Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
OB 1st PNCU
Hochgeladen von
Angelo ErispeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OB 1st PNCU
Hochgeladen von
Angelo ErispeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OB
Revalida: 1st Prenatal Check Up
I. Chief complaint: Missed menses or (+) Pregnancy test
II. HPI & ROS
• Number of months of missed menses
• Number of times she took a pregnancy test & the result/s
• Investigate the signs, symptoms & dangers signs of pregnancy, note if positive or
negative
Presumptive symptoms Nausea +/- vomiting
(History) • Begins at 6w, peaks at 9-10w (corresponds to peak of
hCG secretion)
Disturbances in urination
• 2nd-3rd month while the uterus is still a pelvic organ
• Enlarging uterus puts pressure on urinary bladder
causing: Frequency, irritability, dribbling, nocturia
Fatigue
• Most noticeable during the 1st few weeks of pregnancy
• Due to an increased BMR
Maternal Perception of fetal movement (quickening)
• Primi: 18-20w
• Multi: 16-18w
Breast symptoms
• Estrogen: stimulates mammary duct system
• Progesterone: stimulates alveolar components
• Breast tenderness & engorgement (esp in early
pregnancy)
Presumptive signs Cessation of menstruation
(PE) • Corpus luteum (usually maintained by LH) does not
regress & continues to produce progesterone as it is
now maintained by embryonic hCG
• This will not allow the endometrium to be shed
Anatomical breast changes
• Breast enlargement & vascular engorgement
• Hyperpigmentation of the areola
• Nipples become larger
Chadwick’s sign (6w AOG)
• Purple/dark-bluish color of the vaginal mucosa due to
increased vascularity
Thermal signs
• Perceptible elevation of body temperature for longer
than 3 weeks due to the thermogenic effect of
progesterone
Skin pigmentation changes
• Due to an increase in estrogen and progesterone ->
stimulates Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone ->
hyperpigmentation: Chloasma or melasma
gravidarum (mask of pregnancy), linea nigra
• Due to the enlarging gravid uterus: striae gravidarum
Probable signs Abdominal enlargement (6w AOG onwards)
(PE) • Due to the enlarging gravid uterus
• Fundic height to be explained at the PE section
Hegar’s Sign (6-8w AOG)
• Softening of the uterine isthmus & fundus
Goodell’s Sign (4w AOG)
• Cyanosis of the cervix d/t increased vascularity
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
Softening of the cervix (6-8w AOG)
• Soft consistency = lips, d/t progesterone & estrogen
• Firm consistency = nasal cartilage (non-pregnant)
Crystallization of cervical mucus
• Beaded pattern of cervical mucus
• Progesterone decreases NaCl in mucus while Estrogen
increases it (ferning) à during pregnancy,
progesterone predominates à ferning is inhibited à
cervical mucus will crystallize (beaded pattern)
Braxton-Hicks Contractions (28w AOG)
• False labor pain: strong, palpable/visible, irregular
contractions of short duration
Ballotment (20w AOG)
• Indicates that the amniotic fluid volume is greater
than the fetal volume
• Internal ballotment: Insert IE fingers per vagina, other
hand exerts an upward pressure to the uterine
fundus, release fundus & you will feel a rounded
structure that will hit/bounce back on your finger
• External ballotment: examiner moves uterus from
side to side (with both palms on each side of uterus),
feels like something is floating/bouncing against the
palms
• Only a probable sign, since any intrauterine mass will
present with this finding
Outlining of the fetus
Positive pregnancy test (8-9d post-ovulation)
• Due to hCG detection
• Peak: 60-70d
• Nadir: 14-16w AOG
Positive signs Detection of fetal heart tone
(PE/Ancillaries) • TVS: 6-8 weeks, most accurate
• Doppler: 10-12 weeks
• Stethoscope: 18 weeks
Perception of fetal movement by the examiner (20w AOG)
US recognition of the embryo/fetus
• Gestational sac: 4-5 weeks
• Fetal heart beat: 6-8 weeks
• CRL predictive of gestational age up to 12 weeks
Danger signs of pregnancy Persistent headache – severe feature of pre-eclampsia
Blurring of vision – severe feature of pre-eclampsia
Persistent nausea and vomiting – may indicate GTD
Fever and chills – manifestations of infection
Dysuria – may signify UTI
Hypogastric pain – may signify preterm/premature
labor/abortion
Bloody vaginal discharge – may signify abortion/ectopic
pregnancy/labor/placenta previa/abruptio placenta
Watery vaginal discharge – may signify
preterm/premature/labor
Decreased fetal movement – may signify a hypoxic fetus
Edema of the hands and feet may signify pre-eclampsia
• Note if there is any cough, colds, exposure to radiation, if there are any other prenatal
check-ups from other hospital & reason for transfer
• Also take note of any viral exanthems/teratogen exposure, medications given
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
II. Past Medical History
• Are there any chronic conditions or treatment for those conditions that may impact the
pregnancy? DM, HTN, HIV, PTB, Autoimmune diseases, Asthma, malignancy
• Previous illnesses, surgeries, blood transfusions, allergies
III. Family History
• Hereditary diseases that may impact the pregnancy or may be passed on to the fetus
• DM, HTN, Asthma, malignancy, heart disease
IV. Personal/Social History
• Smoking, alcohol, illicit drug use
V. Menstrual History
• MIDAS
• Menarche: Age at 1st menstruation
• Interval: 28-30 days (N: 28 + 7 days)
• Duration: 5-7 days (N: 4 – 7 days)
• Amount: 3-4 ppd, moderately soaked (MBL <80mL, Iron loss 13mg/cycle)
• Symptoms: (+) Dysmenorrhea Day 1 relieved by
• LMP: February 27, 2016
• PMP: January 28, 2016
VI. Sexual History
• Coitarche: Age at 1st sexual contact
• Sexual Partners: 2
• Symptoms: (-) dyspareunia, (-) post-coital bleeding
• Family planning method: Natural, barrier method, withdrawal, OCPs
VII. Obstetrics History
• GP(TPAL): Gravidity, Parity, (Term-Preterm-Abortion-Living)
• Also note date of deliveries, outcome, mode, complications
• Ex: G2P1 (1001)
DATE PREGNANCY LABORS PUERPERIUM
April 4, 2016 Live, term singleton NSD by an No
male BW 3.1kg, BL Obstetrician at complications
141cm USTH
If CS, note
indication.
VIII. Current Pregnancy
• Duration of pregnancy
o 280 days or 40 weeks from the 1st day of the LMP
o This corresponds to 10 units containing 28 days each
o Divided into 3 trimesters
§ 1st trimester: Up to 14w
§ 2nd trimester: Up to 28w
§ 3rd trimester: Up to 42w
• Estimation of the AOG: MUST BE IN WEEKS!
o 1st trimester ultrasound – most accurate method to estimate AOG
§ Example: US done Dec. 15, 2016 with an AOG of 8 weeks 2 days
• Convert weeks AOG to days
• 8 weeks x (7 days/1week) = 56 days + 2 days à 58 days
§ Date today: April 4, 2017
• Add the number of days that has passed from the US date to the
present date
• Dec: 16 + Jan: 31 + Feb: 28 + March: 31 + April: 4 = 110 days
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
• 58 days (Age indicated in the US) + 110 days (Number of days that
passed since the US)
• 58 + 110 = 168 days x (1week/7days) à 24 weeks AOG as of now
o LMP Method
§ LMP: January 4-8, 2017
§ Date today: April 7, 2017
Month Days
January 31 – 4 = 27
February 28
March 31
April 7
Add the number of days = 93 days
Divide by 7 to convert to weeks: 93/7 = 13.29 à 13-14w AOG by LMP
Use if US results are not yet available & menstrual cycle is regular
• Estimated Date of Delivery
o Naegle’s rule: provides an EDD, although not exact, we can expect delivery to be
+/- 2 weeks from this date
o EDD = -3mo or +9mo, then +7d from the 1st day of LMP
o LMP: January 4-8, 2017
o 01-04-17 (+9mo, +7days)
o EDD: 10-11-17 October 11, 2017
IX. Physical Examination
• Obtain the weight in pounds, height in cm. Compute BMI based on pre-pregnancy
weight
• Abdominal examination
o Inspection: Abdomen is flat/globular
o Auscultation: with Normoactive bowel sounds
o Percussion – please do not percuss pregnant patients
o Palpation
§ Fundic Height
§ Leopold’s Maneuver
§ FHT
• Fundic height (cm)
o Make sure that the bladder is empty! à Ihi po muna kayo
o Use a tape measure in cm and measure from the Upper border of the symphysis
pubis until the uterine fundus only in gravidas with >16-18w AOG
o Fundic height in cm is reflective of AOG during 16w/18w to 32w AOG
§ 20cm = 20 weeks AOG
o 12w – fundus is at the symphysis pubis
o 16-22w – growth is more rapid as uterus rises out of pelvis into the abdomen
o 20w – fundus is felt at the level of the umbilicus
o If uterine size is small for AOG
§ Erroneous dates of LMP
§ Transverse lie
§ IUGR/SGA
§ Oligohydramnios
§ Constitutionally small fetus
o If uterine size is large for AOG
§ Erroneous dates of LMP
§ Multifetal pregnancy
§ Molar pregnancy
§ LGA, constitutionally large fetus
§ Polyhydramnios
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
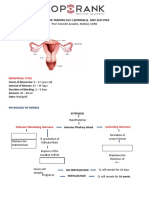
• Leopold’s maneuver
o Abdominal palpation which provides information on fetal position, presenting
part & engagement
o Only performed in the latter stages of gestation >28-30w AOG
Leopold’s Maneuver Determines
LM1: Fundic grip Fetal part occupying the fundus
LM1: Breech – if a large nodular mass
is palpated = buttocks
LM1: Cephalic – hard, freely movable,
ballotable part – fetal head at fundus
LM2: Umbilical Grip Position of the fetal back
Hard resistant convex structure –
fetal back
Numerous nodulations - fetal small
parts
LM2: FB Left or FB Right
LM3: Pawlik’s Grip Fetal part occupying the pelvic inlet
LM3: Cephalic – head is at the inlet
LM3: Breech – buttocks at the inlet
LM4: Pelvic Grip Determine whether head is
extended/flexed or whether
*only LM where the engagement has occurred
examiner faces the
mother’s feet LM4: Negative – fetal head is flexed,
this means engagement has not
occurred
• Fetal heart tone
o 6-8 weeks- could be detected by TVS
o 10-12 weeks- Doppler
o 18-20weeks- Stethoscope: Palpate the fetal back & place the bell of the
stethoscope over the FB and slightly place pressure on it
o Normal: 110-160bpm
• Breast examination
o Always perform!
o Respectfully ask the patient to remove clothing to expose both breasts
o Inspect à palpate outside going in à squeeze the nipples
o Normal: breasts are symmetric, skin colored, no dimpling, nipple not inverted,
no nipple retractions, no palpable masses & no nipple discharge
• Pelvic examination
o Inspect external genitalia for any local lesions that may be present or an
episiotomy scar
§ Normal: Pubic hair is coarse and thick, distributed in an inverted triangle
pattern. The labia majora is hyperpigmented and (not) coaptated. There
is a previous RMLE or ME wound. On palpation, there are no masses,
nor tenderness.
o Speculum examination
§ Describe the cervix and the vaginal discharge
§ Normal: Cervix is smooth, violaceous with minimal whitish non-foul
smelling discharge
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
o Internal examination:
§ Describe the cervix, uterus and adnexa
§ Normal: Cervix soft, long, closed; uterus enlarged to 2 months’ size, no
adnexal masses nor tenderness
§ Adnexae cannot be evaluated if uterus is 3 months’ size
§ If term: Cervix is soft, long, 1 cm dilated, (+) BOW, cephalic, station -3
X. Diagnosis
• G2P1 (1001), Pregnancy Uterine 13-14w AOG by LMP
XI. Labs/Ancillaries
• Transvaginal Ultrasound
o <12w AOG
o Requested to establish
§ Fetal aging & viability
§ Intrauterine pregnancy
• Fetal biometry if > 13w for fetal aging & viability
• Biophysical Profile if > 28w to assess fetal well-being
o AFI
o Fetal tone
o Fetal movement
o Fetal breathing
o FHR
• CBC
o Note for leukocytosis & pregnancy but mostly to assess physiologic anemia of
pregnancy
o 1st trimester: <11g/dl
o 2nd trimester: <10.5g/dl
o 3rd trimester: <11g/dl
o Quantify anemia if mild, moderate or severe
§ Mild: 9.5-10.5g/dl
§ Moderate: 8-9.4g/dl
§ Severe: 6.9-7.9g/dl
• Blood typing
o Just in case blood transfusion be needed during labor/delivery
o It is important to note maternal blood type to assess the possibility/risk for
developing hemolytic disease of the new born
• Urinalysis
o To assess for UTI as this may cause abortion/premature labor if left untreated
o Pus must be < 5/hpf, albumin (proteinuria is needed in the diagnosis of Pre-
eclampsia)
• HbSag
o Near term
o Hepatitis Virus is capable of crossing the placental barrier
o A reactive test may indicate the need for neonatal HB IgG
• VDRL/RPR: Near term
o For appropriate treatment to avoid vertical transmission of these diseases
• Pap Smear – baseline, but usually requested if a gravida presents with signs and
symptoms of cervical cancer (foul-smelling vaginal discharge, weight loss, post-coital
bleeding). This primarily detects premalignant lesions of the cervix as a screening tool
for cervical CA.
• HIV Screening – suggest to the patient as the Philippines has the highest rate of new HIV
cases recorded per day as compared to any other Asian country
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
• Diabetes Screening
o At the first prenatal visit, determine if the gravida is HIGH RISK or not based on
historical and pregnancy risk factors
Historical Risk Factors for the development of GDM
Past pregnancies Abnormal glucose tolerance
Macrosomia (BW > 8 lbs)
Congenital malformations
Recurrent abortions
Unexplained intrauterine death
Present pregnancy Family history (1st degree relation)
Maternal obesity (>180 lbs or BMI >27 kg/m2)
Drugs affecting CHO metabolism (steroids, beta agonists, etc.)
Age 25 years
Racial predilection
Obstetric/gynecologic Hydramnios
risk factors Macrosomic fetus
Fetal abnormality
Recurrent genital tract infections
PCOS
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
XII. Plans
• Multivitamins tablet, 1 tab OD
• Folic Acid 1 tab OD
• Ferrous Sulfate 1 tab OD
• Milk 1 glass OD
• Follow up check-ups
o Non-high risk
§ 1st PNCU to 28w AOG: Every 4 weeks
§ 28-36w AOG: Every 2 weeks
§ 37w AOG onwards: Every week
o High risk
§ May vary depending on the disease
o Or anytime if with problems/danger signs of pregnancy
• Dietary prescription
o 2000 kcal/day, add 300 kcal/day in 2nd and 3rd trimester
§ Normal weight gain: 25-35lbs (1lb/week)
o Iron: 27mg/day of FeSO4, no supplementation during the 1st trimester
o Calcium 400-900mg, recommended to women with poor calcium intake & is
beneficial to those at risk of developing GHPN & Pre-eclampsia.
o Zinc 12mg/day, essential for enzymatic activity required for growth, brain dev’t,
sexual maturation & immune function
o Iodine 220mg/day – given due to the high prevalence of goiter
o Folate 350mcg/day – a deficiency of which is a contributing factor to anemia,
4mg/day if with history of NTDs as this prevents NTDs
• Common concerns of patients
o Air travel is safe up to 36 weeks AOG (ACOG)
o Periodontal disease has been linked to preterm labor but pregnancy is not a
contraindication to dental treatment/radiographs
o Caffeine intake should be <300mg/day: <3 5oz cups daily
o Immunizations
§ Tetanus toxoid
• Give if no/unknown history of immunization
• Give 3 doses starting at the 2nd trimester, 1 month apart and 3rd
dose can be given post-partum
• Tetanus toxoid more than 10 years ago, give 1 booster
§ Influenza Vaccine
• Can be safely given any time during pregnancy
JMFV D2017, UST-FMS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UNAS Ob Surabaya 2017Dokument31 SeitenUNAS Ob Surabaya 2017Zurya UdayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Wise 3RD Year With KeyDokument24 Seiten2017 Wise 3RD Year With KeyAnne Lorraine BringasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLE Sep 2017Dokument178 SeitenPLE Sep 2017Nica Lopez FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Pedro - Training and Monitoring of Midwives For Their Expanded Role in Maternal and Child HealthDokument18 SeitenSan Pedro - Training and Monitoring of Midwives For Their Expanded Role in Maternal and Child HealthHendrix Antonni Amante67% (3)
- Ob NotesDokument16 SeitenOb Noteslily machan100% (3)
- Obgyn Revalida Review 2013 For PrintingDokument96 SeitenObgyn Revalida Review 2013 For PrintingMon Ordona De Guzman100% (2)
- Chap 8 Prenatal CareDokument10 SeitenChap 8 Prenatal CareRem AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Friedmans Curve v2Dokument4 Seiten12 Friedmans Curve v2Jowi Sal100% (1)
- MCN Test BankDokument10 SeitenMCN Test BankMho Pimentel Vanguardia100% (1)
- 09 Pediatrics PLE 2019 RatioDokument66 Seiten09 Pediatrics PLE 2019 RatioMei Bejerano - Roldan100% (1)
- 10 Topnotch Obstetrics Gynecology SuperExam1 PDFDokument84 Seiten10 Topnotch Obstetrics Gynecology SuperExam1 PDFvardhan100% (3)
- Maternal and Child Health Pracice Test 1-2-3Dokument84 SeitenMaternal and Child Health Pracice Test 1-2-3chuppepay100% (1)
- Immunohematology Trans by KTRC (Wala Ito Sa Book)Dokument21 SeitenImmunohematology Trans by KTRC (Wala Ito Sa Book)Angelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment Planning of ImplantsDokument10 SeitenTreatment Planning of ImplantsRussia Al ShboulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese-Medical Terminology 13021Dokument5 SeitenChinese-Medical Terminology 13021YS NateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Medical Billing & CodingDokument86 SeitenBasics of Medical Billing & CodingRic Sánchez100% (3)
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDokument15 SeitenRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resident'S Review: A Webinar Series: PRENATAL CARE by Dr. Cagayan Goals of Prenatal CareDokument12 SeitenResident'S Review: A Webinar Series: PRENATAL CARE by Dr. Cagayan Goals of Prenatal CareAngela SaldajenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB OSCE Reviewer 2014Dokument3 SeitenOB OSCE Reviewer 2014Princess Jeanne Roque GairanodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrapartal Nursing Care 1 in The Delivery Room MrsDokument184 SeitenIntrapartal Nursing Care 1 in The Delivery Room MrsRandy100% (2)
- Ob - Gyne FinalddffDokument28 SeitenOb - Gyne FinalddfffilchibuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Notes - Docx 1Dokument118 SeitenObstetrics and Gynecology Notes - Docx 1Christos Karakatsanis100% (1)
- OB GYN Board Exam QuestionsDokument11 SeitenOB GYN Board Exam QuestionsernestosandNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 101 - Obstetrics ExamDokument14 SeitenNCM 101 - Obstetrics ExamBing58100% (2)
- Obstetrics Test Blue PrintDokument8 SeitenObstetrics Test Blue Printjose carlo araojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM PFC MatrixDokument4 SeitenPM PFC MatrixFamed residentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Codigo 2013Dokument24 SeitenPedia Codigo 2013Denise CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revalida QuestionsDokument9 SeitenRevalida QuestionserwinsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBDokument6 SeitenOBbsn_cathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 4Dokument14 SeitenCase 4bekbekk cabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Medicine COPCDokument20 SeitenFamily Medicine COPCrachellesliedeleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrical Nursing AntepartumDokument28 SeitenObstetrical Nursing AntepartumAyeza DuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IUFDDokument62 SeitenIUFDMae Quito100% (1)
- Gyne - Feu ReviewerDokument87 SeitenGyne - Feu ReviewerKoko RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB Gyne ReviewerDokument52 SeitenOB Gyne ReviewerRaffy Lucmans100% (1)
- Reflection Family MedicineDokument3 SeitenReflection Family MedicineStanley SekwenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- THESIS October 1 (2 Jes)Dokument48 SeitenTHESIS October 1 (2 Jes)darkchrono73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal ObstetricsDokument286 SeitenAbnormal ObstetricsJen Ilagan100% (3)
- Pedia Lecture 1-b Preventive Healthcare in Pediatrics TransDokument10 SeitenPedia Lecture 1-b Preventive Healthcare in Pediatrics TransRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leiomyoma UteriDokument81 SeitenLeiomyoma UteriLea Rose Dictaran Aronza100% (2)
- OBGYN Revalida Review 2019Dokument74 SeitenOBGYN Revalida Review 2019anonymous100% (1)
- CHN Final ExamDokument12 SeitenCHN Final ExamChristine UdhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetric History TakingDokument1 SeiteObstetric History Takingyendagumboy100% (1)
- Pedia Opd Revalida Review 2019Dokument94 SeitenPedia Opd Revalida Review 2019anonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Item Obstetrics-Maternal and Child Health Nursing ExaminationDokument50 Seiten100 Item Obstetrics-Maternal and Child Health Nursing ExaminationMaria Ibarrola100% (1)
- Problem No. 2: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Needs Diagnostic or Therapeutic ModalitiesDokument20 SeitenProblem No. 2: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Needs Diagnostic or Therapeutic ModalitiesBrandone Dave ParagosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics MCQ Questions & Answers - DapzoiDokument21 SeitenObstetrics MCQ Questions & Answers - DapzoiFarah FarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Case Study FormatDokument4 SeitenPedia Case Study FormatJohn Carlo B. Dungca100% (1)
- Topnotch ObGyne PDFDokument36 SeitenTopnotch ObGyne PDFdlucNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB-GynMCQ S BlueprintDokument20 SeitenOB-GynMCQ S BlueprintDivine Sangutan100% (1)
- In The Second Stage of LaborDokument5 SeitenIn The Second Stage of Laborravensclaw001Noch keine Bewertungen
- OB-Reviewer With AlgorithmDokument29 SeitenOB-Reviewer With Algorithmriczen mae vilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal OB, DanielDokument7 SeitenAbnormal OB, DanielBhebz C. GarolNoch keine Bewertungen
- C. Anovulation: C. Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDokument18 SeitenC. Anovulation: C. Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingJan Mikhail Frasco100% (1)
- Preventive Medicine PLE ReviewerDokument4 SeitenPreventive Medicine PLE ReviewerReinhard Ivan MansibangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2 Obstetrics Nursing: Untitled SectionDokument11 SeitenQuiz 2 Obstetrics Nursing: Untitled SectionBeverly DatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics MnemonicsDokument9 SeitenObstetrics MnemonicsJared Khoo Er Hau100% (2)
- CME Miscarriages Combined 1Dokument76 SeitenCME Miscarriages Combined 1syawal zulfitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Signs: The Four P's of LaborDokument4 SeitenClinical Signs: The Four P's of Laborvienny kayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCNDokument11 SeitenMCNArienne Janine MalabananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 2 Review Pregnancy Fetal Development and Labor and DeliveryDokument84 SeitenDay 2 Review Pregnancy Fetal Development and Labor and DeliveryInah SaritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - 5 Weeks AOG 3 Trimester: PeriodDokument4 Seiten4 - 5 Weeks AOG 3 Trimester: PeriodRojales FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationsDokument38 SeitenEarly Pregnancy ComplicationsAzim Syahmi Abd RazakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dystocia in The BitchDokument2 SeitenDystocia in The BitchGissele ParaisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Fetal Well-Being 1. Fetal MovementDokument6 SeitenAssessment of Fetal Well-Being 1. Fetal MovementClaire Julianne CapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icebox CheatsheetDokument32 SeitenIcebox CheatsheetAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture CheatsheetDokument14 SeitenFracture CheatsheetAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caloocan To Olongapo May 9 8pmDokument2 SeitenCaloocan To Olongapo May 9 8pmAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tragedy of Finding PeaceDokument16 SeitenTragedy of Finding PeaceAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bind CheatsheetDokument63 SeitenBind CheatsheetAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webinar - How To Write An Effective Research PaperDokument2 SeitenWebinar - How To Write An Effective Research PaperAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meningitis and Encephalitis: PGI Roddame Angelo ErispeDokument100 SeitenMeningitis and Encephalitis: PGI Roddame Angelo ErispeAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attentive Listening Webinar - ErispeDokument1 SeiteAttentive Listening Webinar - ErispeAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDL Leprosy - ErispeDokument1 SeiteSDL Leprosy - ErispeAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Assertiveness - ErispeDokument2 SeitenAssignment On Assertiveness - ErispeAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Mental Imagery On Free Throw Performance PDFDokument95 SeitenThe Effects of Mental Imagery On Free Throw Performance PDFAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Basic Counseling Skills - ErispeDokument1 SeiteAssignment On Basic Counseling Skills - ErispeAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroDokument5 SeitenSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue ManagementDokument7 SeitenDengue ManagementAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSE1Dokument3 SeitenMSE1Angelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Almonte HistoryDokument3 SeitenAlmonte HistoryAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disease: NmcastroDokument7 SeitenMixed Connective Tissue Disease: NmcastroAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mnemotechniques LanguageDokument5 SeitenMnemotechniques LanguageAngelo ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gale Global PPNU 2019-11-01Dokument410 SeitenGale Global PPNU 2019-11-01s4sigitNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEHealthcare Brochure - Reusable Temperature Probes PDFDokument4 SeitenGEHealthcare Brochure - Reusable Temperature Probes PDFHomeroPerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Teks Debat Bahasa Inggris "Merokok Harus Dilarang" (Smoking Should Be Banned)Dokument3 SeitenContoh Teks Debat Bahasa Inggris "Merokok Harus Dilarang" (Smoking Should Be Banned)Hanna FairussaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pearls of Wisdom Anesthesiology Board Review PDFDokument8 SeitenPearls of Wisdom Anesthesiology Board Review PDFAyman Mustafa0% (1)
- Ese - Arbina JajiDokument6 SeitenEse - Arbina JajiShenasiJajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe001-Activity No. 3.1Dokument3 SeitenPe001-Activity No. 3.1Rea Mariz JordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To KinesiologyDokument23 SeitenIntroduction To Kinesiologynarainder kumar50% (2)
- Community Health Survey: College of NursingDokument3 SeitenCommunity Health Survey: College of NursingMaria Pina Barbado PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piracetam PDFDokument5 SeitenPiracetam PDFAriWahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austere Medicine Books PDFDokument10 SeitenAustere Medicine Books PDFmorrischuck100% (1)
- Institute of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDokument4 SeitenInstitute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciencesshadow gonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NN.19.10 Umbilical Cord CareDokument2 SeitenNN.19.10 Umbilical Cord CareRohit DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psoriatic ArthritisDokument10 SeitenPsoriatic ArthritisSaba AyurvedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root PlainingDokument10 SeitenRoot PlainingSooul MateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggressive Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor of Maxilla Involving Impacted Third Molar - A Rare Case ReportDokument7 SeitenAggressive Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor of Maxilla Involving Impacted Third Molar - A Rare Case ReportRisyaRahmadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Health Nursing BulletsDokument5 SeitenCommunity Health Nursing BulletsDefensor Pison GringgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbortionDokument35 SeitenAbortionHoney May Rollan VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- HFME Hints and Tips For MEDokument124 SeitenHFME Hints and Tips For MEgreenbee100% (1)
- PROCEDURE On AmniocentesisDokument2 SeitenPROCEDURE On AmniocentesisMansiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Exemplar in Mapeh Grade Level Learning Area QuarterDokument8 SeitenLesson Exemplar in Mapeh Grade Level Learning Area QuarterErwin Balid GasconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiss CudyrDokument42 SeitenTiss CudyrRocioQAChioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neral Information Title: Venue: Date: Participants:: Project ProposalDokument2 SeitenNeral Information Title: Venue: Date: Participants:: Project ProposalAida Potacag Buasen100% (1)
- Microbiology SyllabusDokument2 SeitenMicrobiology Syllabusapi-3704804Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bluetongue, Romania: Print CloseDokument2 SeitenBluetongue, Romania: Print CloseAnna Maria MurariuNoch keine Bewertungen
- COURSE OBJECTIVES or NursingDokument5 SeitenCOURSE OBJECTIVES or NursingFil AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global: CDC Health StrategyDokument22 SeitenGlobal: CDC Health StrategyBijay Kumar MahatoNoch keine Bewertungen