
- RX-16 - MRIL 6 inDokument15 SeitenRX-16 - MRIL 6 inManu MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Nhap FPDokument1 Seite2021 Nhap FPChristine DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garrett GT1544Dokument1 SeiteGarrett GT1544Patricio IvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E1f 220V, 1ø, 2W+G E-1f 220V, 1ø, 2W+G E-Mp1 380y/220v, 3ø, 4W+G E-Mp2 380y/220v, 3ø, 4W+GDokument1 SeiteE1f 220V, 1ø, 2W+G E-1f 220V, 1ø, 2W+G E-Mp1 380y/220v, 3ø, 4W+G E-Mp2 380y/220v, 3ø, 4W+GAndy ArenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A005 DOORS Old Drawing FOR SPOT DETAIL ONLYDokument13 SeitenA005 DOORS Old Drawing FOR SPOT DETAIL ONLYJessica PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FB-77 Series (Spec)Dokument8 SeitenFB-77 Series (Spec)tuanhnguyen2121990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomic Effects of Foreign Exchange ReserveDokument15 SeitenMacroeconomic Effects of Foreign Exchange ReserveAsadul HoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rop Sinaw Cable & Water Line RouteDokument1 SeiteRop Sinaw Cable & Water Line RouteAkbar DahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of Aluminum Doors and Windows: A S S O C I A T E SDokument1 SeiteSchedule of Aluminum Doors and Windows: A S S O C I A T E SLeonardo Jr. SasingNoch keine Bewertungen
- En - HR 60 - 150dpiDokument2 SeitenEn - HR 60 - 150dpiAndré GraeffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated WindowsDokument1 SeiteUpdated Windowsfrancis sebastian lagamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2 PlanDokument1 SeiteP2 PlanFrancis Lloyd MalganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of Doors & Windows: D1 D2 D4 D3 W1Dokument1 SeiteSchedule of Doors & Windows: D1 D2 D4 D3 W1Jay HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIIIIDokument1 SeiteSIIIIBam SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aemax: Schedule of DoorsDokument1 SeiteAemax: Schedule of DoorsMary Mae MinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of WindowsDokument1 SeiteSchedule of Windowsfrancis sebastian lagamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAJAJFINSERVDokument2 SeitenBAJAJFINSERVStuart BroodNoch keine Bewertungen
- StaticsDokument7 SeitenStaticsBYREGOWDANoch keine Bewertungen
- MTP CAD 1-Layout3Dokument1 SeiteMTP CAD 1-Layout3Laurence Emmanuel BenedictosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Longitudinal Section: Schedule of DoorsDokument1 SeiteLongitudinal Section: Schedule of DoorsMark Allan RojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allele 100bp DNA LadderDokument1 SeiteAllele 100bp DNA LadderAlleleBiotechNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 21 (Rev-00) - Abut-8Dokument4 Seiten18 21 (Rev-00) - Abut-8S.m. MoniruzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propeller Can Be Sized Within or Above The Speed Range ShownDokument3 SeitenPropeller Can Be Sized Within or Above The Speed Range ShownadelsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korea Exchange KRXDokument4 SeitenKorea Exchange KRXAyoub BourkikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Silo PDFDokument1 SeiteCement Silo PDFBrajnandan Arya67% (3)
- Platform Ölçüleri̇Dokument1 SeitePlatform Ölçüleri̇nrobisetiawan17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Garrett GT1544 454082-2 454083-2Dokument40 SeitenGarrett GT1544 454082-2 454083-2Simo SalonenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Best-Selling Platform Lift: Aritco 7000Dokument2 SeitenOur Best-Selling Platform Lift: Aritco 7000Lê Văn HoạtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40 - Southern Cross - Iso Pump - 125 X 100 - 250 - 1200 3000 RPMDokument1 Seite40 - Southern Cross - Iso Pump - 125 X 100 - 250 - 1200 3000 RPMJAZZ KING PROJECTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pdf24 MergedDokument6 SeitenPdf24 Mergedmursa4mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Truss Detail: Location: Brgy. Tambler G.S.C. Project Title: Proposed Galvanizing Plant and Shop BuildingDokument1 SeiteHalf Truss Detail: Location: Brgy. Tambler G.S.C. Project Title: Proposed Galvanizing Plant and Shop BuildingLarry Jay Enaga ConstantinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variation of Armature Current and Voltage Against Speed: V (V) I (A)Dokument4 SeitenVariation of Armature Current and Voltage Against Speed: V (V) I (A)Amjasd MasdhashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pac56 Mx13specsheet 2021 Final DigitalhiresDokument2 SeitenPac56 Mx13specsheet 2021 Final Digitalhiresgaurao.pandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MX 13 Spec SheetDokument2 SeitenMX 13 Spec SheetHarish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Station 1D2 Acy Base Slab Plan Legend: To Claim Previously ClaimedDokument1 SeiteStation 1D2 Acy Base Slab Plan Legend: To Claim Previously ClaimedTullao Mark CarloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aritco Public Lift Access Datasheet-1Dokument2 SeitenAritco Public Lift Access Datasheet-1Nancy StarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PB - Stingblade 17.5 - BoliviaDokument1 SeitePB - Stingblade 17.5 - BoliviapendexxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aritco Publiclift Access: Datasheet 2021Dokument2 SeitenAritco Publiclift Access: Datasheet 2021Lê Văn HoạtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 TH - Layout 2,5 Lantai LT - 50 m2Dokument1 Seite5 TH - Layout 2,5 Lantai LT - 50 m2SeptiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A0-2223-UTT-EIA-DWG-02-NEW CONTROLL ROOM UPDATED 05-12-22LAYOUT-ModelDokument1 SeiteA0-2223-UTT-EIA-DWG-02-NEW CONTROLL ROOM UPDATED 05-12-22LAYOUT-ModelSmart ShivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single-Storey CruzDokument1 SeiteSingle-Storey CruzBe AmazedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seletividade - Easy PowerDokument1 SeiteSeletividade - Easy PowerHerickWallaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETV/ETM 318/320/325: Electric Reach Truck (1,800/2,000/2,500 KG)Dokument4 SeitenETV/ETM 318/320/325: Electric Reach Truck (1,800/2,000/2,500 KG)MA TotalforkliftNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Topo 2 Icosahedron 4Dokument1 SeiteE Topo 2 Icosahedron 4argaborNoch keine Bewertungen
- FR95017.01 Isb 6.7 230 HPDokument2 SeitenFR95017.01 Isb 6.7 230 HPlancelotinternacionalsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan at El (+) 16.200/el (+) 15.500M Level: Up UpDokument1 SeitePlan at El (+) 16.200/el (+) 15.500M Level: Up Upsubramanian SivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow V/s Differential Pressure Calculation For Orifice Plate (EOP Oil Flow)Dokument2 SeitenFlow V/s Differential Pressure Calculation For Orifice Plate (EOP Oil Flow)ajaycpNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 1Dokument1 SeiteA 1joseph arao-araoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A301 Section Aa and BBDokument1 SeiteA301 Section Aa and BBDavidson DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legend:: Reflected Ceiling PlanDokument1 SeiteLegend:: Reflected Ceiling PlanJoane ColipanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESTRADADokument1 SeiteESTRADABryan Rudolph PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Bldg. at Poman, VASAI: Description REV DateDokument1 SeiteCommercial Bldg. at Poman, VASAI: Description REV Datenimish.aquamarineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planta Da Nave de CriaçãoDokument1 SeitePlanta Da Nave de CriaçãoGilson PedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoorsDokument1 SeiteDoorsTeresa JiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 1 D 2 D 3 D 4: Schedule of Doors and WindowsDokument1 SeiteD 1 D 2 D 3 D 4: Schedule of Doors and WindowsJoenyl Fernand CaingcoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids and Protein SynthesisDokument27 SeitenNucleic Acids and Protein SynthesisindraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Biology Short Question and AnswersDokument218 SeitenIntroduction To Biology Short Question and AnswersNadeem ArainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Translation in ProkaryotesDokument7 SeitenTranslation in ProkaryotesAkachukwu ObunikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1Dokument2 SeitenBiology 1alyssa mae antonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biokem PRC QuestionsDokument13 SeitenBiokem PRC Questionsyanafk33% (3)
- AMC Test Sample PaperDokument36 SeitenAMC Test Sample PaperArsalan HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- SARAS 12th Bio Zoology Guide English Medium For Tamilnadu State BoardDokument39 SeitenSARAS 12th Bio Zoology Guide English Medium For Tamilnadu State BoardCOMMON MANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Cell Biology An Introduction TDokument14 SeitenEssential Cell Biology An Introduction TAni IoanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription Sample Old Essay PDFDokument7 SeitenTranscription Sample Old Essay PDFOccamsRazorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Endocrine SystemDokument38 SeitenChapter 10 Endocrine SystemMacthalas QuiazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namma Kalvi 11th Bio-Botany Study Material English Medium 219431Dokument51 SeitenNamma Kalvi 11th Bio-Botany Study Material English Medium 219431Prasanth PrasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna, Rna, Transcription, Translation & Protein Synthesis PDFDokument14 SeitenDna, Rna, Transcription, Translation & Protein Synthesis PDFSaeed Khan100% (1)
- AP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16Dokument32 SeitenAP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16EUNAH LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition Griffiths Solutions ManualDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition Griffiths Solutions Manualunlearnalternitycc8y100% (29)
- SBI4U - Unit 3 AssignmentDokument16 SeitenSBI4U - Unit 3 AssignmentSageofsix980 Sageofsix980Noch keine Bewertungen
- SL Paper 2: Do Not Accept Energy StorageDokument73 SeitenSL Paper 2: Do Not Accept Energy StoragemanrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Review Activity Booklet - Teacher 2014-15 - KEYDokument79 SeitenBiology Review Activity Booklet - Teacher 2014-15 - KEYJestony Matilla0% (1)
- As Biology AnswersDokument303 SeitenAs Biology AnswersWael TareqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04Dokument8 SeitenUtility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04u77Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument130 SeitenPDFexam robotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4546-LacOperon InstsDokument14 Seiten4546-LacOperon InstsScribd_is_GreatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 2024 Syllabus PDFDokument16 Seiten2022 2024 Syllabus PDFViditi DhaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Molecular Biology - What We Know & How We Found It (SecoDokument474 SeitenCell and Molecular Biology - What We Know & How We Found It (SecophyaraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV. Nucleic AcidsDokument44 SeitenIV. Nucleic AcidsAngel Hope MacedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Model Examination For Grade 12 in The Year 2007 E.CDokument15 SeitenBiology Model Examination For Grade 12 in The Year 2007 E.CDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Sheet 4 - GSP22T04S-ark6d2Dokument38 SeitenAnswer Sheet 4 - GSP22T04S-ark6d2rohit95patnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMDVDokument29 SeitenFMDVmateus_laguardiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample QuestionsDokument52 SeitenSample QuestionsMiri HahiashvilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- s15 Miller Chap 8a LectureDokument36 Seitens15 Miller Chap 8a LectureShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNoch keine Bewertungen