Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
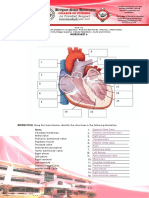
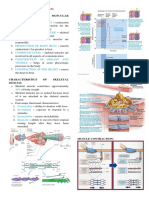
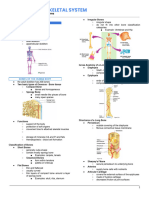
Skeletal System Reviewer
Hochgeladen von
KIRSTEN ALEXI ANGELES0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
305 Ansichten3 SeitenThe skeletal system is composed of 206 bones that provide structure, protect organs, allow movement, and maintain mineral balance. Bones are classified by shape as long, short, flat, or irregular. The skeletal system includes bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Bone tissue contains compact and spongy bone and bone marrow that produces blood cells. Joints connect bones and can be immovable, slightly movable, or freely movable. Fractures heal through inflammation, callus formation, and remodeling. Osteoporosis is a loss of bone mass leading to brittle bones.
Originalbeschreibung:
General overview of the skeletal system for Human Biology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe skeletal system is composed of 206 bones that provide structure, protect organs, allow movement, and maintain mineral balance. Bones are classified by shape as long, short, flat, or irregular. The skeletal system includes bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Bone tissue contains compact and spongy bone and bone marrow that produces blood cells. Joints connect bones and can be immovable, slightly movable, or freely movable. Fractures heal through inflammation, callus formation, and remodeling. Osteoporosis is a loss of bone mass leading to brittle bones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
305 Ansichten3 SeitenSkeletal System Reviewer
Hochgeladen von
KIRSTEN ALEXI ANGELESThe skeletal system is composed of 206 bones that provide structure, protect organs, allow movement, and maintain mineral balance. Bones are classified by shape as long, short, flat, or irregular. The skeletal system includes bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Bone tissue contains compact and spongy bone and bone marrow that produces blood cells. Joints connect bones and can be immovable, slightly movable, or freely movable. Fractures heal through inflammation, callus formation, and remodeling. Osteoporosis is a loss of bone mass leading to brittle bones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
BIO 11.
01 ○ On demand, bone releases
SKELETAL SYSTEM REVIEWER minerals into the blood to
KIRSTEN ANGELES maintain critical mineral
Note that this reviewer is not as detailed as it could
balances (homeostasis)
be. For more details visit the Principles of Anatomy
and Physiology ● Blood cell production through red
bone marrow
Bones ● Triglyceride storage through yellow
● Bone - an organ made up of several bone marrow
different tissues working together
○ Bone (osseous) tissue
○ Cartilage Classification by Shape
○ Dense connective tissue 1. Long bone - bone in greater length
○ Epithelium than width
○ Adipose tissue ● Diaphysis - bone shaft or
○ Nervous tissue body
● Familiar bones ● Epiphysis - proximal and
○ Hip (pelvic) bones distal ends
○ Ribs ● Examples - humerus (arm
○ Sternum (breastbone), bone)
○ Vertebrae (backbones) 2. Flat bones
○ Skull ● Examples - parietal bone (on
○ Humerus (arm bone) skull)
○ Femur (thigh bone). 3. Short bones
● Human skeleton - 206 bones ● Examples - carpals (on wrist)
Functions 4. Irregular bones
● Support and structure for soft tissues ● Examples - vertebra (small
● Protects vital organs bones forming the backbone)
● Assistance in movement
○ Skeletal muscles attach to Types of Systems
bones, when contracted, 1. Hydrostatic skeleton - supported by
produces movement water/fluid pressure
● Mineral homeostasis (Storage and ● Soft-bodied animals i.e.
release) earthworms, sea anemones
○ Bone tissue makes up about ● Circular muscles squeeze
18% of the weight of the body
human body ● Longitudinal muscles shorten
○ Stores several minerals, the body
especially calcium and 2. Exoskeleton - external skeleton
phosphorus, which contribute supporting animal’s body
to the strength of bone ● Arthropods i.e. insects,
○ Bone tissue stores about spiders
99% of the body’s calcium ● Internal skeleton made of
chitin (a carbohydrate)
●Muscles attach to the ○ Provides protection and
exoskeleton - flexible at joints support and resists stresses
3. Endoskeleton - internal skeleton produced by weight and
● Vertebrates movement
● Made of cartilage/bone ● Spongy bone
● Bone and cartilage; living ○ Location of red bone marrow
tissue (connective tissue) ○ Located in interior of bone
○ Light, reduces all over weight
Exoskeleton vs Endoskeleton of bone, so that bone can
● Exoskeleton move more readily
○ Prevents growth ● Marrow cavity
○ When they burst out it’s ○ Yellow marrow
painful
○ Heavier
● Endoskeleton Bone marrow
○ More protection, less mobility 1. Red bone marrow
● Found in flat bones of
Cartilage sternum, ribs, and ileum
● Cartilage tissue consists of ● Hemopoiesis
chondrocytes (cartilage cells) in a ○ Produces red blood
matrix of collagen protein cells, white blood
● Tough, flexible material that pads cells, and platelets;
joints hemoglobin
● Found in nose and ears ○ consists of
developing blood
Bone Tissue cells, adipocytes,
● Bone is made up of one cells in a fibroblasts, and
matrix of collagen and minerals macrophages within a
● Addition of minerals and nutrients network of reticular
fibers
Bone cells ○ Present in developing
● Osteocytes - bone cell bones of the fetus
● Osteoblasts - precursor and in some adult
● Osteoclasts - old bone cell bones
2. Yellow bone marrow
Bones may be made of ● Found in shaft of long bones
● Compact bone tissue ● Contains fat and connective
○ Contains few spaces tissue
○ Strongest form of bone tissue ● Triglyceride storage
○ found beneath the ○ Yellow bone marrow
periosteum of all bones and consists mainly of
makes up the bulk of the adipose cells, which
diaphyses of long bones store triglycerides.
The stored
triglycerides are a Healing Fractures
potential chemical ● Fracture - break in the continuity of
energy reserve. one
Joints Phases
● Doesn’t give support but gives 1. Reactive
flexibility ● Inflammation, blood clot
● Area where bones meet 2. Reparative
● Holds bones together while allowing ● Callus
the body to move ● Cartilage replaces clot
Types 3. Remodeling
1. Synarthrosis - immovable i.e. skull ● Tigas
2. Amphiarthrosis - slightly movable i.e. ● Cast - to make it straight and
vertebral joints stable
3. Diarthrosis/Synovial - freely Osteoporosis
moveable i.e. shoulders, hips ● Loss of bone mass
● Found at all limb articulations ● Leads to brittle bones
● Surface covered with ● Note: just the endpoint of the
cartilage problem
● Joint cavity covered with Contributors
tough fibrous capsule ● Age
● Cavity lined with synovial ● Lack of calcium and vitamin D
membrane, filled with ● Sedentary
synovial fluid (serous ● Multiple pregnancies
membrane) ● Menopause, alcohol
● Smoking
Ligaments
● Bands of connective tissue
connecting bone to bone
● Either limits/enhances movement
● Provides joint stability
● Enhances joint strength
Tendon
● Fibrous connective tissue bands that
connect bone to muscle
● Enables bones to move when the
muscles contract
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Skeletal System-Lecture NotesDokument9 SeitenSkeletal System-Lecture Notesjcali06100% (5)
- Systems Final Lab ReportDokument8 SeitenSystems Final Lab Reportapi-307749075Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bloom and FawcettDokument30 SeitenBloom and FawcettFarhan RosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDokument49 SeitenChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Endocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDokument5 SeitenEndocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDani Anyika100% (1)
- Reviewer Muscular SystemDokument9 SeitenReviewer Muscular Systemjessa prendol100% (1)
- Pmls Notes (Lesson 5)Dokument5 SeitenPmls Notes (Lesson 5)Eloisa LourdesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDokument27 SeitenThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Worksheet AnswersDokument4 SeitenAssessment Worksheet AnswersLouis UranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemAngelica JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetDokument3 SeitenBiology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetAbhay MonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength Training For WomenDokument232 SeitenStrength Training For WomenGanescu Vlad100% (3)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyAaron Jacob Omaña100% (1)
- Skeletal System ReviewerDokument6 SeitenSkeletal System ReviewerleyluuuuuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 MODULE CHAPTER 3&4 AnaPhy 2020-2021 PDFDokument51 Seiten2 MODULE CHAPTER 3&4 AnaPhy 2020-2021 PDFJosh MagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary System and Disorders IntroductionDokument23 SeitenUrinary System and Disorders IntroductionHananya ManroeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissues ReviewerDokument5 SeitenTissues ReviewerJoannah MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal System 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of BonesDokument5 SeitenSkeletal System 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of Boneslabibah mahmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Prelims ReviewerDokument11 SeitenAnaphy Prelims ReviewerMariz Elizabeth TaytayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: The Human OrganismDokument9 SeitenChapter 1: The Human OrganismMidnight Rosenfield100% (1)
- Skeletal System: Bone CellsDokument3 SeitenSkeletal System: Bone CellsDenise Jezzamine NievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Vessels Review SheetDokument6 SeitenBlood Vessels Review Sheet9Speed93% (14)
- Enzyme Classification Nomenclature PDFDokument11 SeitenEnzyme Classification Nomenclature PDFramsrivatsan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokument13 SeitenCell Structure and FunctionNatalie KwokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seeley's EndocrineDokument5 SeitenSeeley's EndocrineEllä PabustanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityDokument68 SeitenChapter 19 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityAurea Nazaire100% (2)
- Skeletal System ReportDokument8 SeitenSkeletal System ReportRanin, Manilac Melissa S100% (2)
- Digestive SystemDokument60 SeitenDigestive Systemsureshdass50% (2)
- Anaphy TransesDokument3 SeitenAnaphy TransesJoyce ElizaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of at RiskDokument7 SeitenNursing Care of at RiskdominicjimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell: Transport Mechanisms and Cell Permeability: Physioex 1Dokument28 SeitenThe Cell: Transport Mechanisms and Cell Permeability: Physioex 1mdarln808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary SystemDokument20 SeitenUrinary SystemKelvin Mallari100% (1)
- Acidosis and AlkolosisDokument4 SeitenAcidosis and AlkolosisDani PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close Right Arm Fracture: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingDokument12 SeitenClose Right Arm Fracture: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingBrylle Capili100% (1)
- Anaphy LEGIT REVIEWER CHAP1-5Dokument21 SeitenAnaphy LEGIT REVIEWER CHAP1-5stephanie lagdaan100% (1)
- Cardiovascular WorksheetDokument9 SeitenCardiovascular WorksheetPANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Organism ReviewerDokument2 SeitenThe Human Organism ReviewerAliyah and IomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology II - Blood Basics - (Week 3) Flashcards - QuizletDokument7 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology II - Blood Basics - (Week 3) Flashcards - QuizletDani AnyikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4Dokument6 SeitenLesson 4doldol ocampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure and Function of The Digestive SystemDokument3 SeitenThe Structure and Function of The Digestive SystemArnel M. CasapaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wise Laboratory Manual Seeleys 12eDokument3 SeitenWise Laboratory Manual Seeleys 12eEricka LingaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Human Anatomy Divisions of Human PhysiologyDokument16 SeitenChapter 1: Human Anatomy Divisions of Human PhysiologyBeverly A PanganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolysaccharidesDokument12 SeitenPolysaccharidesMuhammad AzimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connective TissueDokument7 SeitenConnective TissueSheena Pasion100% (1)
- Muscular SystemDokument94 SeitenMuscular SystemSpace DragonlordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Anaphy MariebDokument26 SeitenChapter 1 Anaphy MariebKeanna ZurriagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 26 Urinary SystemDokument17 SeitenChapter 26 Urinary SystemAmy Lalringhluani100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To The Human BodyDokument6 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To The Human BodyChristina Markwart100% (1)
- Skeletal SystemDokument103 SeitenSkeletal SystemiamarrhinneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To BiochemistryDokument32 SeitenIntroduction To BiochemistryHazel LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal SystemDokument6 Seiten511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNoch keine Bewertungen
- A&p Lab Ex 06aDokument6 SeitenA&p Lab Ex 06amarycox1989100% (6)
- An Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomyDokument28 SeitenAn Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomydishkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19 Reproductive SystemDokument59 SeitenChapter 19 Reproductive SystemJulianyael TabocoldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument125 SeitenSkeletal SystemJem Pantig100% (4)
- Muscular System ReviewerDokument10 SeitenMuscular System ReviewerGaille DacilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDokument11 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerKyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANAPHY 1st ExamDokument12 SeitenANAPHY 1st ExamVine OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications - Denaturation PDFDokument2 SeitenApplications - Denaturation PDFeleaphoebe16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy - Lec (C6-8)Dokument11 SeitenAnaphy - Lec (C6-8)karelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Chapter AnaphyDokument8 Seiten5 Chapter Anaphyjeanbecera19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Jurnal ReadingDokument35 SeitenLaporan Jurnal ReadingfadiahannisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureDokument6 SeitenMnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureBianx Flores DosdosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteoporosis, Rickets and OsteomalaciaDokument43 SeitenOsteoporosis, Rickets and OsteomalaciahasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anormalidades No Esqueleto de OvinosDokument10 SeitenAnormalidades No Esqueleto de OvinosGildeniAguiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implants in Bone: Part II. Research On Implant OsseointegrationDokument19 SeitenImplants in Bone: Part II. Research On Implant Osseointegrationcarol colmenaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marshal Cavendish Science - Activity Book With Answer - Stage 4 - C02Dokument17 SeitenMarshal Cavendish Science - Activity Book With Answer - Stage 4 - C02Syed JunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induced Membrane Technique Pearls and Pitfalls.9Dokument3 SeitenInduced Membrane Technique Pearls and Pitfalls.9Residentes IJF 2016Noch keine Bewertungen
- 233-Article Text-355-1-10-20200213Dokument17 Seiten233-Article Text-355-1-10-20200213Kristina ParasNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Xrays Reporting FormatesDokument21 SeitenAll Xrays Reporting FormatesMubin BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menopause Complete 2022Dokument35 SeitenMenopause Complete 2022CALVO, JUAN BERNARDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment MusculoskeletalDokument33 SeitenAssessment MusculoskeletalRubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Module4 TasksBC-DiazDokument5 SeitenAP Module4 TasksBC-DiazJohn Rafael DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alveolar Bone GraftDokument12 SeitenAlveolar Bone Graftanon_620185252Noch keine Bewertungen
- Correlation of Soft Tissue and Skeletal Injuries in Cases of Violent Death: A Retrospective Study of Autopsy Cases For Forensic AnthropologyDokument7 SeitenCorrelation of Soft Tissue and Skeletal Injuries in Cases of Violent Death: A Retrospective Study of Autopsy Cases For Forensic AnthropologyanggunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The A To Z of Surface AnatomyDokument236 SeitenThe A To Z of Surface AnatomyAspenPharma83% (6)
- Ortho Instruments & ImplantsDokument106 SeitenOrtho Instruments & ImplantsBi PinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masquelet MainDokument5 SeitenMasquelet MainKlausNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2peggshellasanalternativechalk FinalDokument75 Seiten2peggshellasanalternativechalk FinalEsona Rachelyn P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maja Musculo Sceletal-NovaDokument18 SeitenMaja Musculo Sceletal-NovaLuka KoloskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Bone Formation and RemodelingDokument4 SeitenNormal Bone Formation and RemodelingFernando AnibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giant Cell Lesions of Oral CavityDokument4 SeitenGiant Cell Lesions of Oral CavityPreetam PatnalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utritional Isorders: Dr. Anamika DevDokument66 SeitenUtritional Isorders: Dr. Anamika DevANIKANoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDokument157 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver Talip100% (1)
- Uman Hysiology: Endocrine Control of Growth and MetabolismDokument24 SeitenUman Hysiology: Endocrine Control of Growth and Metabolismpanairina03026273Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT SIX: Forensic Science Text QuestionsDokument2 SeitenUNIT SIX: Forensic Science Text QuestionsGabo ArtiedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revise Anatomy in 15 Days K Raviraj VD AgrawalDokument9 SeitenRevise Anatomy in 15 Days K Raviraj VD AgrawalNelson LoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The Musculoskeletal SystemDokument245 SeitenDisorders of The Musculoskeletal SystemFirifan DiribaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danger of Brittle Bones - 04Dokument5 SeitenDanger of Brittle Bones - 04vksk1951Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osteotomy at Low-Speed Drilling Without Irrigation Versus High-Speed Drilling With Irrigation: An Experimental StudyDokument6 SeitenOsteotomy at Low-Speed Drilling Without Irrigation Versus High-Speed Drilling With Irrigation: An Experimental Studyanilsamuel0077418Noch keine Bewertungen