Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Module 1 - Forces and Motion Long Quiz
Hochgeladen von
Rowena Sta Maria0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
50 Ansichten2 Seiten1. The document is a quiz on forces and motion that covers classifying quantities as vector or scalar, filling in blanks about motion concepts, defining variables in equations of motion, and identifying Newton's three laws of motion.
2. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
3. Newton's second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, stating that acceleration is produced when a net force acts on an object and the greater the net force the greater the acceleration.
Originalbeschreibung:
Test on laws of motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1. The document is a quiz on forces and motion that covers classifying quantities as vector or scalar, filling in blanks about motion concepts, defining variables in equations of motion, and identifying Newton's three laws of motion.
2. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
3. Newton's second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, stating that acceleration is produced when a net force acts on an object and the greater the net force the greater the acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
50 Ansichten2 SeitenModule 1 - Forces and Motion Long Quiz
Hochgeladen von
Rowena Sta Maria1. The document is a quiz on forces and motion that covers classifying quantities as vector or scalar, filling in blanks about motion concepts, defining variables in equations of motion, and identifying Newton's three laws of motion.
2. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
3. Newton's second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, stating that acceleration is produced when a net force acts on an object and the greater the net force the greater the acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Module 1: Forces and Motion - Long Quiz
A. Classify the following as vector or scalar quantity.
1. 5 m/s2 6. 5 m/s east
2. 120 kg 7. 50 N downward
3. 24 hrs 8. 5 m/s
0
4. 37 Celsius 9. 5 m/s2 left
5. 10 km 10. 100 km south of west
B. Fill in the blanks. Supply the missing words.
1. A ____________ quantity has both magnitude and direction
2. A __________quantity has magnitude only.
3. The movement of an object is called ________.
4. We know that an object moves when there is ____________ in its position.
5. The motion in a straight line is called _____.
6. ________explains why an object tends to keep moving forward or to remain at rest unless acted upon by force.
7. __________is the force which opposes the movement of one object over another object.
8. ________ is the amount of matter in an object.
9. Distance-over-time describes a quantity called ____________.
10. Mass multiplied to acceleration describes a quantity called ________________
11. The unit of force is _______________.
C. What does each of the variables mean?
12. F = _________________
13. m = _________________
14. a = _________________
D. What unit of measurement must be used with each variable?
15. F = ___________________
16. m = __________________
17. a = ___________________
E. Complete the statement below;
NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION
Newton’s first law of motion is also known as the LAW OF _____(18)__________. Newton’s first law says that an object that IS NOT
MOVING, or is at ____(19)____ will stay at ____(20)_____ and an object that IS MOVING will keep moving with constant
V__(21)____ which means at the same S____(22)___ and in the same D____(23)_ UNLESS an O__ (24)____ force acts on that
object.
NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION
Newton’s second law of motion is also known as the LAW OF A________(25)______Newton’s second law says that when an
U___( 26)_____ force is applied to a M___(27)___(OBJECT), it causes it to A_______(28)_
The greater the force that is applied, the G_____(29)___ the acceleration.
The lesser the force that is applied, the L___(30)_____ the acceleration.
If the same force is applied to an object with a large mass, it will have a L_____(31)____ acceleration.
If the same force is applied to an object with a small mass, it will have a G _____(32)___ acceleration.
The equation that is used to solve second law problems is _ (33)________
NEWTON’S THIRD LAW OF MOTION
Newton’s third law of motion is also known as the LAW OF A (34) – R (35)___
Newton’s third law says that every time there is an A____(36)___ force, there is also a R_____(37)______ force that is E____(38)___
in size and acts in the O____(39)______direction.
Newton’s third law states that forces must ALWAYS occur in P____(40)____.
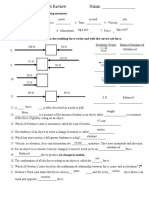
F.Label each of the following images/descriptions below as being examples of 1st, 2nd, or 3rd law.
41. 4 2. 43. 44. 45.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Activity 1 Set ADokument3 SeitenActivity 1 Set ARobert obispoNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8-SCIENCE-Q1-Week-2-LAS-1Dokument1 SeiteG8-SCIENCE-Q1-Week-2-LAS-1shalinee.daydayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-8 (1ST Quarterly)Dokument3 SeitenScience-8 (1ST Quarterly)juliusvaldez07201996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion 2Dokument9 SeitenLaws of Motion 2愛.NiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8-Week1-2 WorksheetDokument6 SeitenG8-Week1-2 WorksheetTeacher MelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is P - 3 Laws ReviewDokument5 SeitenIs P - 3 Laws Reviewapi-308247166Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion and Force ConceptsDokument59 SeitenNewton's Laws of Motion and Force ConceptsAndrea Perez92% (24)
- Saman Rizvi - Newton - S Laws WorksheetDokument3 SeitenSaman Rizvi - Newton - S Laws Worksheet45375Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Directions:: (2pts. Each)Dokument2 SeitenGeneral Directions:: (2pts. Each)Sayeeh MaruhomNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1: Module 11, Quarter 1, Week 4Dokument10 SeitenGeneral Physics 1: Module 11, Quarter 1, Week 4xyxycalabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of MotionDokument2 SeitenLaws of MotionJun DulogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 5 Review 7th (2) - 2Dokument4 SeitenTest 5 Review 7th (2) - 2Pranav MaheshwaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz - ForcesDokument2 SeitenQuiz - ForcesmisterbrownerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science Newton's Laws of MotionDokument2 SeitenGrade 8 Science Newton's Laws of MotionJohnRobin AmoguisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton Laws CWDokument1 SeiteNewton Laws CWEthan-Dale BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test+Review+TMD 2Dokument4 SeitenTest+Review+TMD 2Deborah OlofinkuadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Motion Study Guide - Student-SantiagoSerranoBalzaDokument5 SeitenForce and Motion Study Guide - Student-SantiagoSerranoBalzasawgumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical science summative testsDokument2 SeitenPhysical science summative testsMariter PidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDokument6 SeitenName: - Date: - Section: - ScoreMary Luz Dolente EderNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 8 1st PrelimDokument2 SeitenSCIENCE 8 1st Prelimjuliusvaldez07201996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 ScienceDokument2 SeitenGrade 8 ScienceBart PorcadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY 1 - Module 4Dokument25 SeitenPHY 1 - Module 4mtalquisola2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 1:: Class X Chapter 1 - ForceDokument38 SeitenSolution 1:: Class X Chapter 1 - ForceVansh AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Motion ModuleDokument3 SeitenForces and Motion ModuleBENNY CALLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyDokument7 SeitenSci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyCherry Beth PagenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics1 PDFDokument25 SeitenPhysics1 PDFClarisse TadeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science - Unit 2 - Force and Motion TestDokument7 SeitenScience - Unit 2 - Force and Motion Testlinhtranthuy0601Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1Dokument2 SeitenGeneral Physics 1Ali KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Module 1Dokument58 SeitenUnit 1 Module 1Justine Keith De CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons 2nd Law Practice ProblemsDokument3 SeitenNewtons 2nd Law Practice ProblemsJehmmaRosalesCarpisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Test FORCEDokument5 SeitenChapter Test FORCEArnulfo Villasfer SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenUnit 1 Study Guideapi-88097510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adv. Physics Revised1st QDokument33 SeitenAdv. Physics Revised1st QYlena AllejeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collinear ForcesDokument4 SeitenCollinear ForcesFernando BrandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 6 6th Grade CH 6Dokument2 SeitenExam 6 6th Grade CH 6Maranyelis ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math physics quiz reviewDokument2 SeitenMath physics quiz reviewMohammad Bilal AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion and Forces Test Review With AnswersDokument3 SeitenMotion and Forces Test Review With AnswersMary Love Juanico33% (3)
- Grade-4 Q3 SCIENCEDokument3 SeitenGrade-4 Q3 SCIENCEjoel paolo ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Motion Guided NotesDokument13 SeitenForces and Motion Guided NotesJaelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion QuizDokument1 SeiteNewton's Laws of Motion QuizElma SolibagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative in Science 8Dokument3 SeitenSummative in Science 8Melvin Gayta FailagaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Q1 Week 1Dokument12 SeitenScience 8 Q1 Week 1Alyssa Gomez100% (1)
- Summative QuizDokument1 SeiteSummative Quizapi-253346895Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Newton's Law of Motion-Law of InteractionDokument13 SeitenScience: Newton's Law of Motion-Law of InteractionFe Pakias GullodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 - Elevate Science - WorkbookDokument38 SeitenGrade 3 - Elevate Science - WorkbookMahmoud SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Learner: - Date: - Grade/Section: - TeacherDokument12 SeitenName of Learner: - Date: - Grade/Section: - TeacherPox DulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDokument8 SeitenName: - Date: - Section: - ScoreMary Luz Dolente EderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 Week 2 Module 4 Uniform Circular Motion - 102603Dokument22 SeitenQ1 Week 2 Module 4 Uniform Circular Motion - 102603Chay PalaypayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonus 2 PhyDokument3 SeitenBonus 2 PhyAirin RosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- QI Module 2 Week 2Dokument3 SeitenQI Module 2 Week 2Angel May RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write TRUE If The Statement Is Correct and FALSE If It Is Not Then Write The Correct Answer of The Following Statement. (2pts.)Dokument2 SeitenWrite TRUE If The Statement Is Correct and FALSE If It Is Not Then Write The Correct Answer of The Following Statement. (2pts.)divine grace s. nejar100% (1)
- MELC 34: Describe horizontal and vertical motions of projectilesDokument5 SeitenMELC 34: Describe horizontal and vertical motions of projectilesBlinDspotted FinaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.4 SecstudygdDokument4 Seiten7.4 SecstudygdLila AlwaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 - Science - CompleteDokument19 SeitenGrade 10 - Science - CompleteLucille Gacutan AramburoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and MotionDokument2 SeitenForce and MotionChaela ApplebyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE MOMENTUMDokument23 SeitenSCIENCE MOMENTUMRhyan Zero-four BaluyutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet-Third-Law-of-MotionDokument3 SeitenWorksheet-Third-Law-of-MotionJhey EscasinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: The Periodic Table of ElementsDokument5 SeitenUnit 1: The Periodic Table of ElementsRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Final Test in Science VII NAME: - GRADE/ SECTION: - SCORE: - Parent's Signature: - Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDokument3 SeitenSemi-Final Test in Science VII NAME: - GRADE/ SECTION: - SCORE: - Parent's Signature: - Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE EXAMDokument38 SeitenSCIENCE EXAMJennie Ann GalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3RD Quarter Exam Grade 7 ScienceDokument2 Seiten3RD Quarter Exam Grade 7 Sciencegerald83% (6)
- Budget of Work in Science: Quarter: 3rd Grade Level: Grade 7 School: M.B. Asistio Sr. High School - MainDokument2 SeitenBudget of Work in Science: Quarter: 3rd Grade Level: Grade 7 School: M.B. Asistio Sr. High School - MainRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Matter G7 Q1.W1.D2Dokument4 SeitenDLL Matter G7 Q1.W1.D2Rowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Matter G7 Q1.W4 5.D1Dokument6 SeitenDLL Matter G7 Q1.W4 5.D1Rowena Sta Maria50% (2)
- DLL Matter G7 Q1.W4 5.D1Dokument6 SeitenDLL Matter G7 Q1.W4 5.D1Rowena Sta Maria50% (2)
- DLL-MATTER-G7-Q1.W2-3.D3 and D7Dokument7 SeitenDLL-MATTER-G7-Q1.W2-3.D3 and D7Rowena Sta Maria100% (1)
- DLL MatterDokument5 SeitenDLL MatterRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Weekly Home Learning Plan Source: Appendix D. MEMORANDUM DM-CI-2020-00162, From DIOSDADO M. SAN ANTONIO UndersecretaryDokument10 SeitenSample Weekly Home Learning Plan Source: Appendix D. MEMORANDUM DM-CI-2020-00162, From DIOSDADO M. SAN ANTONIO UndersecretaryBrielle LagascaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classifying Elements in the Periodic TableDokument2 SeitenClassifying Elements in the Periodic TableRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiographic Factors)Dokument2 SeitenPhysiographic Factors)Rowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3RD QUARTER MELCsDokument8 Seiten3RD QUARTER MELCsRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Q1 W1 LC1 Fair TestDokument12 SeitenDLL Q1 W1 LC1 Fair TestRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd QT Summative Test 3 CELLDokument1 Seite2nd QT Summative Test 3 CELLRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M. B. A S - H S (M) : Sistio R IGH Chool AINDokument4 SeitenM. B. A S - H S (M) : Sistio R IGH Chool AINRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd QT Summative Test 2 LEVELSDokument2 Seiten2nd QT Summative Test 2 LEVELSRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Lesson Plan: Rubrics On Assessing The Performance of Group ActivityDokument1 SeiteScience Lesson Plan: Rubrics On Assessing The Performance of Group ActivityRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome Back Grade 7: Armenia, Cambodia, China, Cyprus and PhilippinesDokument13 SeitenWelcome Back Grade 7: Armenia, Cambodia, China, Cyprus and PhilippinesRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caloocan City School Highlights Importance of Ecosystem BalanceDokument4 SeitenCaloocan City School Highlights Importance of Ecosystem BalanceRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Date:: WWW - Bbc.co - Uk/ni/learning/pfocusDokument6 SeitenDate Date:: WWW - Bbc.co - Uk/ni/learning/pfocusRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M. B. A S - H S (M) : Sistio R IGH Chool AINDokument5 SeitenM. B. A S - H S (M) : Sistio R IGH Chool AINRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP56 - 7es-3q-AccelerationDokument1 SeiteDLP56 - 7es-3q-AccelerationRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd QT Summative Test 3 CELLDokument1 Seite2nd QT Summative Test 3 CELLRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M. B. A S - H S (M) : Sistio R IGH Chool AINDokument5 SeitenM. B. A S - H S (M) : Sistio R IGH Chool AINRowena Sta Maria100% (2)
- 2nd QT Summative Test 2 LEVELSDokument1 Seite2nd QT Summative Test 2 LEVELSRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio ModularDokument7 SeitenPortfolio ModularRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Nobook W1Dokument7 SeitenScience Nobook W1Rowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What I Learned (Generalization) : Elements and Compounds ElementsDokument2 SeitenWhat I Learned (Generalization) : Elements and Compounds ElementsRowena Sta MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Science EnvironmentDokument28 SeitenGeneral Science EnvironmentHamza MujahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- P198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0Dokument10 SeitenP198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0cm08909Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPT ProcedureDokument3 SeitenDPT ProcedureAmit HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Da Memorandum Order No 6 Implementation Guidelines of The Kadiwa Ni Ani at Kita ProjectDokument17 SeitenDa Memorandum Order No 6 Implementation Guidelines of The Kadiwa Ni Ani at Kita ProjectMildred VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria Epidemiology & PreventionDokument92 SeitenMalaria Epidemiology & PreventionritikaritikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ross 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFDokument16 SeitenRoss 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFJORGE GALVISNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsDokument108 SeitenGeneral Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsharleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte Turns On The Solar Cell: 2009 Project SummaryDokument1 SeiteElectrolyte Turns On The Solar Cell: 2009 Project SummaryAshu SarasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical PropertiesDokument4 SeitenPhysical PropertiesKolliparaDeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- EBARA FS513CT-R0E pump manualDokument6 SeitenEBARA FS513CT-R0E pump manualApriliyanto Rahadi PradanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Report 52Dokument196 SeitenWeekly Report 52Erceanu DanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19174the Rise of Industrial Big Data WP Gft834Dokument6 Seiten19174the Rise of Industrial Big Data WP Gft834em01803257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Design and Optimization MethodsDokument38 SeitenExperimental Design and Optimization MethodssudalaiyandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodDokument18 SeitenMacroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodMartin GutovskieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ego7 Manual enDokument76 SeitenEgo7 Manual ensullivanj69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGDokument53 SeitenInstrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGxilef84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anorexia NervosaDokument2 SeitenAnorexia NervosaDhea Mae MadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar 360 KWDokument6 SeitenCaterpillar 360 KWAde WawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Ph Induction MotorDokument246 Seiten3-Ph Induction MotorAn00pgadzillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Painting, DrawingDokument22 SeitenPainting, DrawingMithilesh_Kuma_7083Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryDokument12 SeitenChapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryLaurindo Paulo Ribeiro TchinhamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aminet 110 en PDFDokument17 SeitenAminet 110 en PDFWahid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Semester All Courses-100Dokument194 Seiten2nd Semester All Courses-100Ejiade PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastercam 8.1 Beta 4: New Verification Engine in Beta 4! Sub-Programs Post ChangesDokument48 SeitenMastercam 8.1 Beta 4: New Verification Engine in Beta 4! Sub-Programs Post ChangesSaul Saldana LoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRP104 Course Outline: Introduction to Key Topics in Human GeographyDokument26 SeitenGRP104 Course Outline: Introduction to Key Topics in Human GeographyKelvin WatkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreDokument8 SeitenWire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreQuynh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DA1 Learning - Ans KeyDokument4 SeitenDA1 Learning - Ans KeyDolon DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPRESSED AIR VALIDATION SYSTEMDokument13 SeitenCOMPRESSED AIR VALIDATION SYSTEMbpharmba100% (5)
- User Manual HDL 30 ADokument36 SeitenUser Manual HDL 30 AAgung KurniandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- M700-70 Series Programming Manual (M-Type) - IB1500072-F (ENG)Dokument601 SeitenM700-70 Series Programming Manual (M-Type) - IB1500072-F (ENG)Mert SertNoch keine Bewertungen