Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Measuring The Center Summary
Hochgeladen von
JayOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Measuring The Center Summary
Hochgeladen von
JayCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SMARTLY
ONE-VARIABLE STATISTICS
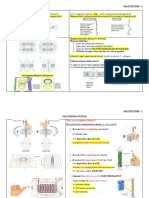
MEASURING THE CENTER
Averages, Quartiles, and the Five Number Summary
Descriptive statistics: A way to quickly summarize data within a
set using just a few numbers.
Mean: The average of a set calculated by adding all the values in
the set and dividing by the number of values in the set.
Outlier: A value or values significantly higher or lower than the rest The mean is very sensitive to
of the set that can skew the mean of a set.
outliers, while the median is not.
Median: The middle value in a data set.
Mode: The value that appears most often in the set.
When a set has two modes it is called bimodal. When it has
more than two modes, it is multimodal.
√Σ
Standard deviation: A measurement of the amount of variation 1 N 2
from the mean in a data set.
σ= (xi µ)
N i=1
For example, if a data set has a mean of 50 units and a standard
deviation of 20 units, we can conclude that most of the data will σ = standard deviation
fall between 30 and 70 units. th
xi = the value of the i
Five number summary: The minimum, first quartile, median, third observation
quartile, and maximum of a data set. N = Number of data points
Each quartile represents 25% of the data within a set. µ = mean of data values
The first and third quartiles can be found by identifying the
medians of the lower and upper halves of the data.
Range: The distance between the maximum and minimum.
Interquartile range (IQR): The distance between the third and first
quartiles.
min median max
Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
©2017 Pedago, LLC. All rights reserved.
ONE-VARIABLE STATISTICS SMARTLY
Graphical Organization
Boxplot: A graph representing the five number summary. Boxplot
The boxed area represents the IQR with the median at the Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
center.
Frequency distribution: A table that sorts data into equally-sized
classes.
Ages of Mobile Phone Customers min median max
Cumulative Relative Cumulative 20 30 40 50 60
Class Frequency Frequency Frequency Relative Frequency
If Q1 and the If Q3 and the
20 ≤ X < 30 17 17 34.00% 34.00%
minimum are the maximum are
30 ≤ X < 40 16 33 32.00% 66.00% same value, you the same, there
40 ≤ X < 50 12 45 24.00% 90.00% won’t see a tail will be no tail on
50 ≤ X < 60 4 49 8.00% 98.00% on the left side. the right.
60 ≤ X < 70 1 50 2.00% 100.00%
Total 50 100.00%
Frequency: The amount of data points that fall into each class.
Cumulative frequency: The running total of the frequencies.
Relative frequency: The frequency divided by the total number of
data points.
Cumulative relative frequency: The running total of the relative
frequencies.
Histogram: A frequency distribution shown in graph form.
Positive skew (right skew): Negative skew (left skew):
When values pull a chart to When values pull a chart to
the right. the left.
35 35
35 35 35
30 30
25 25
25
20 20
20 20
15
15
10
10
10 10 10
5
5 5 5 5
$35
$45
$55
$65
$75
$85
$95
$115
$35
$45
$55
$65
$75
$85
$95
$115
$105
$125
$105
$125
In a histogram with a positive In a histogram with a negative
skew, the mean is greater skew, the median is greater
than the median. than the mean.
©2017 Pedago, LLC. All rights reserved.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Answers To Quiz No 19Dokument5 SeitenAnswers To Quiz No 19Your Public Profile100% (4)
- List of Ala-Carte Paid ChannelsDokument4 SeitenList of Ala-Carte Paid ChannelsJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konica Adding Email AddressDokument2 SeitenKonica Adding Email AddressJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Management: Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB 0131 650 5899 Mfelici@inf - Ed.ac - UkDokument20 SeitenProject Management: Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB 0131 650 5899 Mfelici@inf - Ed.ac - UkvelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accupressure DiabetesDokument2 SeitenAccupressure DiabetesJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication SkillsDokument21 SeitenCommunication Skillskarthi1it100% (2)
- Python Tutorial PDFDokument155 SeitenPython Tutorial PDFDiana RusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garudatri 1Dokument10 SeitenGarudatri 1JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Memory Techniques From One-Mind-One-Energy PDFDokument5 SeitenFree Memory Techniques From One-Mind-One-Energy PDFJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet Basics SummaryDokument2 SeitenBalance Sheet Basics SummaryJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- And The Brain: BristolDokument1 SeiteAnd The Brain: BristolJay JayasankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Education System in Singapore: CollegesDokument17 SeitenEducation System in Singapore: CollegesJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professionalism: A Concise Guide: Get Hired: Showcasing YourselfDokument2 SeitenProfessionalism: A Concise Guide: Get Hired: Showcasing YourselfJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet Basics SummaryDokument2 SeitenBalance Sheet Basics SummaryJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signature Not Verified: Digitally Signed by Ravi Shankar Jayaram Date: 2019.02.07 13:44:15 IST Location: BengaluruDokument1 SeiteSignature Not Verified: Digitally Signed by Ravi Shankar Jayaram Date: 2019.02.07 13:44:15 IST Location: BengaluruJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utility and ElasticityDokument2 SeitenUtility and ElasticityJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- And The Brain: BristolDokument1 SeiteAnd The Brain: BristolJay JayasankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Ala-Carte Paid ChannelsDokument4 SeitenList of Ala-Carte Paid ChannelsJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utility and ElasticityDokument2 SeitenUtility and ElasticityJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Ala-Carte Paid ChannelsDokument4 SeitenList of Ala-Carte Paid ChannelsJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Memory Techniques From One-Mind-One-Energy PDFDokument5 SeitenFree Memory Techniques From One-Mind-One-Energy PDFJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Practice of Accounting SummaryDokument2 SeitenThe Practice of Accounting SummaryJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Practice of Accounting SummaryDokument2 SeitenThe Practice of Accounting SummaryJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing FundamentalsDokument2 SeitenMarketing FundamentalsJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVDokument1 SeiteCVJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utility and ElasticityDokument2 SeitenUtility and ElasticityJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet Basics SummaryDokument2 SeitenBalance Sheet Basics SummaryJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional ResumeDokument3 SeitenProfessional ResumeRam KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harbin Institute of TechnologyDokument7 SeitenHarbin Institute of TechnologyWei LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Dokument4 SeitenName: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Kartikeya ThadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre T&C Checklist (3 Language) - Updated - 2022 DavidDokument1 SeitePre T&C Checklist (3 Language) - Updated - 2022 Davidmuhammad farisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous WorkshopDokument5 SeitenPresent Continuous WorkshopPaula Camila Castelblanco (Jenni y Paula)Noch keine Bewertungen
- L 1 One On A Page PDFDokument128 SeitenL 1 One On A Page PDFNana Kwame Osei AsareNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC Donald'sDokument30 SeitenMC Donald'sAbdullahWaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weill Cornell Medicine International Tax QuestionaireDokument2 SeitenWeill Cornell Medicine International Tax QuestionaireboxeritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- W 26728Dokument42 SeitenW 26728Sebastián MoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monastery in Buddhist ArchitectureDokument8 SeitenMonastery in Buddhist ArchitectureabdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Financial PlanDokument38 SeitenSample Financial PlanPatrick IlaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Pricing 8Dokument34 SeitenTransfer Pricing 8nigam_miniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Thesis - Table of ContentsDokument13 SeitenPHD Thesis - Table of ContentsDr Amit Rangnekar100% (15)
- International Gustav-Bumcke-Competition Berlin / July 25th - August 1st 2021Dokument5 SeitenInternational Gustav-Bumcke-Competition Berlin / July 25th - August 1st 2021Raul CuarteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA-2 AasthaDokument4 SeitenCA-2 AasthaJaswant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism 1Dokument4 SeitenMagnetism 1krichenkyandex.ruNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Dokument106 SeitenDe Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Mai PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Linguistic Turn in Philosophy - Stenlund2002 PDFDokument40 SeitenOn The Linguistic Turn in Philosophy - Stenlund2002 PDFPablo BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comprehensive Guide To HR Best Practices You Need To Know This Year (Infographic)Dokument42 SeitenA Comprehensive Guide To HR Best Practices You Need To Know This Year (Infographic)MALATHI MNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9francisco Gutierrez Et Al. v. Juan CarpioDokument4 Seiten9francisco Gutierrez Et Al. v. Juan Carpiosensya na pogi langNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Fonction Compositionnelle Des Modulateurs en Anneau Dans: MantraDokument6 SeitenLa Fonction Compositionnelle Des Modulateurs en Anneau Dans: MantracmescogenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.597 B CAT en AccessoriesDokument60 Seiten15.597 B CAT en AccessoriesMohamed Choukri Azzoula100% (1)
- Nursing Education and Nursing Service ProgramsDokument10 SeitenNursing Education and Nursing Service ProgramsLevy DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ain Tsila Development Main EPC Contract A-CNT-CON-000-00282: Visual Inspection Test Procedure B-QAC-PRO-210-39162Dokument14 SeitenAin Tsila Development Main EPC Contract A-CNT-CON-000-00282: Visual Inspection Test Procedure B-QAC-PRO-210-39162ZaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Sastra Semester Genap KLS Xi 2023Dokument3 SeitenSoal Bahasa Inggris Sastra Semester Genap KLS Xi 2023Ika Endah MadyasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPU Self Reflection Peer ReviewDokument3 SeitenMPU Self Reflection Peer ReviewysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Control SystemDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To Control SystemAbdulhakam Abubakar YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gee 103 L3 Ay 22 23 PDFDokument34 SeitenGee 103 L3 Ay 22 23 PDFlhyka nogalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3Dokument81 SeitenRoman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3The Glamorgan-Gwent Archaeological Trust LtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymeric Nanoparticles - Recent Development in Synthesis and Application-2016Dokument19 SeitenPolymeric Nanoparticles - Recent Development in Synthesis and Application-2016alex robayoNoch keine Bewertungen