Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fundamentals of Assurance Services
Hochgeladen von
Mitzi Catemprate0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten4 Seiten1) Assurance services involve a three-party relationship where a practitioner provides a report to intended users on a responsible party's subject matter or assertion.
2) Key elements of assurance services include having an appropriate subject matter, suitable criteria to evaluate the subject matter, sufficient evidence, and a written report.
3) The responsible party measures or evaluates the subject matter against the criteria and may provide a written assertion, while the intended users are the individuals who rely on the assurance report.
Originalbeschreibung:
fundamentals of auditing and assurance services
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1) Assurance services involve a three-party relationship where a practitioner provides a report to intended users on a responsible party's subject matter or assertion.
2) Key elements of assurance services include having an appropriate subject matter, suitable criteria to evaluate the subject matter, sufficient evidence, and a written report.
3) The responsible party measures or evaluates the subject matter against the criteria and may provide a written assertion, while the intended users are the individuals who rely on the assurance report.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten4 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance Services
Hochgeladen von
Mitzi Catemprate1) Assurance services involve a three-party relationship where a practitioner provides a report to intended users on a responsible party's subject matter or assertion.
2) Key elements of assurance services include having an appropriate subject matter, suitable criteria to evaluate the subject matter, sufficient evidence, and a written report.
3) The responsible party measures or evaluates the subject matter against the criteria and may provide a written assertion, while the intended users are the individuals who rely on the assurance report.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
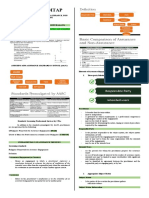
Assurance on the balloting of contests
Chapter 1
Academy awards
Fundamentals of Assurance Reporting on compliance with laws, rules and regulations
Services Elements of assurance services
- Three-party relationship
Practitioner (CPA), responsible party and intended users
The Concept of Assurance - Appropriate subject matter
Reliable information - Suitable criteria
- Fairly stated - Sufficient appropriate evidence
- Presents a true and fair view of what it purports to be - Written assurance report
- Reliability of information depends on: In the form appropriate to a reasonable/limited assurance
Credibility of the source of information engagement
Ability to verify its accuracy or fairness *All must be present for an engagement to be classified as an assurance
- “TO ASSURE” engagement.
To give confidence or conviction
Three-Party Relationship
Assurance Services Practitioner
Assurance services/engagements - Broader than the term “auditor”
- AUDITOR
- Three-party contracts in which assurers (such as CPAs) report on
the QUALITY OF INFORMATION Relates only to practitioners performing audit or review
- Intended to enhance the CREDIBILITY OF INFORMATION engagements with respect to historical financial information
about a subject matter (such as financial statements) by - A practitioner SHOULD NOT ACCEPT an engagement if
evaluating whether the subject matter conforms in all material preliminary knowledge of the engagement circumstances
respects with suitable criteria indicates that ethical requirements regarding professional
- Examples: competence will not be satisfied. *(p. 5)
Audits of FS of listed and non-listed entities
assurance engagement regarding a report it has
Responsible party prepared about its own sustainability practices
- Person/s responsible for the subject matter (SM) or the subject
matter information (SMI) [the assertion] in an assurance
engagement
Intended users
- May or may not be the party who engages the practitioner (the - Person/s or class of persons whom the practitioner prepares the
engaging party) assurance report
- Ordinarily provides the practitioner with a written representation - The responsible party can be one of the intended users, BUT
that evaluates or measures the subject matter against the NOT THE ONLY ONE.
identified criteria, whether or not it is to be made available as an - *(p.6)
assertion to intended users People involved in determining engagement requirements
Financial statement audit - Whenever practical, intended users or their represantatives are
SUBJECT Financial position, financial performance and involved with the practitioner and the responsible party (and the
MATTER cash flows of an enterprise engaging party, if different) in determining the requirements of
Financial statements of an enterprise (balance the engagement.
SUBJECT
sheet, income statement, statement of changes - Regardless of the involvement of others however, the
MATTER
in equity, statement of cash flows, and related PRACTITIONER is responsible for determining the nature,
INFORMATION
notes)
timing and extent of procedures to be performed in the
RESPONSIBLE
Client or entity engagement engagement.
PARTY
- In addition, the PRACTITIONER is required to pursue any
Extent of responsibility of the responsible party matter which the practitioner becomes aware of where such
(Philippine Framework for Assurance Engagements) matter may lead to a MATERIAL ADJUSTMENT OR
Responsible MODIFICATION to the subject matter.
Sample Assurance Engagement
for… Assurance Engagements for a Specific Purpose
A government organization engages a practitioner - In some cases, intended users impose a requirement on or request
to perform an assurance engagement regarding a
the responsible party (or engaging party, if different) to arrange
SMI only report about a private company’s sustainability
practices that the organization has prepared and is for, an assurance engagement to be performed for a SPECIFIC
to distribute to intended users PURPOSE.
SM and SMI An entity engages a practitioner to perform an
- When engagements are designed for specified intended users or a Suitable Criteria (SC)
specific purpose, the practitioner considers including a - Required for REASONABLY consistent evaluation/measurement
RESTRICTION in the assurance report that limits its use to those of a SM within the contest of professional judgment
users or that purpose. - Without the frame of reference provided by SC, any conclusion is
Subject Matter open to individual interpretation and misunderstanding.
Appropriate Subject Matter - Context-sensitive
- Identifiable, capable of consistent evaluation/measurement Relevant to the engagement circumstances
against the identified criteria, and capable of being subjected to - For the same SM, there can be different criteria.
procedures for gathering sufficient appropriate evidence - The evaluation/measurement of a SM merely on the basis of the
- Characteristics: practitione’s own expectations, judgments, and individual
Qualitative vs. quantitative experiences WOULD NOT constitute suitable criteria.
Objective vs. subjective Characteristics of Suitable Criteria
Historical vs. prospective - RELEVANCE
Relates to a point in time vs. covers a period Contribute to conclusions that ASSIST DECISION-MAKING
- Such characteristics affect the precision with which the SM can by the intended users
be evaluated or measured against criteria and the persuasiveness - COMPLETENESS
of available evidence. Criteria are sufficiently complete when relevant factors that
- *Table 1-5 (p. 7) could affect the conclusions in the context of engagement
Suitable Criteria circumstances are NOT OMITTED.
Criteria Complete criteria include, where relevant, benchmarks for
- Benchmarks used to evaluate/measure the subject matter presentation and disclosure.
Including, when relevant, benchmarks for presentation and - RELIABILITY
disclosure Allows reasonably consistent evaluation/measurement of the
- Formal or less formal SM including where relevant, presentation and disclosure
- *Table 1-6 (p. 8) - NEUTRALITY
- Less formal criteria Contributes to conclusions that are FREE FROM BIAS
Internally developed code of conduct - UNDERSTANDABILITY
Agreed level of performance Contribute to conclusions that are:
CLEAR
COMPREHENSIVE
NOT SUBJECT TO SIGNIFICANTLY DIFFERENT
INTERPRETATIONS
Established Criteria and Specifically Developed Criteria
Established Criteria
- Those embodied in laws or regulations, or issued by authorized or
recognized bodies of expe
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- c6 Aud TheoryDokument11 Seitenc6 Aud TheoryRachel Anne RascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One Fundamentals of Assurance Services I. The Concept of AssuranceDokument11 SeitenChapter One Fundamentals of Assurance Services I. The Concept of AssuranceJeremy Lorenzo Teodoro VirataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. ASSURANCE SERVICESDokument4 SeitenChapter 1. ASSURANCE SERVICESyo poNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Assurance Services FinalDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance Services FinalLv ValenzonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Assurance Services - Docx'Dokument8 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance Services - Docx'jhell dela cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 6 11 Audit TheoryDokument43 SeitenCHAPTER 6 11 Audit TheoryYstefani ValderamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit&Assurance Ireneo-Summary NotesDokument7 SeitenAudit&Assurance Ireneo-Summary NotesMa. BeatriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF 1 Fundamentals of Assurance Services Final DDDokument4 SeitenPDF 1 Fundamentals of Assurance Services Final DDKimberly PacificoNoch keine Bewertungen
- At Ho Overview of AuditDokument3 SeitenAt Ho Overview of AuditJamikka DistalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing Theory: Elements of An Assurance Engagement 1.) Suitable CriteriaDokument14 SeitenAuditing Theory: Elements of An Assurance Engagement 1.) Suitable CriteriaIm NayeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesEdgie Trinidad TusiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSA 100 Phil Framework For Assurance EngagementsDokument4 SeitenPSA 100 Phil Framework For Assurance EngagementsSkye LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDokument5 SeitenLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDenny June CraususNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument22 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance ServicesxxpinkywitchxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Lecture Notes On AuditapDokument3 SeitenPrelim Lecture Notes On AuditapCharvie Kyle RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Accountancy: Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument8 SeitenDepartment of Accountancy: Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesLv ValenzonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument28 SeitenChapter 6 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesJoyce Anne Garduque100% (1)
- At 01 Assurance Engagements and Related ServicesDokument7 SeitenAt 01 Assurance Engagements and Related ServicesJobby JaranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assurance Engagements OverviewDokument5 SeitenAssurance Engagements OverviewprestinejanepanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0103-Fundamentals of Assurance and Non-Assurance EngagementsDokument8 SeitenLecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0103-Fundamentals of Assurance and Non-Assurance EngagementsMaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT EscalaDokument249 SeitenAT EscalaAM83% (6)
- Individual Assignment: 01 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument4 SeitenIndividual Assignment: 01 Fundamentals of Assurance Servicesacilegna mercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assurance Engagements & Other Services of A PractitionerDokument22 SeitenAssurance Engagements & Other Services of A PractitionerkngnhngNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT.1201 - Fundamentals of Assurance and Non Assurance Engagements - StudentsDokument8 SeitenAT.1201 - Fundamentals of Assurance and Non Assurance Engagements - Studentsdave excelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 AuditingDokument24 SeitenChapter 6 AuditingMisshtaCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lagcao Claire Ann 01 JournalDokument4 SeitenLagcao Claire Ann 01 JournalLagcao Claire Ann M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceDokument7 Seiten01 Intro To Audit and AssuranceBts Army ForeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDokument9 SeitenPhilippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsKlo MonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assurance StandardsDokument7 SeitenAssurance Standardsmitali bangiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Assurance EngagementsDokument7 SeitenLesson 1 Assurance EngagementsMark TaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acct 318 Audit and Assurance 1Dokument61 SeitenAcct 318 Audit and Assurance 1Alokha VincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument32 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance ServicesDavid alfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUDITING PRINCIPLES Chap 6 and 7 SummaryDokument13 SeitenAUDITING PRINCIPLES Chap 6 and 7 SummaryAlexius GucilatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- c1 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument15 Seitenc1 Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesEpfie SanchesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDokument38 SeitenAuditing and Assurance PrinciplesBryzan Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal 1Dokument6 SeitenJournal 1Sittie Ainna A. UnteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module - Auditing - Chapter 1Dokument14 SeitenModule - Auditing - Chapter 1Kathleen Ebuen EncinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Notes - Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDokument7 SeitenSummary Notes - Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsLaila ContadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDokument5 SeitenLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoFídely PierréNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Operational Audit FrameworkDokument6 SeitenModule 2 Operational Audit FrameworkEric CauilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing and AssuranceDokument3 SeitenAuditing and AssuranceRaven ChelseaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 An Auditor's ServicesDokument22 SeitenChapter 4 An Auditor's ServicesAisa TriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim TopicDokument60 SeitenPrelim TopicRhia Mae PaceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Audit P ReviewerDokument66 Seiten0 Audit P ReviewerRiza Mae Ramos AddatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCTG 163 Review 1 - New 2017Dokument7 SeitenACCTG 163 Review 1 - New 2017Tressa Salarza PendangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report That Limits Its Use To Those Users or ThatDokument7 SeitenReport That Limits Its Use To Those Users or Thatkate bautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assurance EngagementsDokument4 SeitenAssurance EngagementsJayson DemdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assurance EngagementsDokument35 SeitenAssurance EngagementsThembela MkandlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing and AssuranceDokument78 SeitenAuditing and Assurance03LJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Framework of Assurance ServicesDokument14 SeitenFramework of Assurance ServicesI am JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Audit PresDokument4 SeitenChapter 4 Audit PreswahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 JournalDokument5 Seiten01 JournalJohn CPANoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Assurance EngagementDokument26 SeitenFundamentals of Assurance EngagementVonna TerribleNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMPC 312 M1Dokument32 SeitenCMPC 312 M1Jonnette DamasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audtheory - Fundamentals of Assurance ServicesDokument1 SeiteAudtheory - Fundamentals of Assurance Servicesfarah mae raquinioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rodriguez Zyra-Denelle 01 JournalDokument10 SeitenRodriguez Zyra-Denelle 01 JournalDaena NicodemusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acct 318 Audit and Assurance 1Dokument74 SeitenAcct 318 Audit and Assurance 1demolaojaomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet - Module 2Dokument4 SeitenActivity Sheet - Module 2Elisabeth HenangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCTG 163 Review 1 - New 2017Dokument7 SeitenACCTG 163 Review 1 - New 2017F RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Incidents and Event Management With Qradar (Foundation)Dokument4 SeitenSecurity Incidents and Event Management With Qradar (Foundation)igrowrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPI Lesson 1 - Surveys & Investigation PDFDokument60 SeitenBPI Lesson 1 - Surveys & Investigation PDFMayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itinerary KigaliDokument2 SeitenItinerary KigaliDaniel Kyeyune Muwanga100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Accounting PrinciplesDokument45 SeitenChapter 11 Accounting PrinciplesElaine Dondoyano100% (1)
- Postcolonial FeministReadingDokument10 SeitenPostcolonial FeministReadinganushkamahraj1998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Teen Age PregnancyDokument2 SeitenProposal Teen Age Pregnancymountain girlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visi Dan Misi Kementerian Keuangan:: ANTAM's Vision 2030Dokument5 SeitenVisi Dan Misi Kementerian Keuangan:: ANTAM's Vision 2030Willy DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Randy Rowles: HAI's 2021-22 Chairman Keeps Moving ForwardDokument76 SeitenRandy Rowles: HAI's 2021-22 Chairman Keeps Moving Forwardnestorin111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmic Education Montessori Bauhaus andDokument10 SeitenCosmic Education Montessori Bauhaus andEmma RicciNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Secrets Behind Disney's Captivating Marketing StrategyDokument10 Seiten4 Secrets Behind Disney's Captivating Marketing StrategyJuan Camilo Giorgi MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Social Responsibility in Bangladesh:: A Comparative Study of Commercial Banks of BangladeshDokument12 SeitenCorporate Social Responsibility in Bangladesh:: A Comparative Study of Commercial Banks of BangladeshSaima Binte IkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Star Wars Canon Timeline MythBankDokument25 SeitenStar Wars Canon Timeline MythBankJonathan Carson100% (1)
- IJHSS - A Penetrating Evaluation of Jibanananda Das' Sensibilities A Calm Anguished Vision - 3Dokument10 SeitenIJHSS - A Penetrating Evaluation of Jibanananda Das' Sensibilities A Calm Anguished Vision - 3iaset123Noch keine Bewertungen
- EVNDokument180 SeitenEVNMíša SteklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital List (Noida & GZB)Dokument3 SeitenHospital List (Noida & GZB)prince.bhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCTADokument5 SeitenGCTAPatty CabañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPFContributionRatesTable 1jan2022Dokument5 SeitenCPFContributionRatesTable 1jan2022ysam90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hack Tata Docomo For Free G..Dokument3 SeitenHack Tata Docomo For Free G..Bala Rama Krishna BellamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dua AdzkarDokument5 SeitenDua AdzkarIrHam 45roriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scupin and DeCorse Chapter 20Dokument29 SeitenScupin and DeCorse Chapter 20Sana FarshbafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction Strategic Project Management (Compatibility Mode)Dokument39 Seiten1 Introduction Strategic Project Management (Compatibility Mode)Pratik TagwaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Richard Neutra - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument10 SeitenRichard Neutra - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNada PejicNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA 122.2 Accounts Receivable Audit Simulation Working Paper Group 6 WFWDokument5 SeitenBA 122.2 Accounts Receivable Audit Simulation Working Paper Group 6 WFWjvNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCRIPT IRFANsDokument2 SeitenSCRIPT IRFANsMUHAMMAD IRFAN BIN AZMAN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sibayan, Patrick Jorge - Weekly Accomplishment (July 8-14, 2019)Dokument2 SeitenSibayan, Patrick Jorge - Weekly Accomplishment (July 8-14, 2019)Patrick Jorge SibayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Commerce AssignmentDokument40 SeitenE Commerce AssignmentHaseeb Khan100% (3)
- Procure To Pay (p2p) R12 - ErpSchoolsDokument20 SeitenProcure To Pay (p2p) R12 - ErpSchoolsMadhusudhan Reddy VangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jordan Leavy Carter Criminal ComplaintDokument10 SeitenJordan Leavy Carter Criminal ComplaintFOX 11 NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Shift ScheduleDokument32 SeitenEmployee Shift ScheduleRishane RajapakseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk AssessmentDokument11 SeitenRisk AssessmentRutha KidaneNoch keine Bewertungen