Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
24 - B - SC - Fashion Tech - & Costume Designing Syllabus (2017-18)
Hochgeladen von
Palanisamy KOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
24 - B - SC - Fashion Tech - & Costume Designing Syllabus (2017-18)
Hochgeladen von
Palanisamy KCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
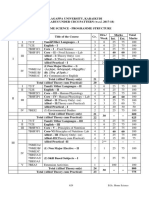
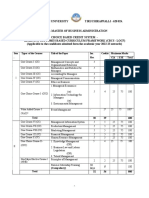
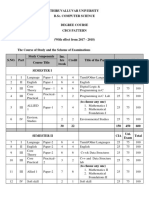
ALAGAPPA UNIVERSITY, KARAIKUDI
NEW SYLLABUS UNDER CBCS PATTERN (w.e.f.2017-18)
B.Sc., FASHION TECHNOLOGY& COSTUME DESIGNING PROGRAMMING STRUCTURE
Course Hrs./ Max. Marks
Sem. Part Title of the Course
Code Cr. Week Int. Ext. Total
I 711T Tamil/other languages – I 3 6 25 75 100
II 712E English – I 3 6 25 75 100
7BFC1C1 Core – I– Fashion Designing 4 6 25 75 100
7BFC1C2 Core–II– Basic Sewing Techniques 4 6 25 75 100
III Allied – I (Theory only) (or) 5 5 25 75 100
Allied – I(Theory cum Practical) 4 3 15 60 75
I
Allied Practical – I - 2** -- -- ---
Non-Major Elective – I –
7NME1A/ A)jkpo;nkhopapd; mbg;gilfs;/
IV 2 1 25 75 100
7NME1B/ B) ,f;fhy ,yf;fpak; /
7NME1C C) Communicative English
Total(Allied -Theory only) 21 600
30 - -
Total(Allied -Theory cum Practical) 20 575
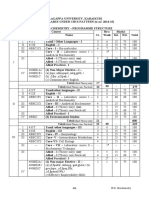
I 721T Tamil/other languages – II 3 6 25 75 100
II 722E English – II 3 6 25 75 100
7BFC2C1 Core – III – Textile Science 4 6 25 75 100
7BFC2P1 Core-IV–Fashion Designing -Practical 4 5 40 60 100
II Allied–II(Theory only) (or) 5 5 25 75 100
III Allied–II(Theory cum Practical) 4 3 15 60 75
Allied Practical – II 2 2 20 30 50
IV 7BES2 (3) Environmental Studies 2 2 25 75 100
Total(Allied -Theory only) 21 600
30 - -
Total(Allied -Theory cum Practical) 22 625
I 731T Tamil /other languages – III 3 6 25 75 100
II 732E English – III 3 6 25 75 100
7BFC3C1 Core–V–Principles of Pattern Making 4 5 25 75 100
Core–VI–Basic Sewing Techniques
7BFC3P1 4 5 40 60 100
and Pattern Making -Practical
III Allied–III (Theory only) (or) 5 5 25 75 100
Allied–III(Theory cum Practical) 4 3 15 60 75
III Allied Practical – III -- 2** -- -- --
(1) Non-major Elective – II –
7NME3A/ (A),yf;fpaKk;nkhopg;gad;ghLk;/
7NME3B/ (B)goe;jkpo; ,yf;fpaq;fSk; 2 1 25 75 100
7NME3C ,yf;fpa tuyhWk; /
IV
(C) Effective Employability Skills
7SBS3A1/
7SBS3A2/ (2) Skill Based Subjects – I 2 2 25 75 100
7SBS3A3
V 7BEA3 Extension activities 1 -- 100 -- 100
Total(Allied -Theory only) 24 30 - - 800
606 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
Total(Allied -Theory cum Practical) 23 775
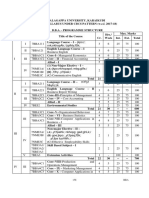
I 741T Tamil /other languages – IV 3 6 25 75 100
II 742E English – IV 3 6 25 75 100
7BFC4C1 Core–VII–Textile Dyeing and Printing 4 4 25 75 100
Core –VIII– Fabric Embellishment - 100
7BFC4P1 4 5 40 60
Practical
Allied – IV-(Theory only) (or) 5 5 25 75 100
Allied–IV-(Theory cum Practical) 4 3 15 60 75
IV III Allied Practical – IV 2 2 20 30 50
IV 7SBS4B1/ (2) Skill Based Subjects – II
7SBS4B2/ 2 2 25 75 100
7SBS4B3
IV 7BVE4/ (4) Value Education /
7BMY4/ Manavalakalai Yoga / 2 2 25 75 100
7BWS4 Women’s Studies
Total(Allied -Theory only) 23 700
30 - -
Total(Allied -Theory cum Practical) 24 725
7BFC5C1 Core–IX–Garment Manufacturing 4 6 25 75 100
Technology
III 7BFC5P1 Core–X– Fabric Structure and Design 4 5 40 60 100
– Practical
7BFC5P2 Core–XI– Women’s Apparel – 4 5 40 60 100
Practical
7BFC1E1/ Elective–I-A) Fabric Structure and
V 7BFC1E2 Design (or) B) Fashion Clothing 5 5 25 75 100
Psychology
7BFC2E1/ Elective – II- A) Visual Merchandising
7BFC2E2 (or) B) Apparel Merchandising and 5 5 25 75 100
Marketing
IV 7SBS5A4/ (2) Skill Based Subjects – III 2 2 25 75 100
7SBS5A5/ (2) Skill Based Subjects – IV 2 2 25 75 100
7SBS5A6/
7SBS5A7
Total 26 30 - - 700
7BFC6C1 Core–XII–Textile Testing 4 4 25 75 100
7BFC6P1 Core–XIII–Textile Testing–Practical 4 6 40 60 100
7BFC6P2 Core–XIV–Men’s Apparel–Practical 4 6 40 60 100
Core – XV – Computer Aided 4 5 40 60 100
III 7BFC6P3
Designing - Practical
VI 7BFC3E1/ Elective – III-A) Garment Quality and
7BFC3E2 Specifications (or) B) Indian 5 5 25 75 100
Traditional Textiles and Embroidery.
IV 7SBS6B4/ (2) Skill Based Subjects – V 2 2 25 75 100
7SBS6B5/
7SBS6B6/ 25 75
(2) Skill Based Subjects – VI 2 2 100
7SBS6B7
Total 25 30 - - 700
Grand Total 140 180 - - 4100
** University Examinations will be held in the Even semesters.
607 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
B.Sc., FASHION TECHNOLOGY& COSTUME DESIGNING
I YEAR – I SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC1C1
CORE COURSE - I - FASHION DESIGNING
Unit – I FASHION CONCEPT
Terms related to the Fashion Industry - Fashion, Style, Fad, Classic, Collection, Chic,
Mannequin, Fashion Show, Trend, Haute Couture. Meaning of Fashion, Origin of Fashion,
Meaning of Fashion Designing, Classification of Fashion, Influence of Fashion; Fashion
illustration and Fashion cycle, Fashion Theory
Unit – II DESIGN & ELEMENTS OF DESIGN
Design –Definition, Types- Structural and Decorative Design, Requirements of a
Good Structural and Decorative Design. Application of Structural and Decorative Design in
the Dress, Elements of Design -Line, Shape or Form, Color, Size and Texture.
Unit – III PRINCIPLES OF DESIGN, ACCESSORIES & TRIMMINGS
Principles of Design – Balance, Rhythm, Harmony, Emphasis and Proportion.
Fashion Accessories- Shoes, Hand Bags, Hats and Tie -Different Types/Shapes. Trimmings,
Decorations and its application, Lace, Ric Rac, Appliqué, Embroidery, Smocking, fasteners,
Belts and Bows, Faggoting, Ruffles, Patch work and Quilting.
Unit – IV COLOURS
Colours – Importance. Dimensions of colour,Colour Theory – Prang colour chart.
Colour Harmonies - Monochromatic, Analogus, Complimentary - Double Complimentary
Split Complimentary, Traid Colours,,. Cool Colours and Warm Colours. CMYK Colours.
Moods of Colour.
Unit – V FIGURE IRREGULARITIES
Designing dress for unusual figures becoming and unbecoming, for the following
Figure Types - Stout Figure, Thin Figure, Slender Figure, Narrow Shoulders, Broad
Shoulders, Round Shoulders, Large Bust, Flat Chest , Large Hip, Large Abdomen, Round
Face, Large Face, Small Face, Prominent Chin and Jaw, Prominent forehead.
Text books:
1. Khurana and Sethi, Introduction to Fashion Technology, Fire Well Publication, New
Delhi, 2007.
2. Pundir. N, Fashion Technology Today and Tomorrow, Mittal Publication, New Delhi,
2007
3. Mary Mathews, Practical Clothing Construction-Part I, Cosmic Press, Chennai, 1997.
Books for Reference:
1. Narang, Hand Book of Fashion Technology, Asia Pacific Business Press Inc, New
Delhi.
2. Fashion Designing- Study Material prepared by the Department.
3. Gupta et al, Text Book of Clothing and Textiles and Laundry, Kalyani Publishers,
New Delhi, 2005.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
608 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
I YEAR – I SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC1C2
CORE COURSE –II-BASIC SEWING TECHNIQUES
Unit –I SEWING EQUIPMENT
Sewing machines- parts and their function, care and maintenance. Tools for
measuring, marking, cutting & pressing. Selection of thread and needle for various types of
fabric
Unit – II SEAMS AND FULLNESS
Seams : Definition, types of seams and seam finishes, factors to be considered in
selection of seam
Fullness: Definition, Types of fullness – Darts, Tucks, Pleats, flares, godets, gathers, shirrs &
frills. Calculating material requirements
Unit – III SLEEVES AND SKIRTS.
Sleeves:- Classification of sleeves, types of sleeves- plain, puff at top, bottom, bell,
bishop, circular, leg-o-mutton, sleeveless styles, kimono & raglan. Pattern preparation for
these sleeves. Skirts: Different types of skirts – Drafting patterns for semicircular and circular
skirts.
Unit – IV NECK FINISHES AND YOKES
Neck finishes: -Definition, Bias- definition, joining bias and uses. Bias facing and
bias binding. Collars – definition, parts of collar, factors to be considered in designing collar,
classification of collar. Drafting for peter pan, cape, scallop, puritan, sailors, Chinese and
Turtleneck collar.
Yokes: - Definition, selection of yoke design, creating variety in yoke. Drafting
patterns for yoke without fullness, yoke with fullness within the yoke & yoke supporting or
releasing fullness. Attachment of yokes
Unit – V POCKETS AND PLACKETS
Pockets - Definition, classification, selection of pocket and creating variety in
pockets. Plackets - Definition, characteristics of a good placket, classification – continuous
bound, bound & faced, fly opening, zipper, tailored and center front / shirt placket.
Text Books:
1. Mary Mathews, Practical Clothing Construction Part-II. Designing, Drafting and
Tailoring Bhattarams Reprographics (P) Ltd., Chennai 2001
2. Zarapkar K.R, System of Cutting, Navneet Publications India 2005
3. Helen Joseph-Pattern Making for Fashion Design, Armstrong Pearson Education,
Delhi, 2000.
Books for Reference:
1. Hilary Campbell,” Designing Patterns Om Book Services, New Delhi, 2003.
2. Mary Mulasi, Garments with style, Chiton Book Company,Pennsylvania,1995.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
609 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
I YEAR – II SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC2C1
CORE COURSE – III- TEXTILE SCIENCE
Unit – I FIBER MANUFACTURING
Introduction to the Fibers - Classification of Textile Fibers- Natural and Manmade
fibers, Characteristics - Primary and Secondary properties of Textile Fibers. Manufacturing
Process, Properties, Uses, application of Fibers. – Cotton, silk, wool, rayon, jute, polyester,
recent textile fibers in market.
Unit – II YARN MANUFACTURING
Yarn - Conventional ring spinning method, chemical spinning method, others -
Electrostatic spinning, Airjet spinning, Twistless spinning. Yarn twist, yarn count. Types and
characteristics of yarns – ply yarns, cable yarns, double yarns and novelty yarns and its types.
Unit – III WEAVING
Preparation for weaving (warping, sizing, looming) Basic loom structure. Weaving-
Definition, Primary motion – shedding – Definition and a brief explanation, picking (shuttle
and shuttle less looms), beating up. Secondary motion – Definition and Ancillary motion.
Types of selvedges. Construction of cloth designs - Design, draft and peg plan. Classification
of weaves – plain weave, twill, Satin, Crepe, Pile, double cloth, (Climax) dobby and
Jacquard, (double lift double cylinder) Identification of woven fabric defects.
Unit – IV KNITTING
Knitting – Definition, Comparison between woven fabrics and knitted fabric.
Classification of knitted fabrics weft knitting – plain knit stitch, Rib stitch, Warp knitting -
Tricot knit, Raschel Knit, Milanese Knit, (Jacquard knit, pile knit, Terry knit, velour knit)
Identification of knitted fabric defects.
Unit – V FELTED AND NON WOVEN FABRICS
Felted fabrics – Felting process. Types of felt, properties and uses of felt. Non woven
– Definition, classification of non-woven fabrics, web forming techniques, bonding
techniques, and finishing techniques. Characteristics of non-woven, uses of non-woven
fabrics
Text Books:
1. Corbman B.P Fibre to Fabric, International Students Edition Mc Graw Hill Book Co-
Singapore, 2000.
2. Sara J. Cadolph and Anna L. Lang Ford, Textiles, Prentice hall, New York, 2002.
Books for Reference:
1. Smith, J.L. Textile processing, Abhishek Publications, Chandigarh, 2003.
2. Gokarneshan U, Fabric Structure and Design, New age International Publishers 2004.
3. Kate Wells, Fabric Dyeing and Printing, Conran Octopus 2000
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
610 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
I YEAR – II SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC2P1
CORE COURSE – IV- FASHION DESIGNING - PRACTICAL
A. PREPARE SKETCHES FOR THE FOLLOWING
Introduction to free hand drawing and basics of shading
1. Fashion Figure - 8 head theory .
2. Facial features- Eyes, nose, lips, ears.
3. Face, Hands, Legs-Different Positions.
4. Different Hairstyle for women –any five
5. Different poses of fashion figure (women and men)- any five
B. DRAW & SHADE THE FOLLOWING WITH SUITABLE SHAPE &SIZE
1. Different types of Collars.
2. Different types of Sleeves.
3. Different types of Necklines.
4. Different types of Skirts.
5. Different types of Ladies Tops.
6. Different types of Shirt.
7. Different types of Pant (full and half).
8. Different types of Salwar Kameez with Fashion Figure.
9. Different types of Accessories-Bags, Foot wear, Hats.
10. Different types of Ornaments – Traditional, Modern and Antique.
C. ILLUSTRATE FIGURES AND DESIGN GARMENTS
1. Casual wear, formal wear and stylish wear
D. PREPARE THE FOLLOWING CHARTS
Prang Colour Charts
Value Chart
Intensity Chart
E. ILLUSTRATE GARMENT DESIGNS FOR THE ELEMENTS OF DESIGN
Line, Color, Texture, Shape, Size
F. ILLUSTRATE GARMENT DESIGNS FOR THE PRINCIPLES OF DESIGN
Balance, Harmony, Emphasis, Proportion, Rhythm
G. RESS DESIGN FOR THE FOLLOWING FIGURE IRREGULARITIES
Thin figure, Stout figure, Broad shoulders, Large bust, Round face
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
611 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
II YEAR – III SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC3C1
CORE COURSE - V - PRINCIPLES OF PATTERN MAKING
Unit – I BODY MEASUREMENTS AND TOOLS
Body Measurements – Importance, Preparation for Measuring. Ladies Measurements,
Children’s measurement, Boy’s and Men’s measurements. Tools used – Cutting tools,
measuring tools, marking tools, general tools, pressing tools.
Unit – II FABRIC PREPARATION & LAYOUT PLANNING:
Fabric preparation: Preparing the fabric for cutting, Importance of grain in fabric
cutting and garment construction. Methods of straightening fabric grains.
Lay planning- Introduction, Rule to remember in pattern layout. Types of layout.
Transferring pattern markings, stay stitching, ease stitching.
Unit – III DRAFTING, DRAPING AND FLAT PATTERN TECHNIQUES
Drafting: Preparation of paper patterns. Advantages of paper pattern. Pattern drafting
with personal measurement. Principles for pattern drafting. Preparing draft for basic bodice,
sleeve and skirt pattern.
Draping: Definition, types of dress form, preparation of adhesive paper dress form,
Draping technique. Draping basic blocks (bodice, sleeve & skirts.).
Flat pattern Techniques: Definition, Pivot method, Slash & spread method,
measurement method. Creating styles through dart manipulation and relocation of dart.
Unit – IV COMMERCIAL PATTERN AND PATTERN GRADING:
Commercial pattern: Definition, merits and demerits, Development of commercial
pattern.Pattern Grading: Definition, Grading terminology, selecting a grading system, grading
techniques, their advantages and disadvantages. Computer grading. Grading procedures.
Grading of basic block using draft grading systems.
Unit – V PATTERN ALTERATION, GARMENT FITTING AND ASSEMBLING
Pattern alteration: Methods of identifying pattern alteration. General principles for
pattern alteration. Common pattern alteration in a fitted bodice pattern.Garment fitting and
Assembling Standards for a good fit, checking for good fit, solving fitting problems and
remedies.
Text Book:
1. Mary Mathews, Practical Clothing Construction – Part I & II, Cosmic Press, Chennai,
1974.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
612 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
II YEAR – III SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC3P1
CORE COURSE –VI- BASIC SEWING TECHNIQUES AND PATTERN MAKING -
PRACTICAL
1. Preparation of samples for Seams and Seam Finishes.
2. Preparation of samples for Hems.
3. Preparation of samples for Fullness.
4. Preparation of samples for Facings and Binding.
5. Preparation of samples for Plackets and Fasteners.
6. Preparation of samples for Sleeves - Plain Sleeve/Puff Sleeve (any one type).
7. Preparation of samples for Yokes -with and without Fullness.
8. Preparation of samples for Collar- Peter Pan Collar, Full Shirt Collar and Shawl
Collar.
9. Preparation of samples for Pocket - Patch, Bound and Side Seam.
10. Preparation of basic bodice pattern
11. Preparation and grading of patterns for women’s garments
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
613 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
II YEAR – IV SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC4C1
CORE COURSE -VII – TEXTILE DYEING AND PRINTING
Unit – I TEXTILE PROCESS
Water, water Hardness, types, quality required for wet processing industries, softening
process, preparatory process sequence for woven and knitted fabric. Need for processing -
Dry and wet processing for fabrics – Preparatory wet processing – Singeing, desizing,
scouring, bleaching, mercerizing, degumming and carbonizing.
Unit – II DYEING
Classification of dyes – Natural Dyes, mordants and its types, mordanting techniques.
Dyeing method, Advantages & Disadvantages of natural dyes. Synthetic dyes – Basic dyes,
Direct dyes, vat, sulphur, Napthol, Reactive, Azoic, acid, and disperse dyes.
Unit – III DYEING METHODS
Stages of dyeing Methods of Dyeing - Batch, Winch, Jigger, Package, hank dyeing.
Colourfastness tests. Recent advancement and technology in dyeing.
Unit – IV PRINTING
Printing-introduction to printing, Differences between printing and dyeing, preparation of
fabric for printing-cotton, polyester, wool and silk, Methods of Printing, Preparation of
printing paste, Selection of thickening agents.
Unit – V PRINTING METHODS
Direct Printing: Block Printing, Stencil printing, Screen printing, Discharge Printing,
Resist printing – batik and tie and dye. Other Printing Methods: Mino printing Inkjet printing,
Heat transfer printing, photo printing.
Text Books:
1. Textile Dyeing and Finishing- Study Material prepared by the Department.
2. Needles.H.L, Textile Fibers, Dyes, Finishes and Processes , Noyes Publications, 2011.
3. Smith.J.L, Textile Processing, Printing Dyeing, Finishing, Abhishek Publications,
Chandigarh, 2006.
4. Beginners Guide to fabric Dyeing and Printing – Stuart & Robinson, Technical
Books, London (1982)
Books for Reference:
1. Singh.K.V.P, Elementary Idea of Textile Dyeing, Printing and Finishing ,Kalyani
Publishers, 2009.
2. Corbman.B.P, Textile Fiber to Fabric, MCGRAW, HILL International Edition, Sixth
Edition, 2009.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
614 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
II YEAR – IV SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC4P1
CORE COURSE - VIII - FABRIC EMBELLISHMENT-PRACTICAL
1. Basic Hand Stitches
a) Running – Whipped Running Stitch, Threaded Running Stitch
b) Hemming
c) Back Stitch - Whipped Back Stitch, Threaded Back Stitch
2. Basic Embroidery Stitches
a) Chain stitch and its types
b) Fern Stitch
c) Stem Stitch
d) Lazy Daisy Stitch and its types
e) Blanket (or) Button Hole Stitch
f) Satin
3. Advanced Embroidery Stitches
a) French Knot,
b) Bullion Knot
c) Feather – Double Feather Stitch, Closed Feather Stitch
d) Herring bone and its types
e) Cross Stitch
4. Other surface Embroidery
a) Cut work
b) Mirror work
c) Applique/ Patch – Hand Applique, Machine Applique
d) Bead and sequence
e) Zardosi
f) Tasseled – Corded Tassled
g) Fringes
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
615 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC5C1
CORE COURSE - IX–GARMENT MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
Unit – I
Planning, drawing and reproduction of the marker. The requirements of marker
planning. Efficiency of the marker plan. The spreading of the fabric to form a lay. The
requirement of the spreading process. Methods of spreading, nature of fabric packages. The
cutting of fabric, objectivenes of cutting and methods of cutting
Unit – II
The properties of seam, seam types, stitch types. Sewing machine feed mechanism,
sewing machine needles, Sewing threads, fiber type, construction of thread finishes. Thread
sizing, thread packages, cost, properties and seam performance. Sewing problems, Problems
of stitch formation. Problem of pucker, problems of Damage to fabric along the stitch line.
Testing for sewability and Tailorability.
Unit – III
Basic sewing machines and associated work aids, simple automation . The use of
components & trims – Labels and motifs, lining, Interlining, wadding, lace, braids & elastics,
Hooks and loop fastening, Seam binding and tape, Shoulder pad, Eyelets & laces, Zip
fastener, Buttons,Tack buttons,Snap fasteners and Rivets,Performance properties of
components and trims.
Unit – IV
Fusing – Definition, advantages of fusible interlinings, Fusing process. The means of
fusing, Fusing equipments, Methods of fusing, quality control in fusing. Alternative of fusible
interlining.
Unit – V
Pressing: the purpose of pressing, categories of pressing, means of pressing, pressing
equipments and methods, pleating, permanent press. Pressing practices in Indian Industries
Text Books:
1. Introduction to clothing production management – 2nd edition, A.J. Chutter, Blackwell
Science, New Delhi.,2000
2. Gerry Cooklin, Garment technology for Fashion Designers –Blackwell Science,
3. New Delhi ,2000.
4. Gerry cooklin, Introduction to clothing manufacture–Blackwell Science,New
Delhi,2000.
5. Dudeja.V.D., Professional Management of Fashion Industry, Gangandeep
Publications, New Delhi, 2005.
Books for Reference:
1. Philip Kotler and Kevin Lane, Marketing Management, Keller,Pearson Education
Inc., Delhi,. 2006.
2. Kitty G. Dickerson, Inside the Fashion Business, Pearson Education, Singapore,2003.
3. Kathryn Mokelvey, Janine Munslow, Fashion Design Process, Innovation And
Practice, Black Well Science Ltd, U.K,2005.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
616 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC5P1
CORE COURSE - X– FABRIC STRUCTURE AND DESIGN – PRACTICAL
IDENTIFICATIONS OF THE FOLLOWING WEAVE DESIGN AND DRAFT A PEG
PLAN FOR THE SAME:
1. Plain Weave
2. Twill Weave
3. Satin
4. Sateen
5. Honey Comb Weave
6. Huck a Back Weave
7. Mock-leno Weave
8. Extra Warp Figuring
9. Extra Weft Figuring
10. Double Cloth-any one type
11. Pile fabric
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
617 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC5P2
CORE COURSE -XI– WOMEN’S APPAREL -PRACTICAL
Designing, Draft and construct the following Garments
1. Infant wears- Bib, Panty and Jabla
2. Baba suit / Romper.
3. Children’s frock - 2 variety
4. Knickers - Elastic Waist.
5. Saree Petticoat- Six Panel, Decorative Bottom.
6. Blouse- Front/Back Open, Fashioned Neck, Waist Band at Front, with Sleeve.
7. Ladies tops
8. Salwar / Churidhar
9. Kameez with/ without Slit, with /without Flare, with/without Opening, with/ with
out Panels, with/ without Sleeve.
10. Nightie / Maxi with / without fullness, with/without opening, with/without yokes,
with/without puff sleeve.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
618 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC1E1
ELECTIVE COURSE- I (A) – FABRIC STRUCTURE AND DESIGN
Unit – I WOVEN DESIGN FUNDAMENTALS
Introduction, Classification of Woven structures, Methods of weave Representation,
Weave repeat, basic elements of a woven design, Types of draft plans. Weaves – Plain, Rib
Twill, Satin and Sateen. End uses of the above weaves.
Unit – II HEAVY FABRICS
Honey Comb - ordinary, brighten. Weaves – Huck a Back, Crepe and Mock Leno.
End uses of the above weaves.
Unit – III FIGURED FABRICS
Backed Fabrics - Warp and Weft, Difference between warp and weft backed fabrics.
Extra warp and extra weft figuring – single and two colours, Difference between extra warp
and extra weft figuring. End uses of the above weaves.
Unit – IV PILE FABRICS
Pile Fabric- Types of velveteen, Weft plush, Terry pile – 3 pile, 4 pile, 5 pile, 6 pile,
length density and fastness of no pile. End uses of the above weaves.
Unit – V DOUBLE CLOTH
Double Cloth- Classification, warp, Weft and centre stitched double cloth. Self-
Stitched- back to Face. End uses of the above weaves.
Text Book:
1. N.Gokarneshan, Fabric Structure and Design, , New Age International (P) Ltd,
Publishers, New Delhi, 2006.
Books for Reference:
1. M.G. Mahadevan, Textiles Spinning, Weaving and Designing, First Edition,
Abhishek Publications Chandigarh, 2005.
2. W.S. Murphy, Textile Weaving and Design, First Indian Edition, Abhishek
Publications, Chandigarh, 2007.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
619 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC1E2
ELECTIVE COURSE - I (B) – FASHION CLOTHING PSYCHOLOGY
Unit – I FASHION TERMS
Terms related to the Fashion Industry - Fashion, Style, Fad, Classic, Collection, Chic,
Mannequin, Fashion Show, Trend, Haute Couture. Fashion Forecasting.
Unit – II FASHION PSYCHOLOGY
Factors influencing Fashion Changes-Psychological Needs of Fashion, Social
Psychology of Fashion, Technological, Economical, Political, Legal and Seasonal Influence.
Role of Costume as a Status Symbol, Personality and Dress, Repetition of Fashion
Unit – III FASHION CHANGES AND CONSUMER ACCEPTANCE
Fashion Leaders, Fashion Innovators, Fashion Motivation, Fashion Victim, Fashion
followers. Adoption of V – Trickle Down, Trickle up and Trickle Across Theory. Fashion
Forecasting - Market Research, Evaluating the Collection, Fashion Services, Colours
Services, Video Services, Newsletter Services, Websites, Directories and references.
Unit – IV FASHION DESIGNERS
Indian Designers-Rohit Khosla, Gitanjal Ksshyap, Hemant Trivedi, J.J. Valaya, Ritu
Kumar, Rohit Bal, Tarun Tahiliani, Sangeethe Chopra, Bhamini Subramaniam, Anju Modi,
Ravi Bajaj, Ritu Beri
Unit – V WORLD WIDE FASHION CENTERS
World fashion Centers- France, Italy, England, Germany, Canada, New York.
Text Books:
1. Elaine Stone, The Dynamics of Fashion, Fairchild Publications, New York, 2001.
2. Jenny Davis, A Complete Guide to Fashion Designing, 1st Edition, Abhishek
Publication, Chandigarh, 2009.
3. Frings, Fashion from Concept to Consumer, 7th Edition, Dorling Kindersley
Publishing Inc, India, 2008.
4. Man Meet Sodhia, History of Fashion, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, 2009.
5. Man Meet Sodhia, History of Fashion, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, 2007.
6. Pundir,Fashion Technology Today and Tomorrow,A Mittal Publication,New Delhi,
2007.
7. M.R.Soloman & N.J. Rabolt, Consumer Behaviour in Fashion, Dorling Kindersley
Publishing Inc, India, 2006.
Books for Reference:
1. Benneett, “Femina Book of Fashion”, coleman & Co., Ltd., Mumbai (1998)
2. Jeaneettee A. Jarnow, Miriarn Guerrerio, “Inside the Fashion Business”, Mecmillion
Publishing Company, New York
3. Harriet T, Mc Jimsey, “Art and fashion in clothing selection”, The lowa state
University Press, Ames, Lowa
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
620 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC2E1
ELECTIVE COURSE - II (A) - VISUAL MERCHANDISING
Unit – I INTRODUCTION TO MERCHANDSING
Visual Merchandising – Definition and Function, History of visual merchandising,
Role of visual merchandising, Understanding retail in India.
Unit – II STORE PLANNING AND FIXTURES
Store planning and fixtures – Floor plan, The purpose of planning fixtures, types of
fixtures.
Unit – III CIRCULATION PLAN
Circulation plan – Rules of circulation, Types of Circulation plans – Free flow, Grid,
Race track, Herringbone and spin.
Unit – IV MERCHANDISE PRESENTAION
Merchandise presentation – meaning, principles of merchandise presentation,
categories in merchandise presentation, Dominance factor in merchandise presentation,
elementary of display – Store Exteriors and Interiors.
Unit – V WINDOW DISPLAY
Promotional Display Vs Institutional Display, Types of Mannequins, Lighting, Visual
Merchandising Tool Kit, Quality and process in Visual Merchandising.
Text Book:
1. Bhallo.S, Anuraya.S, Visual Merchandising, Tata MC Graw Hill Education Private
Limited, New Delhi, 2010.
Books for Reference:
1. Rajesh, Managing Productivity in Apparel Industry.
2. Banotia.V, Marketing Managemen, Mangal Deep Publications, 2001.
3. Jones.R.M, The Apparel Industry.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
621 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – V SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC2E2
ELECTIVE COURSE – II (B) - APPAREL MERCHANDISING AND MARKETING
Unit – I MARKETING
Marketing Concepts -Definition, Apparel and Fashion Marketing - Planning, Apparel
Market, Environment - Micro and Macro Marketing, Environment trends. Apparel Market
and Segments.
Unit – II MERCHANDISING
Merchandising - Definition, Merchandising as Business Function - Role of
Merchandiser Evolution of Merchandising in Apparel Industry, Merchandising Organization,
Buying Preparation, National Brands vs Private Labels.
Unit – III VISUAL MERCHANDISING
Definition, Function, Significance of Display, Types of Displays- Window Displays,
Interior Display, Exterior Display, Elements of Display, lighting. Fashion show-Definition,
Planning, Budgeting, location, Timings, Selection of Models, Collection, Set Design, Music,
Preparing the Commentary, Rehearsal.
Unit – IV MERCHANDISING PRESENTATION
Merchandising Presentation - Principles of Merchandising Presentation, Placement of
Merchandise, Categories of Merchandise Presentation, Dominance Factors in Merchandising
Presentation, Cross Merchandising.
Unit – V EXPORT MARKETING AND DOCUMENTATION
Export Marketing of Apparel, Prospects for Indian in Overseas Market, Globalization.
Text Books:
1. Sodia and Chatley , Fashion Marketing and Merchandising, Kalyani Publication, New
Delhi, 2008.
2. Frings, Fashion from Concept to Consumer, Seventh Edition, Dorling Kindersley
Publishing Inc, India, 2008.
3. Kotler et al, Marketing Management, 13th edition, Dorling Kindersley Publishing Inc,
India, 2009.
4. Anurag.S. and Bhalla, Visual Merchandising, Tata McGraw Hill Education Private
Limited, New Delhi, 2010.
Books for Reference:
1. Davis Burns and Bryant, The Business of Fashion, Fair Child Publications, New
York, 2002.
2. Goworek, Careers in Fashion and Textiles, Blackwell Publishing, NewDelhi, 2006.
3. Elaine Stone, The Dynamics of Fashion (2001), Fairchild publications, New York.
4. Michanel R. Soloman& Nancy J. Rabolt, Consumer Behaviour in Fashion.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
622 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – VI SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC6C1
CORE COURSE -XII– TEXTILE TESTING
Unit – I QUALITY CONTROL: DEFINITION AND ITS IMPORTANCE.
Humidity: Definition and its influence on fiber properties Standard atmospheric
condition, Standard testing atmosphere. Standard regain, Moisture content and regain.
Measurement of atmospheric condition – wet and dry bulb Hygrometer and sling
Hygrometer.
Unit – II FIBRE TESTING
Fiber Testing: Fiber length – Baer sorter and Fibrograph, Fiber strength – Stelometer,
Fiber fineness – Micronaire, Fiber maturity, Trash content - determination – Trash analyzer.
Unit – III YARN TESTING
Yarn testing: Determination of yarn count – quadrant, Analytical & Beesley balance.
Twist – Direction of twist and amount of twist, Twist effect on fabric properties. Strength of
yarn-Single yarn strength tester. Crimp – Shirley crimp tester.Yarn appearance tester.
Evenness – Uster Evenness tester, Hairiness – Uster Hairiness tester.
Unit – IV FABRIC TESTING
Fabric Testing: Fabric strength tester – Tensile strength, tearing strength & bursting
strength. Abrasion – Types of abrasion – pilling – Martindale pill box tester.
Unit – V FABRIC TESTING
Drape – Drape meter, Fabric stiffness - Shirley stiffness Tester, crease recovery –
Shirley crease recovery tester. Thermal conductivity, water absorbency test, Water repellency
tester.
Books for Reference:
1. Principles of textile testing by J.E. Booth., C.B.S., publishers & distributors, New
Delhi, 1996.
2. Mishra S.P and Kesavan B.K, “Fibre Science”, Kumarapalayam, S.S.M. Institute of
Textile Technology
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
623 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – VI SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC6P1
CORE COURSE - XIII– TEXTILE TESTING – PRACTICAL
I. YARN TEST
1. To identify the yarn and fibers using binocular microscopic test
2. To determine the yarn count using single yarn twist tester.
3. To determine the yarn count using beesley balance method.
4. To determine the yarn count using quadrant balance.
5. To determine the coarse length form knitted fabric.
II.FABRIC TEST
6. To determine the thickness of a fabric using thickness tester.
7. To determine the stiffness of a fabric using stiffness tester.
8. To determine the drape of a fabric using drape meter.
9. To determine the shrinkage of a fabric using shrinkage template and scale.
10. To determine the strength of a fabric using tensile strength tester.
11. To determine the bursting strength of a fabric using bursting tester.
12. To determine the crease recovery of the fabric using crease recovery tester
13. To determine the rubbing fastness of a dyed fabric using Crock Meter with grey scale
Book for Reference:
1. Principles of textile testing by J.E. Booth., C.B.S., publishers & distributors, New
Delhi, 1996.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
624 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – VI SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC6P2
CORE COURSE - XIV–MEN’S APPAREL – PRACTICAL
Designing, Draft and construct the following Garments
1. S.B Vest-with/without Collar, Button attached, Sleeveless.
2. T-Shirt-Front Half Open, Zip Attached, With Collar.
3. Slack Shirt-with Collar, Half Sleeve, Patch Pocket.
4. Kalidhar Kurta -Kali Piece, Side Pocket, Round Neck, Half Open.
5. Nehru Kurta-Half Open, Stand Collar, with/without Pocket, Full Sleeve.
6. Pyjama/Bermudas-Elastic/Tape attached Waist, with/without fly.
7. One piece pant – fly attached, separate belt attached, front and back dart.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
625 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – VI SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC6P3
CORE COURSE - XV – COMPUTER AIDED DESIGNING – PRACTICAL
CREATE THE FOLLOWING DESIGNS
Motifs
1. Embroidery Designs for Kerchiefs.
2. Necklines.
3. Chest Prints.
4. T-Shirt.
Children’s Garments
1. Jabla
2. Frocks
3. Sun Suit
Women’s Garments
1. One Piece Dress
2. Middi & Tops
3. Salwar Kameez
4. House Coat
5. Nighty
Men’s Garments
1. SB Vest
2. T-Shirt
3. Shirt
4. Kurta
5. Pant
Create Logos for Branded Companies.
Create Label for Garments Companies.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
626 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – VI SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC3E1
ELECTIVE COURSE – III (A) – GARMENT QUALITY AND SPECIFICATIONS
Unit – I BASICS OF QUALITY CONTROL
Definition and Scope of Quality Control – Establishing Merchandising Standards –
Establishing Raw Material Quality Control specifications – Quality Control of Raw Material.
Inspection system – 4 point, 10 point system
Unit – II QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
Establishing Processing quality specification – Training Quality Control Personnel –
The Quality Standard Control – Quality Control Inspection, Procedures for processing –
Quality control of finished garments – Quality control and Government contacts – Quality
Control for Packaging, Warehousing and shipping – Statistical Quality Control, Sampling
plans – industry – wide quality standards.
Unit – III BASICS OF PRODUCTION CONTROL
Function of Production control – Production, Analysis – Quality Specifications –
Quantitative specifications – Scope of Apparel Manufacturing Activity – Co-ordinating
Departmental Activities – Distribution of Documents and Records.
Unit – IV PRODUCTION CONTROL SYSTEM
Type of Control forms – Basic Production Systems – Principles for Choosing a
Production System – Evaluating Production Systems – Flow Process Grids and Charts –
Basic Flow Process Grid Construction – Flow Process Grids for Production control –
Scheduling Producing Many Styles Simultaneously – Producing Many styles consecutively in
one line.
Unit – V COST CONTROL
Function of Cost Control: Types of Costs and Expenses – Apparel Manufacturing
Cost Categories – Sales Cost Control – Purchasing Cost Control – Production Cost Control –
Administration cost control – Cost Ration Policies – the manufacturing Budget – Cash flow
Control – Standard Cost Sheet, Break–Even Charts.
Books for Reference:
1. Patty Brown, Janett Rice,-Ready to wear apparel analysis,Prentice Hall,1998.
2. Salinger, Jacob Apparel, “Manufacturing Analylsis”, New York, Textile Books Futs,
2001
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
627 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
III YEAR – VI SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: 7BFC3E2
ELECTIVE COURSE - III (B) - INDIAN TRADITIONAL TEXTILES AND
EMBROIDERY
Unit – I INTRODUCTION TO INDIAN COSTUMES
Indian costume – Introduction, Indian Costumes from the earliest times to the
beginning of the historical period – Indus valley civilization costumes, Indo Aryans and
Vedic Ages, Mauryan and the Sunga period, Satavahana period, Kushan period Mughal
period.
Unit – II TRADITIONAL COSTUMES OF INDIA
Introduction to traditional Indian dress. Costumes of Punjab, Himachal Pradesh,
Gujarat, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Tamil Nadu,
Kerala, Andhra Pradesh,, Karnataka
Unit – III EMBROIDERIES OF INDIA
Kashmir Embroidery, Kanthas of Bengal, Chamba rummal of Himachal Pradesh,
Chickenkari of Uttar Pradesh, Pulkhari of Punjab, Kasuthi Embroidery, Kutch Embroidery.
Unit – IV TRADITIONAL WOVEN TEXTILES
Introduction to woven textiles of India – Brocades of Banaras, Himrus, Amrus
Baluchari, Pithambar, Tamilnadu Saree. Types of woven Kashmir shawls – Do- shala, Do-
rookha, Kasubha shawl,
Unit – V TRADITIONAL PRINTED AND DYED TEXTILES
Printed textiles – Kalamkari, Block printing, Roghan printing and other printed and
painted textiles (Mata-mi-pachedi, Pabuji-ka-pad) Dyed textiles – Ikat, Patola, Bandhani,
Laharia, Mashru.
Text Books:
1. Parul Bhatnagar, Traditional Indian costumes and Textiles, First Edition, Abhishak
Publications, Chandigarh, India, 2004.
2. Manmeet Sodhia, History of Fashion, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, 2007.
3. Manmeet Sodhia, History of Fashion, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, 2009.
4. History of Costumes and Textiles – Study Material prepared by the Department.
♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣♣
628 B.Sc., Fashion Tech.&CD
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
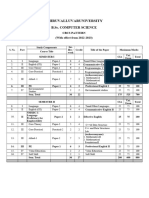
- 26 - B - SC - Computer Science Syllabus (2017-18)Dokument32 Seiten26 - B - SC - Computer Science Syllabus (2017-18)RAJESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 - B - SC - Computer Science Syllabus (2017-18)Dokument32 Seiten26 - B - SC - Computer Science Syllabus (2017-18)wahitha banuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27 B SC Information Tech Syllabus (2017-18) (1) ModifyDokument27 Seiten27 B SC Information Tech Syllabus (2017-18) (1) Modifyveera jothimaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 - B - SC - Maths Syllabus (2017-18)Dokument24 Seiten12 - B - SC - Maths Syllabus (2017-18)roby sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC .-CS 2017-2014Dokument123 SeitenB.SC .-CS 2017-2014SathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 - B - SC - , Home Sciene Syllabus (2017-18)Dokument28 Seiten25 - B - SC - , Home Sciene Syllabus (2017-18)quickdannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 - B - SC - Botany Syllabus (2017-18)Dokument59 Seiten17 - B - SC - Botany Syllabus (2017-18)roby sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11-b.sc., Maths Syllabus (2014-17)Dokument25 Seiten11-b.sc., Maths Syllabus (2014-17)roby sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15-b.sc. Biochemistry Syllabus (2014-17)Dokument23 Seiten15-b.sc. Biochemistry Syllabus (2014-17)roby sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alagappa University Syllabus - BBA Syllabus2017 18Dokument26 SeitenAlagappa University Syllabus - BBA Syllabus2017 18sheik2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moculas Syllabus (2014-17)Dokument30 SeitenMoculas Syllabus (2014-17)Maha RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - B - Com - CA Syllabus (2017-18)Dokument27 Seiten10 - B - Com - CA Syllabus (2017-18)roby sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BComCA PDFDokument31 SeitenBComCA PDFRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bca New Syllabus - Tiruvalluvar UniversityDokument52 SeitenBca New Syllabus - Tiruvalluvar UniversityBabu100% (2)
- B.SC Physics - 2019-2020Dokument90 SeitenB.SC Physics - 2019-2020Babitha DhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17-b.sc. Zoology Syllabus (2014-17)Dokument28 Seiten17-b.sc. Zoology Syllabus (2014-17)roby sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. Visual Communication Syllabus - 2020Dokument43 SeitenB.Sc. Visual Communication Syllabus - 2020TSG PUBGTECHNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Syllabus 2022Dokument160 SeitenMBA Syllabus 2022Trichy MaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC BioinformaticsDokument31 SeitenBSC BioinformaticsAjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thiruvalluvar University: Cbcs PatternDokument52 SeitenThiruvalluvar University: Cbcs PatternKirubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. B.Sc. Zoology - Course Structure Under CBCSDokument21 SeitenBharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. B.Sc. Zoology - Course Structure Under CBCSLeena AneesNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.SC Computer-ScienceDokument76 SeitenM.SC Computer-ScienceGokula KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Syllabus 2022-23Dokument162 SeitenMBA Syllabus 2022-23Trichy MaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Sc. Textile and Fashion Designing PDFDokument66 SeitenM.Sc. Textile and Fashion Designing PDFcharanpreet singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Aircraft MainDokument35 SeitenBSC Aircraft MainAyem perumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ba TamilDokument60 SeitenBa Tamildrsakthivel03Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Computer ScienceDokument45 SeitenBSC Computer ScienceRaksha RajpurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costume Design BSC 1718 PDFDokument37 SeitenCostume Design BSC 1718 PDFAkila RinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KGCE SyllabusDokument49 SeitenKGCE SyllabusRenganathanPadmanabhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thiruvalluvar University: Cbcs PatternDokument92 SeitenThiruvalluvar University: Cbcs PatternAvinash KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pol Science CBCSDokument30 SeitenPol Science CBCShoperuths1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus: Periyar University Salem - 11Dokument32 SeitenSyllabus: Periyar University Salem - 11athiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC - Chemistry.2022-23 Naan Mudhalvan Scheme PDFDokument75 SeitenB.SC - Chemistry.2022-23 Naan Mudhalvan Scheme PDFapstvlNoch keine Bewertungen
- B SCDokument68 SeitenB SCKANTHAVEL TNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC CDF - Col - 10-11Dokument4 SeitenB.SC CDF - Col - 10-11kvaruncdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus (2020-2021)Dokument26 SeitenSyllabus (2020-2021)selvam sNoch keine Bewertungen
- C.A Bharathidasan UniversityDokument30 SeitenC.A Bharathidasan UniversityWise MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thiruvalluvaruniversity Bachelor of Computer Applications Degree Course Cbcs Pattern (With Effect From 2020-2021)Dokument70 SeitenThiruvalluvaruniversity Bachelor of Computer Applications Degree Course Cbcs Pattern (With Effect From 2020-2021)JachasNoch keine Bewertungen
- APT 22-23 Syllabus Naan Mudhalvan 09.02.23Dokument4 SeitenAPT 22-23 Syllabus Naan Mudhalvan 09.02.23karthickmani374Noch keine Bewertungen
- BCA 2022-2023 OnwardsDokument48 SeitenBCA 2022-2023 OnwardsDr. A. Haja Abdul KhaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCom Third Year 202122 ADokument39 SeitenBCom Third Year 202122 Arathodkishan11022003Noch keine Bewertungen
- BBA Business AdministartionDokument60 SeitenBBA Business AdministartionCool EfxNoch keine Bewertungen
- B SC - COMPUTER-SCIENCEDokument135 SeitenB SC - COMPUTER-SCIENCEjayasankari kumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYLLABUSDokument168 SeitenSYLLABUSP.Jermi Arockia PravinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008-09 B. E. Mechanical EngineeringDokument37 Seiten2008-09 B. E. Mechanical EngineeringprafullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Bca PDFDokument140 Seiten11 Bca PDFPreethy Papa33Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Cs 1819 Aff CollDokument17 SeitenBSC Cs 1819 Aff CollKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCCADokument30 SeitenBCCASureshkumaraschool SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furniture StylesDokument41 SeitenFurniture StylesKarthi Keyan RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under-Graduate Programme in Commerce Courses of Study, Schemes of Examinations & SyllabiDokument73 SeitenUnder-Graduate Programme in Commerce Courses of Study, Schemes of Examinations & Syllabiviswes waranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBA Final Syllabus 2020Dokument72 SeitenBBA Final Syllabus 2020kingsley_psbNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Computer Science PDFDokument56 SeitenBSC Computer Science PDFB.ArulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bca On 16Dokument51 SeitenBca On 16C.MadhumathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatisticsDokument31 SeitenStatisticsDivyaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC MathematicsDokument60 SeitenB.SC MathematicsammujvpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Computer Applications Syllabus For B.C.A. Under Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) For Candidates Admitted From 2019 - 2020Dokument39 SeitenDepartment of Computer Applications Syllabus For B.C.A. Under Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) For Candidates Admitted From 2019 - 2020Saran VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bca PDFDokument40 SeitenBca PDFPoornima MuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Methods: Industrial Use from Model to the CodeVon EverandFormal Methods: Industrial Use from Model to the CodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibonacci and Gann Applications in Financial Markets: Practical Applications of Natural and Synthetic Ratios in Technical AnalysisVon EverandFibonacci and Gann Applications in Financial Markets: Practical Applications of Natural and Synthetic Ratios in Technical AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Schaum's Outline of Principles of Accounting I, Fifth EditionVon EverandSchaum's Outline of Principles of Accounting I, Fifth EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- DRESSMAKING-10 Q4 Mod4 USLeM-RTPDokument10 SeitenDRESSMAKING-10 Q4 Mod4 USLeM-RTPApsimachiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Quarter Assessment: Region I La Union Schools Division Office Caba National High School Caba, La UnionDokument8 SeitenSecond Quarter Assessment: Region I La Union Schools Division Office Caba National High School Caba, La UnionLordy B. PicarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creative Machine Embroidery - January, February 2015 PDFDokument68 SeitenCreative Machine Embroidery - January, February 2015 PDFAdriana Gavril100% (1)
- Project Plan For Childrens WearDokument6 SeitenProject Plan For Childrens WearMary Jane Repaja Canaya68% (19)
- Sewing MachinesDokument65 SeitenSewing Machinesiriscassinelli100% (4)
- Passport 2-0 3-0 Manual ENDokument32 SeitenPassport 2-0 3-0 Manual ENrkxvdrfiaiqrootgfjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haku Scarf Embroidery InstructionsDokument5 SeitenHaku Scarf Embroidery Instructionspikksi0% (1)
- Duck Quilt Two Colorways TEXT FIGSDokument12 SeitenDuck Quilt Two Colorways TEXT FIGSgiuli3101Noch keine Bewertungen
- DRESSMAKING Week 7B Sewing Machine Troubles and RemediesDokument17 SeitenDRESSMAKING Week 7B Sewing Machine Troubles and RemediesJane “Ria” MeldivesNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make An Amigurumi Robot: MaterialsDokument2 SeitenHow To Make An Amigurumi Robot: MaterialsbizarreworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument3 SeitenResumeapi-259841700Noch keine Bewertungen
- Craft Ideas and Restaurant PDFDokument55 SeitenCraft Ideas and Restaurant PDFmessapos100% (1)
- Wheeler & Wilson No 9 Form 41 - TextDokument8 SeitenWheeler & Wilson No 9 Form 41 - TextGramma JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Breakdown PDFDokument1 SeiteOperation Breakdown PDFCHARUVI RANJANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Flow Chart of Garments ManufacturingDokument3 SeitenProcess Flow Chart of Garments ManufacturingMahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Bulletin 42 - Applying Accession Numbers Part IDokument4 SeitenTechnical Bulletin 42 - Applying Accession Numbers Part IBernardo ArribadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 091 Cross Stitch Pattern Free PDF Watering CansDokument2 Seiten091 Cross Stitch Pattern Free PDF Watering CansSofia PrasetyadewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defects PDFDokument128 SeitenDefects PDFBhaswati PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fsex100 Week 2 Devils DefinitionDokument2 SeitenFsex100 Week 2 Devils Definitionapi-370083817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 1Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan 1api-306690720Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning: Department of Ed Uc AtionDokument10 SeitenLearning: Department of Ed Uc AtionKeen HelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thread ConsumptionDokument15 SeitenThread ConsumptionshaharyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barudan N Series Manual MecanicoDokument121 SeitenBarudan N Series Manual MecanicoDidier H Torres G75% (4)
- Euro-Pro Sewing Machine 998BDokument14 SeitenEuro-Pro Sewing Machine 998BFred RománNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewing Project RubricDokument1 SeiteSewing Project Rubricapple munda crruz67% (6)
- LO1 lp1-7Dokument7 SeitenLO1 lp1-7Lily Cathylene Balongis EstoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Looper and KnifeDokument4 SeitenLower Looper and KnifeTauqeer RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pfaff 260 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDokument55 SeitenPfaff 260 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yamato Engineering HandbookDokument149 SeitenYamato Engineering HandbookFrancisco Fabio Ferreira86% (7)
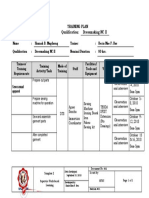
- Training Plan Qualification: Dressmaking NC II: Template 2 Supervise Work-Based Learning Document No. Issued By: SfistDokument1 SeiteTraining Plan Qualification: Dressmaking NC II: Template 2 Supervise Work-Based Learning Document No. Issued By: SfistArts of Ma LeyNoch keine Bewertungen