Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Intro To Philosophy
Hochgeladen von
omgOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Intro To Philosophy
Hochgeladen von
omgCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
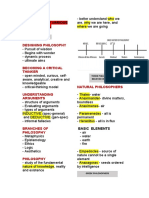
INTRO TO PHILOSOPHY PAMIMILOSOPO- Is someone who’s trying
to be clever and may sometimes irritate us or
amuse us.
PHILO + SOPHIA PYTHAGORAS
“Love” of “Wisdom” and his followers
THE BEGINNING OF DOING PHILOSOPHY
PYTHAGORAS MILETUS- trade hub of ancient times
- Leader of the Pythagoreans - Millesians
- Philosophy is a way of life like religion - It is where philosophy is born
- Gave importance to contemplative life - Melting pot of ideas
- Anything could be explained through THE PRE-SOCRATIC PHILOSOPHY
numbers -Miletus as fishing village and center for trade
PHILOSOPHY Was the ideal place for the first practice of
1) Set of principles people live by. philosophy to emerge
2) General guideline in life THE MILESIANS
3) Personal Codes THALES
4) Purposes in life
*way of seeing and making sense of the world.
*Having a philosophy does not mean that a
person is automatically Philosophical
GREEK IONA- Ancient greek
PHUSIS- Nature of things, ‘Nature’ in English. ANAXIMANDER ANAXIMENES
TRIUMVIRATE
RATIONAL- Reasons
RADICAL- Deep thinking SOCRATES
600 BC- Thales the militus diverged from the PLATO
mythological tradition.
“How do things come to be, change and pass away” ARISTOTLE- richest tutor in history
SOCRATES
- Exemplary philosopher ALEXANDER THE GREAT
- WISEST of the Athenians
*NOT BECAUSE HE KNOWS, BUT HE HYLOZOIST
KNOWS THAT HE DOES NOT KNOW HYLO- stuff or things
ZOE- Life
SOCRATES AND THALES
-Curiosity THALES- the earth is flat
REVOLUTION
-Thirst for knowledge -mathematician
= Change
-Humility -astronomer
PHILOSOPHICAL QUESTIONS ANAXIMANDER- reality is infinite or apeiron
-Open ended -earth is cylindrical
3 characteristics of Philosophical questions -Attempted to be the first cartographer
according to Isaiah Berlin ANAXIMENES- air holds our soul together
1) Often broad or very general -supported thales with flat erth theory
2) No single Methodology -all heavenly matters are likesaucers floating in the
3) No practical utility air
EAST AND WEST PHILO.
Study of Art What can life be
WEST- REALITY- curiosity about world and Esthetics
and beauty like?
reality
-make use of heavy logic
-Breaks down ideas SYNOPTIC- WHOLE TO WHOLE
-‘I’ individually DIALECTIC- (+) thesis
EAST- RELIGION- to satisfy their Gods and - (-) antithesis
people -(=) Synthesis
-Makes heavy se of religion ROMANTIC- FEELINGS
-focuses more on integration of ideas DEDUCTIVE- WHOLE TO PARTS
-“We” oneness INDUCTIVE- PARTS TO WHOLE
ANALYTIC- PART – PART
CHRONOLOGICAL DIVISION OF
PHILOSOPHY METHODS OF PHILOSOPHIZING
ANCIENT A B C D
UNDERSTANDING REASONING BELIEF ILLUSION
MEDIEVAL -Using SMA -Using the Forming Perception
intellect new Of senses
MODERN ideas
from
external
CONTEMPORARY
objects
APPROACHES TO PHILOSOPHY
WORLD OF FORMS WORLD OF IDEAS
1) ANALYTIC- part to part
-philosophical questions are not solved but it
DIVIDED LINE- (Knowledge and opinion)
dissolves
-Primary
2) SPECULTIVE- Methaphysical philosophy
-Secondary
-find an underlying explanation or general principle
-Tertiary- poets and artist should be banished acc.
that could explain reality
To plato
- Aims to reach some general conclusions as to the
-Belief should not be the basis for real knowledge
nature of the universe
-for platoREASON is higher the
3) REDUCTION- understanding of complex
UNDERSTANDING
ideas by reducing them to the parts or individul
4) HOLISTIC- System as a whole
PLATO’S METHAPHYICAL SYSTE
- Absolute, unchanging, ageless, eternal
THEORY AND PRACTICE - Everything in this world is considered as
T W/O P- Daydream
apperances (representation)
P W/O T- Nightmare
- Knowledge must have an ultimate bases for
T W/ P – Reality
it is absolute and unchanging for knowledge
Study of is remembered
Metaphysics What's out there?
Reality - The World of soul has immediate and direct
contact
Study of How do I know
Epistemology Good
Knowledge about it?
Study of Right What should I Abstract
Ethics
or Wrong do?
Mathematical
Study of What actions are
Politics
Governance permissible?
Material objects
THE ALLEGORY OF THE CAVE TYPES OF KNOWLEDGE
-Fire is the source of everything FORMAL EMPIRICAL
- as the prisoner is dragged out he will then realize - Corresponds to - Correspond to
that the sun is the source of true and knowledge whos the knowledge
good of all things main concern is whos main
THE SOCRATIC METHOD the validation. concern is the
- Known as the series of questions and - Characterized by faculty of
answers the consistency experience
of the system - the formal
METHOD BY SYSTEMATIC DOUBT
knowledge
- Exercise in skepticism could be
rejected
- Experience
could prove you
wrong later on.
NATURE OF KNOWLEDGE
COHERENCE THEORY
-The self - Concerned with the well formed formulas
-The GOD (WWF)
-The material objects - Definitions are considered as tautologies. –
-REASON is an important source in gaining the saying of the same thing twice.
knowledge about reality PRAGMATIC THEORY OF TRUTH
-DOUBTING Is a form of thinking - Gives value to the successful application of
concepts and statements to the world.
KNOWLEDGE, WISDOM AND OPINION
- Knowledge and wisdom start with opinion SOURCES OF KNOWLEDGE
and assumptions
STAGES OF APPREHENSIONS FACULTY OF REASON
PERCEPTION- the way that you notice or - The peple in the side of knowledge are
understand something using your senses called rationalist philosophers.
-EXTERNAL and INTERNAL - Construed as an analytic faculty
ABSTRACTION- Involves the use of intellect - Also known as sense of perception
CONCEPTS- Building blocks of knowledge FACULTY OF EXPERIENCE
JUDGEMENT- Involves proposition making that - Has to do with the use of the five senses
could either be true or false about the world - It use the correspondence theory of truth in
verifying the truth of these empirical
SENTENCES- Has no true value statements
STATEMENT FACULTY OF INTUITION
- Deals with the immediate or direct
ANALYTIC EMPIRICAL recognition of self evident truth
Truth or falsity of The truth or falsity on
knowledge clam could the experience
be found within the
statement -posteriori statement
-priori statement
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Problems of Philosophy (Barnes & Noble Library of Essential Reading)Von EverandThe Problems of Philosophy (Barnes & Noble Library of Essential Reading)Noch keine Bewertungen
- And Hestoid For Filling People's Heads With Fanatic TalesDokument2 SeitenAnd Hestoid For Filling People's Heads With Fanatic TalesCrestNoch keine Bewertungen
- W1 - PhiloDokument2 SeitenW1 - PhiloJasMJaJungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo St1 q1 ReviewerDokument3 SeitenPhilo St1 q1 ReviewerCzenia BarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Philosophy Reviewer QeDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Philosophy Reviewer QeSashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uts NotesDokument10 SeitenUts NotesBato, Apple R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- PhilosophyDokument16 SeitenPhilosophyJamie MarrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iphp ReviewerDokument2 SeitenIphp ReviewerMichelle GumarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Philosophy MidtermDokument10 SeitenReviewer in Philosophy MidtermElla DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHILOSOPHYDokument18 SeitenPHILOSOPHYLaurence BaguangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument2 SeitenReviewerJadzferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Philosophy - NotesDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To Philosophy - NotesSAMANTHA ANN GUINTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy-Module 1Dokument6 SeitenPhilosophy-Module 1gericj7dsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To PhilosophyDokument2 SeitenIntro To PhilosophyDaniela CodmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iphp - Quarter 1 - ReviewerDokument7 SeitenIphp - Quarter 1 - ReviewerChricellFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy ReviewerDokument5 SeitenPhilosophy Reviewer1901169Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Philosophy SubjectDokument4 SeitenReviewer Philosophy SubjectTawki BakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhilosophyDokument4 SeitenPhilosophyblabla blablaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHILO ReviewerDokument4 SeitenPHILO ReviewerJadzferNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATEphilo ReviewerDokument6 SeitenATEphilo ReviewerBeandra Judeen MarcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Wonder Is The Feeling of A Philosopher, and Philosophy Begins in Wonder" - SocratesDokument2 Seiten"Wonder Is The Feeling of A Philosopher, and Philosophy Begins in Wonder" - SocratesAlfred AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Invitation To PhilosophyDokument2 SeitenAn Invitation To PhilosophyFelicity BondocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 HUMSS 1st Quarter ReviewerDokument16 Seiten12 HUMSS 1st Quarter Revieweriori chenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Doing PhilosophyDokument52 SeitenModule 1 - Doing PhilosophyJoyce AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo ReviewerDokument9 SeitenPhilo Reviewerdok yeommieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in PhilosophyDokument6 SeitenReviewer in PhilosophyCatherine Keira IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy ReviewerDokument6 SeitenPhilosophy ReviewerLykaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPHPDokument11 SeitenIPHPTeumie CrantariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhilosophyDokument1 SeitePhilosophySTEM H-Cerillano, Zcier MeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHILOSOPHYDokument7 SeitenPHILOSOPHYMadelyn IquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy LuwiDokument19 SeitenPhilosophy LuwiLouielette GuanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MidtermDokument8 SeitenMidtermNur-Aiza AlamhaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Reviewer-1Dokument3 SeitenPhilosophy Reviewer-1Justin JaranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: What Is Philosophy?Dokument3 SeitenChapter 1: What Is Philosophy?Camille EboraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo PrintablesDokument6 SeitenPhilo PrintablesAlthea RevidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Classicakl Ethical PhilosophiesDokument2 Seiten5 Classicakl Ethical PhilosophiesKanekio ShinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PhilosophyDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To PhilosophyStephany RivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Philosophy 1st Quarter NotesDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Philosophy 1st Quarter NotesKate Jasmine AlinabonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHL01 Co1-Co3Dokument7 SeitenPHL01 Co1-Co3Aerielle BassigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Philo BernardinoDokument2 SeitenReviewer in Philo BernardinoTrisha BildaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in PhilosophyDokument6 SeitenReviewer in PhilosophyCatherine Keira IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTS - Prelims NotesDokument8 SeitenUTS - Prelims NotesDhon Aldrin CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 Reviewer (Philo)Dokument3 SeitenQ1 Reviewer (Philo)kris krossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy ReviewerDokument2 SeitenPhilosophy ReviewerZhynna SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To Philosophizing FinalDokument65 SeitenWelcome To Philosophizing FinalCourtney Kate VilasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction UNDS: Philosophical Perspective On SelfDokument2 SeitenIntroduction UNDS: Philosophical Perspective On SelfWallen LagradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCO - BPA1101 Summary of Notes For UNDERSTANDING THE SELFDokument9 SeitenCCO - BPA1101 Summary of Notes For UNDERSTANDING THE SELFrayzamakulit123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philo Pursuing Wisdom and Facing Challenges in The 21ST CenturyDokument4 SeitenPhilo Pursuing Wisdom and Facing Challenges in The 21ST CenturyAndreaRoseRacelis100% (2)
- Introduction To Philosophy ReviewerDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Philosophy ReviewerAllyza Princess Peradilla Magpantay100% (1)
- Reviewer in PhilosophyDokument2 SeitenReviewer in PhilosophyMadeline Chloe PlataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Technology and SocietyDokument21 SeitenScience Technology and SocietyJanna pnlbNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhilosophyDokument15 SeitenPhilosophyKheyt Adelyn PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uts Reviewer MidtermsDokument5 SeitenUts Reviewer MidtermsNorjannah PintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo - MidtermsDokument3 SeitenPhilo - MidtermsDianne CarreonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonEscala, John KeithNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHILO ReviewerDokument2 SeitenPHILO Reviewerczgf4rgjgkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Notes Copy 2Dokument3 SeitenPhilosophy Notes Copy 2Maria Natalia LibariosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy First Sem NotesDokument13 SeitenPhilosophy First Sem NotesDanica DespiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy NotesDokument2 SeitenPhilosophy NotesrosezedcapsabuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test I. Matching Type: Match Column A To Column B (Letters Only)Dokument1 SeiteTest I. Matching Type: Match Column A To Column B (Letters Only)omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macro Draft.1Dokument2 SeitenMacro Draft.1omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rizal Act2 ExplanationDokument1 SeiteRizal Act2 ExplanationomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Activity 2 InstructionsDokument5 SeitenFinal Activity 2 InstructionsomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guerra Narrative PaperDokument1 SeiteGuerra Narrative PaperomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guerra Narrative PaperDokument1 SeiteGuerra Narrative PaperomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- GUERRA - ROSE - THC 1101 Midterm FA 1Dokument1 SeiteGUERRA - ROSE - THC 1101 Midterm FA 1omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- RISK Management F1Dokument1 SeiteRISK Management F1omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fl1-Learning Activity No.1Dokument3 SeitenFl1-Learning Activity No.1omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- GUERRA - Rose Marie - THC1101 - SA - P1 - SEC1Dokument2 SeitenGUERRA - Rose Marie - THC1101 - SA - P1 - SEC1omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hip-Hop Dance With Mr. Salvilla. I Felt Empowered and Good After. I Think It Motivated Me ToDokument2 SeitenHip-Hop Dance With Mr. Salvilla. I Felt Empowered and Good After. I Think It Motivated Me ToomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pateros Catholic School: Accountancy Business and ManagementDokument25 SeitenPateros Catholic School: Accountancy Business and ManagementomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple InterestDokument12 SeitenSimple InterestomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fa5 Guerra Sec13Dokument1 SeiteFa5 Guerra Sec13omgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pateros Catholic School: Accountancy Business and ManagementDokument25 SeitenPateros Catholic School: Accountancy Business and ManagementomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Here Is The Full Transcript of Stanford Mathematics Professor Jo BoalerDokument7 SeitenHere Is The Full Transcript of Stanford Mathematics Professor Jo BoaleromgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Paper On How Can You Be Good at Math, and Other Surprising Facts About LearningDokument1 SeiteReflection Paper On How Can You Be Good at Math, and Other Surprising Facts About LearningomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example DATA-GATHERING-PROCEDUREDokument1 SeiteExample DATA-GATHERING-PROCEDUREomgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vetoset CA541: Thickbed Cementitious Tile AdhesiveDokument2 SeitenVetoset CA541: Thickbed Cementitious Tile Adhesivemus3b1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- MLX90614Dokument44 SeitenMLX90614ehsan1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Template Budget ProposalDokument4 SeitenTemplate Budget ProposalimamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blake Mouton Managerial GridDokument3 SeitenBlake Mouton Managerial GridRashwanth Tc100% (1)
- BSS Troubleshooting Manual PDFDokument220 SeitenBSS Troubleshooting Manual PDFleonardomarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha Técnica Panel Solar 590W LuxenDokument2 SeitenFicha Técnica Panel Solar 590W LuxenyolmarcfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring-Engineering-And-Technology-Grade-6 1Dokument5 SeitenExploring-Engineering-And-Technology-Grade-6 1api-349870595Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Part2 csc159Dokument26 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Part2 csc159Wan Syazwan ImanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 Ray Optics Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDokument10 Seiten23 Ray Optics Formula Sheets Getmarks AppSiddhant KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes - ExamDokument3 SeitenEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes - ExamEddie Padilla LugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply List & Resource Sheet: Granulation Techniques DemystifiedDokument6 SeitenSupply List & Resource Sheet: Granulation Techniques DemystifiedknhartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 PrinciplesDokument17 SeitenUnit 1 PrinciplesRohit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSWIP-WP-19-08 Review of Welding Procedures 2nd Edition February 2017Dokument6 SeitenCSWIP-WP-19-08 Review of Welding Procedures 2nd Edition February 2017oberai100% (1)
- Homework 9Dokument1 SeiteHomework 9Nat Dabuét0% (1)
- Understanding The Contribution of HRM Bundles For Employee Outcomes Across The Life-SpanDokument15 SeitenUnderstanding The Contribution of HRM Bundles For Employee Outcomes Across The Life-SpanPhuong NgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taylor Series PDFDokument147 SeitenTaylor Series PDFDean HaynesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.0. Design, Protection and Sizing of Low Voltage Electrical Installations (Wiring) To IEE Wiring Regulations BS 7671 MS IEC (IEC) 60364 - 16&17.12.15Dokument2 Seiten2.0. Design, Protection and Sizing of Low Voltage Electrical Installations (Wiring) To IEE Wiring Regulations BS 7671 MS IEC (IEC) 60364 - 16&17.12.15Edison LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Status Monitoring System For Port Machinery: RMGC/RTGCDokument2 SeitenIntelligent Status Monitoring System For Port Machinery: RMGC/RTGCfatsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar ObatDokument18 SeitenDaftar Obatyuyun hanakoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ValvesDokument95 SeitenControl ValvesHardik Acharya100% (1)
- Assignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramDokument2 SeitenAssignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramShivam ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJRHAL - Exploring The Journey of Steel Authority of India (SAIL) As A Maharatna CompanyDokument12 SeitenIJRHAL - Exploring The Journey of Steel Authority of India (SAIL) As A Maharatna CompanyImpact JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audi A4-7Dokument532 SeitenAudi A4-7Anonymous QRVqOsa5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stability Analysis of Geocell Reinforced Slopes by Considering Bending EffectDokument13 SeitenStability Analysis of Geocell Reinforced Slopes by Considering Bending EffectRakesh KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto M288-17 Product Selection GuideDokument1 SeiteAashto M288-17 Product Selection GuideDem DemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meta100 AP Brochure WebDokument15 SeitenMeta100 AP Brochure WebFirman RamdhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- LC For Akij Biax Films Limited: CO2012102 0 December 22, 2020Dokument2 SeitenLC For Akij Biax Films Limited: CO2012102 0 December 22, 2020Mahadi Hassan ShemulNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPA Smith Osborne21632Dokument28 SeitenIPA Smith Osborne21632johnrobertbilo.bertilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH CIDAM - PRECALCULUS (Midterm)Dokument4 SeitenMATH CIDAM - PRECALCULUS (Midterm)Amy MendiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Design Basis ReportDokument31 SeitenStructural Design Basis ReportRajaram100% (1)