Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
B 9421 F 2642743 A 9 Ebce 8
Hochgeladen von
api-2306408280 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
2K Ansichten6 SeitenOriginaltitel
b9421f2642743a9ebce8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
2K Ansichten6 SeitenB 9421 F 2642743 A 9 Ebce 8
Hochgeladen von
api-230640828Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
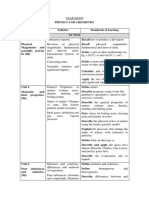
YEAR NINE
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY
Unit Syllabus Standards of leaning
1st Term
Unit 1. The cell; types of cells; Describe the cell; types of cells; the
the anatomy and anatomy and funcion of organelles.
General
funcion of organelles.
organisation of Define the different transport systems
Transport systems
the human across the cell membrane: diffusion;
across the cell
body. [6h] osmosis; active transport; endocytosis and
membrane exocytosis.
The organisation of the State the organisation of the human body:
human body: cells, cells, tissues, organs, systems.
tissues, organs,
systems. The Discuss the importance of chemical
importance of chemical compounds in organisms, including ions,
compounds in acids and bases.
organisms, including Apply knowledge of chemical formulation
ions, acids and bases. and the IUPAC rules of naming inorganic
Revision of chemical compounds.
formulation and the
IUPAC rules of naming
inorganic compounds.
Unit 2. Concepts of health and Define the concepts of health and illness
illness according to the WHO.
Health and
illness. [5h] Infectious and Outline the differences between infectious
noninfectious diseases. and noninfectious diseases.
Hygiene and the State examples of infectious and
prevention of diseases. noninfectious diseases.
The immune system. Describe the transmission of infectious
Vaccines. diseases.
Addictive substances:
Demonstrate the importance of hygiene
tabacco, alcohol and and the prevention of diseases.
other drugs. Their
associated problems. Recall the most important methods of
treating diseases: serumtherapy; drug
therapy and antibiotics.
State the concept of pathogen, antigen and
antibody.
Describe the external defences of the
immune system.
Outline the function of lymphocytes B
and T as part of the internal defences of
the immune system.
Describe vaccination.
Summarise the issue of addictive
substances, including tobacco, alcohol and
other drugs.
Unit 3. Nutrition, food and Outline the concepts of nutrition, food
health. and healthy eating.
Nutrition.
[15h] Nutrients, foods and Define the principle nutrients and state
healthy eating habits. their functions in the human body.
Eating disorders. Describe the function of nutrition.
The function of Define digestion.
nutrition.
Define food intake and balanced diet.
The anatomy and
physiology of the Design a balanced diet.
digestive, respiratory, Describe the main characteristics of the
circulatory and Mediterranean diet.
excretory systems.
Discuss eating disorders and diseases
Common disorders and related to eating habits.
illnesses in the above
systems, and possible Outline the anatomy and physiology of
preventions. the digestive, respiratory, circulatory and
excretory systems.
Advice for a healthy
lifestyle. Label diagrams of the digestive,
respiratory, circulatory and excretory
systems.
Outline the role of enzymes in digestion.
Summarise the role each organ of the
digestive system plays in digestion.
Describe the process of inhalation and
exhalation.
Explain gas exchange in the alveoli with
reference to diffusion.
Describe how the alveoli are well-adapted
to their function.
State the composition of blood and
describe its function.
Define the 3 types of blood cells and
outline their functions.
Describe the 3 types of blood vessels and
suggest how their structure is realted to
their function.
Describe the heart´s structure and
function.
Outline the movement of blood around
the body and summarise the changes in
its composition.
State the different components of the
excretory system and explain why they
are considered part of the excretory
system.
Describe the anatomy and physiology of
the kidney.
Label diagrams of a kidney and a
nephron.
Describe the production of urine.
Describe common disorders and illnesses
in the above systems, and possible
preventions.
Present advice for a healthy lifestyle.
Unit 4. Interaction with the Outline how organisms interact with their
internal and external environment.
Interaction
environment.
and Describe the nervous system: the
coordination The nervous system and locomotor system; organization and
[6h] the endocrine system. functional relationship between bones and
Coordination and the muscles.
nervous system. Describe how information is registered,
Organisation and processed and delivered so the body
function. responds.
The endocrine system: Label a diagrams of nerves and neurones.
glands and their
functions. The main Outline the role of the spinal cord in
disorders of the reflex actions.
endocrine system. Describe the structure and function of the
different areas of the brain.
Describe the sense organs: structure and
function, care and hygiene.
State advice for prevention of injuries.
Identify the differences between the
nervous sytem and the endocrine system.
Describe the endocrine system: its
function; glands and possible disorders.
Outline the role of hormones in controling
processes in the body.
State examples of glands and the
hormones they produce (insuline,
glucagon and adrenaline).
2nd Term
Unit 5. Human reproduction. Define the concept of human
reproduction.
Reproduction. Anatomy and
[8h] physiology of State the differences between sexual and
reproductive systems. asexual reproduction.
Physical and Describe the anatomy and physiology of
psychological changes the male and female reproductive
during adolescence. systems.
The menstrual cycle. Label diagrams of human reproductive
Fertilization, pregnancy systems, structures within themand the
and childbirth gametes.
Different contraceptive Describe the process of gametogenesis.
methods. Assisted Outline physical and psychological
reproduction changes during adolescence.
techniques.
Summarise the menstrual cycle and
Sexually transmitted outline the role of the 4 main hormones.
diseases and prevention
techniques. Apply knowledge to explain diagrams that
represent the menstrual cycle.
Human sexual
responses. Describe fertilization, pregnancy,
childbirth and assisted reproduction
Sex and sexuality.
techniques.
Sexual health and Analyse different contraceptive methods.
hygiene.
Outline examples of sexually transmitted
diseases and prevention techniques.
Define sexual health.
Discuss sex and sexuality.
Unit 6. The structure of the Describe the structure of the nucleus and
nucleus and its its functions.
Genetics I.
functions.
[12h] Outline the differences between
The cell cycle: mitosis chromatine and chomosomes.
and meiosis. Explain the cell cycle.
Inheritance and the Define mitosis and meiosis.
transmission of
characteristics. Label diagrams of the cell cycle and cell
division.
The introduction and
development of Identify the main stages of the cell cycle
Mendel’s Laws. and cell division and state what processes
are occuring in each.
Genetic problems using
Punnett squares State at which stage of meiosis genetic
variation is produced and describe the
Chromosomal
mechanisms.
foundations of
Outline the difference between diploid
Mendel’s Laws. and haploid cells; homozygous and
heterozygous organisms.
Application of
Mendel’s Laws Define genotype; phenotype; allele;
dominant; recessive;
complete/incomplete/co-dominance.
Apply knowledge of heredity and the
inheritence of characteristics.
Describe Mendel´s laws of inheritence.
Solve genetic problems using Punnett
squares for alleles with
complete/incomplete/co-dominance; sex-
linked and mono/dihybrid crosses.
Apply Mendel´s laws to the inheritence of
alleles.
Outline factors that affect Mendel´s ratios.
Unit 7. The nucleic acids. Draw the nucleic acids.
Genetics II. DNA and molecular Describe the structure of DNA.
[12h] genetics. Outline the process of DNA replication.
The process of DNA Define the concept of a gene.
replication.
Explain the genetic code and how genetic
The concept of a gene. information is expressed refering to
How genetic transcription and translation and the role
information is of RNA.
expressed. The Genetic Define the concept of mutation and
code. Mutations. discuss its relationship with evolution.
Relationship to
evolution. Define genetic engineering.
Genetic engineering: Outline the role of enzymes in genetic
techniques and engineering.
applications. Describe the applications of genetic
engineering.
3rd Term
Unit 8. Theories of the origins Summarise the 4 main theories of the
of life on Earth. origins of life on Earth.
Evolution
[10h] Theories of evolution. Define evolution.
The fact and Describe the differences between the
mechanisms of theories of Lamarck and Darwin.
evolution. Explain Darwin´s theory of evolution.
Human evolution: the Apply Darwin´s 3 observations of 2
process of conclusions to a given example.
anthropogenesis.
Describe neo-Darwinism.
Explain the evidence and mechanisms of
evolution.
Apply the modern theory of evolution to
given examples.
Unit 9. The structure of Describe the structure of ecosystems.
ecosystems.
Ecology and Define species, population and
the Components of an community.
environment. ecosystem: Define the biotic and abiotic components
[12h] communities and of an ecosystem.
habitats.
Explain interspecific and intraspecific
Trophic relations in relationships.
foodchains and
foodwebs. Interpret trophic relations in foodchains
and foodwebs.
Habitats and ecological
niches. Define habitats and ecological niches.
Limiting factors and Explain limiting factors and adaptations.
adaptations. Explain the cycle of matter and energy
The cycle of matter and flow through ecosystems.
energy. Ecological Define biomass.
pyramids. Biochemical
cycles. Analyse ecological pyramids.
Impacts and evaluation Describe biogeochemical cycles.
of human activities on Analyse and explain impacts of human
ecosystems. activities on ecosystems.
Overpopulation and its Discuss overpopulation and its
consequences, consequences, including: deforestation,
including: overfishing, fires.
deforestation,
overfishing, fires.
Unit 10. The origin and history Describe the origin and history of the
of the Earth. Earth.
Dynamic
Earth. [10h] Geological time and Outline the physical characteristics of the
historical ideas on the Earth.
age of the Earth. Discuss the concept of geological time and
Principles and evaluate historical ideas on the age of the
procedures that allow Earth.
historical Describe methods that allow us to
reconstruction. calculate the age of the Earth and its
Geological eras and interior.
time periods. The State the location of important geological
location of important and biological events.
geological and
biological events.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Draft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Dokument13 SeitenDraft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Patrick PenachosNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Convert Files To Binary FormatDokument1 SeiteHow To Convert Files To Binary FormatAhmed Riyadh100% (1)
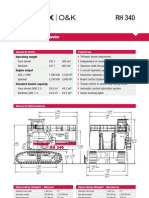
- Hydraulic Mining ExcavatorDokument8 SeitenHydraulic Mining Excavatorasditia_07100% (1)
- Top 100 Chemical CompaniesDokument11 SeitenTop 100 Chemical Companiestawhide_islamicNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNN 6Th YearDokument5 SeitenCCNN 6Th Yearapi-230640828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Criteria Y6 and 7Dokument5 SeitenAssessment Criteria Y6 and 7api-230640828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Define A Unit As Either Fundamental (M,: KG, S, K (ºC), or Derived (N, L, CM)Dokument5 SeitenDefine A Unit As Either Fundamental (M,: KG, S, K (ºC), or Derived (N, L, CM)api-230640828Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Ec 4 BB 419 Cdab 2 D 5 C 3 F 3Dokument4 Seiten4 Ec 4 BB 419 Cdab 2 D 5 C 3 F 3api-2306408280% (1)
- Binary OptionsDokument24 SeitenBinary Optionssamsa7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Antibodies PropertiesDokument3 SeitenNotes On Antibodies PropertiesBidur Acharya100% (1)
- Importance of Communications 05sept2023Dokument14 SeitenImportance of Communications 05sept2023Sajib BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence Techniques For Encrypt Images Based On The Chaotic System Implemented On Field-Programmable Gate ArrayDokument10 SeitenArtificial Intelligence Techniques For Encrypt Images Based On The Chaotic System Implemented On Field-Programmable Gate ArrayIAES IJAINoch keine Bewertungen
- JFC 180BBDokument2 SeitenJFC 180BBnazmulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (R)Dokument23 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project (R)BhagyashreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aakriti 1Dokument92 SeitenAakriti 1raghav bansalNoch keine Bewertungen
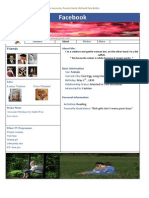
- Facebook: Daisy BuchananDokument5 SeitenFacebook: Daisy BuchananbelenrichardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mahesh R Pujar: (Volume3, Issue2)Dokument6 SeitenMahesh R Pujar: (Volume3, Issue2)Ignited MindsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 1Dokument6 SeitenAcc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 12022825274100% (1)
- EN 50122-1 January 2011 Corrientes RetornoDokument81 SeitenEN 50122-1 January 2011 Corrientes RetornoConrad Ziebold VanakenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odisha State Museum-1Dokument26 SeitenOdisha State Museum-1ajitkpatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- SreenuDokument2 SeitenSreenuSubbareddy NvNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument3 SeitenResumeapi-280300136Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mosharaf HossainDokument2 SeitenMosharaf HossainRuhul RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacacay South Hris1Dokument7.327 SeitenBacacay South Hris1Lito ObstaculoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dreaded Attack - Voyages Community Map Rules v1Dokument2 SeitenDreaded Attack - Voyages Community Map Rules v1jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Native VLAN and Default VLANDokument6 SeitenNative VLAN and Default VLANAaliyah WinkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Report Format For Associate Degree ProgramDokument5 SeitenInternship Report Format For Associate Degree ProgramBisma AmjaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specifications (018-001) : WarningDokument6 SeitenSpecifications (018-001) : WarningRómulo Simón Lizarraga LeónNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC-MEPC.2-Circ.17 - 2019 Guidelines For The Carriage of Blends OfBiofuels and Marpol Annex I Cargoes (Secretariat)Dokument4 SeitenMSC-MEPC.2-Circ.17 - 2019 Guidelines For The Carriage of Blends OfBiofuels and Marpol Annex I Cargoes (Secretariat)DeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP 12math Term 1Dokument11 SeitenQP 12math Term 1sarthakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Guide Ay 2021-2022: Dr. Gloria Lacson Foundation Colleges, IncDokument9 SeitenCurriculum Guide Ay 2021-2022: Dr. Gloria Lacson Foundation Colleges, IncJean Marie Itang GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1Dokument11 SeitenSteel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument8 SeitenChapter 2Fahmia MidtimbangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-1. Drifting & Tunneling Drilling Tools PDFDokument9 Seiten2-1. Drifting & Tunneling Drilling Tools PDFSubhash KediaNoch keine Bewertungen