Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rdme 3
Hochgeladen von
pradip panthaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rdme 3
Hochgeladen von
pradip panthaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE)
ISSN(e) : 2278-1684, ISSN(p) : 2320–334X, PP : 15-21
www.iosrjournals.org
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
S. H. Gawande, L. G. Navale, A. A. Keste
(Department of Mechanical Engineering, M. E.S. Collegeof Engineering, Pune, India)
ABSTRACT :The Sand Washer machine is used to wash off impurities like clay, silt, and other unwanted
particles from sand to make it fit for use. This sand washer is specially designed to wash sand used in
construction and make it comply with Indian Standard. The USP of this machine is that it combines all three
steps; screening, conveying, and washing, into one robust, compact machine. The screening is done with the
help of a wire mesh. Sand is conveyed and washed simultaneously by a paddle screw conveyor. The rotary
bucket elevator scoops up the sand from the tub and on its way to delivery, drains water from sand. In this
context, the objective of this work was to design the transmission system to drive the machine to maintain the
output of washed sand at 6m3/hr by A particular design was subsequently narrowed down with reference to
certain criteria viz. Relative ease of use, ruggedness, space constraints and availability. While doing so, we
explored manual as well as computer assisted design. A comprehensive account of such design-centric efforts
and finite element analysis is furnished in the present work. The design, analysis, manufacturing and testing
work is carried at Deccan Construction Equipment and Machinery, Pune.
Keywords -Sand Washing Machine, USP, FEA
I. INTRODUCTION
TheDeccan Construction Equipment & Machinery Pvt. Ltd is an ISO 9001:2008 certified company and one of
the leading names engaged in manufacturing and supplying of construction machines in India. The company is
widely acclaimed for offering a qualitative range of machines that stands high in terms of sturdiness and
performance, conforming to international standards of quality.Leveraging on expertise and potentiality of
workforce, they have developed innovative technology that is used in manufacturing of qualitative range of
construction machines like bar cutting machine, bar bending machine, mini lift, multi rider, tower hoist, etc.
Their range of machines not only caters to requirement of clients in domestic arena but they are in process of
expanding their business in Europe, China, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Australia, Far East and Sri Lanka.
II. PROBLEM FORMULATION AND OBJECTIVE
According to Bureau of Indian Standards the sand used for construction purpose must meet the quality stated by
IS383:1970 and IS650:1991. For different construction of works requires different standards of sands. For
brick works requires the finest module of fine sand should be 1.2 to 1.5 and silt content should not be more
than 4 %. For plastering works requires the finest module of fine sand, it should not be less than 1.5 and silt
content should not be more than 4 %. For Concerting Works worksrequires the coarse sand with the finest
modulus 2.5 to 3.5 and silt contents should not be more than 4%.Silt is granular material of a size somewhere
between sand and clay whose mineral origin is quartz and feldspar. In this context, the project team at Deccan
Construction Equipment and Machinery was asked to maintain the output of washed sand at 6m 3/hr. In order to
satisfy these requirements following objectives were set:
Calculating power required to drive the sand washing machine by considering the various power
losses in the system.
Ensuring a sand delivery at rate of 6m3/hr by selecting the appropriate prime mover based on power
calculation.
Designing a single stage worm type reduction gear box and a roller chain drive.
To accommodate the power line within an area of 1x1m and design the required mountings.
To perform structural analysis of chassis.
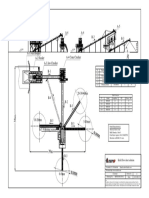
III. CAD MODEL OF SAND WASHER MACHINE
The main components of the developed sand washer machine for technical specifications as given in Table1 as
shown in Fig.1 [A, B] are as follows:
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 15 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
1. Screen
2. Chassis
3. Screw Conveyor
4. Rotary Bucket Elevator
5. Transmission
TABLE 1 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
Wheel bucket diameter (mm) 920
Speed of impeller (rpm) 8.89
Output of washed sand (m3/hr) 6
Screw diameter (mm) 490
Pitch of screw (mm) 670
No. of paddles 8
Screen designation (mm) 20
Length of tub (mm) 1430
Overall dimensions (L × B × H) (mm) 2400 × 1015 × 1721
Fig.1 [A] CAD model of Sand Washer machine
Fig. 1[B] CAD model of Sand Washer machine
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 16 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
Screen
A sand screen is typically categorized based on the size of hole of the weld mesh. This helps in preventing large
stone particles present in sand from getting into the screw conveyor. The screen consists of a two rectangular
frame arranged at right angles to each other. A mesh is formed by arranging 3mm wire diameter in rectangular
array as shown in the Fig.2. The screen designation for this machine is decided based on gap between the screw
blade and tub, which is 20mm. If a particle with larger size enters the machine it might jam it, hence causing
damage to the machine.
Fig. 2 Screen
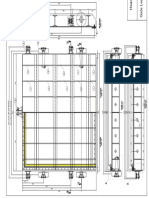
Chassis
The chassis forms the basic structure of the machine [Fig.2]. It is a skeletal frame made by welding mild steel
channels and angles together. The chassis is the seat on which trough, screw conveyor and the rotary elevator
are mounted. It provides the machine with high strength and flexibility. The chassis supports the load of
machine and also withstands various shocks and forces produced. The chassis is provided with wheels which
makes the machine highly portable. The chassis’ structure dimensions as shown in Fig.2 are: 2400 × 1015 ×
1721 (L × B × H) mm.
Fig. 2 Chassis
Screw Conveyor
It is a mechanism [Fig.3] that uses a rotating helical screw mounted on the shaft along with the bucket elevator
and this is mounted in a trough made out of 3mm hot rolled sheet in which the water is contained. When the
machine is started this screw conveyor churns and pushes the sand towards the rotary elevator. In this action the
silt content in it dissolves in water and the washed sand is picked up and discharged by the rotary elevator. To
avoid the saturation of the silt a continuous supply of water is maintained. The water flow required depends on
the silt contained in sand. The rate of volume transfer is proportional to the rotation rate of the shaft. The screw
conveyor is of paddle type which consists of eight blades arranged in a helical pattern of pitch 67mm and length
1430mm.
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 17 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
Fig.3 Screw Conveyor
Rotary Bucket Elevator
It is a mechanism for hauling flowable bulk materials as shown in Fig.4. It consists of buckets to contain the
material. The buckets are made from perforated sheet to drain out water. The rotary elevator is formed by
welding bent plates between two rimmed discs. The plates are so arranged that they form 12 trapezoidal
buckets. Each bucket can hold a maximum of 0.832 litres of wet sand. It receives sand and water mixture from
the screw conveyor which is collected in the circular tub. During its operation it scoops up the wet sand from the
circular tub and discharges. The direction of rotation is as shown in the Fig.4 below.
Fig. 4 Rotary Elevator
Transmission Rotary Bucket Elevator
It transmits power from the electric prime mover to screw conveyor and rotary elevator through worm type
reduction gearbox as shown in Fig.5. The transmission system consists of 5 HP foot mounted electric motor
coupled with flexible roller chain coupling. The ratio of the gearbox is 50:1.There is a second reduction
between gearbox and screw conveyor coupled by 25.4 mm pitch chain and sprocket. The system is mounted on
the chassis above the rotary elevator within an area of 1m x 1m.
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 18 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
Fig.5 Transmission
IV. WORKING OF SAND WASHER MACHINE
1. The electric motor runs the impeller after decelerated by the gear wheels and chain drive.
2. Sand and water flow into the washing tub in opposite direction with each other, rolls with the impeller,
and grinds with each other.
3. The impurity covering the sand is washed away with the cross flow.
4. By adding more water, the strong water flow will take away waste and some low-weight wastes from
the washing launder.
5. Through the above process the cleaning function is done.
6. The clean sand is lifted up by the rotor buckets and when it goes up the water remaining in clean sand
begins to drop from the holes in the buckets.
V. DESIGN VALIDATION
This section focus on the validation of the design performed by using CAD software explained in
earlier section to maintain the output of washed sand at 6m 3/hr.
Gear Box Efficiency:
As per the technical specification of sand washer machine in Table 1 and for the selected specifications of the
gearbox we have,
Velocity Ratio (V.R.) = 50
We have relation for lead angle (λ) and velocity ratio as,
Cot3λ = V.R.
Cot3λ = 50
Lead angle, λ = 15.18
𝜋×𝐷𝑤 ×𝑁𝑤
Rubbing velocity, 𝑣𝑟 =
cos 𝜆
Where; Dw= Pitch circle diameter of worm(m)
Nw= Speed of worm(rpm)
𝜋×0.04712 ×1440
𝑣𝑟 =
cos 15.18
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 19 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
𝒗𝒓 = 220.872 m/min
𝑟 𝑣
Coefficient of friction, µ= 0.025 + 18000
220 .872
µ= 0.025 + 18000
... (Since 𝑣𝑟 is greater than 180 m/min)
µ= 0.0372
Angle of friction, ɸ1 = tan-1
ɸ1 = tan-1 ×0.0372
ɸ1 = 2.134
tan 𝜆
Efficiency Of Gear Drive, ƞ = tan (𝜆+ ɸ
1)
tan 15.18
ƞ=
tan
(15.18+2.134 )
ƞ = 87.03 %
Flow Calculation:
Using the above selected specifications for the prime mover, gear box and chain drive we have,
Speed of Motor = 1440 rpm
Gearbox Reduction = 50:1
Chain Drive Reduction = 2.643
Actual Speed of Screw Shaft (n):
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑𝑜𝑓𝑚𝑜𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑠 ℎ 𝑎𝑓𝑡
n = 𝐺𝑒𝑎𝑟𝐵𝑜𝑥𝑅𝑒𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ×𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑖𝑛𝐷𝑟𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑅𝑒𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
1440
n =
50 ×2.643
n = 10.89 rpm
Actual Sand Delivery Rate:
Sand delivery rate (Q’):
Q’ = 60 × (π/8 ×D2) S n ×ψ C
Where; Q’= max wet sand discharge
S = pitch of screw in m
Ψ = loading efficiency
n = actual rpm of the screw shaft
C = fac tor for inclination to horizontal
D = screw diameter in m
Q’= 60 (π/8 0.4322) 0.67 10.89 0.3 1
Q’ = 9.625 m3 / hr.
The flow able bulk is a mixture of sand and water. Thus for the volume of sand discharged by the screw
conveyor;
(Sand occupancy assumed to be 65% for proper churning to take place.)
Q= 0.65 Q’
3
Q = 6.545 m / hr.
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 20 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Design, Development & Validation of Sand Washing Machine
Advantages:
1. Simple structure: The structure is made of standard material and size in an orthodox shape making
manufacturing easy.
2. Low Maintenance: The machine is robust and can be used at construction sites.
3. Transmission isolation: The power train is placed in a separate compartment above the machine, hence
isolating it.
4. No pollution: Electric motor is used to operate the washer.
5. High Durability: The machine can operate even in harsh working conditions.
6. Less wastage of sand:Unlike manual labour where sand is cleaned by blowing off impurities which also
results in wastage of fine sand, the sand washer uses water for cleaning.
7. Higher Discharge: More output in a given time frame over manual labour.
8. User friendly: No skilled labour required for operating the machine.
9. Portability: Wheels are provided to enhance mobility
Applications:
The developed sand washer machine for given technical specifications can be widely used for cleaning
materials in the following industries:
1. Quarry
2. Minerals
3. Building materials
4. Transportation
5. Chemical industry
6. Hydropower
7. Cement mixture station
8. Especially applicable for washing construction and paving sand.
VI. CONCLUSION
In this paper the stated objective to design of the sand washer machine with advanced transmission system to
maintain the output of washed sand at 6m3/hr is presented. The paper confined to carry out the selection with
justification and validation of the setup by developing the 3D model of the machine and related design
calculations. In the second part of this paper detailed finite element analysis to perform structural analysis is
explained. It is anticipated that our design centric efforts would contribute to some extent in realizing the
objectives of the modifying the Sand Washer System for Deccan Construction Equipment and Machinery Ltd.
REFERENCES
1. Design Data,Faculty of Mechanical Enginnering, PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore,(1978).
2. R. S. Khurmi , Machine Design, S.Chand and Company Ltd., New Delhi, (2012).
3. J. E.Shigley, Mechanical Engineering Design, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd, New
Delhi(2001).
4. V.B.Bhandari, Introduction to Machine Design, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd, New Delhi.
(2001).
Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering 21 | Page
M.E.Society's College of Engineering, Pune, India
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Catalogue ALL COMBINED PDFDokument28 SeitenCatalogue ALL COMBINED PDFpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Structures in Power Plants - DHI Solution2 PDFDokument2 SeitenHydraulic Structures in Power Plants - DHI Solution2 PDFpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEFID QUOTATION OF 50tph Crushing PlantDokument9 SeitenKEFID QUOTATION OF 50tph Crushing Plantpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Energy Handbook: HydroelectricityDokument12 SeitenSustainable Energy Handbook: Hydroelectricitypradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEFID 100-150 TPH Crushing PlantDokument1 SeiteKEFID 100-150 TPH Crushing Plantpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling of Run-of-River IntakesDokument10 SeitenComputational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling of Run-of-River Intakespradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Controls For Hydroelectric Powerplant Noise Reduction PDFDokument33 SeitenEngineering Controls For Hydroelectric Powerplant Noise Reduction PDFpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract Breach and Payment For Environmental Services: A Case From The Kulekhani III Hydroelectric Project in NepalDokument7 SeitenContract Breach and Payment For Environmental Services: A Case From The Kulekhani III Hydroelectric Project in Nepalpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Pressure Tunnels of Hydro Power Plant Ermenek: Conference PaperDokument7 SeitenDesign of Pressure Tunnels of Hydro Power Plant Ermenek: Conference Paperpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainability 12 01676 PDFDokument40 SeitenSustainability 12 01676 PDFpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Infrastructure - Plants and Switchyards: Design Standards No. 4Dokument48 SeitenElectrical Infrastructure - Plants and Switchyards: Design Standards No. 4pradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME B31.3 Questions and Answers-SignedDokument5 SeitenASME B31.3 Questions and Answers-Signedpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Road Network of NepalDokument15 SeitenStrategic Road Network of Nepalpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical Fixed Wheel Gate-02Dokument1 SeiteVertical Fixed Wheel Gate-02pradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication Details of Bend-Pressure Penstock PipeDokument1 SeiteFabrication Details of Bend-Pressure Penstock Pipepradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trash Rack Cleaning MachineDokument9 SeitenTrash Rack Cleaning Machinepradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation Purpose Boq HM PDFDokument1 SeiteQuotation Purpose Boq HM PDFpradip panthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- GSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFDokument27 SeitenGSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFAbdul GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscular System NotesDokument6 SeitenMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Construction Manager in ST Louis MO Resume Mark JensenDokument3 SeitenCivil Engineering Construction Manager in ST Louis MO Resume Mark JensenMark JensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMDokument18 SeitenAngles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMmheojhun0% (1)
- G5 Series User ManualDokument22 SeitenG5 Series User ManualDaniel MekonnenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Installation Rules For Connection To Electricity Network (See Chapter 14)Dokument83 SeitenService Installation Rules For Connection To Electricity Network (See Chapter 14)EduardoMorcilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPM Pert Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDokument2 SeitenCPM Pert Multiple Choice Questions and Answersptarwatkar123Noch keine Bewertungen
- LAC BrigadaDokument6 SeitenLAC BrigadaRina Mae LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShowimgDokument76 SeitenShowimgROSHAN ROBERTNoch keine Bewertungen
- PL SQL Exercise6Dokument2 SeitenPL SQL Exercise6Nishant AndhaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board of DirectorsDokument2 SeitenBoard of DirectorsjonahsalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual of CHISON IVis 60 EXPERT PDFDokument164 SeitenUser Manual of CHISON IVis 60 EXPERT PDFJuan Carlos GoyzuetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IHRM Midterm ASHUVANI 201903040007Dokument9 SeitenIHRM Midterm ASHUVANI 201903040007ashu vaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media EthicsDokument11 SeitenMedia EthicsSreekanth Reddy100% (2)
- Drive Engineering - Practical Implementation SEW Disc Brakes 09202218 - G1Dokument90 SeitenDrive Engineering - Practical Implementation SEW Disc Brakes 09202218 - G1Anonymous ntE0hG2TPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment of Officers in Grade B' (General) - DR - By-2019Dokument2 SeitenRecruitment of Officers in Grade B' (General) - DR - By-2019Shalom NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Definition of Manufacturing SystemDokument18 SeitenBasic Definition of Manufacturing SystemRavenjoy ArcegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 329 Cryogenic Valves September 2016Dokument8 Seiten329 Cryogenic Valves September 2016TututSlengeanTapiSopanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math912 2Dokument7 SeitenMath912 2Mbq ManbriquaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0Dokument119 SeitenRobotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0nonfarb14thNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Radar Echo Lagrangian Extrapolation Nowcasting by Blending Numerical Model Wind Information: Statistical Performance of 16 Typhoon CasesDokument22 SeitenImproving Radar Echo Lagrangian Extrapolation Nowcasting by Blending Numerical Model Wind Information: Statistical Performance of 16 Typhoon CasesLinh DinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netflix Annual Report 2010Dokument76 SeitenNetflix Annual Report 2010Arman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirements CompressDokument9 SeitenSoftware Requirements CompressApni Duniya100% (1)
- Examples of Consonant BlendsDokument5 SeitenExamples of Consonant BlendsNim Abd MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover PageDokument209 SeitenCover PageABHISHREE JAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Accounting and Finances Accounting and Finance ProgramDokument3 SeitenDepartment of Accounting and Finances Accounting and Finance Programwossen gebremariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter and Materials (Grade 6 English)Dokument80 SeitenMatter and Materials (Grade 6 English)Primary Science Programme100% (5)
- Electrochemistry DPP-1Dokument2 SeitenElectrochemistry DPP-1tarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- EWC 662 English Writing Critical Group Work Portfolio: Submitted ToDokument31 SeitenEWC 662 English Writing Critical Group Work Portfolio: Submitted ToNurul Nadia MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barclays Personal Savings AccountsDokument10 SeitenBarclays Personal Savings AccountsTHNoch keine Bewertungen