Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
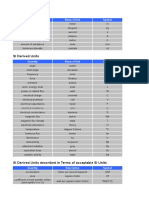
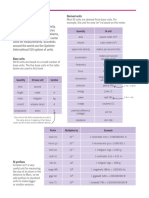
Latin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of Measure
Hochgeladen von
Chase Campbell0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten5 SeitenThis document defines many common symbols used in science and engineering, along with their meanings and standard SI units of measurement. Some key symbols include:
- c for the speed of light in a vacuum (m/s)
- g for acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
- E for energy (J)
- F for force (N)
- h for Planck's constant (J*s)
- m for mass (kg)
- t for time (s)
The document provides translations for both Latin characters and common Greek characters used in scientific notation.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Physics
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document defines many common symbols used in science and engineering, along with their meanings and standard SI units of measurement. Some key symbols include:
- c for the speed of light in a vacuum (m/s)
- g for acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
- E for energy (J)
- F for force (N)
- h for Planck's constant (J*s)
- m for mass (kg)
- t for time (s)
The document provides translations for both Latin characters and common Greek characters used in scientific notation.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten5 SeitenLatin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of Measure
Hochgeladen von
Chase CampbellThis document defines many common symbols used in science and engineering, along with their meanings and standard SI units of measurement. Some key symbols include:
- c for the speed of light in a vacuum (m/s)
- g for acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
- E for energy (J)
- F for force (N)
- h for Planck's constant (J*s)
- m for mass (kg)
- t for time (s)
The document provides translations for both Latin characters and common Greek characters used in scientific notation.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
Latin characters
Symbol Meaning SI Unit of Measure
area
A
magnetic vector potential
meter per second squared (m/s²) or
a acceleration
(ms−2)
magnetic flux density
tesla (T), or equivalently,
also called the magnetic field density or magnetic
weber per square meter (Wb/m²)
induction
capacitance
C heat capacity
constant of integration varied depending on context
speed of light (in a vacuum) Meters per Second (m/s)
c speed of sound Meters per Second (m/s)
specific heat capacity
electric displacement field
coulomb per square meter (C/m²)
also called the electric flux density
distance meter (m)
impact parameter meter (m)
d
diameter
differential (e.g. dx)
differential vector element of surface area A,
with infinitesimally
square meter (m²)
small magnitude and direction normal to surface S
differential element of volume V enclosed by
dV cubic meter (m³)
surface S
electric field volt per meter (V/m)
E energy joule (J)
eccentricity unitless
e 2.71828... (base of the natural
logarithm), electron, elementary charge
force newton (N)
frequency hertz (Hz)
f function
friction
newton meter squared per kilogram
G the gravitational constant
squared (N m²/kg²)
g acceleration due to gravity
magnetic field strength ampere per meter (A/m)
also called just magnetic field
H Hamiltonian joule (J)
height
h
Planck's constant joule second (J s)
joule second (J s)
reduced Planck's constant
action joule second (J s)
intensity watt per square meter (W/m²)
I sound intensity watt per square meter (W/m²)
electric current ampere (A)
moment of inertia
Cartesian x-axis basis unit vector unitless
i intensity watt per square meter (W/m²)
imaginary unit
free current density,
not including polarization or magnetization currents ampere per square meter (A/m²)
bound in a material
j Cartesian y-axis basis unit vector unitless
K kinetic energy joule (J)
Cartesian z-axis basis unit vector unitless
Boltzmann constant joule per kelvin (J/K)
k
wavenumber
wavenumber
inductance henry (H)
L luminosity watt (W)
angular momentum
l length
magnetization ampere per meter (A/m)
M moment of force
newton meter (N m)
often simply called moment or torque
m mass kilogram (kg)
normal vector unit varies depending on context
N
atomic number unitless
refractive index unitless
n
principal quantum number unitless
P power watt (W)
momentum kilogram meter per second (kg m/s)
pressure pascal (Pa)
Electric Charge coulomb (C)
Q
Heat joule (J)
q electric charge coulomb (C)
Electrical resistance ohm (Ω)
R Ricci tensor unitless
radiancy
radius of rotation or distance between two things
such as the masses in Newton's law of universal meter (m)
r gravitation
radius vector (position)
surface area m2
S entropy J/K
action
arc length meter (m)
s
displacement
period second (s)
T Thermodynamic Temperature
kelvin (K)
also called absolute temperature
t time second (s)
four-velocity meter per second (m/s)
potential energy joule (J)
U
internal energy joule (J)
relativistic mass kilogram (kg)
u joule per cubic meter (J/m³) or joule per
energy density
kilogram (J/kg) depending on the context
voltage
volt (V)
also called electric potential difference
V
volume m3
shear force
velocity meter per second (m/s)
W mechanical work
w width m
a generic unknown varied depending on context
x
displacement
Z Electrical impedance
[edit]Greek characters
Symbol Name Meaning SI Unit of Measure
radian per second squared
α alpha angular acceleration
(rad/s²)
β beta velocity in terms of the speed of light c unitless
Lorentz factor unitless
photon
γ gamma
gamma ray
shear strain
a change in a variable (e.g. Δx) unitless
Δ delta
Laplace operator
δ delta displacement (usually small)
permittivity farad per meter (F/m)
ε epsilon
strain unitless
energy efficiency unitless
η eta coefficient of viscosity
pascal second (Pa s)
also called simply viscosity
θ theta angular displacement radian (rad)
torsion coefficient newton meter per radian (N
Κ kappa
also called torsion constant m/rad)
cosmological constant per second squared (s−2)
Λ lambda meter
λ wavelength
(m)
magnetic moment ampere square meter (A m²)
coefficient of friction
mu
dynamic viscosity
permeability (electromagnetism)
frequency hertz (Hz)
ν nu
kinematic viscosity
Ω omega ohm
ω omega angular frequency radian per second (rad/s)
mass density kilogram per cubic meter
usually simply called density (kg/m³)
free electric charge density,
ρ rho coulomb per cubic
not including dipole charges bound in a
meter (C/m³)
material
resistivity
Σ sigma summation operator
electrical conductivity
σ sigma
normal stress
torque newton meter (N m)
τ tau shear stress
time constant s
unit varies depending on
field strength
Φ phi context
magnetic flux
φ phi electric potential
π pi 3.14159... (irrational number)
wave
Ψ unitless
function
ζ zeta damping ratio unitless
[edit]Other characters
Symbol Name Meaning SI Unit of Measure
the divergence operator
nabla dot per meter (m−1)
often pronounced "del dot"
the curl operator
nabla cross per meter (m−1)
often pronounced "del cross"
nabla del (differential operator)
"der", "dow", "die", "partial" or simply partial
"d" derivative (e.g. )
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese SyllabusDokument307 SeitenElectricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese Syllabusdavidegrima100% (17)
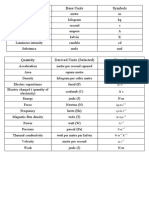
- Base Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical EngineeringDokument39 SeitenBase Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineeringlukhman100% (1)
- CAPE Physics Physical QuantitiesDokument3 SeitenCAPE Physics Physical QuantitiestuvvacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment PDFDokument2 SeitenAssignment PDFMoazzam HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minevent 2006 PDFDokument12 SeitenMinevent 2006 PDFJosé Manuel Berrospi CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesDokument12 SeitenLeo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesVynz JoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Scalar and Units ReviewDokument43 SeitenVector Scalar and Units ReviewGumball DumballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsDokument6 SeitenQuantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsRajkumar ANoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDokument6 SeitenSI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolHazem SobhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Common Physics Notations: Latin CharactersDokument6 SeitenList of Common Physics Notations: Latin CharactersAsit Kumar RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Common NotationsDokument5 SeitenPhysics Common NotationsellayuslianaNoch keine Bewertungen
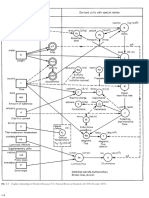
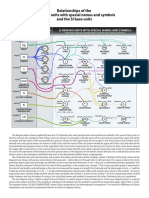
- Graphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)Dokument18 SeitenGraphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)annisa putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SymbolsDokument2 SeitenPhysics SymbolsAbdul SamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Application SumsDokument36 SeitenMaths Application SumsBalakamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 1 Base and Derived UnitsDokument6 SeitenWEEK 1 Base and Derived UnitsannmarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of ElectricalDokument178 SeitenBasics of Electricaludayakumart50% (2)
- Conversion Factors PDFDokument3 SeitenConversion Factors PDFArbenson CNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Dokument5 SeitenThe Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Sama UmateNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnitsDokument16 SeitenUnitsVinayChowdaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1Dokument8 SeitenLesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1GM ShioriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A: The International System of UnitsDokument8 SeitenAppendix A: The International System of UnitsIvan gheorgheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source:: S.I. Units of MeasurementDokument2 SeitenSource:: S.I. Units of Measurementnripen kalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si UnitsDokument2 SeitenSi Unitsmaharshi DaddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Units and Symbols Used in The Guide: Subject Physical Quantity Symbol Name UnitDokument5 SeitenSI Units and Symbols Used in The Guide: Subject Physical Quantity Symbol Name UnitbalaramankrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Symbols For Some Basic QuantitiesDokument2 SeitenPhysics Symbols For Some Basic QuantitiesBidisha MitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNITSDokument9 SeitenUNITSDhayane RedoquerioNoch keine Bewertungen
- M T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDokument3 SeitenM T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolMark ArceNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Mapa 17157Dokument1 SeiteSI Mapa 17157Yary GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si Units PDFDokument4 SeitenSi Units PDFசெல்வ குமார்Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astm 02Dokument623 SeitenAstm 02Bilel RebaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AppendixDokument4 SeitenAppendixResham ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergyDokument19 SeitenPhysics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergySucharita KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CircuitsDokument22 SeitenCircuitsapi-3732151100% (1)
- Notebook 1: Lindsey ShrinerDokument3 SeitenNotebook 1: Lindsey Shrinerapi-338662480Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unidades para Formato ApaDokument4 SeitenUnidades para Formato ApaJaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Field Trainee TestDokument102 SeitenOil Field Trainee TesteditinggroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internatsystem UnitDokument1 SeiteInternatsystem Unitdobridorin2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 Electric MachineDokument42 SeitenChapter1 Electric Machinealif ismaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Units Color Diagram PDFDokument1 SeiteSI Units Color Diagram PDFX800XLNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemPrinc6e - Appendix 1Dokument9 SeitenChemPrinc6e - Appendix 1TilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 978 0 387 23063 4 - BookBackMatterDokument45 Seiten978 0 387 23063 4 - BookBackMatterLei JINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantity Unit ListDokument10 SeitenQuantity Unit ListRaef AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Electric Circuit Theory BTDokument18 SeitenLecture 1 Electric Circuit Theory BTnjuraimelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Formulas AcousticsDokument16 SeitenBasic Formulas Acousticssmani170100% (1)
- Physics Formula RevisionDokument2 SeitenPhysics Formula RevisionAzan Muhammad100% (1)
- Physical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFDokument6 SeitenPhysical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFARAVINDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math FormulasDokument173 SeitenMath Formulasrajkumar.manjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuantityDokument1 SeiteQuantitySu MyatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Units Measurements OKDokument17 Seiten1 Units Measurements OKSARANGMUMBAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 1Dokument11 SeitenReading 1shafyvonommyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Symbols1Dokument7 SeitenPhysics Symbols1ClothoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 1.1Dokument2 SeitenTable 1.1Ma Patricia May RelatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- THBHDK 30Dokument1 SeiteTHBHDK 30RGNitinDevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Level Physics Units & SymbolDokument3 SeitenA Level Physics Units & SymbolXian Cong KoayNoch keine Bewertungen
- KNR2443 - Electrical Engineering Technology: Chapter 1 & 2 International System of Measurement & Electrical CircuitDokument65 SeitenKNR2443 - Electrical Engineering Technology: Chapter 1 & 2 International System of Measurement & Electrical CircuitCyprian Mikael CorgedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GR11 Physics Information SheetsDokument6 SeitenGR11 Physics Information Sheetsowamibosch735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module I-1 Electricity & MagnetismDokument15 SeitenModule I-1 Electricity & MagnetismCarmie BasilloteNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME Secc II D Si UnitsDokument3 SeitenASME Secc II D Si UnitsCARLOS MARIONoch keine Bewertungen
- SI SystemDokument19 SeitenSI SystemmyscribdzoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Von EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsVon EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Artificial Neural NetworkDokument5 SeitenAn Introduction To Artificial Neural NetworkMajin BuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive STatistics For Qualitative DataDokument34 SeitenDescriptive STatistics For Qualitative DataMwanjala GasambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 5Dokument11 SeitenLab Report 5Muhammad SohaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Principles of CompositionDokument10 SeitenThe Principles of CompositionTaka TomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Order Hold Based Discretization Method ofDokument5 SeitenSecond Order Hold Based Discretization Method ofvitinrjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 10 Week 2Dokument10 SeitenMath 10 Week 2Myla MillapreNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study in Ow Assurance of A Pipeline-Riser System Using OLGADokument10 SeitenA Case Study in Ow Assurance of A Pipeline-Riser System Using OLGAAhmed BedhiefNoch keine Bewertungen
- L As Level Physics A 2821 01 January 2008 Question Paper Old g481Dokument16 SeitenL As Level Physics A 2821 01 January 2008 Question Paper Old g481dasha962Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6.6 Notes - Trapezoids and KitesDokument12 Seiten6.6 Notes - Trapezoids and KitesAbrar DirdasawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep Design PDFDokument4 SeitenCreep Design PDFSugumar SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 10Dokument4 SeitenLec 10RKD CinemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- s2 TrigonometryDokument31 Seitens2 TrigonometryClaire PadronesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH60561 2022 23 Pressure Vessel ExerciseDokument3 SeitenMECH60561 2022 23 Pressure Vessel ExerciseAli JabranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mechanism of Activated Digusion Through Silica GlassDokument9 SeitenThe Mechanism of Activated Digusion Through Silica GlassElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01otr 02ourDokument53 Seiten01otr 02ourKeerthana KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial PDE Unit-1 Maths-IVDokument2 SeitenTutorial PDE Unit-1 Maths-IVKshitiz0% (1)
- Standard Test Methods For Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials E 119 - 07Dokument22 SeitenStandard Test Methods For Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials E 119 - 07Frenzy BritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 68 Stress Testing and Other Risk Management ToolsDokument4 SeitenTopic 68 Stress Testing and Other Risk Management ToolsSoumava PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocyclones For Particle Size SeparationDokument7 SeitenHydrocyclones For Particle Size SeparationJean DejardinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIDE Presentation Part 1 PDFDokument7 SeitenPIDE Presentation Part 1 PDFGilmar DemenekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project in Algebra 3rd Grading ProblemsDokument77 SeitenProject in Algebra 3rd Grading Problemsazisah azisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34ee79a9746d853ef9fa1f44acc55afeDokument51 Seiten34ee79a9746d853ef9fa1f44acc55afeSai Pavan MarojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Quantitative Methods QMI1500 Semesters 1 and 2: Tutorial Letter 101/3/2021Dokument26 SeitenElementary Quantitative Methods QMI1500 Semesters 1 and 2: Tutorial Letter 101/3/2021natashasiphokazi2015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Measure of Dispersion Kurtosi, SkiwnessDokument22 SeitenMeasure of Dispersion Kurtosi, SkiwnessJOHN TUMWEBAZENoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Dispersion: Greg C Elvers, PH.DDokument27 SeitenMeasures of Dispersion: Greg C Elvers, PH.DorchuchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Progress of Consolidation in A Clay Layer Increasing-Gibson PDFDokument12 SeitenThe Progress of Consolidation in A Clay Layer Increasing-Gibson PDFAnonymous GnfGTwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 6 DLP 1 - Giving Meaning of Exponent and Base Giving The Value of Numbers Involving Exponent PDFDokument9 SeitenMath 6 DLP 1 - Giving Meaning of Exponent and Base Giving The Value of Numbers Involving Exponent PDFZyreen Joy ServanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Simulations of A Scramjet Isolator Using RANS and LES ApproachesDokument9 SeitenNumerical Simulations of A Scramjet Isolator Using RANS and LES ApproachesHoàng DavidNoch keine Bewertungen