Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Answer Key: Holt Physics
Hochgeladen von
MuhammadOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Answer Key: Holt Physics
Hochgeladen von
MuhammadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
Holt Physics
Answer Key
CHAPTER 11
ESSAY
Answers should include the following: A standing wave is a wave pattern that results when two waves of the same
frequency, wavelength, and amplitude travel in opposite directions and interfere. The passage describes antinodes,
points on the standing wave that have the largest amplitude due to constructive interference, and nodes, points on the
standing wave that have the smallest amplitude due to destructive interference. A standing wave could cause a
bridge to collapse if it caused its parts to vibrate in directions and amplitudes that it was not strong enough to
accommodate.
MATH READING PASSAGES
Item Answer Correlation Item Answer Correlation
1. B 16. E
2. E 17. C
3. D 18. C
4. A 19. E
5. B 20. E
6. C
IMPROVING SENTENCES
7. A
8. E Item Answer Correlation
9. E 21. C
10. B 22. B
23. B
SENTENCE COMPLETION
24. E
Item Answer Correlation
11. E
12. C
13. E
14. A
15. D
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 1 SAT Bellringer
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
Holt Physics: Vibrations and Waves
Essay
DIRECTIONS: The essay gives you an opportunity to show how effectively you can
develop and express ideas. You should, therefore, take care to develop your ideas,
present concepts logically and clearly, and use language precisely.
Your essay must be written on your own paper. You may use both sides of a single
sheet of notebook paper. You will have enough space if you write on every line,
avoid wide margins, and keep your handwriting to a reasonable size. Remember
that people who are not familiar with your handwriting will read what you write.
Try to write or print so that what you are writing is legible to those readers.
IMPORTANT REMINDERS:
• A pencil is required for the essay. An essay written in ink will receive a score of
zero.
• Do not write your essay in your test book. You will receive credit only for what
you write on a single sheet of notebook paper.
• An off-topic essay will receive a score of zero.
Think carefully about the concept presented in the following passage and the
assignment below.
On the morning of November 7, 1940, the Tacoma Narrows Bridge, a 1600-
meter suspension bridge connecting the cities of Tacoma and Gig Harbor in
the state of Washington, began to rock violently due to vibrations caused by
wind gusts. The vibrations created a standing wave in the bridge, such that
certain portions of the bridge experienced constructive interference and
vibrated far from their rest positions, while other portions of the bridge
experienced destructive interference and remained in their rest positions.
Eventually, the standing wave caused the bridge to collapse.
ASSIGNMENT: What is a standing wave? What characteristics of a standing
wave are described in the passage? Why might a standing wave cause a bridge
to collapse? Plan and write an essay in which you address these questions.
Support your explanation with reasoning and examples taken from your
reading, studies, experience, or observations.
Holt Physics: Vibrations and Waves
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 2 SAT Bellringer
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
Mathematics
DIRECTIONS: In this section, solve each problem using any available space on the
page for scratch work. Then decide which of the choices given is best and fill in
the corresponding circle on the answer sheet.
NOTES:
1. The use of a calculator is permitted. All numbers used are real numbers.
2. Figures that accompany problems in this test are intended to provide
information useful in solving the problems. They are drawn as accurately as
possible EXCEPT when it is stated in a specific problem that the figure is not
drawn to scale. All figures lie in a plane unless otherwise indicated.
ag = 9.81 m/s2 Simple Pendulum in Simple Harmonic Motion
Reference Information
L
Hooke’s Law T = 2
Felastic = –kx ag
Wave Equation Mass-Spring System in Simple Harmonic Motion
v = fλ m
T = 2
k
1. If a mass of 0.75 kg attached to a vertical 3. What is the period of a mass-spring
spring stretches the spring 5.0 m from its system with a mass of 25.0 kg and a
original equilibrium position, what is the spring constant of 1.25 N/m?
spring constant? (A) 0.990 s
(A) 0.15 N/m (B) 1.40 s
(B) 1.5 N/m (C) 19.8 s
(C) 2.0 N/m (D) 28.1 s
(D) 2.4 N/m (E) 631 s
(E) 150 N/m
4. What is the period of a metronome that
2. What is the length of a pendulum that vibrates at a frequency of 4.0 Hz?
oscillates with a frequency of 0.21 Hz? (A) 0.25 s
(A) 0.011 m (B) 0.40 s
(B) 0.33 m (C) 2.0 s
(C) 2.1 m (D) 15 s
(D) 4.8 m (E) 240 s
(E) 5.6 m
Mathematics continued
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 3 SAT Bellringer
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
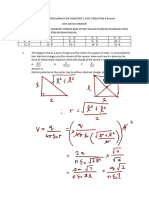
Questions 5–8 are based on the following illustration of a wave traveling in the positive x
direction with a frequency of 33.3 Hz.
5. What is the amplitude of the wave? 8. What is the speed of the wave?
(A) 5.0 cm (A) 0.0300 m/s
(B) 6.0 cm (B) 3.00 m/s
(C) 10.0 cm (C) 33.3 m/s
(D) 12.0 cm (D) 166 m/s
(E) 20.0 cm (E) 333 m/s
9. A sound wave has a frequency of 3400
6. What is the wavelength of the wave?
Hz and a wavelength of 1.5 m in a certain
(A) 5.0 cm medium. What is the speed of the wave
(B) 6.0 cm in that medium?
(C) 10.0 cm (A) 4.4 × 10-4 m/s
(D) 12.0 cm (B) 2.9 × 10-4 m/s
(E) 20.0 cm (C) 1.9 m/s
(D) 2300 m/s
7. What is the period of the wave?
(E) 5100 m/s
(A) 0.0300 s
(B) 3.00 s 10. A wave of frequency 42.5 Hz travels at a
(C) 33.3 s speed of 3.5 m/s. What is the wavelength
of the wave?
(D) 166 s
(A) 0.082 cm
(E) 333 s
(B) 8.2 cm
(C) 12 cm
(D) 150 cm
(E) 15,000 cm
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 4 SAT Bellringer
Holt Physics: Vibrations and Waves
Sentence Completion
DIRECTIONS: For each question in this section, select the best answer from
among the choices given and fill in the corresponding circle on the answer sheet.
11. A pendulum’s ______ stays the same 14. Vibrations in a ______ wave are always
even as its kinetic energy increases parallel to the direction of wave motion,
(if friction is disregarded). while vibrations in a ______ are
(A) speed perpendicular to the direction of wave
(B) height motion.
(C) displacement (A) longitudinal . . transverse
(D) potential energy (B) transverse . . longitudinal
(E) total mechanical energy (C) mechanical . . longitudinal
(D) transverse . . electromagnetic
12. According to Hooke’s law, spring force (E) mechanical . . electromagnetic
can be calculated by knowing the spring
constant and the ______ of the spring. 15. When the compression of one
(A) mass longitudinal wave and the rarefaction of
another combine, there is ______.
(B) thickness
(A) reflection
(C) displacement
(B) an antinode
(D) mechanical energy
(C) a standing wave
(E) equilibrium length
(D) destructive interference
13. The period of a simple pendulum in (E) constructive interference
simple harmonic motion is equal to 2
multiplied by the square root of the
______ of the pendulum divided by the
square root of its ______.
(A) length . . mass
(B) mass . . frequency
(C) frequency . . length
(D) free-fall acceleration . . mass
(E) length . . free-fall acceleration
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 5 Sentence Completion
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
Holt Physics: Vibrations and Waves
Reading Passages
The passages below are followed by questions based on their content; questions
following a pair of related passages may also be based on the relationship between
the paired passages. Answer the questions on the basis of what is stated or implied
in the passages. For each question in this section, select the best answer from the
choices given and fill in the corresponding circle on the answer sheet.
Questions 16-17 are based on the following Questions 18-20 are based on the following
passage. passage.
Tsunamis are large, often devastating When waves meet one another, they
ocean waves that are triggered by great can interact in different ways. The
disturbances to land or water. They overlapping of two or more waves is
Line may be caused by earthquakes, landslides, Line called superposition. Superposition can
5 volcanoes, meteorite strikes, or significant 5 involve constructive or destructive
explosions that take place on land or interference. When the superposition of
underwater. The wave that forms near the waves results in a resultant wave with an
original location of the disturbance has a amplitude that is larger than either of the
relatively small amplitude and large combining waves, the phenomenon is
10 wavelength. However, as the tsunami 10 called constructive interference. When the
nears land, its amplitude grows and its superposition of waves results in a
wavelength shortens, causing destructive resultant wave with an amplitude that is
waves that can be dozens of meters high. smaller than either of the original waves,
the phenomenon is called destructive
16. Lines 1-3 suggest that the term “tsunami” 15 interference.
might also be defined as One laboratory demonstration of a
(A) any wave that moves through land wave interaction involves two partners
(B) an earthquake occurring underwater holding each end of the rope. Both people
generate transverse waves of equal
(C) any wave that moves through water
20 amplitude that move toward each other in
(D) an ocean wave that takes place the rope. At the moment when a crest and
underwater a trough of the waves first overlap in the
(E) the motion of a great disturbance middle of the rope, the amplitude
through water becomes zero.
17. According to lines 11-13, what amplitude 18. The description of the rope experiment
can a tsunami reach at shore? described in lines 16-21 suggests that
(A) 0.3 meters (A) the waves reflected
(B) 3 meters (B) the waves formed nodes
(C) 36 meters (C) the waves interfered destructively
(D) 360 meters (D) the waves interfered constructively
(E) 3600 meters (E) the waves formed a standing wave
Reading Passages continued
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 6 Reading Passages
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
19. In line 14, the word “destructive” means 20. The passage implies that which two
(A) critical words are synonyms?
(B) vicious (A) resultant and original
(C) unhelpful (B) wave and interference
(D) causing ruin (C) phenomenon and amplitude
(E) making smaller (D) constructive and destructive
(E) overlapping and superposition
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 7 Reading Passages
Name:_________________________________ Class:______________________ Date:________________________
Holt Physics: Vibrations and Waves
Improving Sentences
DIRECTIONS: For each question in this section, select the best answer from
among the choices given and fill in the corresponding circle on the answer sheet.
Part of each sentence in items 21 and 22 is Each sentence in items 23 and 24 contains
underlined. Below each sentence are five either a single error or no error at all. If the
ways of phrasing the underlined material. sentence contains an error, choose the one
Choice A repeats the original phrasing; the underlined part that must be changed to
other four choices are different. Choose the make the sentence correct. If the sentence is
answer you think produces the most correct, select choice E.
accurate sentence.
23. Mechanical waves transfer matter by
21. Wave speed equals amplitude multiplied A B
by wavelength. vibrating particles that return to their
(A) amplitude C
original equilibrium positions rather than
(B) energy
D
(C) frequency by carrying the particles along with the
(D) medium
(E) period wave. No error
E
22. In a standing wave on a guitar string, the
antinodes are the points where the string 24. Mechanical waves require a medium,
vibrates with the largest wavelength. A B
while electromagnetic waves can travel
(A) wavelength C
(B) amplitude through a vacuum. No error
(C) frequency D E
(D) period
(E) speed
Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
Holt Physics: Chapter 11 8 Reading Passages
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MP EM Ass 25: Radiation Energy and MomentumDokument9 SeitenMP EM Ass 25: Radiation Energy and MomentumBlueAstro100% (2)
- 323 Tutorial HW PDFDokument40 Seiten323 Tutorial HW PDFBernard LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Practice TestDokument8 SeitenElectricity Practice TestMani MNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Unit 3, 4 & 5 EC339Dokument20 SeitenMCQ Unit 3, 4 & 5 EC339zohaib100% (3)
- Y2 Module 2 Performing Mensuration and CalculationDokument42 SeitenY2 Module 2 Performing Mensuration and CalculationJasmine Gillado100% (1)
- Chapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers Electric Forces and FieldsDokument6 SeitenChapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers Electric Forces and Fieldsmahsan abbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Dokument4 SeitenFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsDokument4 SeitenFLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsChetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wins-Evening Coaching: SECTION-A (Marks 17)Dokument4 SeitenWins-Evening Coaching: SECTION-A (Marks 17)Matti Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- trialstpm2022DatoMansorP2AnswerDokument16 Seitentrialstpm2022DatoMansorP2AnswerASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 2 April 2016 ExamDokument12 SeitenPhysics Paper 2 April 2016 ExamannahiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- SecquizDokument3 SeitenSecquizdeezm579Noch keine Bewertungen
- VJC H2 Prelim Paper 1 2009Dokument19 SeitenVJC H2 Prelim Paper 1 2009twinkylishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul STPM Semester 2 STPM Tahun 2021 Physics JPN KelantanDokument11 SeitenModul STPM Semester 2 STPM Tahun 2021 Physics JPN KelantanMuhammad IllyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom An of Diameter Nucleus A of DiameterDokument11 SeitenAtom An of Diameter Nucleus A of DiameterAhmad OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT8 04S13 ps9Dokument5 SeitenMIT8 04S13 ps9Yul LopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Dokument9 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavNoch keine Bewertungen
- hssp1600t ChaptestaDokument6 Seitenhssp1600t ChaptestabruhymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24Dokument3 SeitenClass 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24PrinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Fields and Circuits ReviewDokument6 SeitenMagnetic Fields and Circuits ReviewJoseph SebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 22.2: M M N/CDokument13 SeitenExercise 22.2: M M N/CMahmoud HamdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrigley William B 194908 Ms 69830Dokument37 SeitenWrigley William B 194908 Ms 69830fire&gasNoch keine Bewertungen
- q1-G8 Science Exam - 2023Dokument4 Seitenq1-G8 Science Exam - 2023Joana Cressel Paballa GratilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ALp Inter 2Dokument11 SeitenPhysics ALp Inter 2Kamran HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emt Test 1 Question PaperDokument8 SeitenEmt Test 1 Question PaperVishnu Prasad MNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics - Q3-Week3 - Equipotential Surface and Electric FieldDokument10 SeitenGeneral Physics - Q3-Week3 - Equipotential Surface and Electric FieldJA Wad LCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam Questions on Fields and OpticsDokument5 SeitenPhysics Exam Questions on Fields and OpticsChishikikudo PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLS Aipmt 16 17 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 8Dokument24 SeitenCLS Aipmt 16 17 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 8Kareena Gupta75% (4)
- CBSE Class 12 Physics 2013Dokument17 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Physics 2013Sonu RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00007211Dokument3 Seiten00007211anjan_debnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- WBJEE 2016 Physics Question Answerkey SolutionsDokument23 SeitenWBJEE 2016 Physics Question Answerkey SolutionsANIKET ROYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Fizik s2 2022 (Question)Dokument11 SeitenTrial Fizik s2 2022 (Question)CHRISTOPHER EMMANUEL RAJ A/L VELLAN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intensive Physics Quiz Practice Online 2021Dokument15 SeitenIntensive Physics Quiz Practice Online 2021MOHD SAIFUNIZAM BIN ZAKARIA MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- James Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDokument48 SeitenJames Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & Solutionsfortnitegamerpro123451Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework PolarizationDokument8 SeitenHomework PolarizationAnonymous MaUfbbzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring 2006 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2Dokument5 SeitenSpring 2006 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2paimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Physics HL - 2025 Questionbank - Space, Time & MotionDokument156 SeitenIB Physics HL - 2025 Questionbank - Space, Time & MotionRahul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 123 PDFDokument9 SeitenAssignment - 123 PDFarun sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 4-Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument14 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 4-Moving Charges and MagnetismSri MeenakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Fields Learning GuideDokument15 SeitenElectric Fields Learning GuideRana MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PaperDokument7 SeitenCBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PapermisostudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creative Solutions PK Design and Communication ServicesDokument12 SeitenCreative Solutions PK Design and Communication ServicesAdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word - COMPILED 2Dokument27 SeitenMicrosoft Word - COMPILED 2Tayseer SaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Physics Class 12 Question Paper 2018-1Dokument17 SeitenKarnataka PUC Board (KSEEB) Physics Class 12 Question Paper 2018-1rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Sample PapersDokument6 SeitenPhysics Sample PapersmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - EV - MCQ 2ndDokument25 SeitenPhysics - EV - MCQ 2ndMaruf MorshedNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSSC 2 Phy Paper PreboardDokument4 SeitenHSSC 2 Phy Paper PreboardEman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Test Term 1 QP Xii 2020 SeptDokument9 SeitenSample Test Term 1 QP Xii 2020 SeptEdwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quest Electrostatics & Electricity 5 KeyDokument20 SeitenQuest Electrostatics & Electricity 5 KeyCarlos Ortiz100% (1)
- Physics 2nd Obj Sub NDokument3 SeitenPhysics 2nd Obj Sub NMisbah sabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Electromagneticinduction tp01Dokument7 Seiten12 Physics Electromagneticinduction tp01vinaykumarnandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 3 2013 PDFDokument9 SeitenTest 3 2013 PDFVishalPandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII-Physics SQP 2018-19 PDFDokument8 SeitenXII-Physics SQP 2018-19 PDFNikhil singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Electro Statics - I Co-Ordinate Systems 1. AttentionDokument38 SeitenUnit I Electro Statics - I Co-Ordinate Systems 1. AttentionraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Physics B-5Dokument10 Seiten12th Physics B-5Riya KakaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP EM Ass 5: Applications of Gauss's LawDokument10 SeitenMP EM Ass 5: Applications of Gauss's LawBlueAstro100% (1)
- Random Phase ApproximatiomDokument54 SeitenRandom Phase ApproximatiomanbalassisNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW01 PDFDokument6 SeitenHW01 PDFSebastian Villamizar GarcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Elex PreboardDokument9 Seiten1 Elex PreboardV1NSKYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part C: Electromagnetic Fields IIVon EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part C: Electromagnetic Fields IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Asexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateDokument4 SeitenAsexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0972 w19 GT PDFDokument1 Seite0972 w19 GT PDFMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decay WorksheetDokument3 SeitenDecay WorksheetMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Worksheet: Name: . DateDokument5 SeitenCells Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curssrency ExcsshangeDokument2 SeitenCurssrency ExcsshangeMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers H.W 2 PDFDokument8 SeitenAnswers H.W 2 PDFMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Licence Agreement: Edexcel Igcse Biology Activeteach Cd-Rom DisclaimerDokument3 SeitenLicence Agreement: Edexcel Igcse Biology Activeteach Cd-Rom DisclaimeryarinaosuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple-Choice Test: 3 EnzymesDokument5 SeitenMultiple-Choice Test: 3 EnzymesMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Coursebook CD-ROMDokument4 SeitenCambridge International AS and A Level Biology Coursebook CD-ROMMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalDokument7 SeitenDo Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- A List of Missing SparknotesDokument8 SeitenA List of Missing SparknotesHolly O'TooleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Videos ExplainingDokument1 SeiteVideos ExplainingMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadmeDokument1 SeiteReadmebhaskar rayNoch keine Bewertungen
- H W PDFDokument4 SeitenH W PDFMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermalDokument9 SeitenThermalMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating the minimum mass of ice required to reduce water temperatureDokument5 SeitenCalculating the minimum mass of ice required to reduce water temperatureMuhammad0% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokument2 SeitenMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0972 w19 GT PDFDokument1 Seite0972 w19 GT PDFMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Grade 10 OctoberDokument2 SeitenQuiz Grade 10 OctoberMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Grade 8Dokument1 SeiteWorksheet Grade 8MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSDFSDFSD FDDGDFGDokument5 SeitenFSDFSDFSD FDDGDFGMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphic Display Calculator IB ReviewDokument6 SeitenGraphic Display Calculator IB ReviewManjari GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ftdpij LKJKFHBDokument4 SeitenFtdpij LKJKFHBMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerDokument11 SeitenChemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerMuhammad80% (5)
- Discovery Lab: The Circumference-Diameter Ratio of A CircleDokument6 SeitenDiscovery Lab: The Circumference-Diameter Ratio of A CircleMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- hs780t ChaptestbDokument6 Seitenhs780t ChaptestbMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- hssp1104t Teachvis3 PDFDokument1 Seitehssp1104t Teachvis3 PDFMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitDokument1 SeiteMeasures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Outline Ch11 STPDokument43 SeitenPhy Outline Ch11 STPMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrations and Waves: Additional Practice DDokument2 SeitenVibrations and Waves: Additional Practice DMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter: 3 / Semester: 2 /WEEK: 3 and 4.b: Concept Notes With Formative Activities LAS For Summative AssessmentDokument5 SeitenQuarter: 3 / Semester: 2 /WEEK: 3 and 4.b: Concept Notes With Formative Activities LAS For Summative AssessmentAngelica RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Conversion WorksheetDokument2 SeitenUnit Conversion WorksheetThea Sophia BuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narora Atomic Power Station Summer TrainDokument41 SeitenNarora Atomic Power Station Summer TrainAli ShazanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure Automatic Voltage RegulatorsDokument6 SeitenConfigure Automatic Voltage RegulatorsElver MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10: Assessment of Learning: Task 1: Circuit AnalysisDokument6 SeitenLesson 10: Assessment of Learning: Task 1: Circuit AnalysisAzmi KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Voltage Control CircuitsDokument17 SeitenLow Voltage Control CircuitsmersiumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Math Mass MeasurementDokument13 SeitenLesson Plan Math Mass MeasurementRyan Goh100% (2)
- SEO-Optimized Title for PWM IC DocumentDokument42 SeitenSEO-Optimized Title for PWM IC DocumentmiharkukNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMMC DownloadDokument29 SeitenPMMC DownloadSaumendra SarangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Δ XYZ: x=29m, y=15m, ∠Z=122°: Law Of Cosines WorksheetDokument3 SeitenΔ XYZ: x=29m, y=15m, ∠Z=122°: Law Of Cosines WorksheetHannah CenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catan YHINFDokument4 SeitenCatan YHINFX RagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Simosec IngDokument4 SeitenCat Simosec IngadhyarthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Standard Models and The Sociology of Cosmology (Lopez Corredoira)Dokument41 SeitenNon-Standard Models and The Sociology of Cosmology (Lopez Corredoira)Dr Abhas MitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swaraj India Public School: Class: 8 Subject: Maths TOPIC: Mensuration EXERCISE: 18.3 Solution of Classwork SumsDokument5 SeitenSwaraj India Public School: Class: 8 Subject: Maths TOPIC: Mensuration EXERCISE: 18.3 Solution of Classwork SumsANUSHKA SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area CapacitanceDokument7 SeitenArea CapacitancesivanagendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110kv Ehv Cable - GtpsDokument2 Seiten110kv Ehv Cable - GtpsBijaya Kumar MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Solutions ch05Dokument190 SeitenFundamentals of Thermodynamics Solutions ch05Cierré No'Middlename Jones100% (10)
- Helukabel Power CablesDokument17 SeitenHelukabel Power CablesperijoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NXA Catalog 2022 - enDokument63 SeitenNXA Catalog 2022 - enMuhammad Jamil ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Chemical 2008Dokument12 SeitenGate Chemical 2008Adil RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On PressureDokument4 SeitenProblems On Pressurevinod kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart GridDokument35 SeitenSmart GridSanjana Ganesh100% (2)
- CL-NG-6460-002-018 Checklist For Oil-Immersed Transformer Rev02Dokument8 SeitenCL-NG-6460-002-018 Checklist For Oil-Immersed Transformer Rev02WajahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 066 Alhqlcrloos 471 K 9 AgaytzqyyDokument3 Seiten066 Alhqlcrloos 471 K 9 AgaytzqyyledNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply and Voltage RegulatorsDokument73 SeitenDC Power Supply and Voltage RegulatorsRalph Justine NevadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Flow & Short Circuit Analysis of 132/33/11KV Substation Using ETAPDokument10 SeitenLoad Flow & Short Circuit Analysis of 132/33/11KV Substation Using ETAPMIRZA SHAHNAWAZ100% (1)
- Model A Refrigerated Gas Plant Workshop: ObjectiveDokument25 SeitenModel A Refrigerated Gas Plant Workshop: Objectivemiri-256Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Bidirectional LLC Resonant Converter With Automatic Forward and Backward Mode TransitiDokument14 SeitenA Bidirectional LLC Resonant Converter With Automatic Forward and Backward Mode TransitiMuhammad Saqib AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL. Electronics (SSCE - Grade 10) - Q1. Week 5. Module 5Dokument28 SeitenFINAL. Electronics (SSCE - Grade 10) - Q1. Week 5. Module 5Buenavides P. Gerundio Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen