Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
IC 4603 L01 Lab Safety
Hochgeladen von
munir.arshad248Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IC 4603 L01 Lab Safety
Hochgeladen von
munir.arshad248Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Laboratory Safety and Procedures
PRE-LAB QUESTIONS
1. Mapping Laboratory Safety: Use the following page to draw a map identifying your safety
elements and where you will complete your lab experiments. If you do not possess a
safety item, indicate the location of the closest one that you can use. Use the list below
to identify items on your map.
a. Clean, dry, uncluttered laboratory workspace
b. Window for ventilation
c. Trash can
d. Sink (eye wash station)
e. First aid kit
f. Fire extinguisher
g. Phone
h. Storage location for your eScience Lab materials when not in use
i. Computer
j. Blanket that can be used to smother a fire (fire blanket)
k. Shower that can be used to wash off spilled chemicals (safety shower)
l. Exit door (Diagram on your map the route you will use to leave the building in
case of an emergency.)
m. Smoke detector
n. Dust pan and broom
©eScience Labs, LLC 2015
Laboratory Safety and Procedures
2. What would you do if you spilled a tiny amount of hydrochloric acid on your hand?
Answer: If a tiny amount of hydrochloric acid spilled on my hand, I will wash my hand
immediately with covered hand gloves
3. Describe a possible danger that can occur if you put food, soda, coffee, pencil erasers,
etc. in your mouth while conducting your chemistry experiments.
Answer: During conducting chemistry experiments in the chemistry lab we should not eat
and drink anything because due to chemical gases there is a great risk of food poisoning
and intake is overall injurious to health during chemistry experiments in the chemistry lab.
4. What information is given on a Safety Data Sheet?
Answer: Safety Data Sheet contains information on the possible dangers regarding
health, fire, reactivity and environmental etc. and how to work safely with the chemical
products. It is also an important preparatory point for the development of a complete
health and safety program.
5. List the optimum clothing, shoes, jewelry, and hair arrangement for your chemistry labs.
Answer: We should wear thick cloths, face masks, hand gloves, aprons and caps during
chemistry experiments in the chemistry lab to ensure optimum safety.
6. What is the date that your fire extinguisher was last examined?
Answer: The date that your fire extinguisher was last examined three months ago by fire
safety team.
7. How old are the batteries in your smoke detector?
Answer: The smoke detector batteries were last replaced two years ago.
8. List the contents from your first aid kit that you will use to treat a minor cut.
Answer: During minor cut Dettol, antiseptic ointment, pain killers, bandages and cottons
can be used to treat a minor cut.
9. List the contents from your first aid kit that you will use to treat a minor burn.
Answer: Firstly, cool down the burnt part of the body then apply an antiseptic ointment and
take a pain killer. Subsequently, bandage the burnt part of the body in open air.
©eScience Labs, LLC 2015
Laboratory Safety and Procedures
EXPERIMENT 1 DATA SHEET
Data Sheet
Table 1: Initial pH Test Results
Additional
Container Chemical Contents pH Results
Observations
Litmus Color Changes
A Distilled Water 7.0 from Orange to Light
Green
B Sodium Bicarbonate 7.5 – 8.0 Green
C Acetic Acid 2.0 – 3.0 Dark Orange
Table 2: Neutralization
Amount of Acid (mL) pH Results
1 8 (Green)
2 8 (Green)
3 7 (Light Green)
4 5 (Pale Green)
5 6 (Very Light Green)
©eScience Labs, LLC 2015
Laboratory Safety and Procedures
Post-Lab Questions:
1. Most of the chemicals included in your Introductory Chemistry Lab kit can be discarded
down a drain with copious amounts of water. Describe a situation in which you would
need to neutralize a chemical (pH 7) before discarding down a drain.
Answer: The chemicals that are weak and non-corrosive can be discarded down the drain.
But some chemicals such as strong corrosive acids HCl, H2SO4 should be neutralized first
before discarding down the drain.
This is because these acids can cause corrosion of pipes which may lead to huge leakage
problems in the plumbing.
These acids also have a very negative effect on the wildlife and environment, as this acidic
water can lead to water body inhabited by aquatic wildlife.
2. Why should one add acid to water rather than add water to acid when preparing
solutions?
Answer: One must always add acid to water because:
The heat of solution of acid and water is exothermic, meaning it will release heat.
If we add a drop of water to a volume of acid, it may evaporate instantaneously due to the
heat of enthalpy, this may explode and spill acid everywhere and may even get some acid in
the user.
If we add a drop of acid to water, there is plenty of water with a high heat capacity, the acid
will be diluted very easily as well as the heat generated
3. At what point was the solution in beaker B neutralized?
Answer: The solution of beaker B was neutralized at pH 7 because this is the neutral point
and both acid and base are neutralized at this pH.
4. Address the following scenarios:
If a stronger solution of sodium bicarbonate was used in beaker B, would it require
more or less acetic acid to neutralize? Why?
If a weaker solution of sodium bicarbonate was used in beaker B, would that solution
require more or less acetic acid to neutralize it? Why?
Answer: strong solution of sodium bicarbonate would have initial pH around 8.1 and for
its neutralization large amount of vinegar would have been needed because than only
large amount of hydrogen ion could come and neutralize hydroxyl ions. But in weak
sodium bicarbonate solution the vinegar is used less due to weak concentration of
hydroxyl ion.
©eScience Labs, LLC 2015
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1315-03 Bioavailability of IronDokument8 Seiten1315-03 Bioavailability of IronBrandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- #5 Chem Lab Report - AgustinDokument6 Seiten#5 Chem Lab Report - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screening Damage Mechanism - 581 & 571Dokument28 SeitenScreening Damage Mechanism - 581 & 571Febri Ramdani NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 31.1 Experiment 9 Synthesis of Organic CompoundsDokument68 SeitenChem 31.1 Experiment 9 Synthesis of Organic Compoundshello87623100% (1)
- Analytical Method Validation for Antacid SuspensionDokument5 SeitenAnalytical Method Validation for Antacid SuspensionPatricia Joyce Malabanan Sunglao100% (1)
- Lira UPVC Pipe Fittings - CompressedDokument28 SeitenLira UPVC Pipe Fittings - Compressedsign0% (1)
- BiochemDokument31 SeitenBiochemsjs6r8wwv9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Public Health EngineeringDokument48 SeitenPublic Health EngineeringrajendrakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering Lab Report AnalysisDokument15 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering Lab Report AnalysisWhitney CartwrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engg Lab ManualDokument8 SeitenEnvironmental Engg Lab ManualAvinash DholiwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taks Obj 1Dokument180 SeitenTaks Obj 1Dan0199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eco. Exp. 7 PHDokument4 SeitenEco. Exp. 7 PHFaneeshwar PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2 PH Testing UpdatedDokument5 SeitenExp 2 PH Testing UpdatedSYIFAANoch keine Bewertungen
- General Lab SafetyDokument4 SeitenGeneral Lab SafetySarah AbdelrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ia - STDokument6 SeitenIa - STapi-423322065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water Sample Testing ProjectDokument35 SeitenWater Sample Testing ProjectVishakha PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- © 2018 Escience Labs, Llc. Adapted With PermissionDokument7 Seiten© 2018 Escience Labs, Llc. Adapted With PermissionNikki AyalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM F110-Lab Manual - 2020-21Dokument36 SeitenCHEM F110-Lab Manual - 2020-21VAIDIK SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering-L Lab Manual FilledDokument43 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering-L Lab Manual FilledAli FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering-L Lab ManualDokument41 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering-L Lab ManualAli FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Lab (Compatibility Mode)Dokument49 SeitenFirst Lab (Compatibility Mode)ahmed94062331Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical or PhysicalDokument11 SeitenChemical or PhysicalRochelle TayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering Laboratory Manual Department Ofcivil EngineeringDokument55 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering Laboratory Manual Department Ofcivil EngineeringSELVA BHARATHINoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 How Much Acid Is in Fruit Juices and Soft DrinksDokument3 Seiten10 How Much Acid Is in Fruit Juices and Soft Drinkshashememad473Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report-12: Environmental Chemistry (ENE-213) Course Instructor: Dr. Sofia BaigDokument6 SeitenLab Report-12: Environmental Chemistry (ENE-213) Course Instructor: Dr. Sofia BaigHaniya SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 12 Where Does Acid Rain Come From and What Does It DoDokument10 SeitenChemistry 12 Where Does Acid Rain Come From and What Does It DoToxicBlueNoch keine Bewertungen
- pH Meter, Acidity and Alkalinity TestsDokument39 SeitenpH Meter, Acidity and Alkalinity TestsJohn Jhong0% (1)
- Expeirment 1Dokument7 SeitenExpeirment 1Djaimee Joyce NimesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 1 Water Quality Test TTS 301115 FinishedDokument9 SeitenReport 1 Water Quality Test TTS 301115 FinishedJeana Lew SCNoch keine Bewertungen
- 225-Manual-Fall 2016 PDFDokument22 Seiten225-Manual-Fall 2016 PDFRichard OletskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDokument10 SeitenReactions in Aqueous SolutionslynxiiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Engineering LabDokument54 SeitenEnvironmental Engineering LabErhom NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lab Manual 24-07-15Dokument59 SeitenChemistry Lab Manual 24-07-15Alphonsa BipinNoch keine Bewertungen
- pH Levels of Water SamplesDokument97 SeitenpH Levels of Water SamplesNehaun ZargarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enviromental Engineering-1 Spring 2019Dokument29 SeitenEnviromental Engineering-1 Spring 2019ZohaibShoukatBalochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lab e Content Updated 2Dokument35 SeitenChemistry Lab e Content Updated 2Debarghya DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry-1 BCHT 201 Lab ManualDokument33 SeitenBiochemistry-1 BCHT 201 Lab ManualBander Al BloyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise No. 7 - Chem 120.1Dokument3 SeitenExercise No. 7 - Chem 120.1Sharmaine DoronNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Sem Solution 29.11.2021Dokument9 SeitenEnd Sem Solution 29.11.2021hp7772858Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1. FST 3112 Lab. Manual FST3112-2012-2013-2 PDFDokument83 SeitenWeek 1. FST 3112 Lab. Manual FST3112-2012-2013-2 PDFchoon lee minNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases in Everyday LifeDokument6 SeitenAcids and Bases in Everyday LifeLothar GraudinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spices and Perfumes: Green Chemistry Module Level: High School RegentsDokument24 SeitenSpices and Perfumes: Green Chemistry Module Level: High School RegentsMehdi MsmNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 332 Environmental Engineering-Lab I (Lab Manual) : Department of Civil EngineeringDokument75 SeitenCE 332 Environmental Engineering-Lab I (Lab Manual) : Department of Civil EngineeringjulesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classifying Solutions Using Red Cabbage ExtractDokument59 SeitenClassifying Solutions Using Red Cabbage Extractmatt clowe jamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Practicals First YearsDokument65 SeitenChemistry Practicals First YearsJAMES MIRICHONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Practical Manual 2021Dokument50 SeitenChemistry Practical Manual 2021Jagdish PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- pH Meter, Acidity and Alkalinity DeterminationDokument40 SeitenpH Meter, Acidity and Alkalinity DeterminationNasrulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 2 SOMNATH ADokument23 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project 2 SOMNATH ARishabh Pawani 11 BNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPBB Laboratory ManualDokument26 SeitenFPBB Laboratory ManualRock StarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitttr Environmental Engineering and Public Health Lab ManualDokument215 SeitenNitttr Environmental Engineering and Public Health Lab Manualkumsai7164% (11)
- CHE 1402 Lab Manual: Boyle's Law & Molar Mass of a VaporDokument62 SeitenCHE 1402 Lab Manual: Boyle's Law & Molar Mass of a VaporSan PophaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual For Acid/Base TitrationDokument27 SeitenLaboratory Manual For Acid/Base TitrationamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Exercise 3Dokument10 SeitenLaboratory Exercise 3Kevin EsperanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY LAB MANUALDokument65 SeitenCHEMISTRY LAB MANUALmark njeru ngigi100% (1)
- Leyte Normal University: Republic of The Philippines Tacloban CityDokument6 SeitenLeyte Normal University: Republic of The Philippines Tacloban CityAdrian VerzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normality N MolarityDokument10 SeitenNormality N Molaritynavigcp100% (9)
- Water Tests TechnicianDokument26 SeitenWater Tests TechnicianJAMES CURRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 15 Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenExperiment 15 Lab Reportapi-480265521Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Chemical Reactions LabDokument7 SeitenTypes of Chemical Reactions LabAndrew NapierNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH GuideDokument57 SeitenPH GuideKshitij MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Lab ManualDokument40 SeitenBiochemistry Lab Manualharpreet0% (1)
- Amount of HCl Commercial Antacids Can NeutralizeDokument23 SeitenAmount of HCl Commercial Antacids Can NeutralizeRishabh Pawani 11 BNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrangeHRM Code OverviewDokument76 SeitenOrangeHRM Code OverviewJaved Pathan50% (2)
- Cef - Hims V.1Dokument1 SeiteCef - Hims V.1munir.arshad248Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Advanced Security Appliances (ASA)Dokument42 SeitenCisco Advanced Security Appliances (ASA)munir.arshad248Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco ASADokument42 SeitenCisco ASAmunir.arshad248Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Advanced Security Appliances (ASA)Dokument42 SeitenCisco Advanced Security Appliances (ASA)munir.arshad248Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPSC Chalan A4 Drilling EngineerDokument1 SeiteFPSC Chalan A4 Drilling EngineerHussain AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahmed Alqaydi AI-Robots PaperDokument5 SeitenAhmed Alqaydi AI-Robots Papermunir.arshad248Noch keine Bewertungen
- Joomla Guide Final PDFDokument41 SeitenJoomla Guide Final PDFa.rharrabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy (Eng) - SSC IDokument4 SeitenPhy (Eng) - SSC IKhalid MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akiya2002 - Roles of Water For Chemical Reactions in High-Temperature WaterDokument26 SeitenAkiya2002 - Roles of Water For Chemical Reactions in High-Temperature Waterfarida_crNoch keine Bewertungen
- Api-602 en 2016Dokument84 SeitenApi-602 en 2016PaulcardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsDokument5 SeitenKate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsKateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 SyllabusDokument12 SeitenClass 10 SyllabusHyper Tech GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ai2TS Class XI-XII Chemistry, Physics, Maths SyllabusDokument2 SeitenAi2TS Class XI-XII Chemistry, Physics, Maths SyllabusVANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6 - QUANTIFICATION OF TOTAL LIPID CONTENT - Vũ Trọng Thức PDFDokument17 SeitenLab 6 - QUANTIFICATION OF TOTAL LIPID CONTENT - Vũ Trọng Thức PDFTu HaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical and Chemical PrinciplesDokument7 SeitenPhysical and Chemical PrinciplesJr DocorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Dokument14 Seiten7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Ain MiorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions For Ch04Dokument16 SeitenSolutions For Ch04wesleyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Folin-Ciocalteu S Phenol Reagent: Product DescriptionDokument2 SeitenFolin-Ciocalteu S Phenol Reagent: Product DescriptionJordan ulloa belloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cabbage ChemistryDokument3 SeitenCabbage ChemistryNeilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Water PDFDokument19 Seiten2.2 Water PDFKalpana ParikhNoch keine Bewertungen
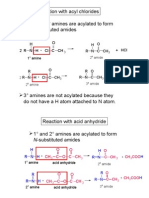
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 2Dokument13 SeitenMatriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 2ridwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH EvaluationsDokument11 SeitenPH Evaluationsapi-333439131Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oas, DSS, Mis, Ai, Nutri NTWRK, GNTC AlgrtmDokument21 SeitenOas, DSS, Mis, Ai, Nutri NTWRK, GNTC AlgrtmsiljaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry. Grade 9. 9.1A. Degree of Dissociation. Strong and Wek Electrolyte. LESSON PLANDokument4 SeitenChemistry. Grade 9. 9.1A. Degree of Dissociation. Strong and Wek Electrolyte. LESSON PLANAikerim DosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- POC-1, University Question PaperDokument8 SeitenPOC-1, University Question Papersatheeshpharma6Noch keine Bewertungen
- High Pressure Flex Tubes: Technical DataDokument4 SeitenHigh Pressure Flex Tubes: Technical DataRidwan AdiwangsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Laboratory Report PH Scale andDokument8 SeitenChemistry Laboratory Report PH Scale andM.NASIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 ExtraDokument8 SeitenRedox, Group 2 and Group 7 ExtraShabnam ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of SCMs and Curing Time On Resistance of Mortars Subjected To Organic AcidsDokument10 SeitenThe Effect of SCMs and Curing Time On Resistance of Mortars Subjected To Organic AcidsLaeli ApriliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fischer Esterification Synthesis of Isoamyl AcetateDokument4 SeitenFischer Esterification Synthesis of Isoamyl AcetateJenny MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDokument35 SeitenLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manualbombyciddispelidok100% (22)
- Nomenclature Homework 1Dokument5 SeitenNomenclature Homework 1James PerriamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate Acid-Base Titration Curves and Determine Equivalence PointsDokument4 SeitenCalculate Acid-Base Titration Curves and Determine Equivalence PointsAlif Alfarisyi SyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Homework - Chemistry11Dokument10 SeitenUnit 7 Homework - Chemistry11NameNoch keine Bewertungen