Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Objective Physics
Hochgeladen von
leoyodapieCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Objective Physics
Hochgeladen von
leoyodapieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics Objective
Intermediate Part-I
Total Marks: 17 Time Allowed: 20 minutes
Q.1 Circle the correct answers:
1. Light year is the unit of :
A. Light B. Time C. Velocity D. Distance
2. ̂i ∙( ĵ × k̂ ) is equal to :
A. k̂ B. 0 C. 1 D. î
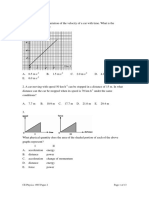
3. The slope of velocity-time graph gives:
A. Distance B. Acceleration C. Area D. Speed
4. A body is executing uniform circular motion. Its angular acceleration is:
A. Zero B. Decreasing C. Increasing D. None of these
5. 10 radians are equal to:
A. 57.3⁰ B. 5730⁰ C. 5.73⁰ D. 573⁰
6. Work has the dimensions as that of :
A. Torque B. Angular momentum C. Linear momentum D. Power
7. Range of the projectile is maximum at angle of
A. 450 B. 900 C. 300 D. 600
8. The weight of the body at the center of the earth is :
A. Slightly less B. Slightly greater C. Zero D. Infinite
9. Which will be more effective in knocking a bear down:
A. A rubber bullet B. A lead bullet C. Both A & B D. none
10. 1 nano is equal to:
A. 1010 B. 10−10 C. 10−9 D. 109
11. Work done is maximum if the angle between F and d is :
A. 180⁰ B. 0⁰ C. 90⁰ D. 45⁰
12. Work done in a closed path is:
A. maximum B. minimum C. zero D. All of these
⃗ in terms of angular velocity 𝝎 is equal to:
13. The angular momentum 𝐋
2
A. mr 𝜔 B. m2r𝜔 C. mr𝜔 2 D. m2r2𝜔 2
14. Potential energy at infinity will be:
A. zero B. maximum C. positive D. None of these
15. If the curvature is increased the centripetal force is :
A. increased B. decreased C. remain same D. zero
16. 1 KWh is equal to:
A. 3.6 X 106 J B. 3.6 X 10−5 J C. 36 X 10−6J D. 3.6 X 10−6J
17. A solar cell is a device which converts solar energy into:
A. Mechanical energy B. Heat energy C. Chemical energy D. Electrical energy
Physics Subjective
Intermediate Part-I
Total Marks: 68 Time Allowed: 2:40 hours
SECTION II
Q2. Write answers of any EIGHT questions: (8×2=16)
i. Define impulse and show that how it is related to linear momentum.
ii. Two vectors have unequal magnitudes. Can their sum be equal to zero? Explain.
iii. How many meters are there in one light year?
iv. Why do we find it useful to have two units for the amount of substance, the kilogram and the
mole?
v. What are two types of errors and how they can be removed?
vi. A 1500 kg car has its velocity reduced from 20 ms-1 to 15 ms-1 in 3.0 sec. How large was the
average retarding force?
vii. Define radian and steradian.
viii. Can a vector have a component greater than its magnitude?
ix. Can the velocity of an object reverse in direction when acceleration remains constant? If so,
give an example.
x. Define unit vector and null vector.
xi. What are the drawbacks of using the period of a simple pendulum as standard for time?
xii. Name the three different conditions that could make⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐀𝟏 × ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐀 𝟐 = 0.
Q3. Write answers of any EIGHT questions: (8×2=16)
i. At what point or points in its path does a projectile have its minimum and maximum speed?
ii. Define impulse and show that how it is related to linear momentum.
iii. What happens when a light body collides with a massive body at rest?
iv. A boy uses a catapult to throw a stone which accidentally smashes a greenhouse window.
What energy changes are involved?
v. Define elastic and in-elastic collision
vi. An object has one Joule of potential energy. Explain what does it mean?
vii. Define escape velocity. Write its value.
viii. When a rocket re-enters the atmosphere, its nose cone becomes very hot. Where does this
heat energy come from?
ix. Calculate the work done in kilo joules in lifting a mass of 10 kg (at a steady velocity)
through a vertical height of 10 m.
x. Show that P = F . V .
xi. Define range and time of flight of a projectile.
xii. Explain the circumstances in which the velocity v and acceleration a of a car are
(i) Parallel (ii) Anti-parallel
Q4. Write answers of any SIX questions: (6×2=12)
i. What is meant by moment of inertia? Explain its significance.
ii. Show that orbital angular momentum 𝑳𝑜 = mvr .
iii. Explain the difference between tangential velocity and angular velocity.
iv. When mud flies off the tyre of a moving bicycle, in what direction it goes? Explain.
v. Differentiate between spin and orbital angular momentum.
vi. Why does a diver change his body positions before and after diving in the pool?
vii. What is the working principle of rocket propulsion?
viii. What is the magnitude of 𝐴⃗ × 𝐴⃗.
ix. Explain the difference between linear momentum and angular momentum?
SECTION II (Essay Type)
Note: Attempt any THREE questions: (8 × 3= 24Marks)
Q5
a) Discuss the elastic collision of two smooth balls in one dimension and find their velocities
after the collision. (5)
^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^
b) Show that the three vectors i + j + k , 2 i − 3 j + k and 4 i + j 5k are mutually
perpendicular. (3)
Q6
a) Define conservative field. Prove that the work done in the earth’s gravitational field is
independent of the path followed. (5)
b) How large a force is required to accelerator an electron (𝑚 = 9.1 × 10−31 𝑘𝑔) from rest to a
speed of 2.0 × 107 𝑚𝑠 −1 through a distance of 5.0 cm?
Q7
a) Explain rotational K.E. Find the rotational K.E of a Disc of radius r. (5)
b) A car of mass 800 kg travelling at 54 kmh-1 is bought to rest in 60 metres. Find the average
retarding force on the car. What has happened to original kinetic energy? (3)
Q8
a) Explain cross product of two vectors. State right hand rule and give at least four
characteristics. (5)
b) A truck weighing 2500 kg and moving with a velocity of 21 m/s collides with stationary car
weighing 1000 kg. The truck and the car move together after the impact. Calculate their
common velocity. (3)
Q9
𝑚𝑣 2
a) Define centripetal force and derive 𝐹 = . (5)
𝑟
0
b) Prove that for angles of projection, which exceed or fall short of 45 by equal amounts, the
range are equal. (3)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemistry MCQ PDFDokument25 SeitenChemistry MCQ PDFNirbhayChaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming With AliceDokument357 SeitenProgramming With AliceUy DinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam Second TermDokument2 SeitenPhysics Exam Second TermsunliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUTMINNA Post-UTME Practice QuestionsDokument69 SeitenFUTMINNA Post-UTME Practice QuestionsJames Oyinloye100% (1)
- ICSE Class 10 PhysicsDokument5 SeitenICSE Class 10 Physicssudhir_narang_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upss Online Lecture Topic:Mapping and Function Class Ss1:: Subject: Further Mathematics by Akpodamure FejiroDokument9 SeitenUpss Online Lecture Topic:Mapping and Function Class Ss1:: Subject: Further Mathematics by Akpodamure FejirocauchyfjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2019Dokument11 SeitenPhysics 2019itaeo1122100% (1)
- Waec PracticalsDokument16 SeitenWaec PracticalsAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Physics - MCQ & EssayDokument15 Seiten2021 Physics - MCQ & Essaynkwochaephraim100% (1)
- 2015 Physics - MCQ & EssayDokument18 Seiten2015 Physics - MCQ & EssayIzundu VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- WASSCE WAEC Core General Mathematics-SyllabusDokument16 SeitenWASSCE WAEC Core General Mathematics-SyllabusEmmanuel Boakye100% (1)
- Ss 1 Further Mathematics Lesson 5Dokument3 SeitenSs 1 Further Mathematics Lesson 5Adio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem PaperDokument4 SeitenChem PaperKeertana SN100% (1)
- Mathematics 2ND Term Note1Dokument42 SeitenMathematics 2ND Term Note1SochiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Paper of Work Energy and PowerDokument3 SeitenTest Paper of Work Energy and PowerShekharPandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Building Orientation On Building Performance (A Case Study of Selected Buildings in Ikotun Area of Lagos)Dokument16 SeitenImpact of Building Orientation On Building Performance (A Case Study of Selected Buildings in Ikotun Area of Lagos)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akwa Ibom State School of Nursing Questions and AnswersDokument51 SeitenAkwa Ibom State School of Nursing Questions and AnswersMk AbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ss2 MathematicsDokument1 SeiteSs2 MathematicsEkpenyong EffiwattNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Jss2 3rd Term E-Learning Notes Revised 2017Dokument14 SeitenNew Jss2 3rd Term E-Learning Notes Revised 2017EMMA EMOLENoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - EV - MCQ 2ndDokument25 SeitenPhysics - EV - MCQ 2ndMaruf MorshedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Motion WorksheetDokument8 SeitenUniform Motion Worksheetnikhil patro100% (1)
- Powerpoint Physics SS2Dokument23 SeitenPowerpoint Physics SS2MARYQUEEN AMARACHUKWUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Metal Workers Theory n1 Question Memo DownloadDokument17 SeitenFree Metal Workers Theory n1 Question Memo DownloadThembelihle HadebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Term Ss2 Further Mathematics 1Dokument3 SeitenFirst Term Ss2 Further Mathematics 1stefala2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Chemistry Question PaperDokument4 SeitenGrade 8 Chemistry Question PaperAly MaknojiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank For Quick Revision PDFDokument33 SeitenQuestion Bank For Quick Revision PDFQSQFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Ss3 MockDokument2 SeitenPhysics Ss3 MockOba Fred AjubolakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths JSS 3 Term 2Dokument228 SeitenMaths JSS 3 Term 2Sahr EinsteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latestnews Kei4z091xhz9sth8 1644584032Dokument97 SeitenLatestnews Kei4z091xhz9sth8 1644584032FlowealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Technology Mock ExaminationDokument3 SeitenBasic Technology Mock ExaminationAkan EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- First School Leaving Certificate Exam Past Questions Primary SixDokument16 SeitenFirst School Leaving Certificate Exam Past Questions Primary SixAMARACHI LILIAN100% (1)
- Quadratic EquationsDokument19 SeitenQuadratic EquationsLoh Chee WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions-1Dokument5 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions-1ArushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th PhysicsDokument3 SeitenImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Physicspavan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 1Dokument10 SeitenApplied Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 1keith magakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology SS1Dokument3 SeitenBiology SS1AYANFE OLAPAGBONoch keine Bewertungen
- Plus One Physics Previous Question Paper Hsslive SajuDokument1 SeitePlus One Physics Previous Question Paper Hsslive SajuSanthosh Anandakurup0% (1)
- RIVISION TEST PAPER - Class 9Dokument4 SeitenRIVISION TEST PAPER - Class 9Teja RajarameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Exercises BiometricDokument3 SeitenSample Exercises BiometricYazanAlomariNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResistanceDokument16 SeitenResistanceDanelNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Reading Comprehesnion: High School Program 2019 Second Mid-Term Exam English A2.2 July-December 2021Dokument5 SeitenI. Reading Comprehesnion: High School Program 2019 Second Mid-Term Exam English A2.2 July-December 2021Lizeth Gabriela Hdez HdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Questions Form 4 2021Dokument70 SeitenRevision Questions Form 4 2021ALI MWALIMUNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics SS3 2ND Term SchemeDokument2 SeitenGeneral Mathematics SS3 2ND Term Schemesam kaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS3 Physics GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AND LAW - PassnownowDokument9 SeitenSS3 Physics GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AND LAW - Passnownowsunlias0% (1)
- Chemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41Dokument5 SeitenChemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41hazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ntse Sample Paper Sat 2 PDFDokument11 SeitenNtse Sample Paper Sat 2 PDFQSQFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Engineering MCQs PDF 3 PDFDokument9 SeitenBasic Electrical Engineering MCQs PDF 3 PDFAdnan QadeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Physics 1985 Paper 2 Page 1 of 13Dokument13 SeitenCE Physics 1985 Paper 2 Page 1 of 13jshfjksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Capital Territory, Abuja: JSSONEDokument152 SeitenFederal Capital Territory, Abuja: JSSONEAsia UcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple BarometerDokument11 SeitenSimple BarometerNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Practical ExaminationDokument13 SeitenPhysics Practical ExaminationAbdul Rasaq MukailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Double AwardDokument38 SeitenScience Double AwardOfficial Bryan Wonder BeatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDokument14 SeitenScience Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 Answerssingh2008adityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Further MathematicsDokument5 SeitenFurther MathematicsBabatunde Victor JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Task Mathematics-VIDokument5 SeitenSummer Task Mathematics-VIUmair IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Months JAMB Study PlanDokument4 Seiten4 Months JAMB Study PlanOMILABU DOYINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Physics StudentDokument20 SeitenGrade 10 Physics Studentapi-655732711Noch keine Bewertungen
- Half BookDokument4 SeitenHalf BookMian Haroon SahilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1st Year Full BookDokument3 SeitenPhysics 1st Year Full BookMukhtar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- World War II - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDokument108 SeitenWorld War II - Britannica Online EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hans Morgenthau EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenHans Morgenthau EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Useful Science Mcqs For Exams PDFDokument1 SeiteUseful Science Mcqs For Exams PDFleoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Law EncyclopediaDokument28 SeitenInternational Law EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Chemistry NotesDokument68 SeitenO Level Chemistry NotesUmar S Rao100% (4)
- Donald Trump EncyclopediaDokument25 SeitenDonald Trump Encyclopedialeoyodapie100% (1)
- Johnny Depp EncyclopediaDokument4 SeitenJohnny Depp EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peter I EncyclopediaDokument12 SeitenPeter I EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winston Churchill EncyclopediaDokument16 SeitenWinston Churchill EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barack Obama EncyclopediaDokument39 SeitenBarack Obama EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Les Paul EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenLes Paul EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Napoleon I EncyclopediaDokument23 SeitenNapoleon I EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- George Washington EncyclopediaDokument27 SeitenGeorge Washington EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nero EncyclopediaDokument5 SeitenNero EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Les Paul EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenLes Paul EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donald Trump EncyclopediaDokument25 SeitenDonald Trump Encyclopedialeoyodapie100% (1)
- Peter I EncyclopediaDokument12 SeitenPeter I EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winston Churchill EncyclopediaDokument16 SeitenWinston Churchill EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johnny Depp EncyclopediaDokument4 SeitenJohnny Depp EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- George Washington EncyclopediaDokument27 SeitenGeorge Washington EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nero EncyclopediaDokument5 SeitenNero EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Napoleon I EncyclopediaDokument23 SeitenNapoleon I EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Year Is The Unit of PDFDokument1 SeiteLight Year Is The Unit of PDFleoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barack Obama EncyclopediaDokument39 SeitenBarack Obama EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hans Morgenthau EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenHans Morgenthau EncyclopedialeoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Useful Science Mcqs For Exams PDFDokument1 SeiteUseful Science Mcqs For Exams PDFleoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude ProblemsDokument2 SeitenHandy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude ProblemsleoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laker LokDokument3 SeitenLaker Lokanon_9210159Noch keine Bewertungen
- Handy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude ProblemsDokument2 SeitenHandy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude ProblemsleoyodapieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For Submittal of Concrete Proportions: Reported by ACI Committee 211Dokument4 SeitenGuide For Submittal of Concrete Proportions: Reported by ACI Committee 211Juan Jose ZaldivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- High School Science Part IDokument294 SeitenHigh School Science Part Iskmrrl100% (1)
- Newtonian Physics IDokument97 SeitenNewtonian Physics IGanesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Laws of Motion Aqa A Level Physics Exam QuestionsDokument29 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motion Aqa A Level Physics Exam QuestionsAlizah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SheetDokument2 SeitenTutorial SheetjatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Motion Multiple Choice-2012!05!15-1Dokument8 SeitenRotational Motion Multiple Choice-2012!05!15-1deepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Formulae For MatriculationDokument16 SeitenPhysics Formulae For MatriculationAliah Fatin Irwani75% (4)
- Adamson University Manila: Experiment 3Dokument9 SeitenAdamson University Manila: Experiment 3Ron PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 2Dokument3 SeitenHW 2JeeveshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Properties of Jacobian1 - Dynamixel in Center PositionDokument9 SeitenMass Properties of Jacobian1 - Dynamixel in Center Positionfad003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coriolli's Component of Acceleration ApparatusDokument7 SeitenCoriolli's Component of Acceleration Apparatustinkusk24Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHM138 Basic Chemistry: Chapter One: Units of Measurements. DR Siti Nor Atika BaharinDokument38 SeitenCHM138 Basic Chemistry: Chapter One: Units of Measurements. DR Siti Nor Atika BaharinSara MaisaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Complemento SPE-28162-MS PDFDokument8 Seiten09 Complemento SPE-28162-MS PDFJORGE ADAN LUNA CARRIZOSANoch keine Bewertungen
- Aakash 02 - Description of Motion in One DimensionDokument8 SeitenAakash 02 - Description of Motion in One DimensionAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Phys6 2 Resources OptB PDFDokument61 SeitenIB Phys6 2 Resources OptB PDFJoseAmador98Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IDokument11 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IMathew G100% (5)
- Laporan Praktikum Hukum Archimedes SMADokument4 SeitenLaporan Praktikum Hukum Archimedes SMAglorianathania01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2020Dokument12 SeitenFiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2020Lohit DakshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 2 Combining Forces: Net N GDokument2 SeitenActivity No. 2 Combining Forces: Net N GRachel B. Inting50% (2)
- Rev5 PDFDokument16 SeitenRev5 PDFErickson AbiolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 7 GravityDokument29 SeitenAct 7 GravityChrise RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Chemistry DensityDokument21 SeitenGrade 7 Chemistry DensitydodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Acceleration Problems With SolutionsDokument9 SeitenUniform Acceleration Problems With SolutionsbingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective Strength Standards - Stronger by ScienceDokument18 SeitenObjective Strength Standards - Stronger by ScienceNam LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise - II: Multiple Choice ProblemDokument3 SeitenExercise - II: Multiple Choice ProblemShashank RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eddy Current and Applications ProjectDokument7 SeitenEddy Current and Applications Projectअभिषेक मान67% (3)
- Fiitjee Concept Recapitulation Test 1Dokument24 SeitenFiitjee Concept Recapitulation Test 1hkhatri18031996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student Performance Q&A: 2001 AP Physics Free-Response QuestionsDokument8 SeitenStudent Performance Q&A: 2001 AP Physics Free-Response QuestionsSTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reidland Middle School: 7 Grade Science Course Syllabus Mrs. TilfordDokument3 SeitenReidland Middle School: 7 Grade Science Course Syllabus Mrs. Tilfordapi-260199648Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 2Dokument2 SeitenSheet 2masNoch keine Bewertungen