Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Maths Class X Sample Paper 09 For Board Exam 2018
Hochgeladen von
Írfäñ MøhdOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Maths Class X Sample Paper 09 For Board Exam 2018
Hochgeladen von
Írfäñ MøhdCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
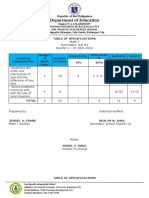
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 09 (2017-18)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041)
BLUE PRINT : CLASS X
VSA SA – I SA – II LA Unit
Unit Chapter Total
(1 mark) (2 marks) (3 marks) (4 marks) Total
Number
system
Real Numbers 1(1) 2(1) 3(1) -- 6(3) 6(3)
Polynomials -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1)
Pair of Linear Equations
Algebra
-- 2(1) 3(1) -- 5(2)
in two variables
20(8)
Quadratic Equations 1(1) -- -- 4(1)* 5(2)
Arithmetic progression 1(1) 2(1) -- 4(1) 7(3)
Coordinate
Geometry
Coordinate Geometry 1(1) 2(1) 3(1)* -- 6(3) 6(3)
Trigonometry
Introduction to
1(1) -- 3(1)* 4(1) 8(3)
Trigonometry
12(4)
Some Applications of
-- -- -- 4(1) 4(1)
Trigonometry
Triangles 1(1) 3(1)* 4(1)* 8(3)
Geometry
Circles -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1) 15(5)
Constructions -- -- -- 4(1) 4(1)
Mensuration
Areas Related to Circles -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1)
10(3)
Surface Areas and
-- -- 3(1)* 4(1) 7(2)
Volumes
Statistics &
probability
Statistics -- -- 3(1) 4(1)* 7(2)
11(4)
Probability -- 4(2) -- -- 4(2)
Total 6(6) 12(6) 30(10) 32(8) 80(30) 80(30)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 09 (2017-18)
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : X DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instruction:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) This question paper contains 30 questions divided into four Sections A, B, C and D.
(iii) Section A comprises of 6 questions of 1 mark each. Section B comprises of 6 questions of 2
marks each. Section C comprises of 10 questions of 3 marks each and Section D comprises of 8
questions of 4 marks each.
(iv) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in four questions of 3
marks each and three questions of 4 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all
such questions.
(v) Use of Calculators is not permitted
SECTION – A
Questions 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
1. Show that 12n cannot end with the digit 0 or 5 for any natural number n.
2
2. If one root of the quadratic equation 6x2 – x – k = 0 is , then find the value of k.
3
3. For what values of k are the points (8, 1), (3, –2k) and (k, –5) collinear ?
5 5
4. Find the 20th term of the A.P. 5, , 0, ,......
2 2
5. If tan9 = cot and 9 < 900, then find the value of cosec5.
6. A girl walks 200 towards East and the she walks 150m towards North. Find the distance of the
girl from the starting point.
SECTION – B
Questions 6 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
7. If two adjacent vertices of a parallelogram are (3, 2) and (−1, 0) and the diagonals intersect at
(2, −5), then find the coordinates of the other two vertices.
8. Prove that 2 is an irrational number.
9. Find the probability that in a leap year there will be 53 Tuesdays.
10. Two different dice are thrown together. Find the probability that the product of the numbers
appeared is less than 18.
11. If seven times the 7th term of an A.P. is equal to eleven times the 11th term, then what will be
its 18th term?
12. Solve for x and y: 47 x 31 y 63;31x 47 y 15 .
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
SECTION – C
Questions 13 to 22 carry 3 marks each.
13. If d is the HCF of 56 and 72, find x, y satisfying d = 56x + 72y. Also show that x and y are not
unique.
14. Diagonals of a trapezium PQRS intersect each other at the point O, PQ RS and PQ = 3 RS.
Find the ratio of the areas of triangles POQ and ROS.
OR
Prove that the area of an equilateral triangle described on one side of a square is equal to half
the area of the equilateral triangle described on one of its diagonals.
15. Show that ∆ ABC with vertices A (–2, 0), B (0, 2) and C (2, 0) is similar to ∆ DEF with vertices
D (–4, 0), F (4, 0) and E (0, 4).
OR
Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining the points (3, –2) and
(–3, –4).
16. Prove that the opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary
angles at the centre of the circle.
17. In the below figure, two circular flower beds have been shown on two sides of a square lawn
ABCD of side 56 m. If the centre of each circular flower bed is the point of intersection O of the
diagonals of the square lawn, find the sum of the areas of the lawn and the flower beds.
18. A solid sphere of diameter 6 cm is dropped in a right circular cylindrical vessel partly filled with
water. The diameter of the cylindrical vessel is 12 cm. If the sphere is completely submerged in
water, by how much will the level of water rise in the cylindrical vessel?
OR
A well of diameter 3 m is dug 14 m deep. The soil taken out of it is spread evenly all around it
to a width of 5 m to form an embankment. Find the height of the embankment.
cos2 400 cos 2 500 4(cos 700 cos ec 200 )
19. Evaluate:
sin 2 400 sin 2 500 7(tan 50 tan 250 tan 450 tan 650 tan 850 )
OR
1 1 1
Prove that: 1 2 1 2 2 4
.
tan A cot A sin A sin A
20. Draw the graphs of the equations 4 x y 8 0; 2 x 3 y 6 0 . Also determine the vertices of
the triangle formed by the lines and x-axis.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
21. If , are the zeroes of the polynomials f(x) = x2 – 3x + 6, then find the value of
1 1
2 2 2
22. The following table show the marks of 85 students of a class X in a school. Find the modal
marks of the distribution:
Marks(Below) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Number of Students 5 9 17 29 45 60 70 78 83 85
SECTION – D
Questions 23 to 30 carry 4 marks each.
23. Draw a circle of radius of 3 cm. Take two points P and Q on one of its diameters extended on
both sides, each at a distance of 7 cm on opposite sides of its centre. Draw tangents to the circle
from these two points P and Q.
24. From the top of a hill, the angles of depression of two consecutive kilometer stones due east are
found to be 45° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the hill.
25. If the quadratic equation (c2 – ab) x2 – 2 (a2 – bc) x + b2 – ac = 0 in x, has equal roots, then show
that either a = 0 or a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc.
OR
In a rectangular park of dimensions 50 m × 40 m, a rectangular pond is constructed so that the
area of grass strip of uniform width surrounding the pond would be 1184 m2. Find the length
and breadth of the pond.
sec A 1 sec A 1
26. Prove that 2 cos ecA .
sec A 1 sec A 1
27. A child puts one five-rupee coin of her saving in the piggy bank on the first day. She increases
her saving by one five-rupee coin daily. If the piggy bank can hold 190 coins of five rupees in
all, find the number of days she can continue to put the five-rupee coins into it and find the total
money she saved. Write your views on the habit of saving.
28. A solid toy is in the form of a hemisphere surmounted by a right circular cone (see the below
figure). The height of the cone is 2 cm and the diameter of the base is 4 cm. Determine the
volume of the toy. If a right circular cylinder circumscribes the toy, find the difference of the
volumes of the cylinder and the toy. (Take π = 3.14)
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
29. Prove that “In a triangle, if the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other
two sides, then the angle opposite to the first side is a right angle.
OR
Prove that “If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in
distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio”.
30. Following is the age distribution of a group of students. Draw the cumulative frequency curve
less than type and hence obtain the median from the graph.
Age(in years) 4-5 5-6 6-7 7-8 8-9 9-10 10-11 11-12 12-13 13-14 14-15 15-16
No. of students 36 42 52 60 68 84 96 82 66 48 50 16
OR
Find the missing frequencies in the following frequency distribution table, if the total frequency
is 100 and median is 32.
Marks 0-10 10-20 20-30 30-40 40-50 50-60
No. of Students 10 x 25 30 y 10
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Module 3 - Intro To PolyhedronDokument27 SeitenModule 3 - Intro To PolyhedronNoel S. De Juan Jr.100% (1)
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDokument6 SeitenSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterPia Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Grade 7Dokument63 SeitenGrade 7PEDRO MARISCAL NHSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018 3Dokument5 SeitenMaths Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018 3Írfäñ MøhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2018 2Dokument5 SeitenMaths Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2018 2Írfäñ MøhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Dokument5 SeitenMaths Class X Sample Paper 03 For Board Exam 2018 4Írfäñ MøhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Sample Question Paper 1Dokument5 SeitenMaths Sample Question Paper 1Írfäñ MøhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Teesri Kasam NotesDokument10 Seiten10th Teesri Kasam NotesÍrfäñ MøhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDokument4 SeitenDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJemuel FraneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number Theory: With Question/Answer AnimationsDokument32 SeitenNumber Theory: With Question/Answer AnimationsSuleeman CabdulaahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unit CircleDokument4 SeitenThe Unit CircleNuur AiisyaahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 Most Likely Questions May 2018 (327 Marks)Dokument76 SeitenPaper 2 Most Likely Questions May 2018 (327 Marks)ishaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 2014 (IAL) MS - C4 EdexcelDokument24 SeitenJanuary 2014 (IAL) MS - C4 EdexcelMomen YasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths O Level Red SpotDokument77 SeitenMaths O Level Red Spotingrid ruvingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cal Reform 2Dokument237 SeitenCal Reform 2abbas zaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number Series For IBPS PO MainsDokument38 SeitenNumber Series For IBPS PO Mainsonlylofisongs22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Sheet - Fall FinalDokument4 SeitenReview Sheet - Fall FinalmykirbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2.4 Functions As Real World Models PDFDokument29 SeitenChapter 2.4 Functions As Real World Models PDFjiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Challenge Quiz: 1. EmailDokument11 SeitenMathematics Challenge Quiz: 1. Emailmangalam manjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRE Math Numeric Entry Practice TestDokument12 SeitenGRE Math Numeric Entry Practice Testpramodkb_cusat100% (2)
- Add Math FuctionDokument21 SeitenAdd Math Fuctionkamil muhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7 Maths Annual Exam 2023-2024 (The Srijan School, Model Town, New Delhi)Dokument3 SeitenClass 7 Maths Annual Exam 2023-2024 (The Srijan School, Model Town, New Delhi)manishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To Secondary Maths Activity Booklet AnswersDokument19 SeitenWelcome To Secondary Maths Activity Booklet AnswersBernardNgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anurag Singh Bcom (H) Business Mathematics Assignment (Fimt)Dokument10 SeitenAnurag Singh Bcom (H) Business Mathematics Assignment (Fimt)Anurag SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Cal - Learner - S Packet Q1 Week 1Dokument17 SeitenPre Cal - Learner - S Packet Q1 Week 1Gladys Angela ValdemoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Test No. 4Dokument4 SeitenAlgebra Test No. 4AMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linx JCSF Mathematics (Problems and Elements)Dokument38 SeitenLinx JCSF Mathematics (Problems and Elements)Kim Howard CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Service Greatest Common Factor 2018 PDFDokument3 SeitenCivil Service Greatest Common Factor 2018 PDFIrhyn Deniña BancasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q - Trigo Ph.2 1Dokument2 SeitenQ - Trigo Ph.2 1Rohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HC Sba Unit1 Test 2 (2013)Dokument2 SeitenHC Sba Unit1 Test 2 (2013)kkkkllllNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire in My FutureDokument34 SeitenFire in My FuturePradipta DashNoch keine Bewertungen
- n5 Rel Homework BookletDokument15 Seitenn5 Rel Homework Bookletapi-298592212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Map ProjectDokument5 SeitenGeometry Map Projectapi-327138530100% (1)
- 1.1 Significant Figures (Part 1)Dokument2 Seiten1.1 Significant Figures (Part 1)Dhanraj RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 The Indefinite Integral 1Dokument10 Seiten1 The Indefinite Integral 1Treesya EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen