Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Effective Online Discussion Data For Teachers Reflective Thinking Using Feature Base Model
Hochgeladen von
BONFRINGOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Effective Online Discussion Data For Teachers Reflective Thinking Using Feature Base Model
Hochgeladen von
BONFRINGCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bonfring International Journal of Software Engineering and Soft Computing, Vol. 9, No.
2, April 2019 47
Effective Online Discussion Data for Teacher’s
Reflective Thinking Using Feature base Model
V. Yasvanth Kumaar and Dr.G. Singaravel
Abstract--- In this paper analysis automatic coding method however, that coverage isn't perpetually thought-about to be
by integrating the inductive content analysis and text data processing.)
classification techniques. In existing model acquire the
In this study, we encoded and visualized the large-scale
reflective thinking categories by conducting an inductive unstructured text data in teachers’ online collaborative
content analysis and base our text classification algorithm on learning activities in order to understanding teachers’
the categories, so we augment the manual method of coding.
reflection levels and evolution, integrating both the qualitative
We apply the trained classification model to a large-scale and content analysis method and educational data mining
unexplored online discussion data set, so we can have a techniques. The qualitative content analysis method revealed
comprehensive understanding of teachers’ reflection. This
that teachers’ reflective thinking included Technical-
paper also provides six types of visualizations of the text Description, Technical-Analysis, Technical-Critique,
classification results: the visualization of teachers’ reflection Personalistic-Description, Personalistic-Analysis, and
level and the visualization of teachers’ reflection evolution. By
Personalistic-Critique. Based on the results of inductive
using the categories gained from inductive content analysis to content analysis, we implemented a single-label text
create a radar map, we visually represent teachers’ reflection classification algorithm to classify the sample data. Then we
level after obtain the results of text classification future
applied the trained classification model on a large-scale and
classification model. unexplored online discussion text data set. After the online
Keywords--- Data Mining, Teacher Reflection Model, TF- discussion text data being classified, two types of
IDF Classification, Visualization Learning. visualizations of the results were provided. By using the
categories gained from inductive content analysis to create a
radar map, teachers’ reflection level had been represented. In
I. INTRODUCTION addition, by defining the variables of the coding scheme as the
nodes and the co-occurrences of nodes within a discussion
D ATA mining is that the method of extracting patterns
from knowledge. Data mining is seen as a progressively
vital tool by fashionable business to transform knowledge into
post as the connections, a cumulative adjacency matrix was
created to characterize the evolution of teachers’ reflective
an informational advantage. It’s presently utilized in a wide thinking.
range of identification practices, like selling, surveillance,
fraud detection, and scientific discovery. II. RELATED WORKS
The connected terms knowledge dredging, knowledge Weize Kong and James Allan [1] evaluated Faceted Web
fishing and knowledge snooping confer with the utilization of Search systems by their utility in assisting users to clarify
knowledge mining techniques to sample parts of the larger search intent and subtopic information. The authors described
population data set that are (or might be) too tiny for reliable how to build reusable test collections for such tasks, and
statistical inferences to be created regarding the validity of any propose an evaluation method that considers both gain and
patterns discovered (see additionally data-snooping bias). cost for users. Faceted search enables users to navigate a
These techniques will but, be utilized in the creation of latest multi-faceted information space by combining text search with
hypothesizes to check against the larger knowledge drill-down options in each facet. For example, when searching
populations. \computer monitor" in an e-commerce site, users can select
Data mining is that the method of applying these strategies brands and monitor types from the the provided facets:
to knowledge with the intention of uncovering hidden patterns. fSamsung, Dell, Acer,... g and f LET-Lit, LCD, OLEDg. This
It’s been used for several years by businesses, scientists and technique has been used successfully for many vertical
governments to sift through volumes of information like applications, including e-commerce and digital libraries.
airline passenger trip records, census knowledge and food Krisztian Balog et al., [2] consider the task of entity
market scanner knowledge to supply research reports. (Note, search and examine to which extent state-of-art information
retrieval (IR) and semantic web (SW) technologies are capable
of answering information needs that focus on entities. We also
V. Yasvanth Kumaar, PG Scholar, Department of Information
Technology, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, India. explore the potential of combining IR with SW technologies to
E-mail: yasvanth123456@gmail.com improve the end-to-end performance on a specific entity
Dr.G. Singaravel, Professor & Head, Department of Information search task. We arrive at and motivate a proposal to combine
Technology, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, India.
E-mail: singaravelg@gmail.com
text-based entity models with semantic information from the
DOI:10.9756/BIJSESC.9022 Linked Open Data cloud. The problem of entity search has
ISSN 2277-5099 | © 2019 Bonfring
Bonfring International Journal of Software Engineering and Soft Computing, Vol. 9, No. 2, April 2019 48
been and is being looked at by both the Information Retrieval reformulated query that involves a particular choice of words
(IR) and Semantic Web (SW) communities and is, in fact, and phrases is explicitly modeled, this framework captures
ranked high on the research agendas of the two communities. dependencies between those query components. On the other
The entity search task comes in several flavors. One is known hand, this framework naturally combines query segmentation,
as entity ranking (given a query and target category, return a query substitution and other possible reformulation operations,
ranked list of relevant entities), another is list completion where all these operations are considered as methods for
(given a query and example entities, return similar entities), generating reformulated queries. In other words, a
and a third is related entity finding (given a source entity, a reformulated query is the output of applying single or multiple
relation and a target type, identify target entities that enjoy the reformulation operations.
specified relation with the source entity and that satisfy the
Mariana Damova, Ivan Koychev [8] presents a survey of
target type constraint.
recent extractive query-based summarization techniques. We
Chengkai Li, Ning Yan et al [3] focused on automatic explore approaches for single document and multi-document
and dynamic faceted interfaces. The facets could not be pre- summarization. Knowledge-based and machine learning
computed due to the query-dependent nature of the system. In methods for choosing the most relevant sentences from
applications where faceted interfaces are deployed for documents with respect to a given query are considered.
relational tuples or schema-available objects, the Further, expose tailored summarization techniques for
tuples/objects are captured by prescribed schemata with particular domains like medical texts. The most recent
clearly defined dimensions (attributes), therefore a query- developments in the fled are presented with opinion
independent static faceted interface (either manually or summarization of blog entries. This survey is motivated by the
automatically generated) may suffice. By contrast, the articles idea of making e-books more intelligent, in particular enabling
in Wikipedia are lacking such predetermined dimensions that them to “answer” users’ queries. To find the needed
could fit all possible dynamic query results. Therefore efforts information in books users usually do not want to spend a long
on static facets would be futile. time searching, browsing or skimming them. They will be
Wisam Dakka et al., [4] presented a set of techniques for happy to have a “guru” nearby that can provide them with the
automatically identifying terms that are useful for building right answer almost simultaneously. For this purpose to had a
faceted hierarchies. The techniques build on the idea that close look at the area of automated text summarization.
external resources, when queried with the appropriate terms, Recently, with the increasing of information available online,
provide useful context that is valuable for locating the facets those approaches have been developed very extensively. In the
that appear in a database of text documents. It is demonstrated realm of automatic summarization different kinds of
the usefulness of Wikipedia, WordNet, and Google as external summarization have been attempted. Along with the study
resources. Experimental results, validated by an extensive distinguish between the following types of summaries
study using human subjects, indicate that our techniques according to specific criteria.
generate facets of high quality that can improve the browsing
experience for users. If efficiency is not a major concern, can III. METHODOLOGY
incorporate multiple such resources in this framework, for a The purposes of this research are 1) to explore the
variety of topics, and use all of them, irrespectively of the categories of teachers’ reflective thinking and realize the
topics that appear in the underlying collection. The automatic classification of the online discussion data by
distributional analysis step of our technique automatically integrating the inductive content analysis and educational data
identifies which concepts are important for the underlying mining techniques; and 2) to analyze teachers’ reflective
database and generates the appropriate facet terms. thinking in the online teacher professional development
Amaç Herdagdelen et al., [5] presents a novel approach program, including teachers’ reflection levels and evolution.
to query reformulation which combines syntactic and semantic Teachers’ online discussion data has been collected and
information by means of generalized Levenshtein distance analyzed for understanding their reflective thinking mainly
algorithms where the substitution operation costs are based on because:
probabilistic term rewrite functions. We investigate
• The peer coaching model has long been used in
unsupervised, compact and efficient models, and provide
professional development programs to enhance
empirical evidence of their effectiveness. Further it explores a
teachers’ teaching practices and students’ learning
generative model of query reformulation and supervised
out-comes. In reciprocal peer coaching, teachers.
combination methods providing improved performance at
• Share the coaching role, discuss with each other, and
variable computational costs. Among other desirable
elicit the reflection [10]. Teachers’ online discussion
properties, our similarity measures incorporate information-
data embodies their reflective thinking.
theoretic interpretations of taxonomic relations such as
specification and generalization. • Based on the understanding of teachers’ reflective
thinking, teacher training managers and educational
X. Xue and W. B. Croft [6] propose a novel framework researchers can design more appropriate online
where the original query is transformed into a distribution of learning activities and provide proper services and
reformulated queries. A reformulated query is generated by interventions to support teachers’ online reflection.
applying different operations including adding or replacing • Content analysis is commonly used to analyze
query words, detecting phrase structures, and so on. Since the transcript of online discussion for educational
ISSN 2277-5099 | © 2019 Bonfring
Bonfring International Journal of Software Engineering and Soft Computing, Vol. 9, No. 2, April 2019 49
purposes. In this study, the coding frameworks, which specific technical terms), so they are diverse and have various
focused on the main content and level of teachers’ synonyms. For example, in the sentence “Trust influences
reflection, had been obtained from inductive content communication between organizations”. To identify the Trust
analysis. In addition, we had developed a Data and communication is an entity of success factor and
collector, the Hawk, to collect posts on OPDP. influences as an influencing relationship.
Therefore, we chose to analyze teachers’ posts for
The relevant and irrelevant sentences are annotated into
understanding their reflective thinking
positive class and negative class respectively. The annotation
Stem Word Document is manually performed by a domain expert based on the given
In this module, enter the given word and stem word using related keywords and those keywords are used as a guideline
text box control and click save button stem word saved into for the annotation. In this module, user can submit the certain
the table. The details are saved in ‘Stemword’ file. The stem keywords which are stored into the KeyWords file.
word details view on view controls.
Subset of Six Levels Preparation
Stop Word Document • Phase 1: A data collection tool to collect teacher-
In this module, enter the stop word using text box control generated online discussion data and obtained 21,388
and click save button stop word saved into the table. The posts by using the data collection tool over a period
details are saved in ‘Stopword’ file. The stop word details of 6 months.
view on view controls. • Phase 2: A random sample (2,000 posts) were drawn
from the online discussion data set and used for
Add Synonym Word Document inductive content analysis.
In this module, enter the given word and synonym word • Phase 3: Three experts who had experience with
using text box control and click save button synonym word qualitative research and familiarity with pre-existing
saved into the table. The details are saved in ‘synonym word’ coding schemes collaborated on the inductive content
file. The synonym word details view on view controls. analysis process. Three experts conducted an
inductive content analysis on the random sample of
Add Test Dataset online discussion data set.
• After phase 3, we obtained the categories used for
The test dataset in this context are different which
text classification.
technical terms are, and hence they are fixed-terms. In other
words, the keywords are natural language like (i.e., not
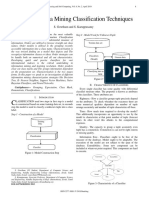
Teacher Generate Online Data Storage
Discussion Data 1 2
Data collect Users/ Research
6
3
Classification Model
(TF-IDF) 4 Code Scheme
Large Scale Text Classified
5
Classification Model Data Storage
(Conational-TF-IDF)
Update Test
8 9
Teacher Generate Online
Discussion Data
ISSN 2277-5099 | © 2019 Bonfring
Bonfring International Journal of Software Engineering and Soft Computing, Vol. 9, No. 2, April 2019 50
• Phase 4: A single-label NaıveBayes Classification TF, all the terms are considered equally important. That
algorithm had been implemented to classify the means, TF counts the term frequency for normal words like
labeled data. Then, we evaluated the performance of “is”, “a”, “what”, etc. Thus we need to know the frequent
the single-label NaıveBayes classification algorithm terms while scaling up the rare ones, by computing the
by comparing it with other commonly used text following: IDF (the) = log_e(Total number of documents /
classification algorithm. Number of documents with term ‘the’ in it).
• Phase 5: Implemented a large-scale text classification For example, Consider a document containing 1000 words,
based on the trained classification model. All the wherein the word give appears 50 times. The TF for give is
online discussion data has been automatically coded. then (50 / 1000) = 0.05. Now, assume that, 10 million
• Phase 6: Visually represented teachers’ reflection documents and the word give appears in 1000 of these. Then,
levels after we obtained the results of large-scale text the IDF is calculated as log(10,000,000 / 1,000) = 4. The TF-
classification. Additionally, we created a cumulative IDF weight is the product
adjacency matrix to characterize the evolution of
teachers’ reflective thinking. Then, the results of text
classification and visualization were sent back to the IV. CONCLUSION
data storage. An inductive content analysis on samples taken from 17,624
posts was implemented and the categories of teachers’
Online Collaborative Learning Approach
reflective thinking were obtained. Based on the results of
The approach of online collaborative learning provides inductive content analysis, we implemented a single-label text
Internet-based professional development opportunities, classification algorithm to classify the sample data. Then, we
including individual reflection, sharing resource, work- shops, applied the trained classification model on a large-scale and
online interactions with colleagues, and mentors unexplored online discussion text data set and two types of
• In the first stage, every teacher reflected the visualizations of the results were provided. By using the
discussion topic individually. After the chief teacher categories gained from inductive content analysis to create a
posted the activity plan and discussion topic onto the radar map, teachers’ reflection level was represented. In
OPDP, every teacher downloaded and read the plan addition, a cumulative adjacency matrix was created to
and topic characterize the evolution of teachers’ reflective thinking. This
• In the second stage, all teaches discussed the topic study could partly explain how teachers reflected in online
collectively. Every teacher expressed their own professional learning environments and brought awareness to
views, and exchanged views with others. This is a educational policy makers, teacher training managers, and
process of externalization. Teachers expressed their education researchers. The considerably better results are
ideas or thoughts about a specific topic via posts. found for the planned technique compared to existing
• In the final stage, every teacher submitted a strategies, regardless of the classifiers used. All the results
document, which recorded his/her learning according in this paper demonstrate the practicability and
experience in the online collaborative learning effectiveness of the planned technique. It’s capable of
activity. This is a process of internalization. Teachers distinctive co-regulated clusters of genes whose average
recorded the knowledge learned from communication expression is strongly related to the sample classes. The
with mentors and colleagues. known gene clusters could contribute to revealing underlying
• Each three-stage online collaborative learning category structures, providing a useful gizmo for the
activity usually lasted for one month. After three explorative analysis of biological information.
stages were completed, the chief teacher and the In future, the here fast algorithm enforced in information
individual teachers summarized the results. set solely, additional planned to implement in numerical
information set. During this application, enforced cancer
• In the three-stage online collaborative learning
dataset solely, in future planned to real time dataset like
activity, teachers’ reflection thinking was expressed
diabetics, pressure so on. Additional a lot of, planned to
in two main ways: the online discussion posts and the
compare with algorithm like naïve bayes, K-Nearest neighbor
reflection documents. In this study, we collected
so on.
teachers’ online discussion posts to analyze their
reflective thinking.
REFERENCES
Term Frequency – Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF)
[1] W. Kong and J. Allan, “Extending faceted search to the general web”, in
The TF measures how frequently a particular term occurs Proc. ACM Int. Conf. Inf. Knowl. Manage., Pp. 839–848, 2014.
in a document. It is calculated by the number of times a word [2] K. Balog, E. Meij and M. De Rijke, “Entity search: Building bridges
appears in a document divided by the total number of words in between two worlds”, In Proc. 3rd Int. Semantic Search Workshop, Pp.
9:1–9:5, 2010.
that document. It is computed as TF (the) = (Number of [3] C. Li, N. Yan, S.B. Roy, L. Lisham and G. Das, “Facetedpedia:
times term the ‘the’ appears in a document) / (Total Dynamic generation of query-dependent faceted interfaces for
number of terms in the document). The IDF measures the Wikipedia”, in Proc. 19th Int. Conf. World Wide Web, Pp. 651–660,
importance of a term. It is calculated by the number of 2010.
[4] W. Dakka and P.G. Ipeirotis, “Automatic extraction of useful facet
documents in the text database divided by the number of hierarchies from text databases”, In Proc. IEEE 24th Int. Conf. Data
documents where a specific term appears. While computing Eng., Pp. 466–475, 2008.
ISSN 2277-5099 | © 2019 Bonfring
Bonfring International Journal of Software Engineering and Soft Computing, Vol. 9, No. 2, April 2019 51
[5] A. Herdagdelen, M. Ciaramita, D. Mahler, M. Holmqvist, K. Hall, S.
Riezler and E. Alfonseca, “Generalized syntactic and semantic models
of query reformulation”, in Proc. 33rd Int. ACM SIGIR Conf. Res.
Develop. Inf. retrieval, Pp. 283–290, 2010.
[6] X. Xue and W. B. Croft, “Modeling reformulation using query
distributions”, ACM Trans. Inf. Syst., Vol. 31, No. 2, Pp. 6:1–6:34,
2013.
[7] L. Bing, W. Lam, T.L. Wong and S. Jameel, “Web query reformulation
via joint modeling of latent topic dependency and term context”, ACM
Trans. Inf. Syst., Vol. 33, No. 2, Pp. 6:1–6:38, 2015.
[8] S.A. Gionis and Y. Maarek, “Improving recommendation for long-tail
queries via templates”, in Proc. 20th Int. Conf. World Wide Web, Pp.
47–56, 2011.
[9] M. Damova and I. Koychev, “Query-based summarization: A survey”,
In Proc. S3T, Pp. 142–146, 2010.
[10] L.K.R. Veni and R. Rajaram, “Afgf: An automatic facet generation
framework for document retrieval”, In Proc. Int. Conf. Adv. Comput.
Eng., Pp. 110–114, 2010.
[11] J. Pound, S. Paparizos and P. Tsaparas, “Facet discovery for structured
web search: A query-log mining approach”, in Proc. ACM SIGMOD Int.
Conf. Manage. Data, Pp. 169–180, 2011.
[12] W. Kong and J. Allan, “Extracting query facets from search results”, In
Proc. 36th Int. ACM SIGIR Conf. Res. Develop. Inf. Retrieval, Pp. 93–
102, 2013.
[13] Y. Liu, R. Song, M. Zhang, Z. Dou, T. Yamamoto, M. P. Kato, H.
Ohshima and K. Zhou, “Overview of the NTCIR-11 imine task”, In
Proc. NTCIR-11, Pp. 8–23, 2014.
ISSN 2277-5099 | © 2019 Bonfring
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Paper Web ClusteringDokument3 SeitenPaper Web ClusteringshitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development-of-a-machine-learning-model-for-knowledge-acquisition-relationship-extraction-and-discovery-in-domain-ontology-engineering-using-jaccord-relationship-extraction-and-neural-network2019International-Jour.pdfDokument9 SeitenDevelopment-of-a-machine-learning-model-for-knowledge-acquisition-relationship-extraction-and-discovery-in-domain-ontology-engineering-using-jaccord-relationship-extraction-and-neural-network2019International-Jour.pdfanon_576957892Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Learning Based Approach For Automatic Text Document ClassificationDokument7 SeitenA Learning Based Approach For Automatic Text Document ClassificationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conference Paper LATENT DIRICHLET ALLOCATION (LDA)Dokument9 SeitenConference Paper LATENT DIRICHLET ALLOCATION (LDA)mahi mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scopus IMPLEMENTATIONOFARTIFICIALINTELLIGENCEDokument11 SeitenScopus IMPLEMENTATIONOFARTIFICIALINTELLIGENCEGPTV AdmissionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incremental Approach of Neural Network in Back Propagation Algorithms For Web Data MiningDokument5 SeitenIncremental Approach of Neural Network in Back Propagation Algorithms For Web Data MiningIAES IJAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Easychair Preprint: Pallavi Kohakade and Sujata JadhavDokument5 SeitenEasychair Preprint: Pallavi Kohakade and Sujata JadhavsauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIRS AnswersDokument12 SeitenIIRS Answers20at1a3145Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey - Ontology Based Information Retrieval in Semantic WebDokument8 SeitenA Survey - Ontology Based Information Retrieval in Semantic WebMayank SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finding Experts in Community Based Question-Answering Services-IJAERDV04I0115724Dokument6 SeitenFinding Experts in Community Based Question-Answering Services-IJAERDV04I0115724Editor IJAERDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Vectorization Using Data Mining MethodsDokument11 SeitenText Vectorization Using Data Mining Methods1494834438Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Graph Based Keyword Extraction Model Using Collective Node WeightDokument9 SeitenA Graph Based Keyword Extraction Model Using Collective Node WeighthalloweenNoch keine Bewertungen
- D04-Prediction Analysis Techniques of Data Mining A ReviewDokument6 SeitenD04-Prediction Analysis Techniques of Data Mining A ReviewHendra Nusa PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning For Efficient Assessment and Prediction of Human (1127) PDFDokument6 SeitenMachine Learning For Efficient Assessment and Prediction of Human (1127) PDFSai PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Hierarchical Review Graph Representations For RecommendationDokument14 SeitenLearning Hierarchical Review Graph Representations For Recommendationruoruo00902000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sentiment Analysis on Tweets using Machine Learning: An SEO-Optimized TitleDokument5 SeitenSentiment Analysis on Tweets using Machine Learning: An SEO-Optimized TitleRicha GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey On Text ClassificationDokument7 SeitenSurvey On Text ClassificationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extending The Student's Performance Via K Means and Blended LearningDokument4 SeitenExtending The Student's Performance Via K Means and Blended LearningIJEACS UKNoch keine Bewertungen
- JurnalDokument19 SeitenJurnalNur WahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal FullDokument8 SeitenJournal FullVinoth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Match SystemDokument6 SeitenResume Match SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Comparative Analysis of Document Ranking ApproachesDokument5 SeitenA Detailed Comparative Analysis of Document Ranking ApproachesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep LearningDokument42 SeitenDeep LearningXimena AñaguayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive Computing and Education and LearningDokument5 SeitenCognitive Computing and Education and LearningEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.PDF - 2Fjcssp.2014.720.722 - Paper 1Dokument3 Seiten1.PDF - 2Fjcssp.2014.720.722 - Paper 1baseera aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kernel Context Recommender System PDFDokument19 SeitenKernel Context Recommender System PDFSri Lalitha MunukutlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probabilistic Topic Modeling and Its Variants - A Survey: Padmaja CH V R S Lakshmi NarayanaDokument5 SeitenProbabilistic Topic Modeling and Its Variants - A Survey: Padmaja CH V R S Lakshmi Narayanaياسر سعد الخزرجيNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S2667096821000215 MainDokument7 Seiten1 s2.0 S2667096821000215 MainShrijan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) Approach To The Development of Student Information Management SystemDokument5 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) Approach To The Development of Student Information Management SystemATSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijermt Jan2019Dokument9 SeitenIjermt Jan2019Deepak RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Project Literature ReviewDokument6 SeitenComputer Science Project Literature Reviewaflsbegdo100% (1)
- Context-Based Sentiment Analysis On Customer Reviews Using Machine Learning Linear ModelsDokument25 SeitenContext-Based Sentiment Analysis On Customer Reviews Using Machine Learning Linear ModelsShahzaib HayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijet V3i5p39Dokument15 SeitenIjet V3i5p39International Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNoch keine Bewertungen
- BKD-Scholarly Knowledge Graphs Through Structuring Scholarly Communication A Review-2022Dokument37 SeitenBKD-Scholarly Knowledge Graphs Through Structuring Scholarly Communication A Review-2022ezoomingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Mining and Its ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenText Mining and Its Applicationscompaq1501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wang 2007Dokument6 SeitenWang 2007amine332Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews and Comments For Cross Domain Recommendations and Decision MakingDokument5 SeitenReviews and Comments For Cross Domain Recommendations and Decision MakingAnkush BabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining: Analysis of Student Database Using Classification TechniquesDokument7 SeitenData Mining: Analysis of Student Database Using Classification TechniquesNicholasRaheNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Knowledge Sharing in Collaborative EnvironmentDokument6 SeitenA Review On Knowledge Sharing in Collaborative EnvironmentEditor IJAERDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Published Research PapersDokument11 SeitenPublished Research PapersHartly BachinichaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance and Feedback AnalyzerDokument6 SeitenPerformance and Feedback AnalyzerIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Clustering of Construction Project Documents Based On Textual SimilarityDokument14 SeitenAutomatic Clustering of Construction Project Documents Based On Textual SimilarityArdi DewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ML Basepaper 2Dokument3 SeitenML Basepaper 2MadhanDhonianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text-Based Intent Analysis Using Deep LearningDokument8 SeitenText-Based Intent Analysis Using Deep LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction Analysis Techniques of Data Mining: A ReviewDokument7 SeitenPrediction Analysis Techniques of Data Mining: A ReviewEdwardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information RetrievalDokument3 SeitenInformation RetrievalGustavo MacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Efficient Pharse Based Pattern Taxonomy Deploying Method For Text Document MiningDokument9 SeitenAn Efficient Pharse Based Pattern Taxonomy Deploying Method For Text Document MiningEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S187705091631167X MainDokument8 Seiten1 s2.0 S187705091631167X MainSouhaila DjaffalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRJET V4I12267 With Cover Page v2Dokument5 SeitenIRJET V4I12267 With Cover Page v2Agusti Frananda Alfonsus NaibahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 8928Dokument4 SeitenPaper 8928IJARSCT JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On The Result Based Analysis of Student Performance Using Data Mining TechniquesDokument5 SeitenA Survey On The Result Based Analysis of Student Performance Using Data Mining TechniquesIIR indiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaman 2019Dokument4 SeitenJaman 2019Jajam haerul jamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitizing Notes Using Optical Character Recognition and Automatic Topic Identification and Classification Using Natural Language ProcessingDokument10 SeitenDigitizing Notes Using Optical Character Recognition and Automatic Topic Identification and Classification Using Natural Language ProcessingIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Categorization Techniques: B. Mahalakshmi, Dr. K. DuraiswamyDokument7 SeitenAn Overview of Categorization Techniques: B. Mahalakshmi, Dr. K. Duraiswamyriddhi sarvaiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 127 1498038923 - 21-06-2017 PDFDokument9 Seiten127 1498038923 - 21-06-2017 PDFEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Question Paper Generation Using MLDokument7 SeitenAutomatic Question Paper Generation Using MLtabrej saiyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S2665917423001265 MainDokument11 Seiten1 s2.0 S2665917423001265 MainVishal KhardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review Computer NetworkingDokument7 SeitenLiterature Review Computer Networkingafdtktocw100% (1)
- Automatic Image Annotation: Fundamentals and ApplicationsVon EverandAutomatic Image Annotation: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultimate Enterprise Data Analysis and Forecasting using Python: Leverage Cloud platforms with Azure Time Series Insights and AWS Forecast Components for Deep learning Modeling using Python (English Edition)Von EverandUltimate Enterprise Data Analysis and Forecasting using Python: Leverage Cloud platforms with Azure Time Series Insights and AWS Forecast Components for Deep learning Modeling using Python (English Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management Practices in MSMEs' Fast Moving Consumer Goods Industries - An Empirical Study With Special References To Mulugu District of TelunganaDokument3 SeitenSupply Chain Management Practices in MSMEs' Fast Moving Consumer Goods Industries - An Empirical Study With Special References To Mulugu District of TelunganaBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Organizational Commitment Among The IT Employees in Chennai CityDokument3 SeitenAn Overview of Organizational Commitment Among The IT Employees in Chennai CityBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Simulation of Film Thickness Formation in A PFI Engine Under Motoring ConditionsDokument5 SeitenNumerical Simulation of Film Thickness Formation in A PFI Engine Under Motoring ConditionsBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Precipitation Hardening On Tensile, Fatigue and Fracture Toughness Behaviour of 8011 Al/ 15%SiCp Metal Matrix CompositeDokument6 SeitenEffect of Precipitation Hardening On Tensile, Fatigue and Fracture Toughness Behaviour of 8011 Al/ 15%SiCp Metal Matrix CompositeBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secure Sharing of Sensitive Data On A Big Data PlatformDokument7 SeitenSecure Sharing of Sensitive Data On A Big Data PlatformBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Home Implementing IOT Technology With Multilingual Speech Recognition SystemDokument6 SeitenSmart Home Implementing IOT Technology With Multilingual Speech Recognition SystemBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Time ManagementDokument5 SeitenA Study On Time ManagementBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhancement of Thermal Performance of Solar Parabolic Trough Concentrator-Techniques - ReviewDokument5 SeitenEnhancement of Thermal Performance of Solar Parabolic Trough Concentrator-Techniques - ReviewBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Behaviour Study of Heat Exchanger With Heat Pipes Using CuO Nano FluidDokument4 SeitenThermal Behaviour Study of Heat Exchanger With Heat Pipes Using CuO Nano FluidBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation ApproachesDokument5 SeitenReview On MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation ApproachesBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Home Implementing IOT Technology With Multilingual Speech Recognition SystemDokument6 SeitenSmart Home Implementing IOT Technology With Multilingual Speech Recognition SystemBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics User Identification Using Pairwise Client CouplingDokument6 SeitenDynamics User Identification Using Pairwise Client CouplingBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secure Sharing of Sensitive Data On A Big Data PlatformDokument7 SeitenSecure Sharing of Sensitive Data On A Big Data PlatformBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novelties and Best Practices of On-Line Banking Sector by Using Mobile Apps For Potential Customer To Avoid Risk FactorsDokument5 SeitenNovelties and Best Practices of On-Line Banking Sector by Using Mobile Apps For Potential Customer To Avoid Risk FactorsBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Artificial IntelligenceDokument4 SeitenA Study On Artificial IntelligenceBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollution Monitoring and Controlling System Using Global System For Mobile Communication NetworkDokument3 SeitenPollution Monitoring and Controlling System Using Global System For Mobile Communication NetworkBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybridization Approach To Classify Big Data Using Social Internet of ThingsDokument5 SeitenHybridization Approach To Classify Big Data Using Social Internet of ThingsBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Chain Technology For Privacy Protection For Cloudlet-Based Medical Data SharingDokument4 SeitenBlock Chain Technology For Privacy Protection For Cloudlet-Based Medical Data SharingBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networks Flaws and Filtering Using KNOD AlgorithmsDokument4 SeitenNetworks Flaws and Filtering Using KNOD AlgorithmsBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Adventure Game Using UnityDokument5 Seiten3D Adventure Game Using UnityBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On Analysis of Chronic Diseases Prediction in Big Health Care Data Using IoT-WBANsDokument5 SeitenA Survey On Analysis of Chronic Diseases Prediction in Big Health Care Data Using IoT-WBANsBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome From Ultrasound Images Using SIFT DescriptorsDokument5 SeitenDetection of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome From Ultrasound Images Using SIFT DescriptorsBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Data Mining Classification TechniquesDokument4 SeitenReview of Data Mining Classification TechniquesBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Based Accident Preventing and Reporting SystemDokument4 SeitenIOT Based Accident Preventing and Reporting SystemBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Provisioning of Data Security For File Transformation On Multi Cloud StorageDokument2 SeitenProvisioning of Data Security For File Transformation On Multi Cloud StorageBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Traffic Profiles For Wireless NetworkDokument3 SeitenDifferent Traffic Profiles For Wireless NetworkBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of Data Storage Security Issues in Cloud ComputingDokument3 SeitenA Study of Data Storage Security Issues in Cloud ComputingBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On Big Data Security and Related Techniques To Improve SecurityDokument4 SeitenA Survey On Big Data Security and Related Techniques To Improve SecurityBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Application Development For Textile IndustryDokument4 SeitenAndroid Application Development For Textile IndustryBONFRINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine LearningDokument17 SeitenMachine Learningjyoti singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 03 - 04Dokument27 SeitenUnit 03 - 04Nigussie WenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet of Things Comparative StudyDokument3 SeitenInternet of Things Comparative StudySriz PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining (WEKA) en FormattedDokument52 SeitenData Mining (WEKA) en FormattedJefther EdwardNoch keine Bewertungen
- My ML Lab ManualDokument21 SeitenMy ML Lab ManualAnonymous qZP5Zyb2Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Framework For Early Detection of Antisocial Behavior On Twitter Using NLP PDFDokument12 SeitenA Framework For Early Detection of Antisocial Behavior On Twitter Using NLP PDFMeandrick MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Mamdani Fuzzy Inference System For ClassificationDokument11 SeitenA Mamdani Fuzzy Inference System For ClassificationAli AzfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yz MakaleDokument12 SeitenYz Makalesal maNoch keine Bewertungen
- REPORT On DECISION TREEDokument40 SeitenREPORT On DECISION TREEAnshul PancholiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQD TestDokument5 SeitenRQD Testkiko auNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of Classification and Pattern Mining: A Discriminative and Frequent Pattern-Based ApproachDokument126 SeitenIntegration of Classification and Pattern Mining: A Discriminative and Frequent Pattern-Based ApproachMadiha ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 771 A18 Lec20Dokument107 Seiten771 A18 Lec20DUDEKULA VIDYASAGARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data MiningDokument40 SeitenData Miningporpy_carol100% (1)
- Yolov3: An Incremental Improvement: Joseph Redmon, Ali FarhadiDokument6 SeitenYolov3: An Incremental Improvement: Joseph Redmon, Ali FarhadiKaran DhingraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance AI & ML Certification Program LearnbayDokument45 SeitenAdvance AI & ML Certification Program LearnbayJeshuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To WEKA Explorer: in Part From: Yizhou Sun 2008Dokument104 SeitenAn Introduction To WEKA Explorer: in Part From: Yizhou Sun 2008Pablo VelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingenireria Del SoftwareDokument201 SeitenIngenireria Del SoftwarecubexlifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kenny-230718-The Ultimate Machine Learning Cheat SheetDokument20 SeitenKenny-230718-The Ultimate Machine Learning Cheat SheetvanjchaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical and Learning Aided Classifier For ECGDokument8 SeitenStatistical and Learning Aided Classifier For ECGAmit RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naivebayes TuteDokument4 SeitenNaivebayes TuteAmit ChandakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Neural Networks - 12: Dr. Aditya AbhyankarDokument42 SeitenArtificial Neural Networks - 12: Dr. Aditya AbhyankaranuragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logistic Regression ExampleDokument22 SeitenLogistic Regression ExampleLUV ARORA100% (1)
- SAX-VSM: Interpretable Time Series Classification Using SAX and Vector Space ModelDokument11 SeitenSAX-VSM: Interpretable Time Series Classification Using SAX and Vector Space Modelworm123_123Noch keine Bewertungen
- White Star Capital 2020 Artificial Intelligence Sector ReportDokument87 SeitenWhite Star Capital 2020 Artificial Intelligence Sector ReportWhite Star Capital100% (1)
- Support Vector Machines: (Vapnik, 1979)Dokument34 SeitenSupport Vector Machines: (Vapnik, 1979)sisda amaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning From Scratch PDFDokument124 SeitenMachine Learning From Scratch PDFCarlosAndrésLópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLVII-Part A Lab ManualDokument57 SeitenCLVII-Part A Lab ManualAditya RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discovery of Urban TypologiesDokument14 SeitenDiscovery of Urban TypologiesjalopesgilNoch keine Bewertungen