Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Formulas For Phisics, 1st Grade
Hochgeladen von
Rozalina Petrova0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
97 Ansichten3 SeitenFormulas for phisics, 1st grade
Originaltitel
Formulas for phisics, 1st grade
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
XLSX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenFormulas for phisics, 1st grade
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als XLSX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
97 Ansichten3 SeitenFormulas For Phisics, 1st Grade
Hochgeladen von
Rozalina PetrovaFormulas for phisics, 1st grade
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als XLSX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
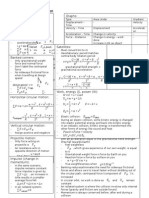
Name Formula Specifications Constants
Speed s=dist/t / a(free fall)
Velocity V=disp/t / gravity
Acceleration a=ΔV/t / Gravitatonal constant
Final Velociy Vf=Vo+at Mostly used for Mass of the Sun
Free Fall and
Final Velociy Vf²=Vo²+2ad Linear Motion Mass of the Earth
Displacement d=Vo²t+½at² Distance Sun Moon
Quad. Equasion x½=-(b±√(b²-2ac))/2a Solve For t Radius of the Earth
Hight(disp. Yaxis) h=½(Vo+Vf)t² Distance Sun Earth
Hight(disp. Yaxis) h=V²sin²Ꝋ/2g Distance Moon Earth
projectile motion
Time A→B t=VsinꝊ/g sin/cos=tan
Range(disp. Xaxis) R=V²(2sincosꝊ)/g
Range(disp. Xaxis) R=Vt
Theta Ꝋ=arctan(y/x)
Force F²=x²+y² Vect ors
(right angle) SOH
X componet x=FcosꝊ CAH TOA
Y component y=FsinꝊ
Weight Force W=mg
Static Friction Fs≤µsFn
Kinetic Friction Fs=µkFn
Normal Force Fn=W if Ꝋ=0
Net Force Fnet=am
Impuls I=FnetΔt
I=p
Momentum p=mΔV
Fn ( elevator problem) Fn=m(ay+g) change in Fn
Normal Force Fn=Wy=WcosꝊ
Incline Problems
Gravitational Force Fg=Wx= WsinꝊ
Centripetal Acceleration Ac=V²/Rad
Centripetal Force Fc=mV²/Rad
Centripetal Force
Velocity V=(2∏Rad)/T Problems
Period T=t/rev
Frequency f=rev/t
Max Velocity V²=(Rg(SinꝊ±µsCosꝊ)/
Min Velocity (CosꝊ∓µsSinꝊ)
Banked Curve
Problems
Velocity w/fric. V²=RgTanꝊ
Acceleration ( non-uniform) a²=Ac²+Atan² Non-uniform
Circular Motion
Tangental Acceleration Atan=(Vf-Vo)/t
Gravitational Force Fg=(GM₁M₂)/R² Grav. Prob.
(T₂/T₁)²=(R₂/R₁)³ Planets→Sun
Kepler´s 3rd Law
GMSUNT2=4∏2R3
Work W=FdCosꝊ
Kinetic Energy KE=mV²/2
Potential Energy PE=mhg
Net Work Wnet=KEf-KEi
Mechanical Energy ME=PE+KE !Conservative F!
Net Force Fnet=Wnet/d
Value
a=9.82m/s²
g=9.82m/s²
G=6.67*10ˉ¹¹Nm²/km²
M=1.99*10³⁰kg
M=5.97*10²⁴kg
R=1.492*10¹¹m
R=6.38*106
R=1.5*10¹¹m
R=3.84*10⁸m
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Homework 6 SolutionsDokument3 SeitenHomework 6 SolutionsSean MccartneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Cheatsheet Unit 3 Ver.3Dokument3 SeitenPhysics Cheatsheet Unit 3 Ver.3Hung TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rover V8 Fuel Injection SystemsDokument16 SeitenRover V8 Fuel Injection SystemsClint Cooper100% (1)
- Physics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol FormulaDokument5 SeitenPhysics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol Formulakaparthy100% (9)
- Form I Integrated Science End of Year ExamDokument10 SeitenForm I Integrated Science End of Year ExamMiss Rambaran100% (2)
- PotentiometryDokument27 SeitenPotentiometryShafique Ahmed100% (2)
- Clase 05 - Chapter 9 - AAS-experimentalDokument44 SeitenClase 05 - Chapter 9 - AAS-experimentalLuisa GallegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 590p Trips and Fault Finding Sds Quick GuidesDokument19 Seiten590p Trips and Fault Finding Sds Quick GuidesHitesh Panigrahi100% (1)
- Physics Formulas: V V U M MDokument5 SeitenPhysics Formulas: V V U M MEXa Krad NoitatpmetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheet Unit 3 MotionDokument1 SeiteCheat Sheet Unit 3 MotionkerrevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latex Math Cheatsheet 2018-01-13Dokument1 SeiteLatex Math Cheatsheet 2018-01-13AT8iNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astrophysics 2 RarDokument67 SeitenAstrophysics 2 Rargaohugh94Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 Momentum: Relationship Between Momentum & ForceDokument2 SeitenCH 6 Momentum: Relationship Between Momentum & ForceSyed Mairaj Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal PhysicsDokument68 SeitenThermal PhysicsAbdul HalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facts and Formulas 3 Ref Physics SATDokument12 SeitenFacts and Formulas 3 Ref Physics SATRicky SugiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration by Parts ProofDokument1 SeiteIntegration by Parts Proofsembe0% (1)
- L TEX Cheat Sheet: Layout Structure The Document Math EquationsDokument2 SeitenL TEX Cheat Sheet: Layout Structure The Document Math EquationsAT8iNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI Physics NumericalsDokument5 SeitenXI Physics NumericalschemistmajidsiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal PhysicsDokument29 SeitenThermal PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs521 Midterm CheatsheetDokument2 SeitenCs521 Midterm CheatsheetFrankXiao0% (1)
- AP Physics NotesDokument18 SeitenAP Physics Notesfhsphysics100% (1)
- Wave Equations SolverDokument14 SeitenWave Equations SolverWilson LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Level FormulaeDokument1 SeiteA Level FormulaeVarun PanickerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP1 Simple Harmonic Motion Presenter W AnswersDokument33 SeitenAP1 Simple Harmonic Motion Presenter W AnswersDamion Mcdowell100% (1)
- Fortran Program: Motion of A Particle Under Central Force (Planetary Motion)Dokument1 SeiteFortran Program: Motion of A Particle Under Central Force (Planetary Motion)Abhijit Kar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics Notes 4Dokument15 SeitenMechanics Notes 4niteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS Physics EquationsDokument1 SeiteAS Physics EquationsAhmad MohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Equation Sheet AQA 2023Dokument2 SeitenPhysics Equation Sheet AQA 2023HazzaYT HicksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItDokument3 SeitenMath 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It Itjokes NerdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics 2 NotesDokument12 SeitenMechanics 2 NotesMaxime Bourgoing100% (1)
- ThePhysicsCafe Summary of JC PhysicsDokument2 SeitenThePhysicsCafe Summary of JC PhysicsLim Zer HeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM PhysicsDokument134 SeitenPahang JUJ 2012 SPM PhysicsJeyShidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porat A Gentle Introduction To Tensors 2014 PDFDokument87 SeitenPorat A Gentle Introduction To Tensors 2014 PDFManuel nuño bustamanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Formula SheetDokument72 SeitenPhysics Formula SheetMikey1010100% (1)
- Fluids Heat and Mass TransferDokument286 SeitenFluids Heat and Mass TransferAnonymous 5ZrExMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Formula List - As at 6 Jul 2011 (Normal)Dokument4 SeitenPhysics Formula List - As at 6 Jul 2011 (Normal)Lim Kew Chong100% (1)
- 4 MotionOneDimensionFull PDFDokument38 Seiten4 MotionOneDimensionFull PDFmagiclcjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 21st Century A Compilation of Contemporary and Emerging TechnologiesDokument239 SeitenPhysics 21st Century A Compilation of Contemporary and Emerging TechnologiesJuiced-IN it100% (1)
- Freivalds' AlgorithmDokument3 SeitenFreivalds' AlgorithmLindrit KqikuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Gravitaional Constant GDokument64 Seiten4 Gravitaional Constant Ggomathi_nellaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillations ExplainedDokument34 SeitenOscillations ExplainedParminder singh parmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Inao 01-06Dokument53 SeitenA Inao 01-06NiZamMAdridistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics FormulasDokument1 SeitePhysics FormulasZahid MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws and Gravitational ForcesDokument16 SeitenNewton's Laws and Gravitational Forcesabrarn179208Noch keine Bewertungen
- S382 Transiting Exoplanets CHAPTER 1 and ACKSDokument46 SeitenS382 Transiting Exoplanets CHAPTER 1 and ACKSWerner JanssensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics FormulasDokument11 SeitenPhysics FormulasTanishk VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics Chapter 3 Motion in Two DimensionsDokument33 SeitenAP Physics Chapter 3 Motion in Two DimensionsStewie Dog100% (1)
- Atom LightDokument23 SeitenAtom LightGharib MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Displacement and Force in Two Dimensions-1Dokument2 SeitenDisplacement and Force in Two Dimensions-1varaprasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen AtomDokument8 SeitenHydrogen AtomElyasse B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- InspireDokument19 SeitenInspireUWC Australia100% (1)
- KinematicsDokument83 SeitenKinematicsKartik KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Physics Syllabus - 2014 CusatDokument42 SeitenMSC Physics Syllabus - 2014 CusatVishnu PushpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics in Two-Dimensions: Lesson 1 Vector OperationsDokument37 SeitenMechanics in Two-Dimensions: Lesson 1 Vector OperationsShaimaa Abdulhamed100% (1)
- Using A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementDokument11 SeitenUsing A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementAndrea KusickiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity Notes JEE Main and AdvancedDokument49 SeitenCurrent Electricity Notes JEE Main and AdvancedHitesh Bhatia0% (1)
- Trigonometry formulae and solving equationsDokument3 SeitenTrigonometry formulae and solving equationsSaiful Hasan MasudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gibbs Distribution and Chemical PotentialDokument24 SeitenGibbs Distribution and Chemical PotentialNingsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet For Grade 10 NewDokument4 SeitenFormula Sheet For Grade 10 NewNo PainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factorization Methods for Discrete Sequential EstimationVon EverandFactorization Methods for Discrete Sequential EstimationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39Von EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brandenz1229 - Physics Final Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenBrandenz1229 - Physics Final Cheat SheetSyeda SadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second condition of equilibrium; ∑τ = 0 Physics Formulas by MeasurementsDokument2 SeitenSecond condition of equilibrium; ∑τ = 0 Physics Formulas by MeasurementsJan AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORMULAS LISTDokument5 SeitenFORMULAS LISTPuebloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speader Valves Hk66b102Dokument12 SeitenSpeader Valves Hk66b102seaqu3stNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE 69708 Experiences Using An ESP Application On Heavy-Oil Cold-Production Automation in Eastern Venezuela FieldsDokument3 SeitenSPE 69708 Experiences Using An ESP Application On Heavy-Oil Cold-Production Automation in Eastern Venezuela FieldsM.Noch keine Bewertungen
- BA L M EPA Carb4 PDFDokument83 SeitenBA L M EPA Carb4 PDFCristiTancuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Breaker Failure Protection BFP Schemes in UtilitiesDokument9 SeitenThe Breaker Failure Protection BFP Schemes in UtilitiesTrigras Bangun PerkasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 - Free Point and Backoff - (Houston)Dokument29 Seiten9 - Free Point and Backoff - (Houston)Usama Bin Sabir100% (2)
- Holec ERM TDRM Restart ModulesDokument6 SeitenHolec ERM TDRM Restart Modules0b0biyd,u,uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ega125 gr05 Emsc SG 0001 20200925Dokument238 SeitenEga125 gr05 Emsc SG 0001 20200925api-292325707Noch keine Bewertungen
- Karthik Krishna Resume Oct2014Dokument3 SeitenKarthik Krishna Resume Oct2014kkrish13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Nucleus Facts and ConceptsDokument24 SeitenAtomic Nucleus Facts and ConceptsKashyap PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miroljub Todorović - ApeironDokument25 SeitenMiroljub Todorović - Apeiron"Mycelium" samizdat publishersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine Heat Rejection and Refrigeration Cycle CalculationsDokument8 SeitenGas Turbine Heat Rejection and Refrigeration Cycle CalculationsRENE JOSHUA PECASONoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Chemical Equilibrium (Theory) Module-3-1Dokument18 Seiten02 - Chemical Equilibrium (Theory) Module-3-1Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- WP 3325 B 3 - 5 Basbooster Incl. N - Pack: Technical DataDokument2 SeitenWP 3325 B 3 - 5 Basbooster Incl. N - Pack: Technical DataMarcos AssialdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pratt & Whitney Canada: Maintenance Manual MANUAL PART NO. 3034342Dokument18 SeitenPratt & Whitney Canada: Maintenance Manual MANUAL PART NO. 3034342EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EHS Compliance Scope of Work for Ather EnergyDokument4 SeitenEHS Compliance Scope of Work for Ather EnergyFazal AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual Ns King - SPH King: 7.5/10/12kVA (1-Phase In/Output) 7.5/10/15/20kVA (3-Phase Input/1-Phase Output)Dokument44 SeitenUser Manual Ns King - SPH King: 7.5/10/12kVA (1-Phase In/Output) 7.5/10/15/20kVA (3-Phase Input/1-Phase Output)a.elwahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice HSC Papers General 2Dokument47 SeitenPractice HSC Papers General 2DarrenPurtillWrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityPARMAR MAHENDRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Greece WasteDokument64 SeitenGreece WasteYiannis AntonopoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Graphene Based Semiconductor Photocatalysts For Solar Energy ConversionDokument27 SeitenAdvances in Graphene Based Semiconductor Photocatalysts For Solar Energy ConversiondevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ductable Fan Coil Unit: Product Selection DataDokument26 SeitenDuctable Fan Coil Unit: Product Selection DataNelson MartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Transformer-ProtectionDokument42 Seiten7 Transformer-Protectionmuaz_aminu1422Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Kinetics of Hydrogen Absorption in Palladium (A - and P-Phase) and Palladium-Silver-AlloysDokument10 SeitenThe Kinetics of Hydrogen Absorption in Palladium (A - and P-Phase) and Palladium-Silver-AlloysJose Fernandez AdellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rr312003 Turbo MachineryDokument8 SeitenRr312003 Turbo MachinerySrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kumera Helical and Bevel Gear Units PDFDokument136 SeitenKumera Helical and Bevel Gear Units PDFanto starlinNoch keine Bewertungen