Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
FortiOS Handbook 5.2 Trang 970 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Dautuso4.0Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FortiOS Handbook 5.2 Trang 970 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Dautuso4.0Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
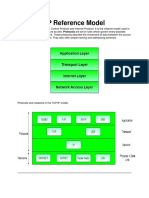
Firewall objects Chapter 9 - Firewall
Depending on which of these protocol categories is choose another set of specifications will can also be defined.
TCP/UDP/SCTP
This is the most commonly used service protocol category. Once this category has been selected the other
available options to choose are an address, either IP or FQDN, and the protocol and port number.
The protocol will be TCP, UDP or SCTP.
ICMP or ICMP6
When ICMP or ICMP6 is chosen the available options are the ICMP Type and its code.
IP
When IP is the chosen protocol type the addition option is the Protocol Number.
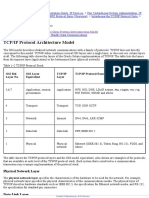
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the core or fundamental protocols of the Internet. It is part of the
Transport Layer of the OSI Model. It is designed to provide reliable delivery of data from a program on one device
on the network or Internet to another program on another device on the network or Internet. TCP achieves its
reliability because it is a connection based protocol. TCP is stream-oriented. It transports streams of data reliably
and in order.
TCP establishes a prior connection link between the hosts before sending data. This is often referred to as the
handshake. Once the link is established the protocol uses checks to verify that the data transmitted. If an error
check fails the data is retransmitted. This makes sure that the data is getting to the destination error free and in
the correct order so that it can be put back together into a form that is identical to the way they were sent.
TCP is configured more for reliability than for speed and because of this TCP will likely be slower than a
connectionless protocol such as UDP. This is why TCP is generally not used for real time applications such as
voice communication or online gaming.
Some of the applications that use TCP are:
l World Wide Web (HTTP and HTTPS)
l Email (SMTP, POP3, IMAP4)
l Remote administration (RDP)
l File transfer (FTP)
UDP
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) like TCP is one of the core protocols of the Internet and part of the Transport
Layer of the OSI Model. UDP is designed more for speed than reliability and is generally used for different
applications than TCP. UDP sends messages, referred to as datagrams across the network or Internet to other
hosts without establishing a prior communication link. In other words, there is no handshake.
UDP is an unreliable service as the datagrams can arrive out of order, duplicated or go missing without any
mechanism to verify them. UDP works on the assumption that any error checking is done by the application or is
not necessary for the function of the application. This way it avoids the overhead that is required to verify the
integrity of the data.
970 FortiOS Handbook for FortiOS 5.2.12
Fortinet Technologies Inc.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TCPIP ModelDokument9 SeitenTCPIP Modelroysayanccp05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is Unit2Dokument63 SeitenIs Unit2002Aadika BhatiaIT1Noch keine Bewertungen
- TCP IP Protocol Explanation 1 (03.01.2024)Dokument5 SeitenTCP IP Protocol Explanation 1 (03.01.2024)aloishp36Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communication and Internet TechnologiesDokument9 SeitenCommunication and Internet Technologiesmuhammad hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 StudyDokument7 Seiten1 StudyAman GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tcp/Ip: How The TCP/IP Protocol Stack Maps To The OSI Model OSI Layers TCP/IP ProtocolsDokument5 SeitenTcp/Ip: How The TCP/IP Protocol Stack Maps To The OSI Model OSI Layers TCP/IP Protocolsajithcoumar351Noch keine Bewertungen
- Key Architectural PrinciplesDokument9 SeitenKey Architectural Principlesablog165Noch keine Bewertungen
- ProtocolsDokument24 SeitenProtocolsToni-ann WillisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2Dokument146 SeitenWeek 2gojan39660Noch keine Bewertungen
- WT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebDokument20 SeitenWT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebSACHIDANAND CHATURVEDINoch keine Bewertungen
- IT309 TaniaDokument6 SeitenIT309 TaniaTania IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- D. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolDokument7 SeitenD. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolEcho greenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet WorkingDokument3 SeitenInternet WorkingGoutami ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMPN 370 - Handout 3.5 Protocol Suites - TCP/IP: Application LayerDokument5 SeitenCMPN 370 - Handout 3.5 Protocol Suites - TCP/IP: Application LayerShania LallNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCN TCP AssignmentDokument11 SeitenDCN TCP Assignmenttalwandi bhindranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2.1.1 Video Explanation - Transport Layer ProtocolsDokument1 Seite5.2.1.1 Video Explanation - Transport Layer ProtocolsLucky ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acn May 2018Dokument45 SeitenAcn May 2018shraddha_mundadadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisVon EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Ethical HackingDokument8 SeitenIntroduction of Ethical HackingNair ShreejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application LayerDokument12 SeitenApplication LayerJunjun BedrijoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techtarget TCPIPDokument3 SeitenTechtarget TCPIPyashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bscit Sem 6 Iot Material Unit 4Dokument11 SeitenBscit Sem 6 Iot Material Unit 4paratevedant1403Noch keine Bewertungen
- TCP vs. Udp: October 2015Dokument10 SeitenTCP vs. Udp: October 2015Kashif ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP/IP Protocol: A Suitable Communication Network: Omusun Yerima, Iroegbu ChibuisiDokument4 SeitenTCP/IP Protocol: A Suitable Communication Network: Omusun Yerima, Iroegbu ChibuisierpublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9IP ModelDokument4 Seiten9IP ModelJawad SandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The TCP/IP Reference ModelDokument4 SeitenThe TCP/IP Reference ModelJawad SandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9IP Model-1Dokument4 Seiten9IP Model-1Jawad SandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- How TCP-IP WorksDokument29 SeitenHow TCP-IP WorksJames GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 (CSS)Dokument9 SeitenUnit 5 (CSS)hasansyedamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between TCP and UDP PDFDokument8 SeitenDifference Between TCP and UDP PDFosama425Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jaringan Komputer Dasar - 9Dokument41 SeitenJaringan Komputer Dasar - 9Catur IswahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)Dokument10 SeitenTransmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)Sanjoy Basak100% (1)
- TCP - IP PROTOCOL AND LayersDokument3 SeitenTCP - IP PROTOCOL AND Layerssimon sylvesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interfaces: Medium Access ControlDokument6 SeitenInterfaces: Medium Access ControlnaziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of TCPDokument9 SeitenComponents of TCPisidhantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networks: Network Protocols: Defines Rules and Conventions For Communication Between Network DevicesDokument5 SeitenNetworks: Network Protocols: Defines Rules and Conventions For Communication Between Network DevicesSadia MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR Lab5 Vlas MihaiDokument17 SeitenPR Lab5 Vlas MihaiAlexey DarievNoch keine Bewertungen
- IncredibleDokument2 SeitenIncredibleDemixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDokument3 SeitenOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network ProtocolsDokument6 SeitenNetwork ProtocolsAnne Margaret EscobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is TCP (03.01.2024)Dokument4 SeitenWhat Is TCP (03.01.2024)aloishp36Noch keine Bewertungen
- UDPDokument7 SeitenUDPMit Thakore100% (1)
- TCP IpDokument8 SeitenTCP IpGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP IP TrbshootDokument20 SeitenTCP IP TrbshootsybaritzNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Commerce UNIT VDokument10 SeitenE-Commerce UNIT Vsri vallideviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Over View of TCPDokument15 SeitenOver View of TCPMkt RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI ModelDokument5 SeitenOSI ModelCustomer CUstomerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linux Unit 5Dokument22 SeitenLinux Unit 5Adeefa AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Network Address TranslationDokument10 SeitenWhat Is Network Address Translationchalie tarekegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal JainDokument13 SeitenSubmitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal Jainpooja guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between The Communication and TransmissionDokument33 SeitenDifference Between The Communication and TransmissionvineetsudevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Server Management L1Dokument7 SeitenInternet Server Management L1chamunorwa100% (1)
- Chapter - 4.1: Tcp/Ip and UrlDokument7 SeitenChapter - 4.1: Tcp/Ip and UrlNandgulabDeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCPIP OSI ModelDokument3 SeitenTCPIP OSI ModelAdarsh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- NETWORKPROGRAMMINGNP8UNITSDokument139 SeitenNETWORKPROGRAMMINGNP8UNITSYogeswaran NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic-User Datagram Protocol (Udp) : Computer Networks - PresentationDokument11 SeitenTopic-User Datagram Protocol (Udp) : Computer Networks - PresentationMihir PesswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions and Answers - ProtocolsDokument4 SeitenQuestions and Answers - ProtocolsVishal PaupiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelDokument5 SeitenTCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelGreen ZoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Need To ReadDokument4 SeitenNeed To ReadKoMin KhantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyVon EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Started With DropboxDokument10 SeitenGet Started With DropboxYan HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Preferred Architecture For Enterprise Collaboration 11.6 Lab v1Dokument187 SeitenCisco Preferred Architecture For Enterprise Collaboration 11.6 Lab v1Dautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Get Started With DropboxDokument10 SeitenGet Started With DropboxYan HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Started With DropboxDokument10 SeitenGet Started With DropboxYan HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- PON DesignDokument57 SeitenPON Design0509035100% (2)
- Read MeDokument1 SeiteRead MeS AdipranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eve Cook Book 1.0Dokument197 SeitenEve Cook Book 1.0msamuelfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Router PerformanceDokument4 SeitenRouter Performancegunm64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Using Two Isps For Redundant Internet ConnectionsDokument5 SeitenUsing Two Isps For Redundant Internet ConnectionsmegarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPRI V 7 0 2015-10-09Dokument128 SeitenCPRI V 7 0 2015-10-09M Xubair Yousaf XaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fotigate MulticastDokument3 SeitenFotigate MulticastDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fotigate MulticastDokument3 SeitenFotigate MulticastDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multicast Forwarding: Sparse ModeDokument1 SeiteMulticast Forwarding: Sparse ModeDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- SsssssDokument1 SeiteSsssssDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Denial of Service (DoS) ProtectionDokument2 SeitenDenial of Service (DoS) ProtectionDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Connecting To The CLIDokument1 SeiteConnecting To The CLIDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- FortiGate 1500D Datasheet PDFDokument6 SeitenFortiGate 1500D Datasheet PDFDautuso4.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fortios Handbook 525 PDFDokument2.853 SeitenFortios Handbook 525 PDFJuan Manuel AlmironNoch keine Bewertungen
- I360 V11.1 Sequence DiagramsDokument132 SeitenI360 V11.1 Sequence Diagramsroutemans100% (1)
- CSC 413: Introduction To Interactive Multimedia Universiti Teknologi Mara (Melaka)Dokument2 SeitenCSC 413: Introduction To Interactive Multimedia Universiti Teknologi Mara (Melaka)nur izzatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GGFHHHRDokument7 SeitenGGFHHHRroberto72080201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assign Security in Fusion ERPDokument18 SeitenAssign Security in Fusion ERPKaviraj MathNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSL602MEF0Dokument51 SeitenTSL602MEF0AlphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (.Docx) Microsoft SharePoint Online For Office 365 Administering and Configuring For The CloudDokument267 Seiten(.Docx) Microsoft SharePoint Online For Office 365 Administering and Configuring For The CloudUmang Soni100% (1)
- ITE 50 Chapter5Dokument61 SeitenITE 50 Chapter5cralemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msi Gx623 User Manual 84c2fd3Dokument86 SeitenMsi Gx623 User Manual 84c2fd3cris_43Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zeevee HDb2380 BrochureDokument3 SeitenZeevee HDb2380 BrochureDavid WardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworksDokument190 SeitenComputer NetworksSourav MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Az America 01Dokument23 SeitenAz America 01morza21Noch keine Bewertungen
- ABAP Proxy - ABAP Server ProxiesDokument14 SeitenABAP Proxy - ABAP Server ProxiesFelipe LeiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lo2 Prepare-InstallerDokument24 SeitenLo2 Prepare-Installermeaww the catNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC2652R Errata, Application Notes, User Guides, White Papers, BlogsDokument3 SeitenCC2652R Errata, Application Notes, User Guides, White Papers, BlogsGustavoAdolfoJimenezGomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Programming - CS609 HandoutsDokument338 SeitenSystem Programming - CS609 HandoutsKing Faisal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onkyo tx-sr876 SMDokument23 SeitenOnkyo tx-sr876 SMMoto MottoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discovery of Ranking Fraud ForDokument10 SeitenDiscovery of Ranking Fraud ForAnubhav GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ensoniq Floppy Diskette FormatDokument13 SeitenEnsoniq Floppy Diskette FormatneoluxNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATE Application Enhancement Tool Overview 1Dokument8 SeitenATE Application Enhancement Tool Overview 1georgetodorov23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Installationguide SpectraproDokument38 SeitenInstallationguide SpectrapromikipitestiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biss KeysDokument13 SeitenBiss KeysrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3par HP Sa Training: Virtual Copy: November 1, 2010Dokument13 Seiten3par HP Sa Training: Virtual Copy: November 1, 2010purush_123Noch keine Bewertungen
- DVD R120 SamsungDokument95 SeitenDVD R120 SamsungPerla Guadalupe Jara JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT+ Command SmsDokument8 SeitenAT+ Command SmsRuangvit SriumphaiviwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting The Most Out of Microsoft Edge: IT Showcase Productivity GuideDokument12 SeitenGetting The Most Out of Microsoft Edge: IT Showcase Productivity GuideBianca StefanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSE SkillsAssessment-Student Exam Ccna 2Dokument20 SeitenRSE SkillsAssessment-Student Exam Ccna 2Alex Morales Navas66% (38)
- GE PPS Getting StartedDokument62 SeitenGE PPS Getting StartedLeonardPrayitnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Elective Focus For Batch 2018 Onwards Ver3 (08jun2018)Dokument2 SeitenCS Elective Focus For Batch 2018 Onwards Ver3 (08jun2018)calcium nitrateNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIX 7.2 Installation, Quick Start Guide PDFDokument4 SeitenAIX 7.2 Installation, Quick Start Guide PDFjohn kookNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM74LS90/DM74LS93 Decade and Binary Counters: General DescriptionDokument10 SeitenDM74LS90/DM74LS93 Decade and Binary Counters: General DescriptionThế giới điện tửNoch keine Bewertungen