Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is Shunt Reactor - Types, Construction & Applications
Hochgeladen von
Prem KumarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is Shunt Reactor - Types, Construction & Applications
Hochgeladen von
Prem KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SPONSORED SEARCHES
electrical transformer electronic circuit 3 phase electricity supply
electrical installation underground electrical cable earthing system
Over Head Lines Power System Transformer
What is Shunt Reactor – Types, Construction & Applications
Electrical Technology 1 3 minutes read
Pulse Discharge Capacitors
High Energy Pulse Capacitors
The Leading Chinese Supplier of Advanced High Voltage Capacitors
cabofs.com OPEN
Why to use Shunt Reactors? Different between Power Transformer & Shunt Reactor
Table of Contents [Hide]
1 What is Shunt Reactor?
2 Different Between Shunt Reactor & Power Transformer
3 Why to use Shunt Reactor ? Applications of Shunt Reactors
4 Construction of Shunt Reactor
5 Types of Shunt Reactors
What is Shunt Reactor?
Shunt reactor is same as power transformer but it has only one winding per phase as compared to power
transformer. Shunt reactors are used to increase the power and energy system efficiency as it absorb &
compensate the reactive power in cables and long high voltage transmission lines. It can be directly connected to
the power line or tertiary winding of three winding transformer.
Related Post: Power Transformer Protection & Faults
123kV, 100 MVAr Shunt Reactor
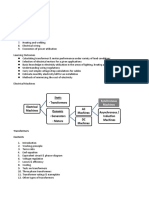
Different Between Shunt Reactor & Power Transformer
Both Shunt reactor and power transformer are same in construction but there are some main difference as well
such as:
Shunt reactor has only single winding while Power transformer has three windings.
Shunt reactor provide lagging VArs (Or it may consume and absorb reactive power) to increase the system
efficiency while power transformer is meant to be operated to transform voltage (i.e. step up or step down)
In shunt reactor, primary AT (Ampere Turns) are equal to secondary AT due to the absence of other windings
while in case of power transformer, Primary AT is the sum of exciting AT and Secondary AT.
Shunt reactor may be designed without air or iron core to prevent the hysteresis loss as there are large
amount of magnetizing current as compared to power transformer.
Shunt Reactors are rated in MVAr while power transformer rated in kVA.
Shunt reactor are used in high voltage systems and cables network to improve the system efficiency while
power transformer are used to transfer the level of voltage.
Related Post: Transformers Insulation Materials in Oil-Immersed & Dry Type T/F
Why to use Shunt Reactor ? Applications of Shunt Reactors
Apart from resistance real electrical circuits have a inductive and/or capacitive component, which causes a
phase shift between voltage and current, as shown in Figure 1, and reactive power (unit: VAr) will flow in the
circuit.
Figure 1 – Phase shift
If inductance (XL = 2πfL = ωL) prevails current will be lagging (Figure 2) and reactive power is called inductive
power.
Where:
XL (Ω – ohm): Inductive reactance. f (Hz – hertz) : frequency. L (H – henry): Inductance. ω = 2πf: Rotational speed
(rad/s or rpm – radians per second or revolutions per minute)
Figure 2 – Current lagging
This is the case of long overhead lines. The consequence of lagging currents is well known (low power factor), as
well as the way to increase power factor (installation capacitor banks).
If capacitance prevails (XC = 1/2πfC = 1/ωC ), which is the case of networks with long underground
cables.Current will be leading (Figure 3) and reactive power is called capacitive power.
Where:
XC(Ω– ohm): Capacitive reactance. C (F – farad): Capacitance.
Figure 3 – Current leading
This situation is also harmful for power transformers and mainly for generators.
Power transformers may be subjected to ferroresonance, an over-voltage phenomenon that can damage the
transformers and/or the surge arresters .In weak networks, functioning as an island and not integrated in a large
and complex electrical network, generators are requested to supply the excessive capacitive power, situation that
will cause overheating and malfunctioning of generators, which will decrease the useful life of the equipment.
That excessive reactive power must be compensated, using shunt reactors, equipments that shall be in
accordance with IEC Standard 60076-7, of which an example is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 – Shunt reactor
Related Post: Maintenance of Transformer & Power Transformers Maintenance, Diagnostic & Monitoring
Construction of Shunt Reactor
As mentioned above, Shunt reactors are similar to power transformers, but they have only one winding per phase.
Those three windings are star connected with the neutral point accessible (YN). The neutral point is connected to
the earthing system of the installation through the tertiary winding of a power transformer or directly. Figure 5
shows a typical connection diagram of a shunt reactor.
Figure 5 – Typical connection diagram of a shunt reactor
Shunt reactors may be oil-immersed type with conservator or dry type.
The built-on protections are the same used in power transformers (Buchholz relay and oil pressure and
temperature sensors for oil-immersed type; windings temperature probes for dry type). Accessories are also similar
to those used in power transformers, mainly in oil-immersed type, in which it must be emphasized the oil pressure
relief valve and the air breather.
Related Post: Transformers Fire Protection System – Causes, Types & Requirements
Types of Shunt Reactors
Common shunt reactors have a fixed rating ( MVAr ; kVAr ) and they may be permanently connected to the
network, or switched in and out, depending on the load and of the capacitance of the underground cables in service.
This functioning and the switching in and out are similar to what is done with capacitor banks.
SPONSORED SEARCHES
electrical transformer circuit schematic
types of shunt reactors electrical and electronics engineering
The more recent technology calls, depending of the characteristics of the network and the variability of the load, for
the use of variable shunt reactors (VSR), which rating can be changed by steps. Common shunt reactors are
mainly used in medium voltage networks (up to 36 kV).
VSR are mainly used in extra high and high voltage networks (rated voltage of the network ≥ 60 kV).
Maximum rated voltage of shunt reactors is nowadays 800 kV and rated power goes up to 300 MVAr.
Same like power transformers, shunt reactors may be designed like Oil-immersed and Dry type transformer as
well.
Related Post: Transformer Efficiency, All day Efficiency & Condition for Maximum Efficiency
Tags shunt reactor diagram Shunt Reactors
One Comment
Thanyalo Kath
Shunt reactor
the sending end voltage is 132 kV and due to ferranti effect the receiving side(132/33 kV, 48 MVA S/S) is 152 kV on no load. so the
department plans to install a shunt reactor
Kindly suggest as to what value of reactor should be used along with the justification thereof.
thank you
Reply
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Differences Between Shunt Reactor and Power Transformer - EEPDokument5 SeitenDifferences Between Shunt Reactor and Power Transformer - EEPvishiwizardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shunt ReactorsDokument29 SeitenShunt ReactorsK Vijay Bhaskar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shunt Reactors Shunt Reactor Protection PDFDokument122 SeitenShunt Reactors Shunt Reactor Protection PDFanoop_jan139885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differences Between Shunt Reactor and Power Transformer - EEPDokument5 SeitenDifferences Between Shunt Reactor and Power Transformer - EEPAdrian M FahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesVon EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shunt Reactor SizingDokument4 SeitenShunt Reactor Sizingrajfab100% (5)
- Power Inverter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument5 SeitenPower Inverter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSubbaReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 132/33kv SubstationDokument44 Seiten132/33kv SubstationAkhileshPP85% (20)
- Interview Questions MS WordDokument20 SeitenInterview Questions MS Wordhassan iftikhar100% (1)
- Shunt ReactorDokument3 SeitenShunt ReactorMichel FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAL Project ReportDokument19 SeitenHAL Project ReportPandu DonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlVon EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chapter 2 Component and Control in X-Ray CircuitDokument62 SeitenChapter 2 Component and Control in X-Ray Circuithailemicael mesfin100% (2)
- CRDR2Dokument54 SeitenCRDR2Austine OsaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Transformer: Laminated CoreDokument8 SeitenPower Transformer: Laminated Coreraymond baliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHEL TRAINING REPORT Transformer-2 PDFDokument65 SeitenBHEL TRAINING REPORT Transformer-2 PDFPAWAN DAYAL100% (1)
- Sri RamachandranDokument7 SeitenSri RamachandranNavaneethakrishnan MurugesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Solar InverterDokument5 SeitenDesign Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Solar InverterSyed ZadaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talking About HV Shunt Reactor Switching - EEPDokument5 SeitenTalking About HV Shunt Reactor Switching - EEPa_mohid17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Description Block DiagramDokument55 SeitenProject Description Block DiagramAnonymous f9RU7fiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 420kv Shunt Reactor Controled SwirchingDokument8 Seiten420kv Shunt Reactor Controled SwirchingElvis BoghiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay Setting (Directional) : Leakage FluxDokument8 SeitenRelay Setting (Directional) : Leakage Fluxjyoti kachareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 Mva Reactor On 230 KV Line DesignDokument6 Seiten25 Mva Reactor On 230 KV Line DesignAshish RegmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumDokument14 SeitenCSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumAshish MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model PrigusniceDokument7 SeitenModel PrigusnicedankorankoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typs of TransformerDokument7 SeitenTyps of TransformermuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Reactor BHELDokument17 SeitenBus Reactor BHELVHMANOHAR100% (2)
- Internship Thesis OriginalDokument15 SeitenInternship Thesis OriginalMuhammad Suleman MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plant ReportDokument17 SeitenPower Plant ReportLanz de la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shunt ReactorsDokument28 SeitenShunt ReactorsDipan GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage ControlDokument37 SeitenVoltage Controlمحمد سليمانNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Reactive PowerDokument9 SeitenAbout Reactive PowerMohammad Khairul Halim RimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Description Block DiagramDokument50 SeitenProject Description Block DiagramRamalingam ShanmugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 2802 - Transformers - Concise NoteDokument10 SeitenEE 2802 - Transformers - Concise NoteLasal RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERDokument4 SeitenElectrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERchico brilliantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Pakistan Ordnance Factory Wah Cantt: Electrical EngineeringDokument11 SeitenIntroduction of Pakistan Ordnance Factory Wah Cantt: Electrical EngineeringNusrat Abbas AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview Questions Electrical EnggDokument21 SeitenInterview Questions Electrical Enggwelcome2twinkle_2272100% (1)
- ReactorsDokument78 SeitenReactorsDanielAlejandroRamosQueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- GL in Kowski 1997Dokument8 SeitenGL in Kowski 1997alvarofranciscooliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Transformers - Definition, Types, and Applications - Electrical4UDokument5 SeitenPower Transformers - Definition, Types, and Applications - Electrical4UHarsh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity Enhancement For Aging Single Wire Earth Return Distribution SystemsDokument8 SeitenCapacity Enhancement For Aging Single Wire Earth Return Distribution SystemsGreg MavhungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acknowledgement: and His Team of Power Grid Agra Substation For Their Active Support andDokument22 SeitenAcknowledgement: and His Team of Power Grid Agra Substation For Their Active Support andMitranshu RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current TransformerDokument22 SeitenCurrent TransformerSaji S Sajivv100% (1)
- Advantages of Static RelaysDokument14 SeitenAdvantages of Static RelaysAbdulyunus AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer TransformerDokument6 SeitenTransformer TransformerKyaw SoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of 20 MVAR Three Phase Shunt Reactor For Voltage Suppression at 230 KV Transmission Line (Kyaukpyu Primary Substation)Dokument10 SeitenDesign and Simulation of 20 MVAR Three Phase Shunt Reactor For Voltage Suppression at 230 KV Transmission Line (Kyaukpyu Primary Substation)umerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTPDokument2 SeitenHTTPRahul SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation UPPTCL 400KV Substation Motiram Adda, GorakhpurDokument23 SeitenPresentation UPPTCL 400KV Substation Motiram Adda, GorakhpurAnik Goyal50% (6)
- Chapter-3Dokument13 SeitenChapter-3Bts ArmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pel Internship ReportDokument44 SeitenPel Internship ReportMuhammad FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trinning FileDokument32 SeitenTrinning FileelsayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences Between Shunt Reactor and Power TransformerDokument4 SeitenDifferences Between Shunt Reactor and Power TransformerUalahMakjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shunt Reactor ProtnDokument14 SeitenShunt Reactor Protnnvenkatrao310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Enhance Technics-Cpe13Dokument204 SeitenPower Enhance Technics-Cpe13Sarath Chandra VNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE Interview Question and AnswersDokument20 SeitenEEE Interview Question and AnswersAlexander JagannathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. S.C. Bansal: (Lecturer)Dokument96 SeitenMr. S.C. Bansal: (Lecturer)Aizat RazakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionVon EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingVon EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICSDokument24 SeitenMICSPrem KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRP Connection DiagramDokument8 SeitenPRP Connection DiagramPrem KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scada Control Room: EFS-A1 EFS-B1Dokument1 SeiteScada Control Room: EFS-A1 EFS-B1Prem KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description: Static VAR CompensatorDokument2 SeitenDescription: Static VAR CompensatorPrem KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AsmDokument2 SeitenAsmChristopher Nicolas A. Illanes FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Multilevel Inverter TopologyDokument22 SeitenNew Multilevel Inverter TopologyAnand KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun Tracking Solar PanelDokument11 SeitenSun Tracking Solar PaneldanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On TransistorsDokument16 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On TransistorsBreajAdarbe50% (2)
- CT 25 L 8 GDokument20 SeitenCT 25 L 8 GkosmitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VHDL Tutorial-Part 1-Adc-SpiDokument7 SeitenVHDL Tutorial-Part 1-Adc-Spihieuhuech1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Model APS-25CH: Installation ManualDokument8 SeitenModel APS-25CH: Installation ManualJorge Alarcon PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transpimedance Amplifiers 4xp3 - TIADokument16 SeitenTranspimedance Amplifiers 4xp3 - TIAMali RibicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Industrial Electronics Engineering, (Pcsir) KarachiDokument11 SeitenInstitute of Industrial Electronics Engineering, (Pcsir) KarachiQuratulain AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece-Vii-optical Fiber Communication NotesDokument254 SeitenEce-Vii-optical Fiber Communication NotesLokesh100% (1)
- Westeweb FM PDFDokument67 SeitenWesteweb FM PDFhellboytonmoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Seller PDFDokument79 SeitenBest Seller PDFari santosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seccionadores ABB PDFDokument8 SeitenSeccionadores ABB PDFLuisManuelTrujilloMartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deld SylubusDokument2 SeitenDeld SylubusMary MorseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6504 Electrical MachinesDokument2 SeitenEe6504 Electrical MachinesanbuelectricalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor MagazineDokument33 SeitenSemiconductor MagazineNational Instruments ItalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Flow (EDA)Dokument2 SeitenDesign Flow (EDA)MarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- C5X Design Rules 45000099 RevTDokument89 SeitenC5X Design Rules 45000099 RevTMohammed TamheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of The General Network Theorem in ADE and ADE XLDokument36 SeitenIntegration of The General Network Theorem in ADE and ADE XLosewoudtNoch keine Bewertungen
- STM32F429 DatasheetDokument226 SeitenSTM32F429 DatasheetBhaskar SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 RF OscillatorDokument27 Seiten2011 RF OscillatordjordjesivcevNoch keine Bewertungen
- 512 Kbit / 1 Mbit / 2 Mbit (x8) Many-Time Programmable FlashDokument23 Seiten512 Kbit / 1 Mbit / 2 Mbit (x8) Many-Time Programmable Flashespia_smith096226Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLC - Input 2 Wire Proximity Switch PDFDokument2 SeitenPLC - Input 2 Wire Proximity Switch PDFCristopher EntenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTCS404 Microprocessors and Assembly Language Programming1Dokument2 SeitenBTCS404 Microprocessors and Assembly Language Programming1Kumar AnoopNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2SK772Dokument4 Seiten2SK772Juan CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITU - T - K.96 - 2014 - Surge Protective Component - Overview of Surge Mitigation Functions and TechnologiesDokument34 SeitenITU - T - K.96 - 2014 - Surge Protective Component - Overview of Surge Mitigation Functions and Technologieschockanan suwanprasertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lic Ect 301Dokument80 SeitenLic Ect 301Arun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vlsi Design UNIT-1: Lecture-2Dokument4 SeitenVlsi Design UNIT-1: Lecture-2Venky VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3: Current and Voltage Characteristics of BJT: 1. ObjectivesDokument5 SeitenLab 3: Current and Voltage Characteristics of BJT: 1. ObjectivesTOBY RANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mems SyllabusDokument2 SeitenMems SyllabusSony RamaNoch keine Bewertungen