Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
PR1
Hochgeladen von
John ReyOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PR1
Hochgeladen von
John ReyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Data-Gathering Instrument Example 1:
The Intrapersonal and Interpersonal Competencies of School Managers:
Basic for the Formulation of the Human Relation Intervention Program
(Cristobal, 2003)
The data gathered to answer the specific questions were drawn by sets of questionnaires, documents, division reports and other
school records.
The questionnaires used were composed of two sets. The first set was for the school managers, it is composed of three parts. First
part was to find out the personal profile, attainment, work values, home atmosphere, home management styles, and level of
religiosity, hobbies, human virtues, health condition and involvement in civic and religious organization. Second set assessed the
awards received by the teachers and students national, regional and district level.
Part 3 assessed the Intrapersonal competency of school principals, which is subdivided into six major variables: Locus of Control,
Machiavellianism, self-esteem, self monitoring, risk taking and type “A” personality. These variables were based from the book of
Stephen Robbin (1996), entitled Organizational Behaviors. Each variable has a minimum of ten indicators.
Part B of the third part assessed the Interpersonal competencies of school managers which is composed of five variables: role in
management, learning and training, understanding and motivating teachers and positive attitude and problem solving techniques.
These variables were based from the book of Ernesto Appodaca (1997) entitled, Human Relations for Supervisors. This was
composed 60 items, 10 per variable.
A parallel questionnaire was designed for the secondary school teachers.
Data-Gathering Instrument Example 2:
Extent of Participation of Nursing Students in Infection Control Practices at the Neo-Natal Intensive Care Unit
(NICU):
Basis for Enhanced RLE Supervisory Program (Quiazon 2007)
The study used a questionnaire as the primary researched instrument. Padua (2001) defined a questionnaire as a list of planned
written questions related to a particular topic with space provided for the responses to each questions. The questionnaire is commonly
used in normative survey and in the measurement of attitudes and opinions (Good, 1991).
In other words, the questionnaire is the best instrument that can supply the necessary information to complete a research study as it
is commonly used in behavioural research in social research (Calderon & Gonzales, 2005).
Two sets of questionnaires were prepared: the first part is for the student respondents and another for the clinical instructors. The
student’s questionnaire included the respondents profile namely: age, gender, civil status and types of hospital assigned. The
second part deals with infection control practices in the NICU. The CI’s questionnaire was similar with student-respondents except
that this not contains the questions on the profile of the student-respondents.
Data-Gathering Instrument Example 3:
Management by Culture of Kapampangan School Managers in Selected Universities
And Colleges (dela Cruz, 2002)
The study called for the development and use of instruments to measure the application of Management by Cultures. These
instruments are the following:
a. Personal Data Sheet- includes the personal attributes of the respondents and other relevant information vital to the study. It
includes the following variables: age, sex, civil status, highest educational attainment, managerial position and experiences and
duration of stay in Pampanga.
b. Questionnaire
1. Managerial Practices- to determine the respondent, a five point scale was used from greater extent, great extent, less
extent, lesser extent and does not practice.
2. Kapampangan Managerial Traits- this includes the top ten desirable and ten undesirable managerial traits.
c. Interview Schedule – this method was used to check (to verify) the accuracy of the impression the researcher gained through
observations.
Data-Gathering Instrument Example 4:
Correlates of English Performance of Second Year Students in Selected High School Congressional District II,
Nueva Ecija (Valenton, 2009)
The main instrument in data-gathering is the survey questionnaire. For the student questionnaire it was divided into three parts,
namely, social demographic characteristics, home factors, and school factors.
The first part of the students’ questionnaire was designed to elicit information on students’ age, sex, parents’ highest educational
attainment, parents’ occupation, monthly family income, extra-curricular activities, favorite subject, and ambition in life and study
habits. The second part was intended to inquire about their home factors in terms of availability of reading materials, language and
dialect spoken and exposure to media and technology. Finally, the last part gathered data on school factors about the exact count of
the school’s instructional and non-instructional resources.
On the other hand, the teachers’ questionnaire was divided into three parts, namely, professional competencies, teaching methods,
and school facilities. The first part comprised a checklist and questions regarding teacher’s age, sex, highest degree earned in a field
of specialization, present position, length of teaching experience, and English related seminar/trainings. The second part was an
evaluation checklist concerning their perceptions on the frequency and effectiveness of teaching methods and approaches they use in
teaching English.
Secondary data like the NAT results, average English grades, and inventory of school resources and facilities were obtained with
permission from official records at the school office.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
1. The most frequently used data collection methods are: individual interviews, group interviews, observations, and
questionnaires.
2. Individual Interviews are conversations designed to obtain specific information. Interview schedules are the tools used for
interviewing. It can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
3. Group Interviews are discussion among several respondents simultaneously. Topic guides are used to facilitate group
interviews and keep them on track while giving respondents room to discuss.
4. Observation is an immersive method of collecting information or data on natural phenomena or behaviour as it is occurs.
Observation guides or checklists are instrument used to facilitate observations.
5. Surveys or questionnaires are the most commonly used instrument in research, and are made of a list of planned written
questions or statements of a particular topic. They are both a method and an instrument, and can be structured or
unstructured.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1-4 ChapterDokument27 Seiten1-4 Chaptercynthia rosalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Buying Behavior of Filipino Teens Related To Facial Care ProductsDokument24 SeitenA Study On Buying Behavior of Filipino Teens Related To Facial Care ProductsRomeo ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Established by Philippine Commission On?Dokument4 SeitenEstablished by Philippine Commission On?Ces Bilog100% (1)
- Foreign StudiesDokument2 SeitenForeign StudiesNebea AdorableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uloe AnswersDokument5 SeitenUloe AnswersJohn Mark MadrazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 IPDokument5 SeitenChapter 3 IPLhorene Hope DueñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity-3-1 Salosagcol, Leobert Yancy GDokument5 SeitenActivity-3-1 Salosagcol, Leobert Yancy GLeobert Yancy SalosagcolNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE 15 Activity 1Dokument5 SeitenGE 15 Activity 1Alyssa Paula Altaya100% (1)
- How Is Technology A Mode of Revealing?Dokument3 SeitenHow Is Technology A Mode of Revealing?Adam CuencaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mindoro State University - Bongabong Campus Labasan, Bongabong, Oriental MindoroDokument58 SeitenMindoro State University - Bongabong Campus Labasan, Bongabong, Oriental MindoroJohn Leo R. Española,Noch keine Bewertungen
- A& P NotesDokument178 SeitenA& P NotesJSeashark100% (3)
- Research PaperDokument10 SeitenResearch Paperapi-242346804Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01 What Is Social PsychologyDokument29 SeitenChapter 01 What Is Social PsychologyLarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling Techniques2Dokument5 SeitenSampling Techniques2MLeidyyy100% (1)
- Cell AnalogyDokument13 SeitenCell AnalogySideTrip SideKickNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUAMETDokument5 SeitenQUAMETedniel maratas100% (2)
- Chapter Vi: Biodiversity and The Healthy Society: Do This!!Dokument3 SeitenChapter Vi: Biodiversity and The Healthy Society: Do This!!joel bentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci Ed Laboratory Activity 6Dokument3 SeitenSci Ed Laboratory Activity 6Norsaidin TungkagNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMW Module 9 (Dona Vie) PDFDokument4 SeitenMMW Module 9 (Dona Vie) PDFRey RoseteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics Quiz 1Dokument2 SeitenEthics Quiz 1Beng BebangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Setting CMTDokument3 SeitenTime Setting CMTJohn Emerald GoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurements in The Laboratory - Procedures, Post-Lab, ConclusionDokument3 SeitenMeasurements in The Laboratory - Procedures, Post-Lab, ConclusionJasmine YiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Exercise11: Topic Learning OutcomeDokument2 SeitenLaboratory Exercise11: Topic Learning OutcomeMyrah Gail BadangayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo Over All HandoutsDokument20 SeitenPhilo Over All HandoutsJan Hidalgo Laroya100% (1)
- Milo Andrea Mariz C Chapter 2 Act 123Dokument5 SeitenMilo Andrea Mariz C Chapter 2 Act 123Precious WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhilosophyDokument37 SeitenPhilosophyLA LA LA LA LA MiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuthenicsDokument10 SeitenEuthenicsAlfred Roi BallatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 6-7: Let'S Check Activity No. 4Dokument4 SeitenWEEK 6-7: Let'S Check Activity No. 4kryzel agravanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Purpose of Art AppreciationDokument3 SeitenThe Purpose of Art AppreciationdfghrtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branches of Science and Sub SciencesDokument5 SeitenBranches of Science and Sub SciencesSha BtstaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey Questionnaire v2Dokument1 SeiteSurvey Questionnaire v2Aixa Dee Madialis100% (1)
- Voting and Apportionment (CH 14) : DensonDokument30 SeitenVoting and Apportionment (CH 14) : DensonJun MagduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CATEGORICAL PROPOSITIONS ExercisesDokument1 SeiteCATEGORICAL PROPOSITIONS ExercisesMhild GandawaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges Encountered by CDWs FinalDokument47 SeitenChallenges Encountered by CDWs FinalMelody MangsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Hilaria M. Barsabal Cagayan State UniversityDokument35 SeitenProf. Hilaria M. Barsabal Cagayan State UniversityDarlene Andres PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possible Questions For Final DefenseDokument9 SeitenPossible Questions For Final DefenseJayson AliaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir BongDokument64 SeitenSir Bongarlene bobadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 4.1 Puzzle ProteinDokument2 SeitenActivity No. 4.1 Puzzle Proteinjalil alnifar0% (1)
- Syllabus PhiloDokument5 SeitenSyllabus PhiloMark Anthony Fabrigas Catubay67% (3)
- Ge 2 Week 1-2Dokument31 SeitenGe 2 Week 1-2Zendy DagasdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medenilla Midterm ExamDokument5 SeitenMedenilla Midterm ExamJulius GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sts Module 8Dokument5 SeitenSts Module 8RONYL JHON PENUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Sci LM U1 - M1Dokument20 Seiten8 Sci LM U1 - M1JoeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAMAWODokument6 SeitenMAMAWOjcb buraga100% (1)
- Ethical Dilemmas of STSDokument2 SeitenEthical Dilemmas of STSGwyneth CartallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 13: Reflex Arc and Reflexes: Learning Outcomes of The Lab ExercisesDokument6 SeitenLab 13: Reflex Arc and Reflexes: Learning Outcomes of The Lab ExercisesNellyWataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Translating Algebraic Phrases 001Dokument2 SeitenAlgebra Translating Algebraic Phrases 001crazyomnislash25% (4)
- Ethics Meaning and ScopeDokument49 SeitenEthics Meaning and ScopeQueenie Rose BacolodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity #8 GE5Dokument4 SeitenActivity #8 GE5Joy MagbutongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDokument12 SeitenRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsCG AmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individualization PrincipleDokument12 SeitenIndividualization PrincipleAqib AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - Exercise 1.1Dokument1 SeiteModule 3 - Exercise 1.1jbsbarretto100% (1)
- Ano ULOdDokument4 SeitenAno ULOdyes yesnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Sosyolohiya-English-Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDokument4 SeitenSyllabus Sosyolohiya-English-Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesCriselda Palomo CoronadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Immersion Requisite of NSTP: An: Lesson TitleDokument3 SeitenCommunity Immersion Requisite of NSTP: An: Lesson TitleAljun Penullar VillafaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HistoryDokument13 SeitenHistoryJeric Valdez MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry - Meaning & ScopeDokument2 SeitenBiochemistry - Meaning & ScopeBasudev GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Central TendencyDokument2 SeitenMeasures of Central TendencyDexusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter IiiDokument4 SeitenChapter IiiHerriet AbelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 MetholoDokument7 SeitenChapter 3 MetholoPoornimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 WordsDokument1 Seite10 WordsJohn ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frederick Taylor and The Scientific ManagementDokument85 SeitenFrederick Taylor and The Scientific ManagementJohn ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Relation Approach Theory G 2Dokument29 SeitenHuman Relation Approach Theory G 2John ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument7 SeitenModule 4John ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender-Based Violence: Action Sheet 4Dokument10 SeitenGender-Based Violence: Action Sheet 4Jadid HoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Gec 13-Contemporary WorldDokument8 SeitenModule in Gec 13-Contemporary WorldJohn ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeheDokument6 SeitenHeheJohn ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical ResearchDokument2 SeitenPractical ResearchJohn ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeheDokument6 SeitenHeheJohn ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Related StudyDokument32 SeitenRelated StudyMayeh Cañada BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- F & B AssignmentDokument8 SeitenF & B AssignmentJacky LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical ResearchDokument7 SeitenPractical ResearchMailene Mae Sion Alarcon67% (6)
- MSDS Buffer Solution PH 4.0Dokument5 SeitenMSDS Buffer Solution PH 4.0Ardhy LazuardyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013-01-28 203445 International Fault Codes Eges350 DTCDokument8 Seiten2013-01-28 203445 International Fault Codes Eges350 DTCVeterano del CaminoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wine TourismDokument9 SeitenWine Tourismyarashovanilufar1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Poster-Shading PaperDokument1 SeitePoster-Shading PaperOsama AljenabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOAVAILABILITY AND BIOEQUIVALANCE STUDIES Final - PPTX'Dokument32 SeitenBIOAVAILABILITY AND BIOEQUIVALANCE STUDIES Final - PPTX'Md TayfuzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- str-w6754 Ds enDokument8 Seitenstr-w6754 Ds enAdah BumbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- .CLP Delta - DVP-ES2 - EX2 - SS2 - SA2 - SX2 - SE&TP-Program - O - EN - 20130222 EDITADODokument782 Seiten.CLP Delta - DVP-ES2 - EX2 - SS2 - SA2 - SX2 - SE&TP-Program - O - EN - 20130222 EDITADOMarcelo JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source:: APJMR-Socio-Economic-Impact-of-Business-Establishments - PDF (Lpubatangas - Edu.ph)Dokument2 SeitenSource:: APJMR-Socio-Economic-Impact-of-Business-Establishments - PDF (Lpubatangas - Edu.ph)Ian EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of The Internet in EducationDokument23 SeitenUse of The Internet in EducationAlbert BelirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum and Minimum PDFDokument3 SeitenMaximum and Minimum PDFChai Usajai UsajaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothDokument111 SeitenRankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothphysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring-Engineering-And-Technology-Grade-6 1Dokument5 SeitenExploring-Engineering-And-Technology-Grade-6 1api-349870595Noch keine Bewertungen
- Man Bni PNT XXX 105 Z015 I17 Dok 886160 03 000Dokument36 SeitenMan Bni PNT XXX 105 Z015 I17 Dok 886160 03 000Eozz JaorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Ombudsman 58Dokument4 SeitenBanking Ombudsman 58Sahil GauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- The University of The West Indies: Application For First Degree, Associate Degree, Diploma and Certificate ProgrammesDokument5 SeitenThe University of The West Indies: Application For First Degree, Associate Degree, Diploma and Certificate ProgrammesDavid Adeyinka RamgobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCD Course List in Sem 2.2020 (FTF or Online) (Updated 02 July 2020)Dokument2 SeitenSCD Course List in Sem 2.2020 (FTF or Online) (Updated 02 July 2020)Nguyễn Hồng AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDokument8 SeitenWWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDestiny EasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blackberry: Terms of Use Find Out MoreDokument21 SeitenBlackberry: Terms of Use Find Out MoreSonu SarswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management SlidesDokument150 SeitenStrategic Management SlidesIqra BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
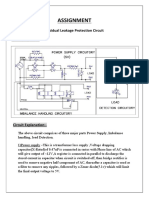
- Assignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramDokument2 SeitenAssignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramShivam ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline ENTR401 - Second Sem 2022 - 2023Dokument6 SeitenCourse Outline ENTR401 - Second Sem 2022 - 2023mahdi khunaiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- KIA SONET BookingDocketDokument7 SeitenKIA SONET BookingDocketRajesh ThulasiramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Governance Operating Model: Structure Oversight Responsibilities Talent and Culture Infrastructu REDokument6 SeitenGovernance Operating Model: Structure Oversight Responsibilities Talent and Culture Infrastructu REBob SolísNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic One ProcurementDokument35 SeitenTopic One ProcurementSaid Sabri KibwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D E S C R I P T I O N: Acknowledgement Receipt For EquipmentDokument2 SeitenD E S C R I P T I O N: Acknowledgement Receipt For EquipmentTindusNiobetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Short Survey On Memory Based RLDokument18 SeitenA Short Survey On Memory Based RLcnt dvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installing Surge Protective Devices With NEC Article 240 and Feeder Tap RuleDokument2 SeitenInstalling Surge Protective Devices With NEC Article 240 and Feeder Tap RuleJonathan Valverde RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM EFATEX Rev D2 3 1 2018 PDFDokument20 SeitenSM EFATEX Rev D2 3 1 2018 PDFGuilhermePlacidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Over BrahmaputraDokument38 SeitenBridge Over BrahmaputraRahul DevNoch keine Bewertungen
- KK AggarwalDokument412 SeitenKK AggarwalEnrico Miguel AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen