Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
IB-PYP Sample Programme of Inquiry PDF
Hochgeladen von
Grace CornerOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IB-PYP Sample Programme of Inquiry PDF
Hochgeladen von
Grace CornerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
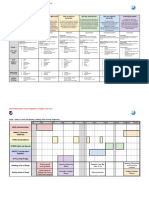
Sample programme of inquiry
Age An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into:
Who we are Where we are in place and time How we express ourselves How the world works How we organize ourselves Sharing the planet
An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs An inquiry into orientation in place and time; An inquiry into the ways in which we An inquiry into the natural world and its An inquiry into the interconnectedness of An inquiry into rights and responsibilities in
and values; personal, physical, mental, personal histories; homes and journeys; the discover and express ideas, feelings, laws; the interaction between the natural human-made systems and communities; the struggle to share finite resources with
social and spiritual health; human discoveries, explorations and migrations of nature, culture, beliefs and values; the world (physical and biological) and human the structure and function of organizations; other people and with other living things;
relationships including families, friends, humankind; the relationships between and ways in which we reflect on, extend and societies; how humans use their societal decision-making; economic communities and the relationships within
communities and cultures; rights and the interconnectedness of individuals and enjoy our creativity; our appreciation of the understanding of scientific principles; the activities and their impact on humankind and between them; access to equal
responsibilities; what it means to be civilizations, from local and global aesthetic. impact of scientific and technological and the environment. opportunities; peace and conflict
human. perspectives. advances on society and on the resolution.
environment.
3–4 Central idea Central idea Central idea* Central idea Central idea Central idea
Increasing awareness of our personal Documenting personal histories allows us to We use play to express our feelings and Our activity is usually connected to the Communities function more effectively Living things have certain requirements in
characteristics and abilities, and those of reflect on and celebrate who we are and ideas and in order to come to new Earth’s natural cycles. when rules and routines are shared with all order to grow and stay healthy.
others, allows our self-identity to develop. where we’ve come from. understandings. members.
Key concepts: change, connection Key concepts: function, responsibility
Key concepts: form, perspective, Key concepts: causation, change Key concepts: function, connection, Key concepts: causation, responsibility,
Related concepts: cycles, interaction Related concepts: classification, living
reflection perspective reflection
Related concepts: development (growth), and non-living
Lines of inquiry
Related concepts: identity, relationships family Related concepts: beliefs, representation Related concepts: community, system
• Night and day cycles (dark and light) Lines of inquiry
Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry • Seasonal changes Lines of inquiry • Characteristics of living things
• Physical, social and emotional • Ways of documenting personal history • Communicating through play • Health and safety as related to climate • Various communities we belong to • Our needs and the needs of other
characteristics • Personal change from birth to present: • Imaginative use of everyday materials and seasonal changes • Purpose of rules and routines living things
• My role within my family self and family • Games and toys • Reaching agreement • Our responsibility for the well-being of
• Recognizing similarities and • Reflecting on past experience other living things
differences between myself and others
4–5 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea
Friendships enrich our lives and require Journeys create change and can lead to new Stories inform and provoke us, and give us Understanding the way materials behave People use a variety of skills and strategies Plants are a life-sustaining resource for us
nurturing in order to develop. opportunities. pleasure. and interact determines how people use that contribute to their role in a community and for other living things.
them. of learners.
Key concepts: causation, responsibility Key concepts: causation, change Key concepts: connection, perspective, Key concepts: form, change, connection
reflection Key concepts: function, change Key concepts: function, responsibility
Related concepts: conflict or cooperation, Related concept: choice Related concepts: interdependence,
interdependence Related concept: communication Related concepts: behaviour, prediction Related concepts: citizenship, systems
Lines of inquiry
independence
Lines of inquiry • Types of journeys people make Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
• How friends are made and kept • Choices and decisions involved in • What a story is • Behaviour and uses of materials Lines of inquiry • What plants provide for us and for
• Why friends are needed making a journey • What stories convey • Changing properties of materials • Being part of a community of learners other living things
• Characteristics that develop healthy • Changes experienced because of a • How stories are created and shared • Manipulation of materials for specific • Skills, strategies and attitudes • The structure of a plant
friendships journey • Feelings and emotions that stories purposes • Making contributions to a community • Caring for plant life
evoke
5–6 Central idea* Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea
Making balanced choices about daily Communities are enriched by their members People recognize important events through All living things go through a process of Transportation systems are directly related People interact with, use and value the
routines enables us to have a healthy and the different perspectives they bring. celebrations and traditions. change. to the needs of a community. natural environment in different ways.
lifestyle.
Key concepts: change, perspective Key concepts: form, perspective Key concepts: change, connection Key concepts: function, connection Key concepts: causation, responsibility,
Key concepts: function, causation, reflection
Related concepts: continuity, diversity Related concepts: beliefs, culture, values Related concepts: cycles, transformation Related concepts: systems
reflection
Related concepts: conservation,
Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
Related concepts: balance, well-being interdependence, order
• What a community is • What traditions are • Life cycles • Specific purposes of different
Lines of inquiry • People within a community • How and why people celebrate • How living things change over their life transportation systems Lines of inquiry
• Daily habits and routines (hygiene, • The personal stories of community • Similarities and differences between time • Factors that affect the kinds of • Local natural environment
sleep, play, eating) members various celebrations • Developmental stages of various living systems that can be developed • Human use of the local environment
• Balanced choices things • Relationship between transportation • Actions that benefit or harm the local
• Consequences of choices systems and the environment environment
Developing a transdisciplinary programme of inquiry Sample programme of inquiry
Age An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into:
Who we are Where we are in place and time How we express ourselves How the world works How we organize ourselves Sharing the planet
6–7 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea* Central idea
Homes reflect personal identity and local Public areas strengthen communities and Imagination is a powerful tool for extending Understanding the properties of air allows Systems need to be in place to maintain People can establish practices in order to
culture. provide people with opportunities to connect. our ability to think, create and express people to make practical applications. organization in communities. sustain and maintain the Earth’s resources.
ourselves.
Key concepts: form, connection, Key concepts: function, connection Key concepts: function, causation Key concepts: connection, responsibility Key concepts: change, responsibility,
perspective Key concepts: causation, perspective, reflection
Related concepts: cooperation, ownership Related concepts: force, energy Related concepts: interdependence,
reflection
Related concepts: creativity, diversity organization, systems Related concepts: lifestyle, resources
Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
Related concepts: empathy, invention,
Lines of inquiry • Different public areas and their functions • The evidence of the existence of air Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
transformation
• The concept of home • How public areas develop • What air can do and how we use it • The concept of organization • Limited nature of the Earth’s resources
• Different types of homes • How these places differ from our homes Lines of inquiry • The relationship between air, light and • Different systems of organization that • Personal choices that can help sustain
• Circumstances that determine where • How we demonstrate and enjoy our sound we use personally the environment
people live imagination • Different systems of organization in • Reusing and recycling different
• How our imagination helps us to our community materials
consider other perspectives • Collection, storage and use of • Reducing waste
• How imagination helps us to solve information for organization
problems
• The value of imagination
7–8 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea
Relationships are enhanced by learning The development of global perspectives is Through the arts people use different The design of buildings and structures is In a workplace people share responsibility Over time, living things need to adapt in
about other people’s perspectives and supported through understanding our place in forms of expression to convey their dependent upon the environment and towards a common purpose. order to survive.
communicating our own. the world in relation to others. uniqueness as human beings. available materials.
Key concepts: function, causation Key concepts: change, connection
Key concepts: perspective, reflection Key concepts: connection, perspective Key concepts: function, perspective, Key concepts: connection, responsibility connection
Related concepts: adaptation, evolution
reflection
Related concepts: communication, Related concepts: context, location, Related concepts: structure, Related concepts: cooperation,
Lines of inquiry
empathy, open-mindedness orientation Related concepts: perception, self- sustainability, transformation employment
• Concept of adaptation
expression
Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry: Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry • Circumstances that lead to adaptation
• Social interactions • How we represent place Lines of inquiry • Considerations to take into account • Purpose of a workplace • How plants and animals adapt or
• Acknowledging others’ perspectives • Representations of place through time • The diverse ways in which people when building a structure • Interconnectedness of people in a respond to environmental conditions
• Managing and resolving conflict • The relationship of our location to other express themselves • How building impacts on the workplace
parts of the world • How everyone can express their environment • Importance of a shared vision or
uniqueness through the arts • Indigenous architecture common purpose
• The role of art in culture and society
8–9 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea* Central idea Central idea
Understanding different ways of learning Family histories provide an insight into A variety of signs and symbols facilitates Human survival is connected to Communities provide interconnected Water is essential to life, and is a limited
enables people to respond to their own cultural and personal identity. local and global communication. understanding the continual changing services designed to meet people’s needs. resource for many people.
learning needs as well as those of others. nature of the Earth.
Key concepts: change, reflection Key concepts: form, connection Key concepts: function, causation, Key concepts: function, responsibility
Key concepts: function, perspective, Key concepts: causation, change, connection
Related concepts: chronology, history, Related concepts: culture, media, pattern Related concepts: conservation, equity,
responsibility connection
tradition Related concept: networks processes
Lines of inquiry
Related concepts: diversity, motivation Related concepts: erosion, geology,
Lines of inquiry • Signs and symbols Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
tectonic plates, movement
Lines of inquiry • Family ancestry • Reasons for the development of • Reasons people live in the local • Sources of water and how water is
• Learning communities • Artifacts, heirlooms or rituals that have communication systems Lines of inquiry community used
• How people construct knowledge meaning in a family • Specialized systems of communication • How the different components of the • Services needed to support a • What happens to water after we have
• Different learning styles • Similarities and differences between Earth are interrelated community used it
• How learning styles impact the way generations within a family • How the Earth has changed and is • Planning services for a community • Distribution and availability of usable
people engage in a learning continuing to change water
community • Why the Earth changes • Responsibilities regarding water
• Human response to the Earth’s
changes
Developing a transdisciplinary programme of inquiry Sample programme of inquiry
Age An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into:
Who we are Where we are in place and time How we express ourselves How the world works How we organize ourselves Sharing the planet
An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs An inquiry into orientation in place and time; An inquiry into the ways in which we An inquiry into the natural world and its An inquiry into the interconnectedness of An inquiry into rights and responsibilities in
and values; personal, physical, mental, personal histories; homes and journeys; the discover and express ideas, feelings, laws; the interaction between the natural human-made systems and communities; the struggle to share finite resources with
social and spiritual health; human discoveries, explorations and migrations of nature, culture, beliefs and values; the world (physical and biological) and human the structure and function of organizations; other people and with other living things;
relationships including families, friends, humankind; the relationships between and ways in which we reflect on, extend and societies; how humans use their societal decision-making; economic communities and the relationships within
communities and cultures; rights and the interconnectedness of individuals and enjoy our creativity; our appreciation of the understanding of scientific principles; the activities and their impact on humankind and between them; access to equal
responsibilities; what it means to be civilizations, from local and global aesthetic. impact of scientific and technological and the environment. opportunities; peace and conflict
human. perspectives. advances on society and on the resolution.
environment.
9–10 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea
What we believe is a part of who we are. Human migration is a response to challenges, Choices of role models reflect the Energy may be converted from one form to Marketplaces depend on the ability to Children worldwide face a variety of
risks and opportunities. characteristics that societies and another and stored in various ways. produce goods and supply services that challenges and risks.
Key concepts: perspective, reflection
individuals value. can be exchanged.
Key concepts: causation, change, Key concepts: form, function, connection Key concepts: function, reflection
Related concepts: diversity, perception
perspective Key concepts: causation, perspective, Key concepts: function, connection
Related concepts: conservation, Related concepts: equality, rights
Lines of inquiry reflection
Related concepts: population, settlement transformation Related concepts: interdependence,
• What we believe Lines of inquiry
Related concepts: self-fulfillment, supply and demand
• How beliefs influence the way we Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry • Challenges and risks that children face
influence
behave • The reasons why people migrate • Forms of energy Lines of inquiry • How children respond to challenges
• The impact of religion and spiritual • Migration throughout history Lines of inquiry • The storage and transformation of • Medium of exchange in various and risks
traditions on society • Effects of migration on communities, • Role models and why we value them energy marketplaces • Ways in which individuals,
cultures and individuals • Why we should develop our own gifts, • Conservation of energy • Ethics of the marketplace organizations and nations work to
talents and interests • Renewable and sustainable energy • How and in what ways we depend on protect children from risk
• How personal strengths can be applied people in other places
to help others • How global movement and
communication affect the availability of
goods and services
10–11 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea
Complex factors contribute to the process Past civilizations shape present day systems Rituals, traditions and artifacts provide a The fact that materials can undergo Governmental systems and decisions can Biodiversity relies on maintaining the
of making decisions that have implications and technologies. window into the beliefs and values of permanent or temporary changes poses promote or deny equal opportunities and interdependent balance of organisms
for ourselves and others. cultures. challenges and provides benefits for social justice. within systems.
Key concepts: causation, change,
society and the environment.
Key concepts: causation, change, perspective Key concepts: function, perspective, Key concepts: function, responsibility Key concepts: connection, responsibility
connection reflection Key concepts: form, function,
Related concepts: continuity, progress, Related concepts: equality, government Related concepts: balance, biodiversity,
responsibility
Related concepts: choice, systems technology Related concepts: beliefs, diversity or governance interdependence
Related concepts: measurement,
Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
transformation
• Factors that influence our decisions • Aspects of past civilizations that have • What constitutes a culture • Types of governance • Interdependence within ecosystems,
• Decision-making processes for groups survived • Significance of rituals and traditions Lines of inquiry • Principles of human rights and social biomes and environments
and individuals • Reasons these systems and technologies • How artifacts symbolize beliefs and • Nature of chemical and physical justice • Ways in which organisms are
• Impact or consequences that decisions developed values changes • The effect of institutional behaviours interconnected in nature
can have • Why modern societies continue to use • Practical applications and implications and attitudes on social justice • How human interaction with the
adaptations of these systems and of change in materials environment can affect the balance of
technologies • Ethical dilemmas associated with systems
• Implications for the future manufacturing processes and by-
products
Developing a transdisciplinary programme of inquiry Sample programme of inquiry
Age An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into: An inquiry into:
Who we are Where we are in place and time How we express ourselves How the world works How we organize ourselves Sharing the planet
11–12 Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea Central idea*
Personal well-being is dependent on a Exploration leads to discovery and develops People’s outward appearance can lead to Reproduction of living things contributes to Technology impacts on the world of work Finding peaceful solutions to conflict leads
complex balance of interconnected factors. new understandings. perceptions and misconceptions. the continuation of the species. and leisure. to a better quality of human life.
Key concepts: change, responsibility Key concepts: form, perspective, reflection Key concepts: function, perspective, Key concepts: change, connection Key concepts: change, connection, Key concepts: causation, perspective,
reflection responsibility responsibility
Related concepts: growth, relationships Related concepts: consequences, Related concepts: cycles, growth
discovery, geography Related concepts: creativity, diversity, Related concepts: communication, Related concepts: conflict, diversity,
Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
stereotypes systems, ethics justice
• The concept of “well-being” Lines of inquiry • Reproduction as part of a life cycle
• Factors that contribute to well-being • Reasons for exploration (historical and Lines of inquiry • Reproductive processes Lines of inquiry Lines of inquiry
(physical, mental, social and spiritual) personal) • Personal adornments, clothing and • Genetics and hereditary factors • Technology and inventions of the • Causes of conflict
• Personal issues affecting our well- • Feelings and attitudes associated with identity home, workplace and leisure activities • Conflict resolution and management
being exploration • Reasons for what people wear • Circumstances that lead to the • Living and working together peacefully
• What we learn through exploration • Impact of first impressions development of important inventions
• Methods of navigation • Countering misconceptions and their impact
• How technology supports/impacts
sustainability
In the students’ final year of the PYP, there are five units of inquiry and the exhibition. The exhibition may be related to any transdisciplinary theme at the discretion of the school. This sample programme of inquiry has included six units of inquiry in the final year, any one of which could
be replaced by the exhibition. Only IB World Schools are required to participate in the exhibition although candidate schools may choose to do so.
* Sample planners have been developed for those units marked with an asterisk.
Developing a transdisciplinary programme of inquiry Sample programme of inquiry
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Programme of InquiryDokument2 SeitenProgramme of InquiryAparna NagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SeisenProgrammeofInquiry2018 19Dokument20 SeitenSeisenProgrammeofInquiry2018 19Andohar PurbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Uoi Ib Pyp FileDokument12 SeitenFinal Uoi Ib Pyp Fileapi-597568531Noch keine Bewertungen
- IB Unit Planner Who We Are With Assessment PDFDokument6 SeitenIB Unit Planner Who We Are With Assessment PDFsugunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Planner GuideDokument4 SeitenUnit Planner Guideapi-502626876Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Pyp Planner RubricDokument4 SeitenEvaluation of Pyp Planner Rubricapi-16307116100% (1)
- How We Express Ourselves 1 17 13Dokument4 SeitenHow We Express Ourselves 1 17 13api-147600993100% (1)
- Sample BIS Enhanced PYP Unit PlannerDokument12 SeitenSample BIS Enhanced PYP Unit PlannerShaily Modh100% (2)
- Adventures in Authentic Learning: 21 Step-by-Step Projects From an Edtech CoachVon EverandAdventures in Authentic Learning: 21 Step-by-Step Projects From an Edtech CoachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart: Update of Action Plan: A: PhilosophyDokument11 SeitenChart: Update of Action Plan: A: Philosophyapi-353859154100% (3)
- Unit of Inquiry For Preschool: Let's Be CreativeDokument11 SeitenUnit of Inquiry For Preschool: Let's Be Creativeami1967100% (1)
- 2020-21 Kramer Pre-K Who We AreDokument12 Seiten2020-21 Kramer Pre-K Who We AreDavyMa100% (2)
- Sharing The Planet PYP Planner ScienceDokument4 SeitenSharing The Planet PYP Planner ScienceDanielRobertson0% (1)
- Dive into Inquiry: Amplify Learning and Empower Student VoiceVon EverandDive into Inquiry: Amplify Learning and Empower Student VoiceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A Model Unit For Grade 1: Who Am I?: I Belong, The Senses, Characteristics of Objects and MaterialsVon EverandA Model Unit For Grade 1: Who Am I?: I Belong, The Senses, Characteristics of Objects and MaterialsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Bubble Planner Where We Are in Palce and TimeDokument6 SeitenYear 1 Bubble Planner Where We Are in Palce and Timeayesha amanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptations Planner PDFDokument4 SeitenAdaptations Planner PDFGrade2 CanaryschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who We Are?: - Transdisciplinary ThemeDokument7 SeitenWho We Are?: - Transdisciplinary ThemeAlka SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Where We Are in Place and TimeDokument1 SeiteWhere We Are in Place and TimeMariana Suarez100% (1)
- Inquiry Mindset: Nurturing the Dreams, Wonders, & Curiosities of Our Youngest LearnersVon EverandInquiry Mindset: Nurturing the Dreams, Wonders, & Curiosities of Our Youngest LearnersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- PYP ClassroomDokument1 SeitePYP ClassroomCristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using ICT in the Early Years: Parents and Practitioners in PartnershipVon EverandUsing ICT in the Early Years: Parents and Practitioners in PartnershipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyp Collaborative Planning Workshop Workbook Cistokyo Oct2013Dokument85 SeitenPyp Collaborative Planning Workshop Workbook Cistokyo Oct2013api-238392079100% (1)
- Where We Are in Place and Time: Unit LetterDokument2 SeitenWhere We Are in Place and Time: Unit LetterJenny Fenton100% (2)
- How We Express OurselvesDokument2 SeitenHow We Express Ourselvessuguna100% (1)
- PYP Newsletter February 2015 PDFDokument6 SeitenPYP Newsletter February 2015 PDFcrdaymentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan - How We Express OurselvesDokument16 SeitenLesson Plan - How We Express OurselvesnehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How We Express Ourselves 1 17 2013Dokument4 SeitenHow We Express Ourselves 1 17 2013api-147600993100% (1)
- Unit 4 Where We Are in Place and Time Grades 3 4 Sy 2013-2014Dokument8 SeitenUnit 4 Where We Are in Place and Time Grades 3 4 Sy 2013-2014api-26437308333% (3)
- Differentiated Assessment in The PYPDokument2 SeitenDifferentiated Assessment in The PYPCristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- gr1 Planner-How The World Works-2013 14Dokument5 Seitengr1 Planner-How The World Works-2013 14api-260939375Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inquiry in The PypDokument49 SeitenInquiry in The PypPima Ajah100% (1)
- 4th Grade Reflection For Sharing The PlanetDokument3 Seiten4th Grade Reflection For Sharing The PlanetKristin CramerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICT Unit Planner - Year 3 Sharing The PlanetDokument1 SeiteICT Unit Planner - Year 3 Sharing The Planetdanny67% (3)
- Bubble Planner Old Where We Are in Place and TimeDokument4 SeitenBubble Planner Old Where We Are in Place and Timeayesha amanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How We Express OurselvesDokument1 SeiteHow We Express OurselvesMariana SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhanced PypDokument5 SeitenEnhanced PypDonche RisteskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PYP-POI - Prep-1 - Grade5Dokument6 SeitenPYP-POI - Prep-1 - Grade5kangan jain100% (1)
- How We Organize Ourselves-CompletedupDokument5 SeitenHow We Organize Ourselves-Completedupapi-147600993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Planning Sharing The Planet Grade 3 4Dokument4 SeitenPlanning Sharing The Planet Grade 3 4api-325889732100% (2)
- Sharing The Planet 1 17 13Dokument4 SeitenSharing The Planet 1 17 13api-147600993100% (1)
- Modern Curriculum for Gifted and Advanced Academic StudentsVon EverandModern Curriculum for Gifted and Advanced Academic StudentsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Sample Unit Planner For The ArtsDokument4 SeitenSample Unit Planner For The Artsapi-261132454100% (1)
- How The World Works Jan 8 2013Dokument4 SeitenHow The World Works Jan 8 2013api-147600993100% (2)
- Hands-On Social Studies for Ontario, Grade 6: An Inquiry ApproachVon EverandHands-On Social Studies for Ontario, Grade 6: An Inquiry ApproachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Assessment 2015-16 Ad RubricDokument2 SeitenSummative Assessment 2015-16 Ad Rubricapi-353859154100% (1)
- How We Express Ourselves RevisedDokument1 SeiteHow We Express Ourselves RevisedMariana SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Unit Express YourselfDokument7 SeitenIB Unit Express YourselfKathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Unit Planner: Who We Are With AssessmentDokument6 SeitenIB Unit Planner: Who We Are With AssessmentMaryanne Oxenrider Lipovsky94% (16)
- PYP Scope and SequenceDokument23 SeitenPYP Scope and SequenceDuré Mustafa100% (1)
- D3 Who We Are Planner PDFDokument4 SeitenD3 Who We Are Planner PDFJenny100% (4)
- Hands-On Science and Technology for Ontario, Grade 6: An Inquiry ApproachVon EverandHands-On Science and Technology for Ontario, Grade 6: An Inquiry ApproachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uoi 3 Parent LetterDokument7 SeitenUoi 3 Parent Letterapi-265511182Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bubble Planner Sharing The PlanetDokument7 SeitenBubble Planner Sharing The Planetasima100% (1)
- Teacher's Final Reflection - IB DocumentDokument1 SeiteTeacher's Final Reflection - IB DocumentCristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2-How The World WorksDokument5 SeitenUnit 2-How The World WorksPushpita NandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing The Learner ProfileDokument5 SeitenDeveloping The Learner ProfileIanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Stage Planner - Where We Are in Place and Time - Grade 5Dokument4 Seiten9 Stage Planner - Where We Are in Place and Time - Grade 5Remi RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- VisualizationDokument21 SeitenVisualizationYolanda NicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excerpt From "Neurobiology and The Development of Human Morality" by Darcia NarvaezDokument19 SeitenExcerpt From "Neurobiology and The Development of Human Morality" by Darcia NarvaezNortonMentalHealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gothic Versus Romantic - A Revaluation of The Gothic NovelDokument10 SeitenGothic Versus Romantic - A Revaluation of The Gothic NovelReinhardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1.2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1.2Ma Cristine LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Advantages of Using Drama As A Method of Education in Elementary SchoolsDokument5 SeitenThe Advantages of Using Drama As A Method of Education in Elementary SchoolsemilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. PesirlaDokument9 SeitenDr. PesirlaAlnudial PaspasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoppelgängerDokument11 SeitenDoppelgängerMaria PucherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 Imagination Play Movement Rhythm ImprovisationDokument7 SeitenLesson 3 Imagination Play Movement Rhythm Improvisationdanaya fabregasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whats The Use of Stories That Arent EveDokument19 SeitenWhats The Use of Stories That Arent EveJhezarie Amsiwen0% (1)
- The Law of Attraction Positive Thinking and Level of Gratitude Towards HappinessDokument9 SeitenThe Law of Attraction Positive Thinking and Level of Gratitude Towards HappinessRifki HardiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece Curriculum and Ece Arts Exam 2nd SemDokument35 SeitenEce Curriculum and Ece Arts Exam 2nd SemIrene MandrizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I. Introduction To Art AppreciationDokument50 SeitenUnit I. Introduction To Art AppreciationArman CatacutanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Aladdins Lamp by Ernest Holmes PDokument5 SeitenYour Aladdins Lamp by Ernest Holmes P11111100% (1)
- Get On Stage H Puchta PDFDokument219 SeitenGet On Stage H Puchta PDFOlgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Paul Lederach The Moral Imagination-Chapter 8Dokument217 SeitenJohn Paul Lederach The Moral Imagination-Chapter 8Alexis Colmenares100% (2)
- Theater: Supply The Empty Circles With Words That Characterize/describe The Word: TheaterDokument10 SeitenTheater: Supply The Empty Circles With Words That Characterize/describe The Word: TheaterJun Greg MaboloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Magic Spells PDF PDFDokument14 SeitenReal Magic Spells PDF PDFAngadveer Singh0% (1)
- Bruce Robertson - Techniques of Fantasy ArtDokument145 SeitenBruce Robertson - Techniques of Fantasy ArtJose Pocoví100% (1)
- Exp No 5Dokument21 SeitenExp No 5Yean MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reconsidering Architecture and UtopiaDokument24 SeitenReconsidering Architecture and UtopiaAnkur ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debate THBT Technology Decreases Creativity Online 2020Dokument5 SeitenDebate THBT Technology Decreases Creativity Online 2020kbr8246Noch keine Bewertungen
- HMEF5023 - V2 - Educational Leadership (930119065022)Dokument14 SeitenHMEF5023 - V2 - Educational Leadership (930119065022)Muniraa MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 eLMS Activity 1greatbooksDokument2 Seiten04 eLMS Activity 1greatbooksangelkaren garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riemann Ideen Zu EinerDokument12 SeitenRiemann Ideen Zu EinerJoon ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discovering The Imaginative Capability oDokument11 SeitenDiscovering The Imaginative Capability oMohammad Adnan RummanNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Inventory of NarratorsDokument1 SeiteAn Inventory of NarratorsLili BalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive Drill TherapyDokument123 SeitenCognitive Drill TherapyAdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implication of Modernism in W.B.Yeats' The Second ComingDokument72 SeitenImplication of Modernism in W.B.Yeats' The Second ComingPratyusha KuilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAQ On NLPDokument2 SeitenFAQ On NLPV Ranga NathanNoch keine Bewertungen