Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lo1 4
Hochgeladen von
Gwen Stephanie Grecia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten2 Seitenabout hygiene
Originaltitel
LO1.4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenabout hygiene
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten2 SeitenLo1 4
Hochgeladen von
Gwen Stephanie Greciaabout hygiene
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
LO 1.
4 STATE THEPROPER PERSONAL HYGIENE
BEFORE AND AFTER WORKING
HYGIENE
Conditions and practices that help to maintain health.
Any practice or activity that you do to keep things healthy and clean.
PERSONAL HYGIENE
Refers to cleanliness of a person’s body.
PROPER HYGIENE BEFORE WORKING:
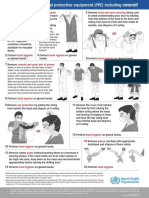
1. WEAR PROPER CLOTHING (PPE) BEFORE ENTERING
THEWORKPLACE
Do not wear short sleeve shirts or short pants when welding.
Safety glasses, or appropriate goggles / face shields are required.
Do not wear ties, loose clothing, long sleeves, jewelry, etc.
2. MAKE SURE THAT YOU HAVE TAKEN A BATH AND WASHED YOUR
HANDS
Bathing will not only cleanse your skin and keep it looking healthier and
more attractive, but it will also help cleanse your body of odors.
3. USE THE RIGHT TOOL, FOR THE RIGHT JOB, IN THE RIGHT WAY
Each tool is precisely designed for a specific purpose choosing the correct
tool will also decrease the amount of effort required to get a job done
without causing damage to either the equipment or the surface being
worked on.
4. IDENTIFY, EVALUATE, AND CONTROL REAL OR POTENTIAL
WORKPLACE ENVIRONMENT STRESSORS OR HAZARDS
Hazards might cause injuries to the workers.
If a hazard is identified, control and eliminate it immediately.
5. WHEN ENTERING HOT WORK
Working with ignition sources near flammable materials is referred to as
"hot work.“
If possible, schedule hot work during shutdown periods.
Additional:
Make sure that all equipment is in good operating order before work starts.
Inspect the work area thoroughly before starting.
Remove any spilled grease, oil, or other combustible liquid.
Move all flammable and combustible materials away from the work area.
PROPER HYGIENE AFTER WORKING:
1. MAKE SURE THAT YOU HAVE TURNED OFF ALL THE APPLIANCES
AND EQUIPMENT AFTER USE
Electricity could be the source of ignition in a potentially flammable or
explosive atmosphere.
2. MAKE SURE THAT YOU HAVE RETURNED THE TOOLS AND
EQUIPMENT TO ITS ORIGINAL PLACE
Preventive maintenance is the systematic care and protection of tools,
equipment, machines and vehicles in order to keep them in a safe, usable
condition limit downtime and extend productivity.
3. CLEANING PROCEDURESAND SCHEDULES
Cleaning will remove any dirt or grease but will not necessarily kill any
bacteria or other pathogens.
Cleaning is the process of removing unwanted substances, such as dirt,
infectious agents, and other impurities, from an object or environment.
4. ROUTINE EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE
The main purpose of regular maintenance is to ensure that
all equipment required for production is always operating at 100%
efficiency.
Lubricate or apply adhesives or other materials to machines, machine parts,
or other equipment, according to specified procedures.
5. SAFE HANDLING OF CHEMICALS
Storing and using chemicals in a safe way is a further foundation for
working with chemicals.
All chemical products must be stored and labeled in accordance with the
instructions on the safety sheet.
6. REPORT POSSIBLE DAMAGES
Inspect or test damaged machine parts and mark defective areas or advise
supervisors of repair needs.
Install, replace, or change machine parts and attachments, according to
production specifications.
GROUP 2
Submitted by:
Aguado, Mark Angelo
Gabrido, Lemuel
Ravena, James Lobel
Suobiron, Christopher Ryan
Tanato, Glenn
Submitted to:
Engr. Jasper Victoriano, Ph.D.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Risk Assessment For External Façade & Canopies CleaningDokument6 SeitenRisk Assessment For External Façade & Canopies Cleaningjulius0% (1)
- MSDS EdtaDokument6 SeitenMSDS EdtaIndah PuspitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA For Foundation Concrete RepairDokument6 SeitenJSA For Foundation Concrete RepairOvais FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6: Varieties and Registers of Spoken and Written Language World EnglishesDokument2 SeitenLesson 6: Varieties and Registers of Spoken and Written Language World EnglishesGwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aom Midterm L4Dokument6 SeitenAom Midterm L4Gwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Introduction of Ethics: Learning OutcomesDokument5 SeitenUnit 1: Introduction of Ethics: Learning OutcomesGwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aom Midterm L3Dokument15 SeitenAom Midterm L3Gwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Segobre, Karl Dominic G. Bsca 2-A July 5, 2019Dokument2 SeitenSegobre, Karl Dominic G. Bsca 2-A July 5, 2019Gwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Addition To My Experience and Personal Qualities, I Have A Solid Educational Foundation and A Passion For Marine EngineeringDokument2 SeitenIn Addition To My Experience and Personal Qualities, I Have A Solid Educational Foundation and A Passion For Marine EngineeringGwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinancialDokument1 SeiteFinancialGwen Stephanie GreciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Flash Guide v2Dokument4 SeitenArc Flash Guide v2tatacpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSE-P-10 Accident-Incident Reporting and Investigation IssueDokument7 SeitenHSE-P-10 Accident-Incident Reporting and Investigation Issueeng20072007100% (1)
- Summary of BRC Global Food Safety Standard Issue 6 Changes Landscape 110111Dokument28 SeitenSummary of BRC Global Food Safety Standard Issue 6 Changes Landscape 110111Poulami DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 121 Semifinal ActivitiesDokument4 SeitenNCM 121 Semifinal ActivitiesKimberly Abellar LatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoja de Seguridad ThalidomideDokument6 SeitenHoja de Seguridad ThalidomideEdgar HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Heptanol MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDokument5 Seiten2-Heptanol MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company Identificationa d e eNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part II - 08 Abrasive BlastingDokument5 SeitenPart II - 08 Abrasive Blastingsalah abddayemNoch keine Bewertungen
- RiskAssessmentHazardChecklist StudentActivitiesDokument1 SeiteRiskAssessmentHazardChecklist StudentActivitieslisaconnollyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evostik Impact Contact Adhesive SdsDokument9 SeitenEvostik Impact Contact Adhesive SdsRuben OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment - DerrickmanDokument19 SeitenAssessment - DerrickmanGeorge LameyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps To Take Off Personal Protective Equipment Including CoverallDokument1 SeiteSteps To Take Off Personal Protective Equipment Including CoverallPraneetha VijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peru - July20.16.m PonenciasDokument230 SeitenPeru - July20.16.m PonenciasedisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORCE INTERNATIONAL BAND SAW 3460015 - ManualDokument40 SeitenFORCE INTERNATIONAL BAND SAW 3460015 - ManualAl CrosbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stromatolyser XP 300Dokument8 SeitenStromatolyser XP 300AhmedJumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 2Dokument15 SeitenLesson Plan 2Jeanne RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPCPSN3023A Fabricate and Install Sanitary StacksDokument37 SeitenCPCPSN3023A Fabricate and Install Sanitary StacksWenhao WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA Cable Pulling and Laying WorksDokument6 SeitenJSA Cable Pulling and Laying Workskabir100% (1)
- Fire-Ball 300 and 425 Grease Pumps: Instructions - Parts ListDokument16 SeitenFire-Ball 300 and 425 Grease Pumps: Instructions - Parts Listgulam husseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Assessment - CableDokument6 SeitenRisk Assessment - Cablemohamad hafiz0% (2)
- Placing BoomDokument80 SeitenPlacing BoomPelonky ManiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Medipure Gas O2 Safety Data Sheet Sds p4638Dokument9 SeitenOxygen Medipure Gas O2 Safety Data Sheet Sds p4638seeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Clauses For Procurement of Uniforms and PPE: VGPB DocumentationDokument2 SeitenModel Clauses For Procurement of Uniforms and PPE: VGPB DocumentationPatrick ChuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM 03 - Cargo Handling Risk AssessmentDokument3 SeitenCM 03 - Cargo Handling Risk AssessmentDmitriy100% (1)
- MST For LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEMDokument12 SeitenMST For LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEMمقاول تكييف كهرباء وصحيNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEA DryCoolers InstalationDokument28 SeitenGEA DryCoolers InstalationArif BinorikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man E3262 LE202, E3268 LE212 Operating Instructions ManualDokument118 SeitenMan E3262 LE202, E3268 LE212 Operating Instructions Manualthuan vu vanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sika - 1Dokument4 SeitenSika - 1rasasiNoch keine Bewertungen