Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 5 Integumentary
Hochgeladen von
Elle Ugaddan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
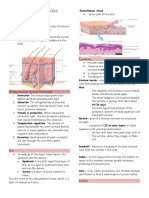
14 Ansichten2 SeitenThe integumentary system consists of the skin and accessory structures. It has several major functions:
1. Protection from abrasion, ultraviolet light, and sensation of touch, temperature, and pain.
2. Temperature regulation through blood flow and sweat glands.
3. Vitamin D production and excretion of waste through skin and glands.
The skin has two layers, the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is superficial stratified squamous epithelium that keratinizes. The dermis is thick connective tissue containing collagen, fibers, vessels and glands. It provides structural strength to the skin.
Originalbeschreibung:
Integumentary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe integumentary system consists of the skin and accessory structures. It has several major functions:
1. Protection from abrasion, ultraviolet light, and sensation of touch, temperature, and pain.
2. Temperature regulation through blood flow and sweat glands.
3. Vitamin D production and excretion of waste through skin and glands.
The skin has two layers, the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is superficial stratified squamous epithelium that keratinizes. The dermis is thick connective tissue containing collagen, fibers, vessels and glands. It provides structural strength to the skin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten2 SeitenChapter 5 Integumentary
Hochgeladen von
Elle UgaddanThe integumentary system consists of the skin and accessory structures. It has several major functions:
1. Protection from abrasion, ultraviolet light, and sensation of touch, temperature, and pain.
2. Temperature regulation through blood flow and sweat glands.
3. Vitamin D production and excretion of waste through skin and glands.
The skin has two layers, the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is superficial stratified squamous epithelium that keratinizes. The dermis is thick connective tissue containing collagen, fibers, vessels and glands. It provides structural strength to the skin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
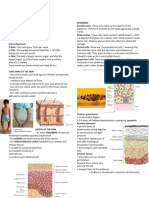
CHAPTER 5: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM protein keratin which makes them more
rigid and durable.
Integumentary System As keratinization proceeds, epithelial cells
- consists of the skin and accessory structures such as die & form dead skin cells.
hair, glands, and nails.
2. DERMIS – layer of dense connective tissue.
- covers the outside of the body and is easily observed. – 10 to 20 times thicker than the epidermis.
– responsible for most of the skin’s structural
Major Functions of the Integumentary System: strength.
– rest on the subcutaneous tissue, layer of
1. Protection. Provides protection against abrasion and
connective tissue.
ultraviolet light.
Subcutaneous tissue is not part of the
2. Sensation. Can detect heat, cold, touch, pressure and skin, connect the skin to underlying
pain. muscle or bone.
3. Temperature regulation. Amount of blood flow ANALOGY: Subcutaneous – foundation of the
beneath the skin’s surface & activity of sweat glands house, Dermis – most of the house Epidermis –
that help regulate body temperature. roof
4. Vitamin D production. Important regulator of – Nerves, hair follicles, smooth muscles,
calcium homeostasis. glands, and lymphatic vessels extend into the
dermis.
5. Excretion. Waste products are lost through the skin
& in gland secretions. Collagen and elastic fibers – responsible
for the structural strength of the dermis.
SKIN It can resist stretch.
Some collagen fibers are oriented more
- made up of two major tissue layers: epidermis and
directions than others, forming cleavage
dermis:
lines.
1. EPIDERMIS – most superficial layer of skin. Cleavage lines, or tension lines, in the
skin, are more resistant to stretch.
– epithelial tissue that rests on the dermis. An incision made parallel with these
lines tends to gap less and produce less scar
– prevents water loss & resists abrasion.
tissue.
– stratified squamous epithelium. If the skin is overstretched for any
reason, the dermis can be damaged, leaving
Process: stretch marks.
Dermis Papillae – upper part of the
New cells are produced by mitosis.
dermis that has projection.
As new cells form, they push older cells to
Contains many blood vessels,
the surface.
supplies overlying epidermis with
During their movement, cells change shape
nutrients.
and chemical composition. It undergoes
keratinization where cells become filled ith Removes waste products
Helps regulate body temperature.
REMEMBER: Injection delivers substances in the body
by puncturing the skin.
1. Intradermal injection – drawing the skin taut and
inserting a small needle at a shallow angle into the
dermis.
Example: Tuberculin skin test.
2. Subcutaneous injection – pinching the skin to form a
“tent” and inserting a short needle in the adipose tissue
of the subcutaneous tissue.
Example: Insulin injection
3. Intramuscular injection – inserting a long needle at a
90-degree angle to the skin into a muscle deep to the
subcutaneous tissue.
Example: Vaccines and certain antibiotics
SKIN COLOR
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Integumentary System - ANAPHYDokument7 SeitenIntegumentary System - ANAPHYmariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System - Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenIntegumentary System - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumDokument5 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Integumentary SystemDokument5 Seiten5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy ReviewerDokument8 SeitenAnaphy ReviewerMark GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology-NotesDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology-NotesAkirah Jewelle JaenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument5 SeitenIntegumentary SystemChan TalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - IntegDokument8 Seiten5 - IntegGel Austin PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument3 SeitenIntegumentary SystemCarmela Cordon FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDokument5 SeitenCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Dokument4 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItDokument9 SeitenA. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItFrancis100% (1)
- Anaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerDokument27 SeitenAnaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerFAITH EFONDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 Integumentary SystemJade Karen Lingo-lingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy&Physiology of SkinDokument45 SeitenAnatomy&Physiology of Skinpreet kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 & 6Dokument18 SeitenTopic 5 & 6PhoebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 176 Anatomy Integumentary SystemDokument29 Seiten176 Anatomy Integumentary SystemJoana Mae PortezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Integumentary System: (Anatomy of The Skin, Hair, and Nails)Dokument3 SeitenThe Integumentary System: (Anatomy of The Skin, Hair, and Nails)Venus Amoroso BaguiosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin ShortDokument10 SeitenSkin ShortKashar SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy MidtermsDokument28 SeitenAnaphy MidtermsxeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap3 Integ Anaphy NotesDokument11 SeitenChap3 Integ Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument7 SeitenChapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Mae MeriñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Dokument4 SeitenZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy - IntegumentaryDokument4 SeitenAnaphy - IntegumentaryYo1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Integumentary SystemDokument5 SeitenChapter 5 - Integumentary SystemLora Mae Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary NotesDokument13 SeitenIntegumentary Noteslovj melNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument6 SeitenIntegumentary SystemRaiza Abegail RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 1 - Integumentary System (Review Material)Dokument13 SeitenGROUP 1 - Integumentary System (Review Material)SALGIE SERNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument6 SeitenIntegumentary Systemericamaeabellanosa22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Corneum and Is Directly Exposed To TheDokument3 SeitenCorneum and Is Directly Exposed To Theydnic alykPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin and Body Membranes HahaDokument6 SeitenSkin and Body Membranes Hahaقى قىNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Lab IntegDokument5 SeitenAnaphy Lab IntegPhoemela Reign GregorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing AnaPhy Integumentary SystemDokument22 SeitenNursing AnaPhy Integumentary SystemGail Chantel Spring PerlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burns SemDokument29 SeitenBurns SemEsther Marie SazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument7 SeitenIntegumentary Systemkuroko tetsuya100% (2)
- Chapter 5-Integumentary SystemPSTMLSDokument7 SeitenChapter 5-Integumentary SystemPSTMLSEricka MasakayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument30 SeitenLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDokument11 SeitenChapter 5 Integumentary SystemJoso LivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument9 SeitenIntegumentary SystemCelyn DeañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument27 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Integumentary DigestiveDokument11 SeitenReviewer Integumentary DigestiveMariah Alexa LibaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Skinbody MemranesDokument3 SeitenModule 3 Skinbody MemranesRaphael SevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S4 Integumentary SystemDokument9 SeitenS4 Integumentary Systemcam broquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angee 11Dokument4 SeitenAngee 11lunadawsonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideDokument3 SeitenChapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideSuperjunior8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skin, Hair, and NailsDokument9 SeitenSkin, Hair, and NailsJustine JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPDokument59 SeitenSkin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPJosephine SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Integumentary SystemDokument38 SeitenPhysiology of Integumentary SystemAnisa AnisatusholihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SkinDokument10 SeitenSkinKaren Mae AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary & Skeletal SystemDokument4 SeitenIntegumentary & Skeletal SystemMaisonette MichNoch keine Bewertungen
- C5-Integumentary SystemDokument7 SeitenC5-Integumentary SystemLorrine MagramoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Premed NewDokument8 SeitenSkin Premed NewJad JawhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Integumentary System?Dokument6 SeitenWhat Is The Integumentary System?Jerneth Nyka FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System: Skin and Body Membranes: Body MembranesDokument16 SeitenIntegumentary System: Skin and Body Membranes: Body MembranesIvan LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System OutlineDokument7 SeitenIntegumentary System OutlineRogie P. BacosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08.16.16 Skin Histo Pathol (Nanney) HandoutDokument14 Seiten08.16.16 Skin Histo Pathol (Nanney) HandoutDan WuiytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Book Activity 9 Ana LabDokument7 SeitenWork Book Activity 9 Ana LabJazmine YvonneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 420-510chapter 1 (5) Introduction To The Integumentary SystemDokument6 Seiten420-510chapter 1 (5) Introduction To The Integumentary Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System 2 Main Regions: Human Anatomy & Physiology Kylie Jan C. SilvaDokument4 SeitenIntegumentary System 2 Main Regions: Human Anatomy & Physiology Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimeter Parts and Functions PDFDokument15 SeitenMultimeter Parts and Functions PDFmarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample SCJP QuestionsDokument23 SeitenSample SCJP QuestionsManuel GalganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kavitha Brunswick: SAP HANA, BODS and BI Consultant - ADOBEDokument6 SeitenKavitha Brunswick: SAP HANA, BODS and BI Consultant - ADOBEparag3482Noch keine Bewertungen
- Galileo Basic CommandsDokument9 SeitenGalileo Basic Commandsbharatstar85% (13)
- UGRD-ECE6205-Signals-Spectra-and-Signal-Processing-legit-not-quizess MidALLDokument19 SeitenUGRD-ECE6205-Signals-Spectra-and-Signal-Processing-legit-not-quizess MidALLJitlee Papa100% (3)
- Soy Sauce Production FinalDokument40 SeitenSoy Sauce Production Finalafidah99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Patiala: End Semester TestDokument2 SeitenThapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Patiala: End Semester TestPritam PiyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Concurrent ForcesDokument6 SeitenNon Concurrent ForcesLeah Rivera0% (1)
- Department of Pre-University Education, Karnataka: PUC Examination Results - 2021Dokument1 SeiteDepartment of Pre-University Education, Karnataka: PUC Examination Results - 2021Sneha GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Design SyllabusDokument6 Seiten3D Design SyllabusIoana PetcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complexity, Liking and FamiliarityDokument12 SeitenComplexity, Liking and FamiliarityAjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Aerodynamic TheoryDokument24 SeitenBasic Aerodynamic TheoryOganga JackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 RADWIN Wireless 2 0Dokument36 Seiten1 RADWIN Wireless 2 0Jose VazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Up SSL On Oracle WebLogic Server (Configuración de Certificado SSL en PeopleSoft)Dokument17 SeitenSetting Up SSL On Oracle WebLogic Server (Configuración de Certificado SSL en PeopleSoft)Jesús ArredondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repulsive Force FieldDokument7 SeitenRepulsive Force FieldSoundararajan SeeranganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laplace Transformation TableDokument1 SeiteLaplace Transformation TableDjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - Book-Vektor Ablerex - MsiiDokument24 SeitenManual - Book-Vektor Ablerex - MsiiIndonesian's LOVENoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Chiller T&C 2011Dokument9 Seiten3 Chiller T&C 2011Dtl SarozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Technologies Limited Price List (Updated 14-06-2020)Dokument21 SeitenSuper Technologies Limited Price List (Updated 14-06-2020)Shania RoopnarineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvoline HTO 32Dokument1 SeiteValvoline HTO 32octo widodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision: Change Description Person Responsible, Name, Signature, Date Remark Revision Index CR NumberDokument67 SeitenRevision: Change Description Person Responsible, Name, Signature, Date Remark Revision Index CR NumberAung Min Htet100% (1)
- The Key of It AllDokument91 SeitenThe Key of It AllSimonida Mona VulićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sardar Raja College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Micro Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenSardar Raja College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Micro Lesson PlanKarthi SathyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncsim SupportDokument22 SeitenNcsim SupportPramod Reddy RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tact Micro Switch 12X12Dokument1 SeiteTact Micro Switch 12X12Solin CozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jis B 1180 2004 EngDokument74 SeitenJis B 1180 2004 EngAyman Hamed MalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22-01 Simple Linear Motion 1Dokument1 Seite22-01 Simple Linear Motion 1David BumbaloughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note CHP 2-Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Dokument74 SeitenNote CHP 2-Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_rye100% (1)
- Tugas Paper Mekanika PatahanDokument1 SeiteTugas Paper Mekanika PatahanRahmandhika Firdauzha Hary HernandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDR DesignGuidelines VAVDokument331 SeitenEDR DesignGuidelines VAVRegina Ng100% (1)