Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bored Piles - Production Method
Hochgeladen von
孟谨0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1 Ansichten10 Seitenbored pile
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenbored pile
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1 Ansichten10 SeitenBored Piles - Production Method
Hochgeladen von
孟谨bored pile
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
Bored Piles
Production Method
Bilfinger Spezialtiefbau GmbH
Goldsteinstrasse 114
D-60528 Frankfurt
Phone: +49 69 6688-345
Fax: +49 69 6688-277
Email: info.spezialtiefbau@bilfinger.com
www.foundation-engineering.bilfinger.com
Large Diameter Bored Piles Pont de Normandie
Large bored piles are used as foundation elements to carry
concentrated building loads into deeper, more stable soil layers.
Furthermore, they can be utilized as piles for retaining walls if there Maumee River Crossing
is not enough space for flat foundation.
In the same way, retaining walls for excavation pits are constructed
by using multiple bored piles as bored pile wall, which later can be
incorporated into the final building.
Bored piles can be easily adapted to the various load and soil
requirements due to the large variety in diameter and construction
techniques. Single pile diameter can vary between 30 and 300 cm.
Piles can be constructed in all kinds of soil condition.
In contrast to driven piles, bored piles enable the immediate In-situ
evaluation of drilled soil layers to revise foundation length due to
changed soil conditions.
The specific pile construction method depends on the soil condition, Bridge L71 across the Heilsau
the ground water elevations, site conditions and the length of the
pile.
Construction methods can be distinguished between Pont de Normandie
• The bore hole stabilization process during excavation Fully
cased, partial cased, uncased and fluid stabilized excavation can
be distinguished Lilla Bommen Tunnel
• The method of installing the casing
Here one can distinguish between driving the casing with a free
fall hammer or weight, vibrating the casing, pneumatic installation
or hydraulic installation with the help of a rotary drive, an oscillator
or rotator.
• The method of excavation
Here one can distinguish between grab excavation, rotary drilling,
airlifting, and flush boring.
Bore Hole Stabilization High Speed Rail Nürnberg -
Ingolstadt, Tunnel Offenbau
Uncased bore holes can only be excavated in stable soil layers. In
general a short starter casing is been used at the pile top.
If uncased excavations run through unstable soil layers, the bore Center for Innovative Medicine,
hole wall has to be stabilized by fluid overpressure. Water or Hamburg
bentonite as well as polymer suspension is used as stabilizing
fluid.
Partially cased bore holes are cased in areas with unstable soils Gallileo Tower, Frankfurt
and deeper and stable soil layers are stabilized by water, bentonite
or polymers, while rock layers do not require any support.
The casing of the borehole has to stabilize the soil and minimize
the relaxation of the surrounding ground. It is always required
whenever unstable soil layers cannot be stabilized with fluids and
there is a risk of soil caving.
CFA piles (Continuous Flight Auger) are drilled uncased by the use
of a continuous hollow auger stem. Stabilization of the borehole
wall during excavation is provided by the soil filled auger. During
pulling of the auger stem, concrete is pumped through the stem,
preventing any soil instability of the bore hole wall.
Methods of casing installation Driving by vibratory hammer
During casing installation, tip resistance and skin friction of the
casing has to be overcome.
Installation by free fall weight Driving by free fall weight
Casings in single length up to 6 m are installed using a fee fall
weight. Suitable soil conditions are required for such driving
practice. During this installation method, casings with extra collars Free wall weight
will be driven, excavated and so-called Jumbo piles are
constructed.
Installation by vibratory hammer
Casings are installed into the ground using externally induced
vibration. Friction between casing and surrounding soil is reduced
by vibration generated from an attached vibro hammer. The casing
penetrates the ground due to this vibration, the weight of the
hammer and its own weight. This installation method has a limited
use due to the soil densification inside the casing and possible
vibration damage on adjacent buildings or structures.
Pneumatic installation by the HW method HW principle
The HW-method, named after Hochstrasser/Weise, uses a
pneumatically-driven swinging arm, sitting on top of the casing, to
drive the casing in a horizontal back and forth movement. End HW swinging arm
stops transfer the rotation impulse of the swinging arm into the
casing, which rotates slightly at each stroke. This considerably
reduces the skin friction between soil and casing. The casing is
excavation by the wire rope guided grab at the same time. Dike rehabilitation Emmerich
The casing is driven into the ground as a result of the reduced skin
friction and under the weight of the casing and swinging arm.
A major advantage of this method is that the excavating crane does
not have to be placed right next to the casing to support the
reaction forces from the swinging movements of the equipment.
The HW unit can therefore be utilized as a separate unit from the
excavating crane, which is an advantage when piles need to be
installed in steep slopes or over water.
Hydraulic casing installation Rotary drilling rig, Galeria
Kaufhof, Alexanderplatz, Berlin
The hydraulic installation method uses an oscillating motion
(Oscillator) or a continuously rotating motion (Rotary Drive or
Rotator) of the casing to reduce the skin friction between casing
and soil. Rotator (RDM)
All of these machines also induce a vertical downward force into the
casing, which in combination with the casing’s own weight enables
penetration of the casing.
Oscillator (VRM)
The casing normally consists of separate sections, which are
connected and bolted during installation.
During the casing installation, the excavating equipment is always
placed right next to the casing and receives the reaction forces from
the rotary motion.
The Method of Excavation HW – Grab, long version with
parallel shells
Grab Excavation
Excavation using a free fall or spherical grab is mostly used when
boreholes are very deep and other methods come to their limits or Ball grab with spherical shells
in combination with the HW method.
The borehole is advanced using grabs consisting of a base body,
the grab shells and the closing mechanism for the shells. One
Flat chisel
distinguishes between single-rope and double-rope operated grabs.
The single-rope grab also uses the lifting rope as a closing rope for
the grab shells. The double-rope grab is used with two ropes, one
for grab lifting and one for closing the shells. Ring chisel
Performance of the grab mainly depends on the correct shell
shape, which is chosen according to soil parameters.
For excavations below the groundwater level, in-the-wet drilling
tools such as gravel pumps or mud cans are available for the
various drilling diameters.
Free-fall chisels are used to drill through large obstructions such as
bricks, boulders or rock layers as well as for the pile penetration
into bedrock. Various sizes and shapes such as cross, flat, stellar,
ring shapes are available. These chisels are equipped with different
blades depending on the various soil properties.
Rotary drilling methods Sketch - drilling rig
During the rotary drilling method, the excavation is advanced using
drilling augers and buckets.
The drilling rig consists of a base carrier and the drilling unit Drilling rig with bucket
mounted on top of the carrier. One distinguishes between short
augers and continuous flight augers.
When drilling with short augers or buckets, the torque and Drilling rig with continuous auger
downward crowd is transferred to the drilling tools via a telescopic
drilling rod (Kelly bar). Drilling and discharging of the excavated
material are alternating operations, which are performed in a swift
order. Depending on soil conditions and pile diameter, various
augers are used. For excavations below the ground water level,
drilling or digging buckets are used. Obstructions or rock layers can
be removed with the help of core barrels. To increase the pile base
area, belling buckets or under-reamers can be employed.
When drilling with continuous flight augers, the auger is
connected directly with the rotary drive without an intermediate
drilling rod and is rotated into the ground for its full length. After
reaching final drilling depth, the filled auger is pulled out of the bore
hole. Therefore the empty bore hole has to be stable enough or
concrete needs to be pumped through the hollow auger stem
immediately. Pile length is limited by the length of the auger and the
size of the drilling rig.
Flush drilling / wet drilling methods Sketch air-lifting drilling method
for bored pile construction
In contrast to the dry drilling method, where the soil is loosened and
excavated by the drilling tools, the wet drilling method only uses
drilling tools to loosen the material and requires a flushing stream
for transportation. Cutting tools like tri-cone bits, roller bits or Air-lifting drilling method
under-reamers are used.
When using the direct flushing method, bentonite or polymer
suspension is pumped down to the piles tip through the hollow
drilling rod. The suspension is then raised up to the piles top in the
annulus between drilling rod and bore hole wall. This method is
most suitable for smaller bore hole diameters.
When using the reversed circulation method, the flushing
suspension is poured directly into the bore hole. Using a vacuum
pump, the soil/suspension mixture is then sucked through the
drilling rods to the pile’s top. Pile length up to 50 m can be drilled
efficiently.
The air-lifting method also pours flushing suspension directly into
the bore hole. By inducing compressed air into the lower end of the
drilling rod below the water level, the expanding air creates an
upward flow, which therefore transports the soil/suspension mixture
to the top of the pile.
Combinations of air-lifting and reversed circulation drilling can drill
bore holes up to 150 m depth efficiently, depending on soil
conditions.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Thermal Stresses and Temperature Control of Mass ConcreteVon EverandThermal Stresses and Temperature Control of Mass ConcreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods and Implementation in Geotechnical Engineering – Part 1Von EverandNumerical Methods and Implementation in Geotechnical Engineering – Part 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechineries Use For Pile InstallationDokument36 SeitenMechineries Use For Pile InstallationAbu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Installing Pile FoundationsDokument5 SeitenMethods of Installing Pile FoundationslaikienfuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bored Piling Method Statement - Planning Engineer EstDokument8 SeitenBored Piling Method Statement - Planning Engineer EstboomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Drill Bored PileDokument4 SeitenHow To Drill Bored Pileezdiani84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bored PileDokument9 SeitenBored PileMichael RootNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT. PAKUBUMI SEMESTA Bored Piling MethodDokument19 SeitenPT. PAKUBUMI SEMESTA Bored Piling MethodjimdabrondNoch keine Bewertungen
- SW Juntas CwsDokument5 SeitenSW Juntas CwsflylilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STATIC LOAD TEST - การทดสอบการรับน้ำหนักของเสาเข็มDokument11 SeitenSTATIC LOAD TEST - การทดสอบการรับน้ำหนักของเสาเข็มWilrutstien WilrutstienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement Geo Technical Investigation: 1. PurposeDokument7 SeitenMethod Statement Geo Technical Investigation: 1. PurposeJ. Kumar Infraprojects LtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Tips / Thumb RulesDokument7 SeitenStructural Tips / Thumb Ruleswindspace3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Keller 20 01EN Bored PilesDokument4 SeitenKeller 20 01EN Bored PilesFauzi FirmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement Horizontal DrainDokument1 SeiteMethod Statement Horizontal DrainAlsonChin100% (1)
- Tale of 2 Deep Singapore Basements and How 3D Modeling Led To A Leaner Design and Keener Construction Programme - EiSandaDokument13 SeitenTale of 2 Deep Singapore Basements and How 3D Modeling Led To A Leaner Design and Keener Construction Programme - EiSandablithevincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Jet GroutingDokument10 SeitenFinal Jet GroutingHaresh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Public Works and HighwaysDokument17 SeitenDepartment of Public Works and HighwaysRolly Marc G. SoteloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant & Guide Wall ConstructionDokument10 SeitenPlant & Guide Wall ConstructionAnonymous S7Cq7ZDgPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaipur Metro East-West Corridor Route DescriptionDokument25 SeitenJaipur Metro East-West Corridor Route DescriptionSonu LovesforuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Jacking & Microtunnelling GuideDokument48 SeitenPipe Jacking & Microtunnelling GuideHizbar ArsjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Soil Investigation - Building ProjectDokument8 SeitenGuidelines For Soil Investigation - Building Projectmaricar_hereNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Type of Retaining WallsDokument3 Seiten3-Type of Retaining Wallsone engNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uae Ground ImprovementDokument12 SeitenUae Ground ImprovementMuhanad SalemNoch keine Bewertungen
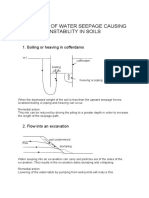
- Boiling or Heaving in CofferdamsDokument2 SeitenBoiling or Heaving in Cofferdamsslawek780303Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Phases Involved in Bored Cast inDokument3 Seiten4 Phases Involved in Bored Cast inRajesh KhadkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pantex Lattice GirdersDokument7 SeitenPantex Lattice GirdersbrodieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthworks Specs JKR 2014Dokument95 SeitenEarthworks Specs JKR 2014Tan ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEEP FOUNDATION TYPES PILES DRILLEDDokument3 SeitenDEEP FOUNDATION TYPES PILES DRILLEDVishnuPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- The New Bugis Station and Associated Tunnels For The Singapore MRTDokument8 SeitenThe New Bugis Station and Associated Tunnels For The Singapore MRThutuguoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Dug Caisson Construction ManualDokument59 SeitenHand Dug Caisson Construction ManualSim Khoon Aun50% (2)
- Gunite & ShortcreteDokument146 SeitenGunite & ShortcreteSushil DhunganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IH-NTCO-X-04-252501-A0 - Method Statement For Surge Shaft ExcavationDokument49 SeitenIH-NTCO-X-04-252501-A0 - Method Statement For Surge Shaft Excavationapi-3827616100% (7)
- Ground Investigation - Pre-Drilling at MTR Protection ZoneDokument26 SeitenGround Investigation - Pre-Drilling at MTR Protection ZoneMan Ho LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bored PileDokument20 SeitenBored PileIwan Dana100% (1)
- Ground Improvement Techniques by GroutingDokument16 SeitenGround Improvement Techniques by GroutingYathish143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Pile Driving Problems and SolutionsDokument4 SeitenCommon Pile Driving Problems and SolutionsRainndrop FonnyryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1 OF Project Management Topic-: Submitted To Submitted byDokument13 SeitenAssignment - 1 OF Project Management Topic-: Submitted To Submitted bynaushavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOS SS-HTB Tightening PartDokument9 SeitenMOS SS-HTB Tightening PartjimdabrondNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGDokument20 SeitenSGThaungMyintNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement of Bored Piles 21Dokument40 SeitenMethod Statement of Bored Piles 21Dharma Pratap LamgadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GabionsDokument9 SeitenGabionsGerard Pierre LouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- PilesDokument47 SeitenPilesnurulselangorNoch keine Bewertungen
- S13-Specification For MicropileDokument9 SeitenS13-Specification For MicropilewongtianhuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech InvestigationDokument10 SeitenGeotech InvestigationanumnedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piling WorksTenderDokument86 SeitenPiling WorksTenderAnonymous 1uGSx8bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthwork Plan Submssion ChecklistDokument4 SeitenEarthwork Plan Submssion ChecklistanlekgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jet GroutingDokument8 SeitenJet GroutingiskeletorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ismailia Road Tunnel Crossing The Suez Canal PDFDokument8 SeitenIsmailia Road Tunnel Crossing The Suez Canal PDFRonald HeijmansNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16AGS - Groundwater Control in Design and Construction of Deep Basement Excavation in Singapore (150910)Dokument15 Seiten16AGS - Groundwater Control in Design and Construction of Deep Basement Excavation in Singapore (150910)krainajackaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPV PresentationDokument66 SeitenPPV PresentationIvan BogdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of underground structuresDokument2 SeitenConstruction of underground structuresHanri PakpahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concreting MethodologyDokument2 SeitenConcreting Methodologyervnglen08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of post-installed rebar connectionsDokument33 SeitenBasics of post-installed rebar connectionsHaitham KayyaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residential Development Diaphragm Wall WorkDokument41 SeitenResidential Development Diaphragm Wall Workjodemode100% (2)
- 17 - Bored Piling Ch. Lis.Dokument19 Seiten17 - Bored Piling Ch. Lis.Dilhara WickramaarachchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS900-General Tunnel Construction - 161026Dokument5 SeitenSS900-General Tunnel Construction - 161026jologscresenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultra-High Capacity Micropiles, Drilled Displacement Steel Piles & Expanded Base PilesDokument1 SeiteUltra-High Capacity Micropiles, Drilled Displacement Steel Piles & Expanded Base PilesAnonymous JZFSB3D0% (1)
- Bored Piles - Production MethodDokument10 SeitenBored Piles - Production MethodFrank Stephens100% (1)
- Methods of Piles InstallationDokument5 SeitenMethods of Piles InstallationAsif KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Instalation MethodsDokument7 SeitenPile Instalation MethodsMuhammadIqbalMughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Slopes, Soil and Fill MaterialDokument1 SeiteCalculating Slopes, Soil and Fill MaterialroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- eLCOSH Roadway Safety ExcavationDokument2 SeiteneLCOSH Roadway Safety ExcavationroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worker Safety Series - Construction - Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationDokument10 SeitenWorker Safety Series - Construction - Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Checklist Trenches and ExcavationsDokument5 SeitenSafety Checklist Trenches and ExcavationsroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitudes Behavior Values Knowledge Skills: Ethical ConsiderationsDokument6 SeitenAttitudes Behavior Values Knowledge Skills: Ethical ConsiderationsroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthworks For New Tracks and Formation Widening ETC-08-01: Technical Specification Track & Civil - ConstructionDokument36 SeitenEarthworks For New Tracks and Formation Widening ETC-08-01: Technical Specification Track & Civil - ConstructionroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Site PremisesDokument28 SeitenConstruction Site PremisesroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roadway Excavation Embankment and Compaction 2019 31 24 13Dokument7 SeitenRoadway Excavation Embankment and Compaction 2019 31 24 13roldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astec Concrete TestingDokument4 SeitenAstec Concrete TestingroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConsfinedspaceDokument18 SeitenConsfinedspaceAldrien CabinteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction - Scaffold Checklist - HSEDokument6 SeitenConstruction - Scaffold Checklist - HSEroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formwork, Scaffolding and Shoring Definition and ProductivityDokument7 SeitenFormwork, Scaffolding and Shoring Definition and ProductivityroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplementary Appendix To ARTC Track & Civil Code of Practice Railway Earthworks ETC-08-02Dokument12 SeitenSupplementary Appendix To ARTC Track & Civil Code of Practice Railway Earthworks ETC-08-02roldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turnout Replacement: Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil - Construction) Category: Technical SpecificationDokument22 SeitenTurnout Replacement: Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil - Construction) Category: Technical SpecificationroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layout Calculation BookDokument137 SeitenLayout Calculation BookUrmila Jangra100% (3)
- Producer Price Index (PPI) Guide To Contract EscalationDokument13 SeitenProducer Price Index (PPI) Guide To Contract EscalationroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Ch11 Slope StabilizationDokument12 SeitenM Ch11 Slope StabilizationSulekha NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBST GuideDokument26 SeitenDBST GuideroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance of National Road No. 3 in CambodiaDokument20 SeitenMaintenance of National Road No. 3 in Cambodiaroldski90% (10)
- SPEC Concrete - 07100 ConcreteDokument124 SeitenSPEC Concrete - 07100 ConcreteroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION 3 Thermite Welding Specifications From AREMADokument3 SeitenSECTION 3 Thermite Welding Specifications From AREMAroldski100% (2)
- PBD InfraDokument104 SeitenPBD Infravicent johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Block PavementsDokument6 SeitenConcrete Block PavementsroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subgrade Compaction and Proof Rolling SpecificationsDokument6 SeitenSubgrade Compaction and Proof Rolling Specificationsroldski100% (1)
- Ballast Regulator M 7 Operation Manual 49458003Dokument71 SeitenBallast Regulator M 7 Operation Manual 49458003roldski100% (1)
- Clinic08 HandoutDokument6 SeitenClinic08 HandoutAynup IrahtakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulk Density Guide for Common Construction MaterialsDokument2 SeitenBulk Density Guide for Common Construction MaterialsroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Capital CostsDokument14 SeitenOf Capital CostsmilikanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directory of British StandardsDokument2 SeitenDirectory of British StandardsroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Monitoring SpecificationDokument22 SeitenVibration Monitoring SpecificationnarcoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR Handbook PDFDokument640 SeitenNR Handbook PDFArvind Sharma100% (1)
- 30 ST Mary AxeDokument29 Seiten30 ST Mary AxeAkrame100% (1)
- BWDB Schedule of Rates - Volume-1, June 2019Dokument178 SeitenBWDB Schedule of Rates - Volume-1, June 2019SDE Kaptai83% (6)
- Earthquake Resistant Design of FoundationDokument11 SeitenEarthquake Resistant Design of FoundationNarayan Roy100% (1)
- STATUS Limestone HopperDokument15 SeitenSTATUS Limestone Hoppershangz1511Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Shallow Foundation ThesisDokument133 SeitenSoftware Shallow Foundation ThesisAbel MulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PILE FOUNDATION DESIGN CALCULATIONSDokument17 SeitenPILE FOUNDATION DESIGN CALCULATIONSisaacjoe77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applicability of Raft (Mat) FoundationsDokument5 SeitenApplicability of Raft (Mat) FoundationsSanjana BhandiwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard BoQ (UAE - DoT) - CESMM4 PDFDokument554 SeitenStandard BoQ (UAE - DoT) - CESMM4 PDFNektarios Matheou86% (44)
- Risk Identification Stage 2Dokument7 SeitenRisk Identification Stage 2Airah GugulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SampleDokument630 SeitenSampleAsgharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For The Use of Steel Piling For Bridge FoundationsDokument21 SeitenGuidelines For The Use of Steel Piling For Bridge FoundationsHermann PankowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proyek Pergudangan Purwakarta Pekerjaan InfrastructureDokument7 SeitenProyek Pergudangan Purwakarta Pekerjaan InfrastructureArief PerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bi-Directional Load TestDokument64 SeitenBi-Directional Load TestAnonymous zpNy2blt100% (3)
- Draft PPT Pile FoundatationDokument14 SeitenDraft PPT Pile FoundatationDwijendra ChanumoluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Resisting Hydrostatic Uplift in Substructures - I H Wong - TUST 2001 PDFDokument10 SeitenMethods of Resisting Hydrostatic Uplift in Substructures - I H Wong - TUST 2001 PDFDarkie LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Integrity TestDokument7 SeitenPile Integrity TestFazren KamarudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- IStructE Chartered Membership Examination 2008Dokument28 SeitenIStructE Chartered Membership Examination 2008shamimzubery75% (4)
- Laterally Loaded Pile Behaviors in Clay With Uncertainty in Strain E50Dokument10 SeitenLaterally Loaded Pile Behaviors in Clay With Uncertainty in Strain E50He WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piling Works Method Statement for Baricho Well Field Protection ProjectDokument23 SeitenPiling Works Method Statement for Baricho Well Field Protection ProjectTheodore Teddy KahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Basement Construction MethodsDokument9 SeitenConcepts of Basement Construction Methodssreejit77100% (4)
- GE July 1976 Foundations and Earthworks For Cylindrical Steel Storage TanksDokument113 SeitenGE July 1976 Foundations and Earthworks For Cylindrical Steel Storage Tanksselvakumar100% (1)
- Handbook For Building ConstructionDokument894 SeitenHandbook For Building Construction2628336988% (24)
- Experimental Investigations Analysis and Design PDFDokument38 SeitenExperimental Investigations Analysis and Design PDFrtwueee fcbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offshore Wind BrochureDokument16 SeitenOffshore Wind BrochureJade KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navdac DM 7.02Dokument271 SeitenNavdac DM 7.02Muhammad Yodha AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPG CAL 50 008 A4 Calculation Genset FoundationDokument11 SeitenSPG CAL 50 008 A4 Calculation Genset FoundationOmar PerpatihNoch keine Bewertungen