Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Waste-Water Treatment
Hochgeladen von
Eevee Cat0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten4 Seitenthe ecosystem
Originaltitel
Ecosystem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenthe ecosystem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten4 SeitenWaste-Water Treatment
Hochgeladen von
Eevee Catthe ecosystem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
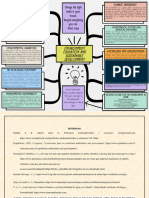
Maintaining the quality of air and soil, Waste-water treatment
providing flood and disease control,
Ecosystems such as wetlands filter
or pollinating crops are some of the
effluents, decompose waste through
‘regulating services' provided by
the biological activity of
ecosystems. They are often invisible
microorganisms, and eliminate
and therefore mostly taken for
harmful pathogens.
granted. When they are damaged,
the resulting losses can be substantial Erosion prevention and maintenance
and difficult to restore. of soil fertility
Local Climate Air Quality Vegetation cover prevents soil
erosion and ensures soil fertility
Ecosystems influence the local
through natural biological processes
climate and air quality. For example,
such as nitrogen fixation. Soil erosion
trees provide shade whilst forests
is a key factor in the process of land
influence rainfall and water
degradation, loss of soil fertility and
availability both locally and
desertification, and contributes to
regionally. Trees or other plants also
decreased productivity of
play an important role in regulating
downstream fisheries.
air quality by removing pollutants
from the atmosphere. Erosion prevention and maintenance
of soil fertility
Carbon sequestration and storage
Vegetation cover prevents soil
Ecosystems regulate the global
erosion and ensures soil fertility
climate by storing greenhouse gases.
through natural biological processes
For example, as trees and plants
such as nitrogen fixation. Soil erosion
grow, they remove carbon dioxide
is a key factor in the process of land
from the atmosphere and effectively
degradation, loss of soil fertility and
lock it away in their tissues.
desertification, and contributes to
Moderation of extreme events decreased productivity of
downstream fisheries.
Ecosystems and living organisms
create buffers against natural Pollination
disasters. They reduce damage from
Insects and wind pollinate plants and
floods, storms, tsunamis, avalanches,
trees which is essential for the
landslides and droughts.
development of fruits, vegetables
and seeds. Animal pollination is an The principal objective of
ecosystem service mainly provided by ecosystem management is the
insects but also by some birds and efficient maintenance and
bats. In agro-ecosystems, pollinators ethical use of natural
are essential for orchard, resources. It is a multifaceted
horticultural and forage production, and holistic approach which
as well as the production of seed for requires a significant change in
many root and fibre crops. Pollinators how the natural and human
such as bees, birds and bats affect 35 environments are identified
percent of the world’s crop
production, increasing outputs of
around 75% of the leading food crops Several approaches to effective
worldwide. ecosystem management engage
conservation efforts at both a local or
Biological control
landscape level and involves:
The activities of predators and adaptive management, natural
parasites in ecosystems that act to resource management, strategic
control populations of potential pest management, and command and
and disease vector. control management.
Regulation of Water Flow Adaptive management is based on
the concept that predicting future
Water flow regulation is a key service
influences/disturbance to an
provided by land cover and
ecosystem is limited and
configuration, but its dynamics are
unclear.Therefore, the goal of
poorly understood by most policy
adaptive management is to manage
makers and land management
the ecosystem so it maintains the
organisations.
greatest amount of ecological
Ecosystem management is a process integrity, but also to utilize
that aims to conserve major management practices that have the
ecological services and restore ability to change based on new
natural resources while meeting the experience and insights.
socioeconomic, political and cultural
The term natural resource
needs of current and future
management is frequently used
generations.
when dealing with a particular
resource for human use rather than Command and control
managing the whole ecosystem.A management utilizes a linear
main objective of natural resources problem solving approach
management is the sustainability for where a perceived problem is
future generations, which appoints solved through controlling
ecosystem managers to balance devices such as laws, threats,
natural resources exploitation and contracts and/or agreements.
conservation over long-term
timeframe. REPUBLIC ACT 9003 ECOLOGICAL
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT ACT
OF 2000
Strategic management encourages
In partnership with
the establishment of goals that will
stakeholders, the law aims to
benefit the ecosystem while keeping adopt a systematic,
socioeconomic and politically comprehensive and
relevant issues in mind. ecological solid waste
management program that
Strategic management differs shall ensure the protection of
from other types of ecosystem public health and
management because it keeps environment. The law ensures
stakeholders involved and proper segregation,
relies on their input to develop collection, storage, treatment
and disposal of solid waste
the best management strategy
through the formulation and
for an ecosystem. Similarly to adaptation of best eco-waste
other modes of ecosystem products.
management, this method REPUBLIC ACT 9275 PHILIPPINE
places a high level of CLEAN WATER ACT OF 2004
importance on evaluating and The law aims to protect the
country's water bodies from
reviewing any changes,
pollution from land-based
progress or negative impacts sources (industries and
and prioritizes flexibility in commercial establishments,
adapting management agriculture and
protocols as a result of new community/household
information. activities). It provides for
comprehensive and
integrated strategy to prevent
and minimize pollution through The Environment Impact
a multi-sectoral and Assessment System was
participatory approach formally established in 1978
involving all the stakeholders. with the enactment of
REPUBLIC ACT 8749 PHILIPPINE Presidential Decree no. 1586 to
CLEAN AIR ACT OF 1999 facilitate the attainment and
The law aims to achieve and maintenance of rational and
maintain clean air that meets orderly balance between
the National Air Quality socio-economic development
guideline values for criteria and environmental protection.
pollutants, throughout the EIA is a planning and
Philippines, while minimizing management tool that will
the possible associated help government, decision
impacts to the economy. makers, the proponents and
REPUBLIC ACT 6969 TOXIC the affected community
SUBSTANCES, HAZARDOUS AND address the negative
NUCLEAR WASTE CONTROL ACT consequences or risks on the
OF 1990 environment. The process
The law aims to regulate assures implementation of
restrict or prohibit the environment-friendly projects.
importation, manufacture,
SOURCES :
processing, sale, distribution,
use and disposal of chemical https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecosystem_mana
substances and mixtures the gement
present unreasonable risk to https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi
human health. It likewise /full/10.1111/1365-2664.12016
prohibits the entry, even in
http://ecac.emb.gov.ph/?page_id=43
transit, of hazardous and
nuclear wastes and their http://www.fao.org/ecosystem-services-
disposal into the Philippine biodiversity/background/regulating-
territorial limits for whatever services/en/
purpose; and to provide https://www.becc.lu.se/research/conservation-
advancement and facilitate of-biodiversity-and-maintenance-of-ecosystem-
research and studies on toxic services
chemicals.
PRESIDENTIAL DECREE 1586
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
STATEMENT (EIS) STATEMENT OF
1978
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Iso 9001:2015Dokument108 SeitenIso 9001:2015hassan faraz100% (30)
- The Seven Environmental PrinciplesDokument2 SeitenThe Seven Environmental PrinciplesGM Alisangco Jarabejo50% (2)
- Vitalis Perry Practice Questions For The Celpip Test SpeakinDokument133 SeitenVitalis Perry Practice Questions For The Celpip Test SpeakinOlga AmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cshpresidentials Proposed 3 Storey Residential BuildingDokument6 SeitenCshpresidentials Proposed 3 Storey Residential BuildingJhune UrabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bu Exit PDFDokument41 SeitenBu Exit PDFFELICITY MONTEFALCONoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental PollutionDokument8 SeitenEnvironmental PollutionsinghytvinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEF IP EcosystemRestoration 2022 10 12Dokument2 SeitenGEF IP EcosystemRestoration 2022 10 12teejeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTPDokument44 SeitenNSTPHacelen VergoniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Environment and Natural ResourcesDokument17 SeitenDepartment of Environment and Natural ResourcesKaren de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A World Without Trees: Saving EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenA World Without Trees: Saving EnvironmentKim CamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenEnvironmentgame lover Vishal gamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument70 SeitenEnvironmental ScienceJumil Beem BalistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity and Climate Change: OutlineDokument8 SeitenBiodiversity and Climate Change: OutlinenilkanthretailenterpriseltdNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Environmental Policy and StrategiesDokument18 SeitenNational Environmental Policy and StrategiesAyushi ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument54 SeitenChapter 5Dol SobariNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 PDFDokument8 SeitenL1 PDFDenialAlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONSERVATION OF BIODIVERSITY (Env Sci)Dokument3 SeitenCONSERVATION OF BIODIVERSITY (Env Sci)Matt Irvin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agriculturreee (1) Ge Elec 1Dokument30 SeitenAgriculturreee (1) Ge Elec 1Domasig, Alnizel A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Management Systems Auditor / Lead Auditor Training Course General EnvironmentDokument26 SeitenEnvironmental Management Systems Auditor / Lead Auditor Training Course General EnvironmentRakesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- USAID Solid Waste ManagementDokument3 SeitenUSAID Solid Waste Managementmajope1966Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bommarco 2013Dokument9 SeitenBommarco 2013Guido BenedettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report On Ecosystem Conservation-ActivityDokument2 SeitenA Report On Ecosystem Conservation-ActivityMary Louisse MagtuboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa ConceptualDokument3 SeitenMapa ConceptualFelipe Gutierrez MachadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystem-Based Adaptation: An Approach Responding To Climate HazardsDokument2 SeitenEcosystem-Based Adaptation: An Approach Responding To Climate HazardsΡομίρ ΓιάνκκιλNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter IV Envi SciDokument5 SeitenChapter IV Envi SciAs YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ways To Conserve Bodiversity To Mitigate Climate Change: Plant Trees Protect Natural HabiatsDokument3 SeitenWays To Conserve Bodiversity To Mitigate Climate Change: Plant Trees Protect Natural HabiatsLinlin PayosNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDG15 BriefDokument2 SeitenSDG15 BriefshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope and Importance of Natural Resource ManagementDokument2 SeitenScope and Importance of Natural Resource Managementabhirup745la23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah Precision AgricultureDokument15 SeitenMakalah Precision AgriculturedailynisyouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Management Student Name Professor's University University Name 17th March 2022Dokument10 SeitenEnvironmental Management Student Name Professor's University University Name 17th March 2022AntakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollution, Land: January 2017Dokument5 SeitenPollution, Land: January 2017dfsdfsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Pollution Published PDFDokument5 SeitenLand Pollution Published PDFMay TampusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument5 SeitenEnvironmental Scienceprincess.pinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Soil ConservationDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Soil ConservationklkNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Sustainable AgricultureDokument10 SeitenWhat Is Sustainable AgriculturedadavimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PublishedDokument5 SeitenPublisheddaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCSH G8 - Deforestation ProposalDokument13 SeitenSCSH G8 - Deforestation ProposalAmier AfzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wylie A3Dokument2 SeitenWylie A3Wylie A. BaguingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1Dokument22 SeitenTopic 1Hacelen VergoniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watershed ConceptDokument16 SeitenWatershed Conceptgowtham.rupa07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Published PDFDokument5 SeitenPublished PDFMahal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystem Services: Literature Review - 1 by Sharvari MuleyDokument12 SeitenEcosystem Services: Literature Review - 1 by Sharvari MuleySharvari MuleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EcosystemservicesDokument2 SeitenEcosystemserviceskojo BUSIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Site InitiativeDokument10 SeitenSustainable Site InitiativeuGWatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environment Planning Assignment - Palin MehtaDokument5 SeitenEnvironment Planning Assignment - Palin MehtaPalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sambhav Daksh Syed AbhimanyuDokument10 SeitenSambhav Daksh Syed AbhimanyuDaksh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Principals Poster - English - 3mm BleedDokument1 SeiteEnvironmental Principals Poster - English - 3mm BleedcsmcitruspatensieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Mulches in AgricultureDokument5 SeitenRole of Mulches in AgricultureDeb137Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title Result References A Review of Environmental Droughts: Increased Risk Under Global Warming?Dokument3 SeitenTitle Result References A Review of Environmental Droughts: Increased Risk Under Global Warming?pangilinanfreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revista ItorDokument6 SeitenRevista ItoritorNoch keine Bewertungen
- PINTANG - ST - Conserve or ConverseDokument2 SeitenPINTANG - ST - Conserve or Conversecharmeljane1110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystem Mangement Programme A New Approach To SustainabilityDokument24 SeitenEcosystem Mangement Programme A New Approach To Sustainabilityshanea bucknorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring The Concept of EnvironmentDokument9 SeitenExploring The Concept of EnvironmentShreyasree PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco FarmingDokument3 SeitenEco FarmingiffatNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTP Environmental ProtectionDokument7 SeitenNSTP Environmental ProtectionAMPONIN EUNICENoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5Dokument11 SeitenTopic 5Jomari TawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Practices For Sustainable Water ManagementDokument17 SeitenPrinciples and Practices For Sustainable Water ManagementShubham kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTP AnswerDokument6 SeitenNSTP AnswerRyzajane DalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection Against Wetland Development or Wetlands PreservationDokument4 SeitenProtection Against Wetland Development or Wetlands PreservationJeremiah MutuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EcosystemsDokument2 SeitenEcosystemsKeira BishopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Soil Resources For Sustainable Development Under A Changing Climate M. M. R. Jahangir, I. Jahan and N. J. MumuDokument12 SeitenManagement of Soil Resources For Sustainable Development Under A Changing Climate M. M. R. Jahangir, I. Jahan and N. J. MumujatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methodology For Pollution Control of Lakes and ManagementDokument19 SeitenMethodology For Pollution Control of Lakes and ManagementESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNoch keine Bewertungen
- PollutionDokument6 SeitenPollutionVijay AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDM B002 3T 202021 Notes On Influencing People - LunesDokument10 SeitenMDM B002 3T 202021 Notes On Influencing People - LunesEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning by GasparDokument3 SeitenPlanning by GasparEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning by CastilloDokument6 SeitenPlanning by CastilloEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociological (Political Culture) ApproachDokument8 SeitenSociological (Political Culture) ApproachEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Approach: Key Concepts To UnderstandDokument3 SeitenStructural Approach: Key Concepts To UnderstandEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Criminal Law Compilation of Modules 8 10Dokument188 SeitenCriminal Law Compilation of Modules 8 10Eevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legislatures: Key Concepts To UnderstandDokument11 SeitenLegislatures: Key Concepts To UnderstandEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institutional ApproachDokument7 SeitenInstitutional ApproachEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legislatures: Key Concepts To UnderstandDokument11 SeitenLegislatures: Key Concepts To UnderstandEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Geopolitical Consequences of China's Demographic TurmoilDokument9 SeitenThe Geopolitical Consequences of China's Demographic TurmoilEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population and Health ConstraintsDokument7 SeitenPopulation and Health ConstraintsEevee CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 3Dokument39 SeitenChapter1 3sheankevinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reuse of Waste Glass in Building Brick Production: Waste Management & Research June 2009Dokument7 SeitenReuse of Waste Glass in Building Brick Production: Waste Management & Research June 2009leNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleng - TLEDokument8 SeitenBleng - TLEAngeli Rose Dela Pe�aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Show Bar Pro16x10W RGBAW IP65Dokument60 SeitenShow Bar Pro16x10W RGBAW IP65BenHaahrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tio2 Simplification Report Iss3Dokument107 SeitenTio2 Simplification Report Iss3Caguioa Mark Anthony G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS BeeswaxDokument6 SeitenMSDS BeeswaxBhavin ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Franke+Pro Value+RangeDokument28 SeitenFranke+Pro Value+RangeDaniel CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CST OutreachDokument5 SeitenCST OutreachKNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds Buffer PH 10 BlueDokument5 SeitenMsds Buffer PH 10 BlueMuhammad Irfan MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deskripsi Dan Spesifikasi CiptaanDokument10 SeitenDeskripsi Dan Spesifikasi CiptaanPuput Dani Prasetyo AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question and AnswerDokument10 SeitenQuestion and AnswerkumarasilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery of Glycerine From Spent Palm Kernel Soap and Palm Oil Soap LyeDokument8 SeitenRecovery of Glycerine From Spent Palm Kernel Soap and Palm Oil Soap LyeNadya Larasati KrdNoch keine Bewertungen
- (EcoWater) 3500and3502ownersmanualDokument45 Seiten(EcoWater) 3500and3502ownersmanualGreg ReynekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green BankingDokument33 SeitenGreen BankingTonu Sarkar100% (3)
- Interlocking Plastic Blocks (IPB)Dokument7 SeitenInterlocking Plastic Blocks (IPB)IJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NT Features03r1Dokument15 SeitenNT Features03r1mistermango100% (2)
- Industry Analysis and ResearchDokument22 SeitenIndustry Analysis and ResearchMrinal Hashishin YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outokumpu Site Visit Tornio PresentationDokument28 SeitenOutokumpu Site Visit Tornio PresentationzosternatNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterPact - UL 489 Listed - 64689Dokument2 SeitenMasterPact - UL 489 Listed - 64689Carlos HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waste Management Among Households in Manarcad PachayathDokument4 SeitenWaste Management Among Households in Manarcad PachayathMerin Mary JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1a: Picture The SceneDokument9 SeitenExercise 1a: Picture The SceneAlin NanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Structural Feasibility of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Based Lightweight Concrete Sandwich Wall PanelsDokument7 Seiten2017 Structural Feasibility of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Based Lightweight Concrete Sandwich Wall PanelsS R Kumar Konathala100% (1)
- SWM System SwotDokument2 SeitenSWM System SwotrbenseghierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zurn LEED Credit Guide Aug09Dokument18 SeitenZurn LEED Credit Guide Aug09Alejandro SasmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video TranscriptDokument2 SeitenVideo TranscriptCRISTINA SOBRINO LIMONESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated-Sludge-Aeration-Tank-Calculations-Si-Units-Final-Locked (For Student)Dokument30 SeitenActivated-Sludge-Aeration-Tank-Calculations-Si-Units-Final-Locked (For Student)Johnclaude Chamandi50% (2)