Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Grade 8 Science - Table of Contents
Hochgeladen von
Clarence Vilbar0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
80 Ansichten3 SeitenOriginaltitel
Grade 8 Science- Table of Contents.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
80 Ansichten3 SeitenGrade 8 Science - Table of Contents
Hochgeladen von
Clarence VilbarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
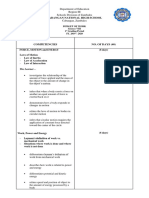
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Title Page i
Table of Contents ii
I. QUARTER 1 FORCE, MOTION AND ENERGY
Investigate the relationship between the amount of force 1
applied and mass of the object to the change in the
object’s motion.
Infer that when a body exerts a force on another, an 5
equal amount of force is exerted back on it.
Demonstrate that when a body exerts a force on another, 8
an equal amount of force is exerted back on it.
Relate the laws of motion to bodies in uniform circular 11
motion .
Infer that circular motion requires the application of 13
constant force directed toward the center of the circle.
Identify situations in which work is done and in which no 16
work is done.
Describe how work is related to power and energy. 18
Differentiate potential and kinetic energy. 21
Relate speed and position of the object to the amount of 23
energy possessed by a body.
Infer how the movement of particles of an object affects 25
the speed of sound through it .
Investigates the effect of temperature to speed of sound 27
through fair testing .
Demonstrate the existence of the color components of 30
visible light using a prism or diffraction grating.
Explain the hierarchy of colors in relation to energy . 33
Explain that red is the least bent and violet the most bent 35
according to their wavelengths or frequencies
Differentiate between heat and temperature at the 38
molecular level.
Infer the relationship between current and charge . 40
Lead to Go, Love to Grow, Live to Glow
Tel. No. (053) 323-8882/ depedleyte.net/ depedleytedivision@gmail.com
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of series and 42
parallel connections in homes .
Differentiate electrical power and electrical energy . 45
Explain the functions of circuit breakers, fuses, earthing, 47
double insulation, and other safety devices in the home.
II. QUARTER 2 EARTH AND SPACE
Using models or illustrations, explain how movements along 49
faults generate an earthquake.
Differentiate the: Epicenter of an earthquake from its focus 52
;Intensity of an earthquake from its magnitude and
Active and inactive faults.
Demonstrate how underwater earthquakes generate 55
tsunamis.
Explain how earthquake waves provide information about 58
the interior of the earth.
Explain how typhoons develop. 61
Infer why the Philippines is prone to typhoons . 65
Explain how landmasses and bodies of water affect 69
typhoons.
Trace the path of typhoons that enter the Philippine Area 72
of Responsibility (PAR) using a map and tracking data.
Compare and contrast comets, meteors, and asteroids. 76
Predict the appearance of comets based on recorded 78
data of previous appearances.
Explain the regular occurrence of meteor showers. 81
III. QUARTER 3 MATTER
Explain the properties of solids, liquids, and gases 84
based on the particle nature of matter .
Explain physical changes in terms of the 86
arrangement and motion of atoms and molecules.
Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and 89
electrons in a particular atom.
Trace the development of the periodic table from 92
observations based on similarities in properties of
elements .
Use the periodic table to predict the chemical behavior 94
of an element.
Lead to Go, Love to Grow, Live to Glow
Tel. No. (053) 323-8882/ depedleyte.net/ depedleytedivision@gmail.com
IV. QUARTER 4 LIVING THINGS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT
Explain ingestion, absorption, assimilation, and excretion. 98
Explain how diseases of the digestive system are 102
prevented, detected, and treated.
Identify healthful practices that affect the digestive 105
system.
Compare mitosis and meiosis, and their role in the cell- 111
division cycle.
Explain the significance of meiosis in maintaining the 118
chromosome number.
Predict phenotypic expressions of traits following simple 122
patterns of inheritance.
Explain the concept of a species. 127
Classify organisms using the hierarchical taxonomic 129
system.
Explain the advantage of high biodiversity in maintaining 133
the stability of an ecosystem.
Describe the transfer of energy through the trophic 136
levels.
Analyze the roles of organisms in the cycling of materials. 140
Explain how materials cycle in an ecosystem. 144
Suggest ways to minimize human impact on the 147
environment.
Answers’ Key 151
List of References 204
List of Writers, Editors and Supervising Heads 205
Lead to Go, Love to Grow, Live to Glow
Tel. No. (053) 323-8882/ depedleyte.net/ depedleytedivision@gmail.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Understanding Resonance in PhysicsDokument11 SeitenUnderstanding Resonance in PhysicsArnel Palomares OrculloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science - Test ItemsDokument205 SeitenGrade 8 Science - Test ItemsKristian Bernard Paano80% (5)
- G8 Q2 - 1 FINALoct 2018Dokument38 SeitenG8 Q2 - 1 FINALoct 2018sarah joy velascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Producers Bank Liable for Employee's ActsDokument2 SeitenProducers Bank Liable for Employee's ActsLesly BriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melcs Science8Dokument8 SeitenMelcs Science8Nurpayda AbangNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCI 8 UNIT PLAN (1st Quarter)Dokument3 SeitenSCI 8 UNIT PLAN (1st Quarter)melicyn higoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan of Food WebDokument4 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan of Food WebCherry MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8A - DAY2 - 4A - Law of InertiaDokument3 SeitenG8A - DAY2 - 4A - Law of InertiaGlenn QuibuyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For ObservationDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan For ObservationRae Kyo ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines v. Jose v. BagtasDokument1 SeitePhilippines v. Jose v. BagtasNicole Marie Abella CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Science and Technology Grade Level: Grade 8 Teachers: Strand(s)Dokument7 SeitenSubject: Science and Technology Grade Level: Grade 8 Teachers: Strand(s)richardsamranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 (Second Demo)Dokument3 SeitenLESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 (Second Demo)Lemuel Jr MitchaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science Subtasking CompleteDokument24 SeitenGrade 8 Science Subtasking CompleteRhodeliza TiotangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSNH Science Lessons on ElectricityDokument4 SeitenGSNH Science Lessons on ElectricityMaám Rosemary B. LandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 1.ADokument4 SeitenDaily Lesson Log Grade 8 1.ARaymund AlilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL School Demo (20-21)Dokument5 SeitenDLL School Demo (20-21)Juliet Defensor Cubita-MagbanuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP in Intro To WavesDokument5 SeitenDLP in Intro To WavesabbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 6 Science Test Item Bank for Eastern VisayasDokument1 SeiteGrade 6 Science Test Item Bank for Eastern VisayasDione Christy Brua100% (1)
- Grade 6 Science Test Item Bank for Eastern VisayasDokument1 SeiteGrade 6 Science Test Item Bank for Eastern VisayasDione Christy Brua100% (1)
- Grade 8 Physics Lesson on WorkDokument2 SeitenGrade 8 Physics Lesson on WorkNapdeo Natka Emuy NatadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item Creation ManualDokument14 SeitenItem Creation ManualasfarjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Plan: Ramon Avanceña National High SchoolDokument3 SeitenDaily Lesson Plan: Ramon Avanceña National High SchoolShane Catherine Besares100% (1)
- Environment Impact AssessmentDokument11 SeitenEnvironment Impact AssessmentBimal AntonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Q4 Episode 7 SLMDokument4 SeitenScience 8 Q4 Episode 7 SLMCaryll BaylonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence Cases v2Dokument29 SeitenEvidence Cases v2Alavitz AslambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot 2Dokument6 SeitenCot 2Veth QuimNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8-Fidelity 1Dokument4 SeitenG8-Fidelity 1Emma T Sogo-anNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP G8 Q1 WK 1 D2 (2) GoldahDokument8 SeitenDLP G8 Q1 WK 1 D2 (2) GoldahClarissa HugasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan I. ObjectivesDokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan I. Objectivesramel gedorNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP (Science 8)Dokument126 SeitenLP (Science 8)mark jay legoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: SCIENCE Grade Level:8: Quarter: 4 Week: 2Dokument7 SeitenSubject: SCIENCE Grade Level:8: Quarter: 4 Week: 2Cathy MoronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Demo - Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenFinal Demo - Lesson Planmichael Batungbakal100% (1)
- Cooling Gel Safety ReportDokument15 SeitenCooling Gel Safety ReportJacek Stanislawski100% (1)
- India refinery configurations-Meeting future demand & regulationsDokument9 SeitenIndia refinery configurations-Meeting future demand & regulationsphantanthanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Science 8 Q1 2022 2023Dokument12 SeitenDLL Science 8 Q1 2022 2023Hakimah C. CauntonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science LESSON PLAN - Week 1Dokument4 SeitenScience LESSON PLAN - Week 1Kathryn Decena CentinalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle StagesDokument6 SeitenCell Cycle StagesCathy MoronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 7845 JS Aspen HYSYS Dynamics Columns FINALDokument20 Seiten11 7845 JS Aspen HYSYS Dynamics Columns FINALkarthick100% (1)
- LAB MANUAL ANALYSIS ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGESDokument56 SeitenLAB MANUAL ANALYSIS ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGESdmshahidch0% (1)
- DLP G8 Q1 WK 3 D1 (11) JaneDokument7 SeitenDLP G8 Q1 WK 3 D1 (11) JaneCathy MoronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP G8 Q1 WK 4 D2 (17) AdelineDokument6 SeitenDLP G8 Q1 WK 4 D2 (17) AdelineCathy MoronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces and Net Force Notes PowerpointDokument27 SeitenBalanced and Unbalanced Forces and Net Force Notes PowerpointJeiril Divino100% (1)
- Understanding Potential EnergyDokument7 SeitenUnderstanding Potential EnergyCathy MoronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infer That Waves Carry Energy : Group Rotations Are Valuable For Keeping The Whole Class EngagedDokument10 SeitenInfer That Waves Carry Energy : Group Rotations Are Valuable For Keeping The Whole Class EngagedRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Forces and Motion Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenGrade 8 Forces and Motion Lesson PlanRebecca Implica TuvillejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL November 7-11, 2022Dokument5 SeitenDLL November 7-11, 2022ANTOLYN DE DIOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visible Light Spectrum ExplainedDokument3 SeitenVisible Light Spectrum ExplainedVanessa Joy SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Science g8-q1-w1 (Ok)Dokument3 SeitenDLL Science g8-q1-w1 (Ok)Rosy AppleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Industrial HygieneDokument50 SeitenLecture 5 - Industrial HygieneDivyashini MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8Dokument14 SeitenGrade 8Juliet Ileto Villaruel - Almonacid100% (1)
- Leave Form 6Dokument7 SeitenLeave Form 6chris orlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Work Done in Science LessonDokument2 SeitenCalculating Work Done in Science LessonLemuel Jr MitchaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dapa National High School Dapa, Surigao Del Norte Joan Marie C. Pelias Science 8 Grade 8 3 Quarter March 18, 2021 30 Mins I. ObjectivesDokument4 SeitenDapa National High School Dapa, Surigao Del Norte Joan Marie C. Pelias Science 8 Grade 8 3 Quarter March 18, 2021 30 Mins I. Objectivesjoan marie PeliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity and Species Presentation Science 8Dokument33 SeitenBiodiversity and Species Presentation Science 8Shemi PagariganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maranatha Christian Academy of Blue Isle Filinvest: Daily Lesson PlanDokument28 SeitenMaranatha Christian Academy of Blue Isle Filinvest: Daily Lesson PlanKristel Joy Marikit AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Q1 Week 6 7Dokument13 SeitenScience 8 Q1 Week 6 7Rachelle Mitch R. TamparongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Study NotebookDokument9 SeitenModule 2 Study NotebookEarlyn Joy Villaruel EniolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan IN Science: Grade 8Dokument37 SeitenLesson Plan IN Science: Grade 8Ericka Niña Fuentevilla MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget of Work Science 8Dokument9 SeitenBudget of Work Science 8Fernadez RodisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheets (Intensity)Dokument2 SeitenActivity Sheets (Intensity)impromtouNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Q1 WK 5 D2 (20) FlorDokument5 SeitenDLP Q1 WK 5 D2 (20) FlorVergil TagalogonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Forces LessonDokument3 SeitenGrade 8 Forces LessonDerly Cirunay DatuinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL W3Dokument7 SeitenDLL W3JingjingAloComendadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural Beginnings: The Four Biological CapacitiesDokument25 SeitenCultural Beginnings: The Four Biological CapacitiesOtencianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Junior High Science Lesson on Seismic WavesDokument6 SeitenJunior High Science Lesson on Seismic WavesNovelyn DurezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Dokument2 SeitenGRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Rosita CayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Module: Potential and Kinetic EnergyDokument2 SeitenLearning Module: Potential and Kinetic EnergyJoyR.AlotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Editing Ni Ate Ging LDM 2 Outputs BELIRDokument29 SeitenFor Editing Ni Ate Ging LDM 2 Outputs BELIREstelita Bercasio-BaluteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amt Plan Science 8Dokument14 SeitenAmt Plan Science 8arvin2life100% (1)
- Table of Contents for Science CurriculumDokument3 SeitenTable of Contents for Science CurriculumClarence VilbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Contents for Science CurriculumDokument3 SeitenTable of Contents for Science CurriculumClarence VilbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling ReactionDokument29 SeitenOrganoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling Reactionratul mahataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 41 Symplocos Racemosa - MonographDokument9 Seiten41 Symplocos Racemosa - MonographMSKCNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Electrochemical Energy-1aDokument3 Seiten1 - Electrochemical Energy-1aMae TadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO130 Sec2 - Lec1and2 - 1pptDokument38 SeitenBIO130 Sec2 - Lec1and2 - 1pptlemonpartymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routes of Drug Delivery To The LungsDokument4 SeitenRoutes of Drug Delivery To The LungsAquiles VaestoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pretreatment in Reverse Osmosis Seawater DesalinatDokument9 SeitenPretreatment in Reverse Osmosis Seawater DesalinataquaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferrx 5000 Magnetic SeparatorDokument6 SeitenFerrx 5000 Magnetic SeparatorleontoledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abrasion & Impact TestDokument10 SeitenAbrasion & Impact TestMuhammad Hafizuddin100% (1)
- Chia Seed Paper PDFDokument7 SeitenChia Seed Paper PDFFARCASANU MARIA-ANDREEANoch keine Bewertungen
- Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant CleanupDokument1 SeitePaducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant CleanupJames BruggersNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLENDEX 587msdsDokument6 SeitenBLENDEX 587msdsAnonymous eq5zSUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mat & Sat-04Dokument32 SeitenMat & Sat-04RamNagalNoch keine Bewertungen
- OTC 15275 Design Challenges of A 48-Inch Pipeline Subsea ManifoldDokument7 SeitenOTC 15275 Design Challenges of A 48-Inch Pipeline Subsea Manifoldgvsha88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Rivet - MS20470Dokument2 SeitenSolid Rivet - MS20470Manoj ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajasthan University and other academic and research institutes contact listDokument67 SeitenRajasthan University and other academic and research institutes contact listRohit SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holcim Portland Cement SpecDokument2 SeitenHolcim Portland Cement SpecAnissa PanlaquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketoprofen Suppository Dosage Forms: in Vitro Release and in Vivo Absorption Studies in RabbitsDokument6 SeitenKetoprofen Suppository Dosage Forms: in Vitro Release and in Vivo Absorption Studies in RabbitsTommyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Operated Water Valve Types WVFX and WVS: Data SheetDokument11 SeitenPressure Operated Water Valve Types WVFX and WVS: Data SheetДаниіл ЩигельськийNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production of MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) From Methanol and Butylene by Catalytic ConversionDokument11 SeitenProduction of MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) From Methanol and Butylene by Catalytic ConversionAsim RafiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set1 Mono-Methylation of H3K4 in S. Cerevisiae Is Advantageous For Survival Under Histidine Starvation Conditions in The Presence of 3-Amino-1,2,4-TriazoleDokument19 SeitenSet1 Mono-Methylation of H3K4 in S. Cerevisiae Is Advantageous For Survival Under Histidine Starvation Conditions in The Presence of 3-Amino-1,2,4-TriazoleAlex GriffithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Amino Acids in Spinach and AppleDokument1 SeiteAnalysis of Amino Acids in Spinach and AppleSilwanus ManaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wang and Helliwell (2001) Determination of Flavonols in Green and Black Tea LeavesDokument5 SeitenWang and Helliwell (2001) Determination of Flavonols in Green and Black Tea LeavesYvonne TongNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS EN 15408-2011 Solid Recovered Fuels - Determination of Sulphur (S), C...Dokument22 SeitenBS EN 15408-2011 Solid Recovered Fuels - Determination of Sulphur (S), C...fadhil muhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marble and Granite Study ReportDokument15 SeitenMarble and Granite Study Reportp156426 Ahmad KhanzadaNoch keine Bewertungen