Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ee6801 Eeguc
Hochgeladen von
srivaas131985Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ee6801 Eeguc
Hochgeladen von
srivaas131985Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SVS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
COIMBATORE 642 109
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
QUESTION BANK
Name of the Faculty : Mr. S. Venkatesh Kumar
Subject : Electric Energy Generation, Utilization
and Conservation
Regulations : R2013
Course Code : EE6801
Branch : EEE
Year & Semester : IV & VIII
Academic Year : 2018 -2019
UNIT-I
ELECTRIC DRIVES AND TRACTION
PART-A
[Two Marks Questions with Answers]
1. What is meant by electrical drives?
Systems employed for motion control are called “DRIVES” and drives employ any of the prime
movers such as, diesel or petrol engines, gas or steam turbines, hydraulic motors and electric motors for
supplying mechanical energy for motion control. Drives employing electric motion known as electrical
drives.
2. What are the factors that influence the choice of electrical drives? [May-2017]
Shaft power and Speed
Speed Range
Efficiency
Environment
Starting torque
Maintenance
Types of drive
3. What are the applications of electrical drives?
Paper mills
Electric traction
Cement mills
Steel mills
4. Draw the speed torque characteristics of an ideal traction system.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
5. What are the requirements of an ideal traction system? [Nov-2012]
The starting tractive effort should be high so as to have rapid acceleration.
The wear on the track should be minimum.
Pollution free
Speed control should be easy.
The equipment should be capable of withstanding large temporary loads.
Low initial and maintenance cost.
There should be no interference to the communication lines running along the lines.
Braking should be such that minimum wear is caused on the brake shoes.
6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of electric traction? [Nov-2013, 14, 17, May-2017]
Advantages:
High starting torque
Less maintenance cost
Cheapest method of traction Rapid acceleration and braking
Less vibration Coefficient of adhesion is better
It has great passenger carrying capacity at higher speed.
Disadvantages:
High capital cost
Problem of supply failure
Additional equipment is required for achieving electric braking and control
The leakage of current from the distribution mains and drop of volts in the track are to be kept
within the prescribed limits.
The electrically operated vehicles have to move on guided track only.
7. Define tractive effort. [Nov-2013, May-2013]
The effective force necessary to propel the train at the wheels of the locomotive to which the motor
is geared is called the geared effort. It is measured in Newtons and is tangential to the driving wheels.
8. Write the formula for tractive effort of an electric train?[May-2014]
The tractive effort is given by,
Ft=Fa+Fg+Fr
Where
Fa = force to overcome linear or angular motion
Fg = Force to overcome effect of gravity,
Fr = Tractive effort to overcome the frictional resistance
9. What are the recent trends in electric traction? [May-2013, 2014]
Development of practical electric vehicles has been completed. Motor selection becomes clear,
Battery trend becomes also clear and components are almost completed.
10. Define crest speed of a train. [Nov-2012]
It is defined as the maximum speed attained by the vehicle during the run.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
11. Define average speed and scheduled speed.
Average speed is the ratio of distance between two consecutive stations to time taken to travel the
distance,
Scheduled speed is the ratio of distance between two consecutive stations to total time taken for
moving including the time for stops.
12. Define specific energy consumption and mention the factors that affect the specific energy
consumption of trains operation at a given schedule speed. [Nov-2012, May-2015]
It is the energy consumed in Wh per tone mass of the train per km length of the run. The factors
that affect the specific energy consumption of trains operation at a given schedule speed,
Distance between stops
Acceleration
Retardation
Maximum speed
Type of train and equipment
Track Configuration
13. Suggest suitable drives for lifts and cranes. [May-2017]
DC Series motor
High starting torque SGIM
Slip ring IM
14. Define gear ratio. [Nov-2017]
The ratio of the angular speed of the initial or driving member of a gear train or equival ent
mechanism to that of the final or driven member.
15. Define dead weight and adhesive weight.
Dead weight
The total weight of locomotive and train to be pulled by the locomotive is known as dead weight.
Adhesive weight
The total weight to be carried on the driving wheels is known as the adhesive weight.
16. Name the various methods of traction motor control.
There are various methods for controlling the speed of d.c series motors. They are
Rheostatic control
Series parallel control
Field control
Buck and Boost method
Metadyne control
Thyristor control
17. What are the basic requirements of braking system?
The basic requirements of a braking system are given below
It should be simple, robust, quick and reliable in action.
Easy to use for driver to operate.
Maintenance should be minimum.
The braking system should be inexhaustible.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
18. Name the factors governing the selection of a motor for a particular purpose.
Mechanical output required
Electrical input required
Environment
Cost
Electrical characteristics
Mechanical characteristics
Size and rating
19. Define braking and mention different types of braking in a dc motor.
In braking, the motor works as a generator developing a negative torque which opposes the
motion. Types of regenerative braking are
Dynamic (or) Rheostat braking
Plugging (or) reverse voltage braking
Regenerative braking
20. Draw the speed time curve of sub-urban service. [May-2014, Nov-2015]
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
PART-B
[Important 16 Marks Questions]
1. Explain the principle and operation of a modern ac locomotive. [May-2015]
2. What are the various types of electric braking used in traction? Discuss in detail. [May-2015]
3. Explain supply system of electric traction in detail. [Nov-2014]
4. Sketch the typical speed-time curve for main line service and to sub-urban services in electric
traction. Find the equation for distance travelled for main line system. [May-2017]
5. State the principle of regenerative braking. Explain regenerative braking in respect of DC motors.
[May-2017, 2015, Nov-2015]
6. Describe the mechanism of train movement with the aid of transmission of tractive effort.
[Nov-2017, 2015]
7. Discuss in detail about series-parallel control of electric traction motor with example. [Nov-2017]
8. Explain in detail about different methods of traction motor control. [Nov-2017]
9. Explain about the types of supply system used in traction system. [Nov-2015, 2014]
10. Discuss the various arrangement of current collection used in electric traction. [May-2015]
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
UNIT-II
ILLUMINATION
PART-A
[Two Marks Questions with Answers]
1. Define illumination.
It is defined as the number of lumens, falling on the surface per unit area is called the illumination.
It is denoted by symbol E and is measured in lumens/m2.
2. Define lumen.[May-2014, Nov-2014]
It is defined as the luminous flux per unit angle from a source 1 candle power. It is the unit of lux.
3. Define lux or metre candle. [May-2014]
It is defined as the luminous flux falling per square metre on the surface, which is everywhere
perpendicular to the rays light from a source of 1 candle power and one metre away from it.
4. Define luminous efficiency. [Nov-2012, 2017, May-2013]
It is defined as the ratio of the total luminous flux to the total radiant flux of an emitting source.
5. Define the term MSCP. [Nov-2017]
It is defined as the mean of candle powers in all directions and in all planes from the source of
light.
6. What is meant by candle power?
It is defined as the number of lumens given out by the source in a unit solid angle in a given
direction. It is denoted by C.P
7. Define the term luminous flux. [Nov-2015]
It is defined as the total quantity of light energy emitted per second from a luminous body. It is
represented by symbol F and is measured in lumens.
8. State the different types of electrical lamps used for illumination. [Nov-2015, 14, May-13]
Incandescent lamp
Tungsten-Halogen lamp
Compact fluorescent lamps
Sodium vapour lamp
Mercury vapour lamp
Neon lamp
9. State the merits of gaseous discharge lamps over filament lamps. [May-2014]
Its efficiency is high and output is more.
It has a long life.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
10. What do you understand by polar curves as applied to light source? [May-2017]
In most lamps or sources of light the luminous intensity is not the same in all directions. If the
luminous intensity, i.e. the candlepower is measured in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis and a curve
is plotted between candle power and the angular position, a curve is obtained is called as horizontal polar
curve. The luminous intensity in all the directions can be represented by polar curves. If the luminous
intensity in a vertical plane is plotted against the angular position, a curve known as vertical polar curve is
obtained.
11. What are the two laws of illumination? [May-2009]
Laws of inverse squares
Lamberts cosine law
12. State the lambert’s cosine law of illumination.[May-2013]
The illumination at a point on a surface is proportional to cosine of the angle which ray makes with
the normal to the surface at that point.
13. State the laws of inverse squares. [May-2009]
This law states that illumination of a surface is inversely proportional to the square of the distance
of the surface from the source of light, under the condition that source is the point source.
14. What is the importance of street lighting system?[Nov-2012]
To reduce the occurrence of accident.
To avoid the theft.
15. What is flood lighting? Where is it generally used? [May-2017]
Flood lighting means flooding of large surfaces with light from powerful projectors.
Uses of Flood Lighting:
It is used for enhancing the beauty of old monument.
It is used for advertisement and for illuminating sports stadium, quarries and railway yards.
16. Why tungsten is selected as the filament material? [Nov-2017]
Pure tungsten has properties including the highest melting point(3695K), lowest vapour pressure
and greatest tensile strength out of all the metals.
17. Specify any four energy efficient lamps.[Nov-2013]
Energy efficient fluorescent lamps
Compact fluorescent lamps
Metal halides lamps
LED
18. Define utilization factor.
It is defined as the ratio of total lumens reaching the working plane to total lumens given out by the
lamp.
Total lumens reaching the working plane
Utilization factor = ----------------------------------------------
Total lumens given out by the lamp
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
19. What is meant by luminance? [May-2012]
It is defined as the luminous intensity per unit projected area of either a surface source of light or a
reflecting surface and is denoted by L.
20. Define space-height ratio. [Nov-2013]
It is defined as the ratio of horizontal distance between adjacent lamps and height of their
mountings.
Horizontal distance between two adjacent lamps
Space-height ratio = ---------------------------------------------------------
Mounting height of lamps above working plane
21. What is stroboscopic effect of fluorescent tubes? [May-2010]
With A.C. supply frequency of 50 cycles per second, discharge through the lamp becomes zero,
100 times in a second. Due to the persistence of vision, our eyes do not notice this. If this light falls on
moving parts, they may appear to be either running slow or in the reverse direction or even may appear
stationary. This effect is called stroboscopic effect.
22. Define beam factor. [May-2009]
The ratio of lumens in the beam of a projector to the lumens given out by lamps is called the beam
factor. This factor takes into account the absorption of light by reflector and front glass of the projector
lamp. Its values vary from 0.3 to 0.6.
23. Mention the types of lighting schemes. [May-2011]
The distribution of the light emitted by lamps is usually controlled to some extent by means of
reflectors and translucent diffusing screens or even lenses. The interior lighting schemes may be classified
as
Direct lighting
Semi-direct lighting
Indirect lighting
Semi-indirect lighting
General lighting
24. What are the requirements of lighting system? [Nov-2012]
The following factors are required to be considered while designing the lighting scheme.
Illumination level
Uniformity of illumination
Colour of light
Shadows
Glare
Mounting height
Spacing of luminaries
Colour of surrounding walls
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
PART-B
[Important 16 Marks Questions]
1. Discuss laws of illumination and its limitations in actual practice. [May-2014, 15, 17, Nov-17]
2. With neat diagram explain the construction and working of CFL lamp. [May-2015]
3. Explain the working of high pressure mercury vapour lamp with a neat sketch. [Nov-2012, May-2014]
4. Explain the various factors to be taken into account for designing schemes for (i) Street lighting,
(ii) flood lighting, (iii) high way lighting. [Nov-2012, 2013, May-2013, 2014]
5. Explain the various steps followed in the calculation of illumination for designing the residential
lighting. [May-2015]
6. Explain the factors affecting the design of lighting system. [May-2013]
7. Explain in detail the principle of operation of fluorescent lamp. [Nov-2017]
8. Explain the working of a sodium vapour lamp with in a neat sketch. [Nov-2015, May-2017]
9. Show different types of indoor and outdoor lighting with neat sketches. [May-2017]
10. List the properties of good lighting. [Nov-2015]
11. Explain the various steps followed in calculation of illumination for designing the flood lighting in
sports ground. [Nov-2015]
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
UNIT-III
HEATING AND WELDING
PART-A
[Two Marks Questions with Answers]
1. What are the advantages of electric heating? [Nov-2011, May-2013, 2014]
The main advantages of electric heating over other systems of heating such as coal, oil or gas
heating are given below.
Economical
Cleanliness
Absence of flue gases
Ease of control or adaptation
Automatic protection
Upper limit of temperature
Special heating features
High efficiency of utilization
Better working conditions
Safety
Heating of non-conducting materials
2. Classify the methods of electric heating. [Nov 2010]
Power frequency heating
o Resistance heating
Direct resistance heating
Indirect resistance heating
Infrared or Radiant heating
o Arc heating
Direct arc heating
Indirect arc heating
High frequency heating
o Induction heating
Direct induction heating
Indirect induction heating
o Dielectric heating
3. What is meant by indirect resistance heating? [May-2014]
In this method, the current is passed through a high resistance wire known as heating element. The
heat produced due to I2 R loss in the element is transmitted by radiation or convection to the body to be
heated. Applications are room heaters, in bimetallic strip used in starters, immersion water heaters and in
domestic and commercial cooking and salt bath furnace.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
4. What is the basic principle of induction heating? [Nov-2005]
High frequency eddy current heating produced by eddy currents induced by electromagnetic action in
the metal to be heated. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction as same as a transformer. It
has a metal disc surrounded by a copper coil in which a.c supply is flowing. The disc has a finite value of
diameter and thickness and is spaced a given distance from the coil and concentric to it. We find that a
secondary current is caused to circulate around the outer surface of the disc.
5. What are the different types of resistance welding? [Nov-2007]
Butt welding
Spot welding
Projection welding
Seam welding
Percussion welding
6. What is meant by infrared / radiant heating? [Nov-2013]
When current possess through a resistive element heat energy is produced and the same is dissipated in
the form of infrared radiation this is focused upon a body to be heated .e.g. to dry the wet paint on an
object.
7. What is meant by dielectric heating?
When a non metallic material is placed between two electrodes at high voltage the dielectric loss is
dissipated in the form of heat which is used for heating purposes.
8. What are the requirements of a good heating material? [May-2014, Nov-2014, 2017]
High resistivity
Low temperature coefficient of resistance
High melting point
Free from oxidation
9. What are the properties of heating element material? [May-2011, 2013, 2015, 2017]
The material of the heating elements should posses the following desirable properties for efficient
operation and long life.
High resistivity
High melting point
Free from oxidation
Low temperature coefficient
10. Write short note on infrared heating. [Nov-2010]
In radiant heating, the elements are of tungsten operating about 2300°C as at this temperature a
greater proportion of infra-red radiation is given off. Heating effect on the charge is greater since the
temperature of the heating element is greater than in the case of resistance heating. Heat emission
intensities up to 7500 watts/sq.m can be obtained leading to heat absorption up to 4300 watts/sq.m. This
reduces the time taken by various drying process.
11. What is LASER welding?
LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) welding is a welding process
that uses the heat from a laser beam impinging on the joint. The process is without a shielding gas and
pressure.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
12. What is meant by resistance welding? [May-2013]
Electric resistance welding(ERW) refers to a group of welding processes such as spot and seam
welding that produce coalescence of faying surfaces where heat to form the weld is generated by the
electrical resistance of material. The time and the force used to hold the materials together during welding.
13. Give the methods of control temperature in arc furnace. [Nov-2012]
Changing the resistance of elements.
Changing the applied voltage to the elements or current passing through the elements.
Changing the ratio of the on-and-off times of the supply.
14. List some steps taken to minimize skin effect in induction heating. [Nov-2012]
By using copper-clad steel wire.
By using low frequency
By reducing the thickness of the laminate or strips.
By using hollow conductor.
15. Mention the applications of dielectric heating? [Nov- 2013]
Plastic welding.
Plastic preheating
Textile drying
Wood glue drying
Food drying
Post bake moisture removal
Pasteurization
Sterilization
Preheating
16. What is meant by electric arc welding? What are the different types of electrodes used and its
applicability? [May-2014, Nov-2014, Nov-2015]
Arc welding is a type of welding that uses a power supply to create an electric arc between an
electrode and the base material to melt the metals at the welding point.
They can use either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) current, and consumable or non-consumable
electrodes. Purpose is to join two metals. Fabrication, ship building and riveting.
17. What is meant by welding?
Welding is a process wherein the metals are joined together by fusion.
18. Mention the factors which limit the choice of frequency in induction and dielectric heating.
[May-2015]
Induction Heating
o Thickness of the surface to be heated
o Time of continuous heating
o Temperature
Dielectric Heating:
o Thickness
o Potential gradient
o Breakdown voltage
o Insulation
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
19. What is meant by arc welding and also list its types? [May-2015]
Arc welding is a type of welding that uses a power supply to create an electric arc between an
electrode and the base material to melt the metals at the welding point.
Different types of arc welding are
Flux-cored are welding (FCAW)
Gas metal arc welding(GMAW)
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW)
Plasma are welding
Shielded metal arc welding
Submerged arc welding
20. Differentiate between core type and coreless type induction furnace. [Nov-2017]
S.No. Core Type Coreless Type
1. The leakage reactance is very high No leakage reactance
2. Crucible of any shape can be used Standard form is used
3. Operation cost is low Operation cost is high
4. High running cost Low running cost
21. Compare A.C. and D.C. sources as source of supply for arc welding.[May-2017]
S.No. A.C. Sources D.C. Sources
1. Low power factor High power factor
2. Operating efficiency is high Operating efficiency is low
3. Non-uniform heating Uniform heating
4. Maintenance cost and operating Maintenance cost and operating cost are
cost are low high
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
PART-B
[Important 16 Marks Questions]
1. Draw a neat sketch of induction furnace and explain its working. [May-2015]
2. Explain with neat sketch the principle and operation application and control methods of Ajax Wyatt
furnace. [May-2014]
3. Explain the principle of arc welding and the difference between carbon and metal arc welding and their
relative merits and demerits. [May-2015]
4. Explain the characteristic of welding transformer. [May-2015]
5. Discuss in detail about any two types of resistance welding. [Nov-2014, May-2017]
6. Explain the process and various methods of electric arc welding. [May-2013, Nov-2012, 2017]
7. Explain the working of core type and coreless type induction furnace. [Nov-2012, 15, May-17]
8. Explain the principle and working of welding transformer. [Nov-2012, 2017]
9. Explain the method of controlling temperature in resistance heating. [Nov-2013]
10. Describe the construction and working principle of dielectric heating. [Nov-2017]
11. Explain the process of dielectric heating and derive the expression for total heat energy.
[May-2014, 2017]
12. With neat sketches explain the function of carbon arc welding and shielded metal arc welding.
[Nov-2015]
13. Explain the characteristics of welding generator. [Nov-2015, May-2015]
14. Explain the principle, operation and different types of induction of heating elaborately. [May-2015]
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
UNIT-IV
SOLAR RADIATION AND SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTORS
PART-A
[Two Marks Questions with Answers]
1. What is meant by Solar Energy?
The energy received in the form of radiation, can be converted directly or indirectly into other
forms of energy, such as heat and electricity, which can be utilized by man.
2. List the drawbacks of Solar Energy.
The intermittent and variable manner in which it arrives at the earth’s surface and
The large area required to collect the energy at a useful rate.
3. Define solar constant.[May-2017]
Solar constant is defined as the amount of energy received in unit time on a unit area perpendicular
to the sun’s direction at the mean distance of the earth from the sun.
4. Define solar time.
Solar time (Local Apparent Time) is measured with reference to solar noon, which is the time
when the sun is crossing the observer’s meridian.
Solar time = Standard time ±4 (Lst-Lloc) +E
Where,
Lst = standard longitude
Lloc = longitude of the observer’s location
E = Equation of time diffused radiation is known as global radiation.
5. What is meant by solar collector? Mention its types.
A solar collector is a device for collecting solar radiation and transfers the energy to a fluid passing
in contact with it. There are two types of collectors:
Non- concentrating or flat plate type solar collector.
Concentrating (focusing) type solar collector.
6. Mention the ways of solar energy can be utilized.
Solar energy can be utilized directly in two ways:
By collecting the radiant heat and using it in a thermal system.
By collecting and converting it directly to electrical energy using a photovoltaic system.
7. List out the advantages and disadvantages of air flat plate collector.
Advantages
It is compact, simple in construction and requires little maintenance.
Corrosion is completely eliminated.
Disadvantages
Heat transfer between the absorber plate and air is poor.
There is less storage of thermal energy due to low heat capacity.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
8. List the application of solar PV system.
Water pumping sets for micro irrigation and drinking water supply, Radio beacons for ship
navigation at ports, Community radio and television sets, Cathodic protection of oil pipe lines, Weather
monitoring, Railway signaling equipment, Battery charging, Street lighting
9. Name the types of concentrating collectors.
The main types of concentrating collectors are:
Parabolic through collector
Mirror strip reflector
Fresnel lens collector
Flat plate collector with adjustable mirrors
Compound parabolic concentrator(CPC)
10. What are the advantages & disadvantages of concentrating collectors over flat plate
type collectors?
Advantages:
Reflecting surfaces required less material and are structurally simpler than flat plate collectors.
The absorber area of a concentrator system is smaller than that of a flat plate system for same
solar energy collection and therefore the insulation intensity is greater.
Disadvantages:
Non-uniform flux on the absorber whereas flux in flat plate collectors is uniform
High initial cost
11. What are the two types of flat plate collectors?
Liquid heating collectors
Solar air heaters
12. What is Green house effect?
The energy we receive from sun in the form of light is a shortwave radiation (not visible to human
eye. When this radiation strikes a solid or liquid it is absorbed and transformed in to heat, the material
becomes heat and conducts it to surrounding materials (air, water or liquids) or reradiates in to other
materials of low temperature as long wave radiation.
13. What is concentration ratio?
Concentration ratio is the ratio between the aperture area and receiver / absorber area of the
collector.
14. Define collector efficiency.[Nov-2017]
Collector efficiency (ɳc) is the collector performance and is defined as the ratio of the useful gain
over anytime period to the incident solar energy over the same time period.
15. List the advantages of solar concentrators.[Nov-2017]
No fuel cost
No pollution and global warming effects.
Using existing industrial base
Large economy.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
16. Write down the energy balance equation for solar collector.[May-2017]
The energy balance equation for the whole solar collector can be written as,
Ac[{HR(τ.α)b +HR((τ.α)d}] = Qu + Ql +Qs
17. Define flat plate collectors.
Solar collectors for home heating usually called flat plate collectors, almost have one or more glass
covers, although various plastic and other transparent materials are often used instead of glass.
18. Define Air Mass(AM).
It is often used as a measure of the distance travelled by beam radiation through the atmosphere
before it reaches a location on the earth surface. It is defined as the ratio of the mass of the atmosphere
through which the beam radiation passes to the mass it would pass through if the sun directly overhead.
19. Name the instruments used to measure the solar radiation and sunshine hours.
Solar radiation flux is usually measured with the help of a Pyranometer or Pyrheliometer.
The duration of bright sunshine in a day measured by means of the sunshine recorder.
20. Give the main components of Flat-plate collectors.
A transparent cover
Tubes, Fins, Passages or channels
Absorber Plate
Insulation
Casing or container
21. What are the different losses occur in solar collector?
Conductive loss
Convective loss
Radiative loss
22. Define fin efficiency
It is used to indicate the effectiveness of a fin in transferring a given quantity of heat.
Actual heat transferred
Fin efficiency = ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Heat which would transfer if entire fin area were at base temperature
23. Define Heat Removal Factor (FR ).
It is defined as the ratio of actual energy collected to the useful energy collected if the entire
collector absorber surface where at the temperature of the fluid entering the collector.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
24. Define Instantaneous solar collector efficiency.
It is defined as the ratio of the actual solar energy collected to the solar incident on or intercepted
by the collector.
25. State Snell’s Law.
The incident and reflected beams are related to each other by Snell’s Law which states that,
sinϴ1 n2
--------------- = -------------
sinϴ2 n1
Where,
ϴ1 = Angle of incidence
ϴ2 = Angle of refraction
n1, n2 = Refractive indices of the two media.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
PART-B
[Important 16 Marks Questions]
1. Explain the operation of solar cell using equivalent circuit and I-V Characteristics. [Nov-2017]
2. Discuss in detail about the performance of cylindrical and parabolic concentrating collector.[Nov-2017]
3. Explain the basic phenomenon of solar energy conversion with suitable diagram. [May-2017]
4. Explain the solar radiation geometry at earth surface. [May-2017]
5. What are the main components of a flat plate solar collector, explain the function of each. [May-2017]
6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of concentrating collectors over a flat plate collector?
[May-2017]
7. What are the reasons for variation in solar radiation reaching the earth than received at the outside of
the atmosphere? Explain.
8. Enumerate the different types of concentrating type collectors.
9. How solar air collectors are classified? What are the main applications of a drier?
10. Enumerate the different main applications of solar energy. Describe a hot water supply system.
11. Describe briefly about the feeding invertors.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
UNIT-V
WIND ENERGY
PART-A
[Two Marks Questions with Answers]
1. Define Wind.
Wind results from motion of air. Air in motion arises from a pressure gradient. The circulation of
air in the atmosphere is caused by the non-uniform heating of the earth’s surface by the sun.
2. What are the different causes of local winds?
Local winds are caused by two mechanisms. They are
Differential heating of land and water
Air heating in hills and mountain sides
3. What are the factors determine the output from a wind energy converter.
The following three factors determine the output from a wind energy converter:
The wind speed
The cross-section of wind swept by rotor
The overall conversion efficiency of the rotor, transmission system and generator or pump.
4. Draw the power Vs wind speed characteristics.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
5. Draw the block diagram of WECS.
6. What are the types of generator drive for the operation of WECS?
The types of generator are suitable for the wind generations are:
DC generator
Synchronous Generator
Induction generator
7. Give the expression for available wind power.
The expression for available wind power is given by,
1
P = ----- ρᴨD2V3 (watts)
8
Where, P = Wind power
ρ = Density of air (ρ =1.225kg/m3 at sea level)
D = Circular diameter in Horizontal Axis Aeroturbines
V = Velocity of air.
8. What are the different types of force acting on propeller type wind turbine?
There are two types of forces which are acting on the blades. They are,
Circumferential force-acting in the direction of wheel rotation that provides the torque.
Axial force-acting in the direction of the wind stream that provides an axial thrust must be
counter acted by proper mechanical design.
9. Give some important factor consider for side selection of WECS.
High annual average wind speed
Availability of anemometry data
Altitude of the proposed site
Terrain and its aerodynamics
Local ecology
Nearness of site to local centre/users
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
10. Define gusts.
Rapid fluctuations in the wind velocity over a wide range of frequencies and amplitudes, due to
turbulence caused by mechanical mixing of lower layers of atmosphere by surface roughness, are
commonly known as gusts.
11. What are the features of VAWT?
The features of VAWT:
It can accept wind from any direction, eliminating the need of yaw control.
The gearbox, generator, etc., are located at the ground, thus eliminating the heavy nacelle at the
top of the tower, thus simplifying the design and installation of the whole structure, including
the tower.
The inspection and maintenance also gets easier
It also reduces the overall cost.
12. Define power coefficient.
The fraction of the free flow wind power that can be extracted by a rotor is called the power-
coefficient.
Power coefficient = Power of wind turbine/Power available in the wind
13. Classify the schemes available for electric generation.
The schemes are available for electric generation is of three categories.
Constant-speed constant frequency systems (CSCF)
Variable speed constant frequency systems (VSCF)
Variable speed variable frequency systems (VSVF)
14. What are the causes of aerodynamic force?[Nov-2017]
All wind turbines extract energy from the wind through aerodynamic forces. There are two
important aerodynamic forces: drag and lift. Drag applies a force on the body in the direction of the
relative flow, while lift applies a force perpendicular to the relative flow. Many machine topologies could
be classified by the primary force used to extract the energy.
15. List the factors responsible for distribution of wind energy on the surface of earth.
[Nov-2017]
The some factors which affect the nature of the wind close to the surface of the earth. They are,
Latitude of the place
Altitude of the place
Topography of place
Scale of the hours, months or year
16. Define wind turbine.
A wind turbine which converts wind power into rotary mechanical power. A wind turbine has
aerofoil blades mounted on the rotor. The wind drives the rotor and produces rotary mechanical energy.
17. List the types of wind turbine[May-2017]
Horizontal axis wind turbine
Vertical axis wind turbine
Darrieus wind turbine
Savonius wind turbine
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
18. Write down the condition for maximum power generation in wind conversion system.
[May-2017]
The condition for maximum power generation from wind conversion system is given by,
dP/dVe = 0
Where 1
P = ------ ρA(Vi + Ve)(Vi2 – Ve2)
4gc
dP/dVe = 0 3Ve2 + 2ViVe – Vi = 0
Solving above expression, we get Ve = Vi and Ve =1/3Vi, only second solution is physically acceptable.
Thus Ve,opt = 1/3Vi
19. What is cut in speed and cutout wind speeds for turbine?
CUT IN SPEED
Wind speed at which wind turbine starts delivering shaft power.
Cut in speed: While operating - 7m/s
While stopping - 5m/s
CUT OUT SPEED
At high velocities during storms, it is necessary to cut out the power conversion of wind turbine by
furling the wind turbine blades. The speed at which power conversion is cut out is called cut out wind
speed or furling wind speed.
Cut out speed: While operating - 20m/s
While stopping - 17m/s
Rated speed - 14m/s
20. What are the major components of WECS?
The major components of WECS are,
Aero turbine
Gearing
Coupling
Generator
Controller
21. What are the types of rotors for HAWT?
The different types of rotor for HAWT are:
Single blade rotor
Two blade rotor
Three blade rotor
Sailing rotor
Chalk multiblade rotor
American multibladed rotor
Dutch type rotor
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
22. What are the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy conversion systems?
Advantages:
Inexhaustible fuel source
No pollution
Often an excellent supplement to other renewable sources
Reduces fossil fuel consumption
Wind power plant create may jobs
Increases local tax revenues
Least reliance on foreign oil
It’s free
Disadvantages:
Large areas are needed
Suitable for wind power generation
Relatively expensive to maintain
Large numbers of wind generators are required to produce useful amount of heat or
electricity
23. Define Tip Speed Ratio (TSR).
The ratio of the speed of the rotor blade tips to the speed of the wind called Tip Speed Ratio
(TSR).
TSR = Vtip/V
Where
Vtip = Speed of the rotor tip(m/s)
T = Free wind speed(m/s)
24. Define Solidity
Solidity is normally defined as the fraction of the total circumferential (either at the tip or
sometimes at two thirds of the tip radius) that contains blades. Numerically it can be expressed as,
S = NC/ᴨD
Where
N = Number of blades,
C = Average breadth of a blade
D = Diameter of the circle described by a blade
25. Define Torque Coefficient.
Torque coefficient is defined as,
CT =T/Tmax
Where
T-Shaft torque
Tmax –Torque at maximum efficiency
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
26. What are the environmental impacts of wind energy systems?
Electromagnetic interference
Noise
Visual effect
Bird life
Risk
PART-B
[Important 16 Marks Questions]
1. Explain the construction and operation of VAWT with its advantages and disadvantages. [Nov-2017]
2. Describe the functions of various blocks of a WECS with the help of block diagram.
[Nov-2017, May-2017]
3. Give some important factors that are considered for site selection of WECS. [May-2017]
4. With the help of neat diagrams explain in detail about the construction and the working principle of
different vertical axis wind turbines. [Apr-2017]
5. Explain the basic principle of wind energy conversion.
6. Derive the expression for power developed due to wind.
7. Describe the different schemes for wind electric generation. Also describe the generator
control schemes.
8. Discuss the analysis of aerodynamic forces acting on the wind blade.
9. Explain briefly about the performances of wind machines.
SVS College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Dept of EEE, EEGUC Question Bank
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsVon EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (19)
- Electric Drives and Traction Systems ExplainedDokument6 SeitenElectric Drives and Traction Systems Explainedmanikandan trNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6601 SSD PDFDokument21 SeitenEe6601 SSD PDFRohithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motor Drives and their Applications with Simulation PracticesVon EverandElectric Motor Drives and their Applications with Simulation PracticesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traction Motors and Speed Estimation Techniques For Sensorless Control of Electric Vehicles: A ReviewDokument6 SeitenTraction Motors and Speed Estimation Techniques For Sensorless Control of Electric Vehicles: A ReviewShovan DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6801 2m Pit GUC QBDokument35 SeitenEE6801 2m Pit GUC QBksrmuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank: Sai Ram Engineering College, Chennai 600 044 An NBA Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified InstitutionDokument55 SeitenQuestion Bank: Sai Ram Engineering College, Chennai 600 044 An NBA Accredited & ISO 9001:2015 Certified InstitutionkalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechatronics of Small Electric Vehicles Research and Education-IjensDokument14 SeitenMechatronics of Small Electric Vehicles Research and Education-IjensSachin AngadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEGUC Unit I Electric Drives Traction Two Marks QuestionsDokument49 SeitenEEGUC Unit I Electric Drives Traction Two Marks QuestionsksrmuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Small Battery Powered Three Wheeler Using PM Hub Motor Prototype IDokument4 SeitenDevelopment of Small Battery Powered Three Wheeler Using PM Hub Motor Prototype IKapish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Generation Through Speed BrakerDokument25 SeitenElectricity Generation Through Speed BrakerVishaldeep Singh CHM PP 8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eficiencia de Un Doble Motor en Un AutomovilDokument10 SeitenEficiencia de Un Doble Motor en Un AutomovilManuelGonzalesGustavsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Drives 2 Marks and 16Dokument34 SeitenSolid State Drives 2 Marks and 16Dhamu DharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car Examples ComparisonDokument14 SeitenCar Examples ComparisonNigamanand RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of dynamic range estimator for battery electric vehiclesDokument13 SeitenSimulation of dynamic range estimator for battery electric vehiclesvale1299Noch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Electric Vehicle Powertrain: Experimental Implementation and Performance AssessmentDokument7 SeitenDevelopment of Electric Vehicle Powertrain: Experimental Implementation and Performance AssessmentBaldau Pratap Singh BundelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Jpe 15-5 1658292190Dokument12 SeitenJournal Jpe 15-5 1658292190Nuri KaraoğlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Generation Through Speed BreakersDokument22 SeitenPower Generation Through Speed BreakersSaikumar MysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey and Comparison of Characteristics of Motor Drives Used in Electric VehiclesDokument4 SeitenA Survey and Comparison of Characteristics of Motor Drives Used in Electric VehiclesGabriel de SáNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Ee6351Dokument23 SeitenUnit I Ee6351karthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6009 PeresDokument89 SeitenEe6009 PeresparthibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper 3Dokument4 SeitenResearch Paper 3Bipasha ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Utilization of Electrical Engineering (UEE)Dokument99 SeitenLecture Notes Utilization of Electrical Engineering (UEE)educatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Svcet: Ee6351-Electrical Drives and ControlsDokument4 SeitenSvcet: Ee6351-Electrical Drives and ControlsBelayneh TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motores de Imánes Permanentes y de InductanciaDokument5 SeitenMotores de Imánes Permanentes y de InductanciaFreddy Julián Chipugsi CaleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering - Modeling, Simulation and Analysis of Electric Vehicle Driven by Induction MotorDokument11 SeitenIOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering - Modeling, Simulation and Analysis of Electric Vehicle Driven by Induction MotorLuong Ngoc MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Simulation of Electric Bus VehicleDokument6 SeitenDynamic Simulation of Electric Bus VehiclethesijNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project Report Phase 2Dokument21 SeitenMini Project Report Phase 2bharathahsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEPCON 2019 Paper 188Dokument7 SeitenMEPCON 2019 Paper 188SanjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6801 Electric Energy Generation and Utilization MCQsDokument20 SeitenEE6801 Electric Energy Generation and Utilization MCQsVenkatesan SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6801 PDFDokument53 SeitenEe6801 PDFHarini KarthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5Dokument17 SeitenModule 5Pragati ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Analysis and Control of A Capacitor Start Induction MotorDokument4 SeitenPerformance Analysis and Control of A Capacitor Start Induction MotorIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Monospiral Motorised Cable Reel in Crane AppliDokument16 SeitenThe Monospiral Motorised Cable Reel in Crane AppliTushar KachhadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDA Notes by Balaji RamakrishnaDokument71 SeitenIDA Notes by Balaji RamakrishnaPkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Motors For Electric Vehicle An OverviewDokument7 SeitenElectrical Motors For Electric Vehicle An OverviewFarhodjon AbdusamatovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Review of Direct-Drive Electrical Machine Systems For Electric and Hybrid Electric VehiclesDokument12 SeitenCritical Review of Direct-Drive Electrical Machine Systems For Electric and Hybrid Electric VehiclesFrankenstein ReichNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE2352 - Solid State DrivesDokument23 SeitenEE2352 - Solid State DrivesSidali ChaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- 146 Ijmperdfeb2018146Dokument16 Seiten146 Ijmperdfeb2018146TJPRC PublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 MohdetalDokument11 Seiten6 Mohdetalsantiagochoaz88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traction Motor DriveDokument15 SeitenTraction Motor Drivejason KlangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panimalar Engineering Collge: Department of Mechanical Engineering Ii Year / Iii SemesterDokument32 SeitenPanimalar Engineering Collge: Department of Mechanical Engineering Ii Year / Iii SemestersivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering and SciencesDokument11 SeitenMechanical Engineering and ScienceswarnoiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility study of electric bike usage and optimal locating of charging stationsDokument7 SeitenFeasibility study of electric bike usage and optimal locating of charging stationsayaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Analysis of Three Phase Full Bridge Converter Controlled DC MotorDokument45 SeitenPerformance Analysis of Three Phase Full Bridge Converter Controlled DC Motoranon_451051243Noch keine Bewertungen
- PE Notes-14Dokument5 SeitenPE Notes-14AR-TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I V 2 Mark Question Answer 16 Mark QuestionsDokument23 SeitenUnit I V 2 Mark Question Answer 16 Mark QuestionspugazhendiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument32 SeitenQuestion BankBhuvaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSD 2 Marks With AnswersDokument35 SeitenSSD 2 Marks With AnswersVijayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Using Different Electric Motors For EVDokument4 SeitenComparative Study of Using Different Electric Motors For EVnaourez benhadjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric - Motorcycle - Modeling - For - Speed - Tracking - and - Range - Travelled - Estimation IEEE ACCESSDokument9 SeitenElectric - Motorcycle - Modeling - For - Speed - Tracking - and - Range - Travelled - Estimation IEEE ACCESSOsito de AguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Optimization and Analysis of An Outer-Rotor Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Motor For Medium-Speed Electric VehicleDokument19 SeitenDesign Optimization and Analysis of An Outer-Rotor Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Motor For Medium-Speed Electric VehicleARUN KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies 12 04615 v2Dokument19 SeitenEnergies 12 04615 v2wgjsesotxjxzosyxjpNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comprehensive Analysis and Implementation of VecDokument24 SeitenA Comprehensive Analysis and Implementation of VecNiccolò NuddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization Approaches and Techniques For Automotive Alternators: Review StudyDokument26 SeitenOptimization Approaches and Techniques For Automotive Alternators: Review StudyMAHMOOD OMAR TALAL MAHMOOD / UPMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies: Energy Consumption of A Battery Electric Vehicle With Infinitely Variable TransmissionDokument21 SeitenEnergies: Energy Consumption of A Battery Electric Vehicle With Infinitely Variable TransmissionGautham NNoch keine Bewertungen
- El 30 4 11Dokument9 SeitenEl 30 4 11daaanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of An Electric Vehicle: International Journal of Mechanical Sciences July 2015Dokument11 SeitenMathematical Modeling and Simulation of An Electric Vehicle: International Journal of Mechanical Sciences July 2015นนฐ์ทกร บุญรักชาติNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of Regenerative Braking SystemDokument41 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Regenerative Braking SystemBT20MEC120 Jyoti ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Type The Document Title) : Criterion 5 Faculty Information and Contributions 200Dokument7 Seiten(Type The Document Title) : Criterion 5 Faculty Information and Contributions 200srivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 04 Electrical Safety PresentationDokument24 Seiten2015 04 Electrical Safety PresentationPaul YstianNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIIC Recruitment 170821Dokument1 SeiteTIIC Recruitment 170821srivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- TIIC Recruitment 170821Dokument1 SeiteTIIC Recruitment 170821srivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aes Int 2 Ans KeyDokument3 SeitenAes Int 2 Ans Keysrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- BE Semester - V - (Electrical) Question Bank (Industrial Instrumentation) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Dokument2 SeitenBE Semester - V - (Electrical) Question Bank (Industrial Instrumentation) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)chandrakanthatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC MathematicsDokument32 SeitenMSC MathematicsAarthi Rajakumar100% (1)
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: (Autonomous Institution Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai)Dokument4 SeitenVivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: (Autonomous Institution Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai)srivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNF Bioenergy 5Dokument12 SeitenUNF Bioenergy 5jacopanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3Dokument13 SeitenQ. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3pulkit patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Instruction Hex Code: MOVE With Immediate DataDokument7 Seiten8051 Instruction Hex Code: MOVE With Immediate DatakskumargieNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument1 SeiteAbstractsrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- RESDokument8 SeitenRESJayam MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branch: Eee Semester: Iv Question Bank Unit - I Part - ADokument7 SeitenBranch: Eee Semester: Iv Question Bank Unit - I Part - AKaree MullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual For Scheme STTP - Short Term Training Program: All India Council For Technical EducationDokument28 SeitenUser Manual For Scheme STTP - Short Term Training Program: All India Council For Technical Educationhitman48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoelectric Material and Its Applications: Prof. Ramesh Chandra MallikDokument38 SeitenThermoelectric Material and Its Applications: Prof. Ramesh Chandra Malliksrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC Generators ExplainedDokument85 SeitenDC Generators Explainedsrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- RESDokument8 SeitenRESJayam MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment 2019Dokument1 SeiteRecruitment 2019srivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Brouchure On Two WorkshopDokument2 SeitenECE Brouchure On Two Workshopsrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University UG PG PPT Presentation FormatDokument21 SeitenAnna University UG PG PPT Presentation FormatVi JäìNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment 2019Dokument1 SeiteRecruitment 2019srivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- AICTE Sponsored Two Week Program on Modeling and Control of Electric VehiclesDokument2 SeitenAICTE Sponsored Two Week Program on Modeling and Control of Electric VehiclesJoshua PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Electrical Machines CourseDokument131 SeitenDesign Electrical Machines CourseSambanna KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation/Erode: Mettur Dam Power HouseDokument20 SeitenGeneration/Erode: Mettur Dam Power Housesrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Innovative ProjectDokument1 SeiteInnovative Projectsrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power System ProtectionDokument1 SeitePower System Protectionsrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Timing Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorDokument29 SeitenTiming Diagram of 8085 Microprocessorsrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Advances in Transmission Insulators - Unit 2 - Module - 1 Introduction and Design of Transmission - Distribution InsulatorsDokument1 SeiteRecent Advances in Transmission Insulators - Unit 2 - Module - 1 Introduction and Design of Transmission - Distribution Insulatorssrivaas131985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine IndicationDokument45 SeitenTurbine IndicationSThaneasMurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skytop Brewster N46Dokument3 SeitenSkytop Brewster N46dvdv vdvdzvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Energy Efficiency of Ring Frame Machine Section of Textile Plant by Walk Through Energy Audit: A Case StudyDokument6 SeitenImproving Energy Efficiency of Ring Frame Machine Section of Textile Plant by Walk Through Energy Audit: A Case StudyPushpak LadheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula 1: The Future: New Cars, New Concepts, New RulesDokument100 SeitenFormula 1: The Future: New Cars, New Concepts, New RulesKashif RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man B&W 6S60MC 704Dokument21 SeitenMan B&W 6S60MC 704Ishan BhatnagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC45MR 3Dokument12 SeitenPC45MR 3LU YONoch keine Bewertungen
- Tata IndiCab Diesel & CNG ManualDokument150 SeitenTata IndiCab Diesel & CNG ManualxtempNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boeckhoff 2010-Operational Experience of The 51-60 DF From MANDokument11 SeitenBoeckhoff 2010-Operational Experience of The 51-60 DF From MANsestoubosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kohler 60RCLA Generator Specs and FeaturesDokument4 SeitenKohler 60RCLA Generator Specs and FeaturesService Brags & Hayes, Inc.Noch keine Bewertungen
- NH 6041351201 PreviewDokument31 SeitenNH 6041351201 PreviewYesenia Gpe Vega100% (1)
- 950C Manual de OperacionDokument1.068 Seiten950C Manual de Operacionglozoya.liumaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual For ICEDokument21 SeitenLab Manual For ICEAmey DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual For YUCHAI Diesel Engine PDFDokument208 SeitenService Manual For YUCHAI Diesel Engine PDFgustavo95% (20)
- Rh120e B BrochureDokument13 SeitenRh120e B BrochureAvaa Amgaa0% (1)
- Volvo Twd1643ge Technical Data PDFDokument2 SeitenVolvo Twd1643ge Technical Data PDFMuhammad rizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komatsu Hydraulic Excavator Pc228uslc 10 Shop ManualDokument20 SeitenKomatsu Hydraulic Excavator Pc228uslc 10 Shop Manualtoni100% (43)
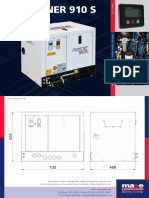
- Mariner 910 S - ENGDokument2 SeitenMariner 910 S - ENGNindi Widia Devi RahmasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Replace fuel pump and fuel tank sensorDokument6 SeitenReplace fuel pump and fuel tank sensorTiga MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Life Building: Supply, Installation, Commissioning Testing of 150 Kva Diesel Generator SetDokument43 SeitenState Life Building: Supply, Installation, Commissioning Testing of 150 Kva Diesel Generator SetZia Ur Rehman100% (1)
- Moog SureFly Infographic123Dokument1 SeiteMoog SureFly Infographic123Rispan GondyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQM Project - Petroleum IndustryDokument29 SeitenTQM Project - Petroleum IndustryDanish Ali0% (1)
- EPM1602 v1Dokument20 SeitenEPM1602 v1rndNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Genset Engine.: kVA at Min RPMDokument2 SeitenThe Genset Engine.: kVA at Min RPMstefanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniDokument2 SeitenBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilanip vsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remote Control For Sulzer Rta EnginesDokument2 SeitenRemote Control For Sulzer Rta EnginesRusuVasileCristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atff FaDokument4 SeitenAtff FaJohn Paul Inovero JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audi 3.0 V6 TFSI Engine With Roots BlowerDokument58 SeitenAudi 3.0 V6 TFSI Engine With Roots Bloweroscar miguel100% (1)
- Motores Caterpillar C12Dokument173 SeitenMotores Caterpillar C12jrrodrigueza297% (31)
- Bedford Middleweight Truck (1954) BrochureDokument20 SeitenBedford Middleweight Truck (1954) BrochureNickiedeposieNoch keine Bewertungen
- MITSUBISHI GENSET MGS1400B-60Hz-480vDokument4 SeitenMITSUBISHI GENSET MGS1400B-60Hz-480vFlavio MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen