Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BdeM Taller No. 2
Hochgeladen von
Luisfer PriceCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BdeM Taller No. 2
Hochgeladen von
Luisfer PriceCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
BALANCE OF MATERIAL IN NON-REACTIVE SYSTEMS - SINGLE UNITS
1) Skim milk is prepared by the removal of some of the fat from whole milk. This skim milk is found to contain
90.5% water, 3.5% protein, 5.1% carbohydrate, 0.1% fat and 0.8% ash. If the original milk contained 4.5% fat,
calculate its composition assuming that fat only was removed to make the skim milk and that there are no
losses in processing.
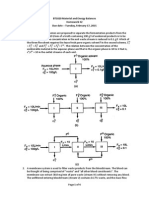
2) 10 kgmol of a feed containing 55 mol. % of a component A and 45 mol. % of B was processed in a distillation
unit. 5 kgmol of distillate with composition of 90 mol. % of A was obtained. What are the amount and
composition of the bottom product?
3) 300 kg of a mixture containing 10 wt. % of a component A, 10 wt. % of B and 80wt % of C is in a storage tank.
The goal is to obtain 500 kg of a mixture with the composition of 20 wt. % of A, and 30 wt. % of B. The
following is available: a mixture AB containing 90 wt.% of A and 10 wt. % of B, A mixture of BC containing 8 wt.
% of B and 92 wt. % of C, and pure component B. What amounts of mixtures AB and BC and pure component B
have to be added to the original mixture?
4) Potatoes are dried from 14% total solids to 93% total solids. What is the product yield from each 1000 kg of
raw potatoes assuming that 8% by weight of the original potatoes is lost in peeling.
5) A continuous filter is used to separate a clear filtrate from alumina particles in a slurry. The slurry is 30% by
weight of alumina that has a specific gravity of 4.5. The cake retains 5% by weight of water. For a feed stream
of 1000 kg/h, determine the following:
1. The mass flow rate of particles and water in the input stream
2. The volumetric flow rate of the inlet stream in m3/s.
3. The mass flow rate of filtrate and cake in kg/s.
6) A distillation column is used to separate a mixture of methanol, ethanol, and isopropyl alcohol. The feed
stream, with a mass flow rate of 300 kg/h, has the following composition:
Component Composition
Methanol 50,1%
Ethanol 25,0%
Isopropyl alcohol 24,9%
Separation of this mixture of alcohol takes place according to the following specifications:
(a) 90% of the methanol in the feed leaves with the distillate stream
(b) 5% of the ethanol in the feed leaves with the distillate stream
(c) 3% of the isopropyl alcohol in the feed leaves with the distillate stream.
Assuming that the volumes of the components are additive, compute the composition and volumetric flow rates of the
distillate and bottom streams (Densities of all alcohols are 0,78 g/cm3)
7) A mixture of ethanol (A) and water (B) is separated in a distillation column. The volumetric flow rate of the
feed stream is 5 m3/h. The concentration of ethanol in the feed is cA = 2.800 mol/m3. The distillate leaves the
column with a concentration of ethanol cA = 13.000 mol/m3. The volumetric flow rate of distillate is one cubic
meter per hour. How much ethanol is lost through the bottoms of the column, in kilograms of ethanol per hour?
8) A ternary mixture of benzene, ethylbenzene, and toluene is fed to a distillation column at a rate of 105 mol/h.
The composition of the mixture in % moles is: 74% benzene, 20% toluene, and 6% ethylbenzene. The distillate
flows at a rate of 75x103 mol/h. The composition of the distillate in % moles is 97,33 % benzene, 2% toluene,
and the rest is ethylbenzene. Find the molar flow rate of the bottoms stream and the mass fractions of the three
components in the distillate and bottoms stream.
9) A complex mixture of aromatic compounds leaves a chemical reactor and is fed to a distillation column. The
mass fractions and flow rates of distillate and bottoms streams are given in Table 4.25. Compute the molar flow
rate and composition, in molar fractions, of the feed stream.
Flow rate and composition of distillate and bottoms streams. (kg/h)
Flow rate ωBenzene ωToluene ωBenzaldehide ωBenzoicAcid ωMethylBenzoate
Distillate 125 0.1 0.85 0.03 0.0 0.02
Bottoms 76 0.0 0.05 0.12 0.8 0.03
10) The indicator dilution method is a technique used to determine flow rate of fluids in channels for which devices
like rotameters and orifice meters cannot be used (e.g., rivers, blood vessels, and large diameter pipelines). A
stream of an easily measured substance (the tracer) is injected into the channel at a known rate and the tracer
concentration is measured at a point far enough downstream of the injection point for the tracer to be
completely mixed with the flowing fluid. The larger the flow rate of fluid, the lower the tracer concentration at
the measurement point. A gas stream that contains 1.50 mole% CO2 flows through a pipeline. 20.0 kg of
CO2/min is injected into the line. A sample of the gas is drawn from a point in the line 150 m downstream of
the injection point and found to contain 2.3 mol% CO2. (a) Estimate the gas flow rate (kmol/min) upstream of
the injection point (after steady state has been reached). (a) If the CO2 concentration at the measurement
points (150 m downstream) begins to rise at 18 s after the additional CO2 was first injected. Assuming that the
tracer travels at the average velocity of the gas in the pipeline (i.e. neglecting diffusion of CO2), estimate the
average velocity (m/s). If the molar gas density is 0.123 kmol/m3, what is the pipe diameter?
11) Two octane-heptane mixtures are contained in separate tanks. The first mixture contains 93 wt% octane and
the second mixture contains 80 wt% octane. In order to have a fuel that can be used in a vehicle, 2.3 kg of the
first mixture is mixed with 1.1 kg of the second mixture. What is the mass and composition of the product? A
schematic of the process is shown below.
12) The effluent from a coal gasifier contains 52 mol% carbon monoxide, 39 mol% hydrogen, and 9 mol% carbon
dioxide. The stream is mixed with water before it enters a water-gas shift reactor where the additional
hydrogen is formed. (a) You require a molar water feed that is 10% larger than the carbon monoxide flow rate.
Determine the mole fractions in the reactor feed.
13) A stream of humid air, containing 10.0 mole% water, enters a condenser in which 95% of the water vapor in
the air is condensed. The flow rate of the condensate (liquid leaving the condenser) is measured and found to
be 225 L/h. Calculate the flow rate of the gas stream leaving the condenser and the mole fractions of O2, N2,
and H2O.
14) A liquid mixture containing 45.0 wt% benzene (B) and 55.0% toluene (T) is fed to a distillation column
operating at steady state. Product streams emerge from the top and bottom of the column. The top product
stream contains 95.0 wt% B, and the bottom product stream contains 8% of the benzene fed to the column. The
volumetric flow rate of the feed stream is 2000 liters/h and the specific gravity of the feed mixture is 0.872.
Determine the mass flow rate of the overhead product stream and the mass flow rate and composition (mass
fractions) of the bottom product stream. Suggestion: start using the approach: draw and label a flow chart, do a
degree of freedom analysis, lay out a solution strategy, and then write equations and solve for the required
quantities.
15) An aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide contains 20% NaOH by mass. It is desired to produce an 8% NaOH
solution by diluting a stream of the 20 % solution with a stream of pure water. Determine the feed rates of 20%
solution and diluting water to produce 2310 lbm/min of the 8% solution and calculate the ratios (g H2O/g feed
solution) and (g product solution/g feed solution).
16) A feed stock available at the rate of 1000 mol/h and consisting of (all in mol%) 20% propane (C3), 30%
isobutane (i-C4), 20% isopentane (i-C5) and 30% n-pentane (nC5) is to be separated into two fractions by
distillation. The distillate is to contain all the propane fed to the unit and 80% of the isopentane fed to the unit
and is to consist of 40% isobutane. The bottoms stream is to contain all the normal pentane fed to the unit.
Calculate the complete distillate and bottoms analysis.
17) The conventional method for separating ethyl alcohol from an alcohol/water mixture is by distillation.
However, this procedure can at best only produce a product 95% by volume alcohol because alcohol and water
form a constant boiling mixture, called an azeotrope, of that composition. Simple distillation cannot eliminate
the azeotrope. Instead, if a pure alcohol product is desired, benzene is added to the feed solution. The benzene
itself forms an azeotrope with water but one, which has a lower boiling point than the alcohol, and thus the
alcohol can be purified.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ejercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFDokument4 SeitenEjercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFMafee VelezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation Aspen HysysDokument66 SeitenDistillation Aspen HysysCzarina MasicatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass BalanceDokument16 SeitenMass BalanceDewi Juliyanti Silaen0% (2)
- Part B - 16 Mark QuestionsDokument5 SeitenPart B - 16 Mark QuestionssubramanikcemechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assig 2 Che422 Spring 2012Dokument3 SeitenAssig 2 Che422 Spring 2012ⵃⴰⵎⵣⴰ ⵖⵉⵢⵜNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1165r05320801 Mass Transfer Operations IIDokument9 Seiten1165r05320801 Mass Transfer Operations IIsobichemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisVon EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Bi Toroid Transformer DiscussionDokument781 SeitenBi Toroid Transformer DiscussionLuisLazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEVEL I - ATA 28 FuelDokument66 SeitenLEVEL I - ATA 28 Fuelwagdi100% (1)
- Visual Inspection Checklist For Piping Systems: Connected Mechanical Equipment, Instrumentation, and Pipe Support SystemsDokument2 SeitenVisual Inspection Checklist For Piping Systems: Connected Mechanical Equipment, Instrumentation, and Pipe Support SystemsrajuajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BdeM Taller No. 2 Una Sola Unidad 2018-VDokument4 SeitenBdeM Taller No. 2 Una Sola Unidad 2018-VMarelbis RangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller Balance Sin RXN QCADokument4 SeitenTaller Balance Sin RXN QCAValentina BaldovinosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checal ReviewerDokument8 SeitenChecal ReviewerChristian Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Part 1 QuestionDokument2 SeitenTutorial 2 Part 1 QuestionMuiz ZahuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDokument33 SeitenTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsBayu Purnama Ridjadi75% (4)
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDokument37 SeitenTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsIndahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDokument34 SeitenTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsMuhammad IkbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems in Chemical Engineering CalculationsDokument1 SeitePractice Problems in Chemical Engineering CalculationsTheresa TuliaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Balance SheetDokument4 SeitenMaterial Balance Sheetsyed waheed ul hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBE 202 Homework #1: Introduction To Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringDokument2 SeitenCBE 202 Homework #1: Introduction To Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering김민성Noch keine Bewertungen
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur Ccb10702 Material Balances Tutorial 2Dokument2 SeitenUniversiti Kuala Lumpur Ccb10702 Material Balances Tutorial 2Surendra Louis DupuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- BdeM Taller No. 1 Variables de Proceso 2017Dokument2 SeitenBdeM Taller No. 1 Variables de Proceso 2017Amilvia Vega OrozcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Fraction and Mol Fraction PDFDokument2 SeitenMass Fraction and Mol Fraction PDFZezy BlueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probset3. MaterialbalancesDokument8 SeitenProbset3. MaterialbalancesAbi MukundNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW #2Dokument4 SeitenHW #2Rohit ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 (2013)Dokument7 SeitenTutorial 2 (2013)Shah AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checal Additional Problems&answersDokument5 SeitenChecal Additional Problems&answersMaridil Joy IsidroNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN Meb 3Dokument22 SeitenLN Meb 3Siti Noranisa hidayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas 2Dokument1 SeiteTugas 2Christy PanjaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpe 420 Tutorial 2Dokument3 SeitenCpe 420 Tutorial 2Muhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- (358004360) 1. Mass Fraction and Mol FractionDokument2 Seiten(358004360) 1. Mass Fraction and Mol FractionZezy Blue100% (1)
- Unit Ops (Supplementary Problem)Dokument2 SeitenUnit Ops (Supplementary Problem)Aduchelab AdamsonuniversityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveDokument4 SeitenLectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveTanmaysainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2-Part 1Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2-Part 1Abdul AddaharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN Meb 4Dokument18 SeitenLN Meb 4Siti Noranisa hidayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 400L Chemical Engr. Past Questions (2012/2013)Dokument52 Seiten400L Chemical Engr. Past Questions (2012/2013)ifiokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled DocumentDokument3 SeitenUntitled DocumentRoxan MoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Absorption 2022Dokument27 SeitenTutorial Absorption 2022Mars Studio0% (1)
- Distillation Process For Recovery of Methyl Isobutyl KetoneDokument5 SeitenDistillation Process For Recovery of Methyl Isobutyl Ketonesolehah misniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 202 Tutorial QuestionDokument6 SeitenCHE 202 Tutorial QuestionFawziyyah AgboolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Assignment 200412Dokument2 SeitenIndividual Assignment 200412Zaidi ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Dokument7 SeitenAssignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Nishanth ChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework1 SKKK1113 1112-2Dokument1 SeiteHomework1 SKKK1113 1112-2Khairul Anwar Abd HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 2FAizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stock Vize ÇalışmaDokument4 SeitenStock Vize ÇalışmaSimay AydoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 DR Azizul PDFDokument4 SeitenAssignment 2 DR Azizul PDFjinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation Processes IDokument3 SeitenSeparation Processes IAmesh Chiyogami100% (1)
- CopyDokument1 SeiteCopyRinaldi Putra ButarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TareaDokument3 SeitenTareaAydee GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2-Part 1Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 2-Part 1Wan AmzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 251 Assignment 3Dokument2 SeitenCHE 251 Assignment 3Appah Ernest OpokuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE211 Problem Set 1Dokument3 SeitenCHE211 Problem Set 1AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation ProcessesDokument3 SeitenSeparation ProcessesJoshua SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Problems On Material Balances PDFDokument4 SeitenAdditional Problems On Material Balances PDFEliot Kh0% (1)
- FALLSEM2015-16 CP3149 04-Aug-2015 RM01 Tutorial-1Dokument2 SeitenFALLSEM2015-16 CP3149 04-Aug-2015 RM01 Tutorial-1ShashwatAgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2-Mass Balance: DR Rashmi G WalvekarDokument1 SeiteTutorial 2-Mass Balance: DR Rashmi G WalvekarBear WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checal 1Dokument2 SeitenChecal 1VaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (I) Amount (In KG) of Water Evaporated and (Ii) Amount (In KG) of Thick Liquor ObtainedDokument2 Seiten(I) Amount (In KG) of Water Evaporated and (Ii) Amount (In KG) of Thick Liquor ObtainedDechenPemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DistillationDokument6 SeitenDistillationanita_shar29Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresVon EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterVon EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellulose Nanocrystals: Properties, Production and ApplicationsVon EverandCellulose Nanocrystals: Properties, Production and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsVon EverandAdvances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsLalit Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics - Physics 122Dokument6 SeitenFluid Mechanics - Physics 122Brian KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Numerical Simulation of Cavitating Flows Using OpenfoamDokument7 SeitenTopic 1 Numerical Simulation of Cavitating Flows Using OpenfoamKumar ByesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classic Service Manual AQV18 24Dokument86 SeitenClassic Service Manual AQV18 24hpss77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Establishment of Standard X-Ray Qualities To Be Used in Diagnostic Level at SsdlsDokument50 SeitenEstablishment of Standard X-Ray Qualities To Be Used in Diagnostic Level at SsdlsHoomi ShbNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEPRA State of Industry Report 2023Dokument266 SeitenNEPRA State of Industry Report 2023imranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bobcat E85 ExcavatorDokument2 SeitenBobcat E85 ExcavatorGoran MatovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biogass DigesterDokument9 SeitenBiogass DigesterHasnain AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Wire Earth Return (SWER) : Course Instructor: Peter ArmstrongDokument16 SeitenSingle Wire Earth Return (SWER) : Course Instructor: Peter ArmstrongnambaccucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Featured in This Edition: SPRING 2021Dokument36 SeitenFeatured in This Edition: SPRING 2021papujapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ttl/Hcmos Crystal Oscillator: MCO-1510A / MCO-1510B (FULL SIZE)Dokument1 SeiteTtl/Hcmos Crystal Oscillator: MCO-1510A / MCO-1510B (FULL SIZE)cutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Analysis of Blue StarDokument42 SeitenCompany Analysis of Blue Stardevika_namajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brakes Design Report: Objective - The Brakes Are One of The Most Important Safety Systems On The Vehicle. The CarDokument17 SeitenBrakes Design Report: Objective - The Brakes Are One of The Most Important Safety Systems On The Vehicle. The CarTavi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Orifice Plates PDFDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Orifice Plates PDFinstrengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signature RedactedDokument49 SeitenSignature RedactedG Pavan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- H1 3 6K S2 CEI 0 21 CertificateDokument7 SeitenH1 3 6K S2 CEI 0 21 Certificatebeydacaltu beydacaltuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caledonian: BS 6346 PVC Insulated, Armored Power and Control CablesDokument28 SeitenCaledonian: BS 6346 PVC Insulated, Armored Power and Control CablessurenediyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WB146 5 PDFDokument10 SeitenWB146 5 PDFLuisAlbertoVerdejoTapia100% (1)
- Topic 1 Electrical Installation System in The BuildingDokument96 SeitenTopic 1 Electrical Installation System in The Buildingnabilnash21100% (5)
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme KelantanDokument11 SeitenSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme Kelantansherry_christyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repuestos Caja PreciosDokument2 SeitenRepuestos Caja PreciosCesar Cauper CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 241 Practice Exam1Dokument14 SeitenCHM 241 Practice Exam1attaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Interview QuestionsDokument8 SeitenElectronics Interview QuestionsshyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADB (2009) Sustainable Energy Efficiency Development Program PDFDokument542 SeitenADB (2009) Sustainable Energy Efficiency Development Program PDFaanchanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viteee - 2020 - Physics 1. Laws of Motion & Work, Energy and PowerDokument2 SeitenViteee - 2020 - Physics 1. Laws of Motion & Work, Energy and PowerAaditya KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUMA (Ba Sar2!07!16 Amb1 En)Dokument60 SeitenAUMA (Ba Sar2!07!16 Amb1 En)cuongnammuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datenblatt Sonnenbatterie Eco 8.0 RowDokument2 SeitenDatenblatt Sonnenbatterie Eco 8.0 RowZindagiDeeNoch keine Bewertungen