Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Experiment 202: Conservation of Momentum: The Ballistic Pendulum
Hochgeladen von
Cassandra Julia de JesusOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Experiment 202: Conservation of Momentum: The Ballistic Pendulum
Hochgeladen von
Cassandra Julia de JesusCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Experiment 202: Conservation of Momentum: The Ballistic Pendulum
Cassandra Julia T. de Jesus
School of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry
Mapua Institute of Technology
I. Conclusion
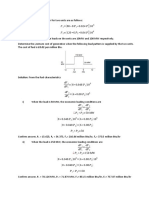
Momentum is the product of the mass of a moving body and its velocity. It could also be defined as the
mass in motion. When an object moves, then that object is said to have momentum because there’s mass and the
object is moving. An object that is moving at a high velocity but light can have a large momentum. Also, a heavy
object moving slowly has a large momentum.
According to Newton’s first law of motion, an object will remain at rest or constantly move unless acted
upon by an external force. Therefore, the forces experienced by a body in a collision changes the momentum of the
system. Without the external forces, the momentum remains the same. The momentum of the objects before the
collision is equal to the momentum of the objects after the collision. Since the mass is constant, the external force
that changes the velocity of the moving object, changes the momentum.
In a closed system, the total momentum and the total energy does not change. There are two types of
collisions which are the inelastic and elastic collision and in these collisions, the total momentum and total energy in
a system is conserved. In an elastic collision the kinetic energy is not conserved. It may be converted to another
form of energy. And that formed energy doesn’t get converted back to a kinetic energy like in a swinging ball tied to
the ceiling where the kinetic energy transforms to potential energy. As the ball goes down, the potential energy gets
converted back to kinetic energy. Nevertheless, the total energy stays the same.
In all kinds of collision, the total momentum is conserved whether in an elastic or in an inelastic collision
as long as the collision occurred in an isolated system. When there’s a collision between two objects in a closed
system, the total momentum of the two objects before and after the collision is the same. Provided that; there are no
external forces.
II. Application
When a large truck moving at a constant velocity is carrying a heavy load has to stop before the red lights
on the stop light turns on. It would be hard to stop the truck even if it is not moving fast because of its large
momentum caused by having a large mass.
When a moving van accidentally hits a non-moving car and the car moves to the direction the force is
applied on it, there’s an elastic collision. Say, the moving van has a momentum of 20,000 kg m/s and the non-
moving car has zero momentum. Once the van hits the non-moving car, the non-moving car would move away from
the van because of the force applied so it would have a velocity, thus having momentum. The car would gain an
amount of momentum say 5000 kg m/s and the moving car would then have a momentum of 15,000 kg m/s. The
total momentum of the system is unchanged and so as the kinetic energy. This also applies to the billiard ball being
hit by another ball.
When a two carts moving towards each other and stick together while moving in a certain velocity , there’s
inelastic collision between them. Assuming that the masses of the cart are the same, and cart 1 as a velocity of 10m/s
while cart to only has a velocity of 6 m/s. Cart 1 would have a larger momentum because of its higher velocity. So
when the carts stick, they would go to the direction in which cart 1 is heading towards to. The kinetic energy would
be transformed into a different form and the total momentum would stay the same.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- M3 Studynotes Impulse and MomentumDokument4 SeitenM3 Studynotes Impulse and MomentumDavid UtahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MotionDokument38 SeitenMotionTareqqqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionDokument5 SeitenModule 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionAllen Simon BaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MomentumDokument18 SeitenMomentumpalicpicantorearichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Linear Momentum 1Dokument19 SeitenConservation of Linear Momentum 1Kella OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimalist Vintage Medieval Brown Museum PresentationDokument9 SeitenMinimalist Vintage Medieval Brown Museum PresentationChaitali agarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Energy Physics by SachaDokument100 SeitenIntroduction To Energy Physics by SachaBalasbramani ThangavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksVon EverandPotential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 7 - Newtons Laws of MotionDokument47 SeitenCHAPTER 7 - Newtons Laws of Motionoman92870164Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 - Newton - S Laws of MotionDokument6 SeitenModule 5 - Newton - S Laws of MotionAllen Simon BaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics - Kinetic Energy & MomentumDokument15 SeitenApplied Mechanics - Kinetic Energy & MomentumfinopectradingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic EnergyDokument2 SeitenKinetic EnergynettextsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 69Dokument5 Seiten69Josh Dominic TeleronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics (CETs)Dokument9 SeitenPhysics (CETs)AkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion Revision NotesDokument14 SeitenCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion Revision NotesBriti DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Energy EquationDokument4 SeitenKinetic Energy Equationapi-150547803Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 2 Part 1Dokument14 SeitenQuarter 2 Part 1yukikyo osamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Energy: Navigation SearchDokument13 SeitenKinetic Energy: Navigation SearchPawan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- q1 Lesson3 Kinetic&Potential EnergyDokument17 Seitenq1 Lesson3 Kinetic&Potential EnergyVincent AbucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impulse - MomentumDokument5 SeitenImpulse - MomentumMichael CaingletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy, Force & Motion: ScienceDokument7 SeitenEnergy, Force & Motion: ScienceRebeccaaaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of Motion Final PDFDokument32 SeitenLaw of Motion Final PDFMark RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Further MechanicsDokument11 SeitenFurther MechanicsBecky TenneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy, Force, & Motion: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsVon EverandEnergy, Force, & Motion: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDokument26 SeitenPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDokument24 SeitenNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Motion: Physical ScienceDokument16 SeitenForce and Motion: Physical ScienceAICKEN N. SAGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1Dokument4 SeitenActivity 1visbarcenillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion-XellentDokument90 SeitenLaws of Motion-Xellentigulati2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Co777Dokument10 SeitenCo777Rafi HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - : ForceDokument10 SeitenName: - : ForceGB SoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFDokument19 SeitenAP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFAbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Week 3Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet Week 3Jaybie TejadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Phys1 - Momentum Skill Based Problems - 2022 02 20Dokument14 SeitenAp Phys1 - Momentum Skill Based Problems - 2022 02 20黃吏維Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of MotionDokument24 SeitenLaws of MotionAna Marie Renton100% (1)
- Angela's Linear Momentum and CollisionDokument13 SeitenAngela's Linear Momentum and CollisionJudith BagasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- LawsDokument63 SeitenLawsJonathan Libo-onNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS1160Dokument17 SeitenPHYS1160supNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyze The Cases and Answer The QuestionsDokument31 SeitenAnalyze The Cases and Answer The QuestionsJohn Lloyd PedresoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momentum Outline 20 PDFDokument7 SeitenMomentum Outline 20 PDFJimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konservasi Energi: Nama: Viona Febrina NIM: 1405119196 Kelas: Fisika A1Dokument4 SeitenKonservasi Energi: Nama: Viona Febrina NIM: 1405119196 Kelas: Fisika A1Viona FebrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Grade 9Dokument5 SeitenReviewer Grade 9Louise Frances HugnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impulse and Momentum For KALAMDokument15 SeitenImpulse and Momentum For KALAMNordin fatihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- VA MSPS LawsofForceandMotion EXPLAIN STEMscopediaDokument7 SeitenVA MSPS LawsofForceandMotion EXPLAIN STEMscopediaNikkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suresh Gyan Vihar University: Physics GA 1 BSC PCM 1 SemesterDokument11 SeitenSuresh Gyan Vihar University: Physics GA 1 BSC PCM 1 SemesterRavan RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inertia and Mass Newton's Laws of Motion Linear Momentum and Its Conservation Impulse Work and Energy Principle of Conservation of EnergyDokument39 SeitenInertia and Mass Newton's Laws of Motion Linear Momentum and Its Conservation Impulse Work and Energy Principle of Conservation of EnergyZaforNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Motion in ScienceDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Motion in ScienceNiñalyn TugbongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksVon EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd ChapterDokument11 Seiten3rd ChapterMushfiqur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momentuminanutshell 170220094913Dokument29 SeitenMomentuminanutshell 170220094913Melerose Dela SernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovDokument16 Seiten02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion 2Dokument30 SeitenNewton's Laws of Motion 2Emmanuel ChachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion 2Dokument30 SeitenNewton's Laws of Motion 2Emmanuel ChachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion 2Dokument30 SeitenNewton's Laws of Motion 2Emmanuel ChachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAED PHYC2121 General Physics 1Dokument5 SeitenBAED PHYC2121 General Physics 1Ezra Orita CeletariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of MotionDokument18 SeitenNewton's Laws of MotionCarah Jean Hurtado GillegaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic EnergyDokument7 SeitenKinetic EnergyWillow SapphireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation of Mechanical EnergyDokument9 SeitenTransformation of Mechanical EnergykairawrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For Practice: Basic Training For Oil and Chemical Tanker Cargo Operation (BTOCTCO)Dokument38 SeitenQuestions For Practice: Basic Training For Oil and Chemical Tanker Cargo Operation (BTOCTCO)Ashok YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flywheel HandoutDokument5 SeitenFlywheel Handoutamanuelfitsum589Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aalborg OL: The Large Capacity Modular Boiler PlantDokument2 SeitenAalborg OL: The Large Capacity Modular Boiler Plantthlim19078656Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument3 SeitenUntitledUsama aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kbuz PDFDokument2 SeitenKbuz PDFAnonymous FH8OunZrXNoch keine Bewertungen
- GA-I (H) D 1000 Series ROBOTDokument1 SeiteGA-I (H) D 1000 Series ROBOTmfarrukhkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Insulated Distribution CablesDokument10 SeitenPaper Insulated Distribution Cablesdeepak2628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spray Dryer DesignDokument38 SeitenSpray Dryer DesignMapa JoyceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Report G60 - 2BDokument21 SeitenTest Report G60 - 2BMr IlchamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsDokument14 SeitenAssessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsKarthik SRSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Structure and Function PDFDokument2 SeitenPlant Structure and Function PDFPT.Susan Angwyn Gemilang 8Noch keine Bewertungen
- 08 FS EtpDokument18 Seiten08 FS EtpKatamaneni KoteswararaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCEN7221 SlidesDokument240 SeitenMCEN7221 SlidesVladJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biefeld-Brown Effect and Space CurvatureDokument6 SeitenBiefeld-Brown Effect and Space CurvaturejayandbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Science of Diet & ExerciseDokument46 SeitenThe Science of Diet & ExerciseRomkar93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Climate Change (The Science of Climate Change)Dokument30 SeitenIntroduction To Climate Change (The Science of Climate Change)enoch taclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument8 SeitenSyllabusSameer SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xylem Company Profile 2012 PortableDokument26 SeitenXylem Company Profile 2012 Portablegeorge_efstratiadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Industry Practices Piping: PIP PNC00003 Process Unit and Offsites Layout GuideDokument15 SeitenProcess Industry Practices Piping: PIP PNC00003 Process Unit and Offsites Layout GuideSunil Sawant100% (1)
- LBO Case Study - Volta Electronics Co. - v3Dokument14 SeitenLBO Case Study - Volta Electronics Co. - v3madamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTC4020 - 55V Buck-Boost Multi-Chemistry Battery ChargerDokument42 SeitenLTC4020 - 55V Buck-Boost Multi-Chemistry Battery ChargerdevchandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Fuel System: Malaysian Institute of Aviation TechnologyDokument15 SeitenAircraft Fuel System: Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technologyrihhh hhNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMD01 Instruction ManualDokument72 SeitenHMD01 Instruction ManualLevonYeghyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fault MVA Calc - PPT (Compatibility MDokument20 SeitenFault MVA Calc - PPT (Compatibility MK.T.100% (1)
- AirPhoton Sampling Station Fact SheetDokument3 SeitenAirPhoton Sampling Station Fact Sheetnguyendacloc1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Problems On RectifiersDokument12 SeitenSolved Problems On RectifiersAravind KarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Dimensions and Piping Details: PX Pressure Exchanger Energy Recovery DeviceDokument2 SeitenExternal Dimensions and Piping Details: PX Pressure Exchanger Energy Recovery Deviceprasad5034Noch keine Bewertungen
- WEEE Calculation Tool ManualDokument39 SeitenWEEE Calculation Tool ManualcanaconaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ToRs For - Nyamugasani GFS - 0Dokument41 SeitenToRs For - Nyamugasani GFS - 0pepegrillo891Noch keine Bewertungen
- I9183en PDFDokument156 SeitenI9183en PDFAulia QoriNoch keine Bewertungen