Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BRITTLE Materials Breaks
Hochgeladen von
callielizza0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten23 SeitenThe document discusses different types of materials and their properties when subjected to forces. Brittle materials break without deforming plastically, plastic materials do not return to their original shape after deformation, and malleable materials can be reshaped. Elastic materials do return to their original shape after deformation. Compressive strength is the force used to compress a material, while tensile strength is the force used to stretch or pull a material. Hooke's law states that for elastic materials, force is proportional to extension when stretched.
Originalbeschreibung:
Physics A level Materials
Originaltitel
Materials
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses different types of materials and their properties when subjected to forces. Brittle materials break without deforming plastically, plastic materials do not return to their original shape after deformation, and malleable materials can be reshaped. Elastic materials do return to their original shape after deformation. Compressive strength is the force used to compress a material, while tensile strength is the force used to stretch or pull a material. Hooke's law states that for elastic materials, force is proportional to extension when stretched.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten23 SeitenBRITTLE Materials Breaks
Hochgeladen von
callielizzaThe document discusses different types of materials and their properties when subjected to forces. Brittle materials break without deforming plastically, plastic materials do not return to their original shape after deformation, and malleable materials can be reshaped. Elastic materials do return to their original shape after deformation. Compressive strength is the force used to compress a material, while tensile strength is the force used to stretch or pull a material. Hooke's law states that for elastic materials, force is proportional to extension when stretched.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 23
M AT E R I A L S
BRITTLE materials breaks
Without plastic deformation
M AT E R I A L S
PLASTIC materials does not return to its original
Shape after being deformed.
MALLEABLE materials can be reshaped
M AT E R I A L S
ELASTIC materials return to its original shape after being
deformed
HARD materials can scratch or indent, and withstand
Being scratched
F O R C E S A C T I N G O N M AT E R I A L S
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH force used to compress a sample
at any time.
TENSILE STRENGTH force used to stretch a sample
at any time.
Hooke’s law states that for certain elastic materials,
Force is proportional to extension, when a sample
Is stretched.
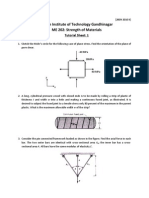
What is the magnitude of the force required to stretch a 20
cm-long spring, with a spring constant of 100 N/m, to a
length of 21 cm?
What is the spring constant of a spring that needs a force
of 3 N to be compressed from 40 cm to 35 cm?
What is the magnitude of the force required to stretch two
springs of constants k1 = 100 N / m and k2 = 200 N / m by
6 cm if they are in parallel?
What is the magnitude of the force required to stretch two
springs of constants 100 N / m and 200 N / m by 6 cm if they
are in series?
How much energy W is needed to compress a spring from 15
cm to 10 cm if the constant of the spring is 150 N / m?
YOUNG’S MODULUS (E)
A nylon string has a diameter of 2 mm, pulled by a force of 100
N. Determine the stress!
A cord has original length of 100 cm is pulled by a force. The
change in length of the cord is 2 mm. Determine the strain!
A string 4 mm in diameter has original length 2 m. The string is
pulled by a force of 200 N. If the final length of the spring is
2.02 m, determine : (a) stress (b) strain (c) Young’s modulus
A string has a diameter of 1 cm and the original length of 2 m.
The string is pulled by a force of 200 N. Determine the change
in length of the string! Young’s modulus of the string = 5 x
109 N/m2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 33 ch9 PDFDokument6 Seiten33 ch9 PDFharwinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress-Strain Relations Plastic and Anisotropic BehaviorDokument53 SeitenStress-Strain Relations Plastic and Anisotropic BehaviorAbdelmoez ElgarfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity: by Prof. Geronimo J. Fiedalan JRDokument55 SeitenElasticity: by Prof. Geronimo J. Fiedalan JRDanya GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESO205 ProblemSheets-8 SolutionsDokument3 SeitenESO205 ProblemSheets-8 SolutionsAjay chouhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastisitas Dan Hukum HookeDokument19 SeitenElastisitas Dan Hukum HookeRISKA PRAMESWARI PUTRINoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.hooks LawDokument10 Seiten4.hooks LawboltuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Principles LO12Dokument84 SeitenMechanical Principles LO12Muammer AlakaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 - Elastic Deformation, Elastic Properties and Stress-Strain RelationshipDokument31 SeitenTopic 2 - Elastic Deformation, Elastic Properties and Stress-Strain RelationshipSezin AYHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity AnswersDokument4 SeitenElasticity AnswersTzuyu RnvchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Som Unit I 2 & 16 MarksDokument7 SeitenSom Unit I 2 & 16 MarksSurjith Bharathi SelvakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Polymers: 1. Polymeric Materials - Basic Definitions, Structure, ClassificationDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Polymers: 1. Polymeric Materials - Basic Definitions, Structure, ClassificationLucas Ferreira da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Elastic ObjectsDokument4 SeitenWhat Are Elastic Objectsraman192021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity With Lecture 2020Dokument5 SeitenElasticity With Lecture 2020mean comiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Solids and Mechanical Properties of FluidsDokument19 SeitenMechanical Properties of Solids and Mechanical Properties of FluidsSasidaran SasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress..strain in Thick PlatesDokument63 SeitenStress..strain in Thick PlatesHitesh MudgilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthodontic WiresDokument116 SeitenOrthodontic WiresAyad Taha100% (2)
- Stress and StrainDokument73 SeitenStress and StrainKarthikeyan MunirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 13Dokument9 SeitenLec 13محمد جاسم محمد عجاجNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 7 Studyguide360Dokument55 SeitenClass 11 Physics Notes Chapter 7 Studyguide360Astrid RedNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Lecture THUR., Jan 31: Spring 2013 PHYS 172: Modern MechanicsDokument23 SeitenNo Lecture THUR., Jan 31: Spring 2013 PHYS 172: Modern MechanicsEkin OrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawDokument15 SeitenHooke's LawHaneen MoosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Young's ModulusDokument7 SeitenYoung's ModulusNgatno100% (1)
- Lecture # 2 Concept of Stress and StrainDokument33 SeitenLecture # 2 Concept of Stress and StrainSohaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Word SubstitutionDokument5 SeitenOne Word SubstitutionKingashiqhussainPanhwerNoch keine Bewertungen
- WiresDokument140 SeitenWiresRushabh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce6302 Notes Rejinpaul - 2 PDFDokument49 SeitenCe6302 Notes Rejinpaul - 2 PDFSekar Dinesh50% (2)
- Lecture # 2 MechanicalPropertiesDokument59 SeitenLecture # 2 MechanicalPropertiesAhmad ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Analysis of Tensile BehaviorDokument13 SeitenTheoretical Analysis of Tensile BehaviorKAMALRAJ0% (1)
- Questionbank SOM RejinpaulDokument13 SeitenQuestionbank SOM Rejinpaularunmct04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I SomDokument4 SeitenUnit I SomVENKATESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawDokument40 SeitenHooke's LawThasreen sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of SolidDokument22 SeitenMechanical Properties of SolidTrillionare HackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.mechanical Properties of MaterialsDokument22 Seiten11.mechanical Properties of MaterialsMazin Al KhateebNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Chap 2Dokument8 Seiten4th Chap 2سيف مهندNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of MatterDokument2 SeitenMechanical Properties of MatterSanal BusherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's Law Young's Modulus Bulk Elastic PropertiesDokument1 SeiteHooke's Law Young's Modulus Bulk Elastic PropertieshlvijaykumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Stress and StrainDokument87 SeitenModule 1 - Stress and StrainIfa IjasNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Pert-4) POLIMER MECH1Dokument48 Seiten(Pert-4) POLIMER MECH1Ajeng IftitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- مقاومه مواد محاضرات د.فراتDokument121 Seitenمقاومه مواد محاضرات د.فراتlana_salahadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics (Elasticity)Dokument2 SeitenPhysics (Elasticity)Julia Nicole BaliberNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNZA PHY 1015 Lecture 8B - Introduction To Mechanical Properties of SolidsDokument12 SeitenUNZA PHY 1015 Lecture 8B - Introduction To Mechanical Properties of SolidsBrian MachachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawV1Dokument7 SeitenHooke's LawV185gks7hq5qNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 Notes 2Dokument11 SeitenChapter 17 Notes 2Rizwan MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSC 2nd Year Physics Volume 2 Chapter 17 - 21Dokument60 SeitenFSC 2nd Year Physics Volume 2 Chapter 17 - 21Kashif Mahmood100% (1)
- What Is Hooke's Law - (Article) - Khan AcademyDokument11 SeitenWhat Is Hooke's Law - (Article) - Khan AcademyDahanyakage WickramathungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity and PlasticityDokument26 SeitenElasticity and PlasticityRAMA BAGAS ADITYA TM 2DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Materials: Chapter 6 and 7 MC Graw HillDokument33 SeitenMechanical Properties of Materials: Chapter 6 and 7 MC Graw HillLily ERc PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deformation of Solid & Elasticity of Materials - Module 2: Michael Adeleye, PH.D, P.G. Dip - EdDokument27 SeitenDeformation of Solid & Elasticity of Materials - Module 2: Michael Adeleye, PH.D, P.G. Dip - Edlar dinchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arch Wires Used in OrthodonticsDokument47 SeitenArch Wires Used in Orthodonticsavanthika krishnaraj100% (1)
- Solid StateDokument2 SeitenSolid StateKimberly SiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch6 ElasticityDokument25 SeitenCh6 ElasticityALIF SYAKIR SATARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7Dokument21 SeitenUnit 7sabirdxb107Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of Project and Model ProjectDokument12 SeitenList of Project and Model ProjectSURESH SURESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Biomechanics SolutionDokument12 SeitenModule 2 Biomechanics SolutionSnehasis RoutrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 312 Physics Eng Lesson8Dokument20 Seiten312 Physics Eng Lesson8alayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch9 NumericalsDokument1 SeiteCh9 NumericalsRaheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Som TS-1Dokument1 SeiteSom TS-1Abhishek KandoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingVon EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Response:: Job Interviewing TutorialDokument7 SeitenSample Response:: Job Interviewing TutorialcallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40 chủ đề IELTS Speaking part 1 và câu trả lờiDokument61 Seiten40 chủ đề IELTS Speaking part 1 và câu trả lờiTạ Nguyễn Anh ThưNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of NmaDokument6 SeitenHistory of NmacallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I'd Been Prepared For Death : - Paul Kalanithi (Page 78)Dokument4 SeitenI'd Been Prepared For Death : - Paul Kalanithi (Page 78)callielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C105 Analysis of Bleach Post-Lab: CalculationsDokument2 SeitenC105 Analysis of Bleach Post-Lab: CalculationscallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Week's Speaking ChallengeDokument2 SeitenThis Week's Speaking ChallengecallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Gathering ProcedureDokument4 SeitenData Gathering ProcedurecallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Practice NOOKDokument19 SeitenEnglish Practice NOOKcallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration (Molarity&Dilution) CalculationsDokument19 SeitenConcentration (Molarity&Dilution) CalculationscallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear FissionDokument2 SeitenNuclear FissioncallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarterly Review 1Dokument24 SeitenQuarterly Review 1callielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS 1Dokument2 SeitenWS 1callielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing CurriculumDokument21 SeitenNursing CurriculumcallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolymerizationDokument8 SeitenPolymerizationcallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Syllabus Final VersionDokument6 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Syllabus Final VersionTim LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDokument2 SeitenScallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter and Chemical Change NotesDokument7 SeitenMatter and Chemical Change NotescallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions: Key ConceptsDokument11 SeitenChapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions: Key ConceptscallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive SentencesDokument5 SeitenDescriptive SentencescallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4.10 Organic Synthesis and AnalysisDokument12 SeitenTopic 4.10 Organic Synthesis and AnalysisPawat SilawattakunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To DistillationDokument33 SeitenIntro To Distillationcallielizza100% (1)
- Packed Distillation Columns: 1. Determination of The Column HeightDokument7 SeitenPacked Distillation Columns: 1. Determination of The Column Heightramsrivatsan1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- DistillationDokument10 SeitenDistillationLiz BargolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chemistry ExercsisesDokument7 SeitenAnalytical Chemistry ExercsisescallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation CalculatorDokument33 SeitenDistillation CalculatorcallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coca-Cola 125 Years BookletDokument27 SeitenCoca-Cola 125 Years BookletShahid Muhammed TawhidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Defi NewDokument5 SeitenIntro Defi NewcallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Data Consumer Health Vitamins and Dietary SupplementsDokument4.418 SeitenSample Data Consumer Health Vitamins and Dietary SupplementscallielizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packed Distillation Columns: 1. Determination of The Column HeightDokument7 SeitenPacked Distillation Columns: 1. Determination of The Column Heightramsrivatsan1992Noch keine Bewertungen