Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
5th Sem & 6th Sem Syllabus Kuk
Hochgeladen von
vivekOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
5th Sem & 6th Sem Syllabus Kuk
Hochgeladen von
vivekCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
B. Tech.
(Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17
MARKS DISTRIBUTION
(ACCORDING TO AUTONOMY)
FOR ALL THEORY COURSES: -
1. On semester evaluation of all theory courses total: 100 marks
Distribution
I. Mid semester exam: 20 marks
II. Mid semester exam: 20 marks
Continues Evaluation Test (CET): 20 marks
Attendance: 20 marks
Teacher‟s assessment: 20 marks
2) End semester (final examination) of all theory courses
Total: 100 marks
3) Total of on semester + end semester evaluation
is of : 200 marks
4) To pass a theory course student should obtain
Minimum: - 40 marks in on semester evaluation.
: - 35 marks in end semester evaluation.
Total: - 80 marks out of 200.
Criterion for passing and failing the theory course: -
a) If students fails in on semester evaluation despite passing in aggregate one will have to
repeat that course.
b) If student pass in on semester evaluation but fails in end semester exam he/ she will be
permitted to appear in supplementary examination.
c) If student is pass both in on semester evaluation and end semester evaluation but fails in
total then he/ she would have to appear in supplementary exam.
d) If attendance in a course is below 75%, the student shall not be permitted to appear in the
End- Semester Examination.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 1
FOR ALL PRACTICAL (LABORATORY) COURSES: -
I) On semester evaluation of all practical (laboratory) courses would be of total: 120 marks.
Distribution
Performance of class practical: 60 marks
Reports of practical: 60 marks
II) End semester evaluation (final lab exam + oral or viva test)
Total: 80 marks
III) Total of on semester evaluation final lab examination + end semester evaluation is of : 200 marks
IV) To pass a lab course student should obtain
Minimum: - 48 marks in on semester evaluation.
28 marks in end semester evaluation.
Total- 80 marks out of -200
Criterion for passing and failing the lab course is just like theory course.
CALCULATION OF SEMESTER GRADE POINT AVERAGE: -
Semester grade point average (SGPA) is the weighted average of the grade for the subjects
registered in a Semester and is computed as follows:
C G i i
SGPA i
C i
i
Ci denotes the Credits (or Units) assigned to the ith subject and Gi denotes the Grade Point
Equivalent to the Letter Grade obtained for the ith subject.
Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) is the weighted average of the grades of the subjects
for the registered in the semester.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 2
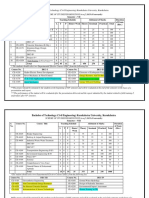
N. C. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, ISRANA
SCHEME OF STUDIES AND EXAMINATION
B.Tech. –CIVIL ENGINEERING
3rd Year (Semester–V) 2015
Teaching Schedule Contact Credits
Hours
Sr. No. Subject Code. Subject BOS
L T P
1 CE-351 Structural Analysis-III CIVIL 3 2 - 5 5
2 CE-352 Design of Concrete Structures-I CIVIL 3 2 - 5 5
3 CE-353 Hydrology CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
4 CE-354 Geotechnology-I CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
5 CE-355 Project Planning & CIVIL 3 - - 3 3
Management
6 CE-356 Engineering Geology CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
7 CE-35P1 Structural Mechanics-II Lab CIVIL - - 2 2 1
8 CE-35P2 Concrete Lab CIVIL - - 2 2 1
9 CE-35P3 Geotechnology Lab CIVIL - - 2 2 1
TOTAL 18 7 6 31 28
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 3
N. C. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, ISRANA
SCHEME OF STUDIES AND EXAMINATION
B.Tech. –CIVIL ENGINEERING
3rd Year (Semester–VI) 2015
Teaching Schedule Contact Credits
Hours
Sr. No. Course no. Subject BOS
L T P
1 CE-361 Design Of Steel Structure-II CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
2 CE-362 Irrigation Engineering CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
3 CE-363 Geotechnology-II CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
4 CE-364 Transportation Engineering-I CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
5 CE-365 Water supply & Treatment CIVIL 3 1 - 4 4
6 Departmental Elective CIVIL 3 - - 3 3
7 CE-366 General Proficiency & Fitness CIVIL - - - - 1
8 CE-36P1 Transportation Engineering Lab CIVIL - - 2 2 1
9 CE-36P2 Environmental Engineering Lab CIVIL - - 2 2 1
Applications of Numerical
10 CE-36P3 CIVIL - - 3 3 2
Methods Lab
11 SSAA-360 Soft Skills and Analytical Ability CIVIL 1 - 2 3 2
Total 19 5 9 33 30
List of Departmental Electives
CE-36E1 Rock Mechanics
CE-36E2 Water Resources & System Engineering
CE-36E3 Remote Sensing & GIS
CE-36E4 Disaster Management
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 4
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS-III
CE-351
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 2 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Influence Lines: Introduction, influence lines for three hinged and two hinged arches, load position
for Max. S.F. and B.M. at a section in the span.
Influence Line for Statically Indeterminate Beams: Muller-Breslau Principle, I.L. for B.M. &
S.F. for continuous Beams.
UNIT-II
Fixed Arches: Expression for H and B.M. at a section, Elastic centre.
Rolling Loads: Introduction, Single concentrated load uniformly distributed load longer than span,
shorter than span, two point loads, several point loads, Max. B.M. and S.F. Absolute, Max. B.M.
UNIT-III
Kani’s Method: Analysis of continuous beams and simple frames, analysis of frames with
different column lengths and end conditions of the bottom storey.
UNIT-IV
Approximate Analysis of Frames: For vertical loads, (ii) for lateral loads by Portal method &
Cantilever method.
Matrix Methods: Introduction, Stiffness Coefficients, Flexibility Coefficients, Development of
flexibility & stiffness matrices for plane frame, Global axis and local axis, analysis of plane frame,
pin jointed and rigid jointed.
Books:
1. Advanced Structural Analysis – AK Jain, Nem Chand & Bros., Roorkee.
2. Structural Analysis – A Unified Approach, D.S. Prakash Rao, University Press, Hyderabad.
3. Structural Analysis – A Unified Classical & Matrix Approach, Ghali & A.M. Neville,
Chapman & Hall, London.
4. Theory of Structures Vol I & II B. C Punmia, Ashok Kumar Jain & Arun K. Jain, Laxmi
Publication, New delhi.
5. Theory of Structures Vol II S. P. Gupta, G. S. Pandit & Rajesh Gupta, Tata McGraw Hill.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 5
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
DESIGN OF CONCRETE STRUCTURES-I
CE-352
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 2 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Elementary Treatment of Concrete Technology: Physical requirements of cement, aggregate,
admixture and reinforcement, Strength and durability, shrinkage and creep. Design of concrete
mixes, Acceptability criterion, I.S. Specifications.
Design Philosophies in Reinforced Concrete: Working stress and limit state methods, limit state
v/s working stress method, building code, normal distribution curve, characteristic strength and
characteristics loads, design values, Partial safety factors and factored loads, stress-strain
relationship for concrete and steel.
UNIT-II
Working Stress Method: Basic assumptions, permissible stresses in concrete and steel, design of
singly and doubly reinforced rectangular and flanged beams in flexure, steel beam theory, inverted
flanged beams, design examples.
Limit State Method: Basic assumptions, analysis and design of singly and doubly reinforced
rectangular flanged beams, minimum and maximum reinforcement requirement, design examples.
UNIT-III
Analysis and Design of Sections in Shear Bond and Torsion: Diagonal tension, shear
reinforcement, development length, anchorage and flexural bond, torsional, stiffness, equivalent
shear, torsional reinforcement, design examples.
Columns and Footings: Effective length, minimum eccentricity, short columns under axial
compression, Uniaxial and biaxial bending, slender columns, isolated and wall footings, design
examples.
Serviceability Limit State: Control of deflection, cracking, slenderness and vibrations, deflection
and moment relationship for limiting values of span to depth, limit state of crack width, design
examples.
UNIT-IV
Concrete Reinforcement and detailing: Requirements of good detailing cover to reinforcement,
spacing of reinforcement, reinforcement splicing, anchoring reinforcing bars in flexure and shear,
curtailment of reinforcement.
One-way and Two-ways Slabs: General considerations, design of one way and two-ways slabs for
distributed and concentrated loads, Non-rectangular slabs, opening in slabs, design examples.
Retaining Walls: Classification, forces on retaining walls, design criteria, stability requirements,
proportioning of cantilever retaining walls, counterfort retaining walls, criteria for design of
counterforts, design examples.
Books:
1. Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures by P.Dayaratnam, Oxford & IBM Pub., N.Delhi
2. Reinforced Concrete – Limit State Design, AK Jain, Nem Chand & Bros., Roorkee.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 6
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
HYDROLOGY
CE-353
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Introduction: Hydrologic cycle, scope and application of hydrology to engineering problems,
drainage basins and its characteristics, stream geometry hypsometric curves.
Precipitation: Forms and types of precipitation, characteristics of precipitation in India,
measurement of precipitation, recording and non recording raingages, raingage station, raingage
network, estimation of missing data, presentation of rainfall data, mean precipitation, depth – area –
duration relationship, frequency of point rainfall, intensity-duration-frequency curves, probable
max. precipitation.
UNIT-II
Evaporation & Transpiration: Process, evaporimeters and empirical relationships, analytical
method reservoir evaporation and methods of its control transpiration, evapotranspiration and its
measurement, Penman‟s equation and potential evapotranspiration.
Infiltration: Infiltration process, initial loss, infiltration capacity and measurement of infiltration,
infiltration indices.
UNIT-III
Runoff: Factor affecting run-off, estimation of runoff, rainfall-run off relationships, measurement
of stage-staff gauge, wire gauge, automatic stage recorder and stage hydrograph, measurement of
velocity-current meters, floats, area velocity method, moving boat and slope area method,
electromagnetic, ultra-sonic and dilution methods of stream flow measurement, stage discharge
relationship.
Hydrograph: Discharge hydrograph, components and factors affecting shape of hydrograph,
effective rainfall, unit hydrograph and its derivation, unit hydrograph of different durations, use and
limitations of UH, triangular UH, Snyder‟s synthetic UH, floods, rational methods, empirical
formulae, UH method, flood frequency methods, Gumbel‟s method, graphical method, design
flood.
UNIT-IV
Ground Water: Occurrence, types of aquifers, compressibility of aquifers, water table and its
effects on fluctuations, wells and springs, movement of ground water, Darcy‟s law, permeability
and its determination, porosity, specific yield and specific retention, storage coefficient,
transmissibility.
Well Hydraulics: Steady state flow to well in unconfined and confined aquifers.
Books:
1. Hydrology by H.M. Raghunath
2. Elementary Hydrology by V.P. Singh
3. Hydrology for Engineers by Linsely, Kohler, Paulhus
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 7
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
GEOTECHNOLOGY-I
CE-354
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the whole
syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Sub-surface Exploration: Purpose, stages in soil exploration, depth and lateral extent of exploration,
guidelines for various types of structures, ground water observations, excavation and boring methods, soil
sampling and disturbance, major types of samplers, sounding methods-SCPT, DCPT, SPT and
interpretation, geophysical methods, pressure-meter test, exploration logs.
Drainage & Dewatering: Introduction, ditches and sumps, well point systems, shallow well system, deep
well drainage, vacuum method, Electro-osmosis, consolidation by sand piles.
UNIT-II
Shallow Foundations-I: Design criteria for structural safety of foundation (i) location of footing, (ii) shear
failure criterion, (iii) settlement criterion, ultimate bearing capacity, modes of shear failure, Rankine‟s
analysis Tergazi‟s theory, Skempton‟s formula, effect of fluctuation of G.W.T., effect of eccentricity on
bearing capacity, inclined load, I.S. Code recommendations, factors affecting bearing capacity, methods of
improving bearing capacity.
Shallow Foundations-II: Various causes of settlement of foundation, allowable bearing pressure based on
settlement, settlement calculation, elastic and consolidation settlement, allowable settlement according to
I.S. Code. Plate load test and its interpretation, bearing capacity from penetration tests, design bearing
capacity.
Shallow Foundation-III: Situation suitable for the shallow foundations, types of shallow foundations and
their relative merits, depth of foundation, footing on slopes, uplift of footings, conventional procedure of
proportioning of footings, combined footings, raft foundations, bearing capacity of raft in sands and clays,
various methods of designing rafts, floating foundations.
UNIT-III
Pile Foundations-I: Introduction, necessity of pile foundations, classification of piles, load capacity, static
analysis, analysis of pile capacity in sands and clays, dynamic analysis, pile load tests, negative skin friction,
batter piles, lateral load capacity, uplift capacity of single pile, under-reamed pile.
Pile Foundations-II: Group action in piles, pile spacing, pile group capacity, stress on lower strata,
settlement analysis, design of pile caps, negative skin friction of pile group, uplift resistance of pile group,
lateral resistance, batter pile group.
UNIT-IV
Drilled Piers and Caisson Foundations: Drilled piers-types, uses, bearing capacity, settlement,
construction procedure. Caissons-Types, bearing capacity and settlement, construction procedure well
foundation-shapes, depth of well foundations, components, factors affecting well foundation design lateral
stability, construction procedure, sinking of wells, rectification of tilts and shifts, recommended values of
tilts & shifts as per I.S. 3955.
Books:
1. Basic and Applied Soil Mechanics by Gopal Ranjan & ASR Rao, New Age Int. (P) Ltd.
2. Analysis and Design of Sub-Structures by Swamisaran, IBH & Oxford.
3. Principles of Foundation Engineering by B.M.Das, PWS Kent, Boston.
4. Foundation Analysis & Design by J.E. Bowles, McGraw-Hills
5. Foundation Design by Teng, Prentice Hall, India
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 8
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
PROJECT PLANNING &MANAGEMENT
CE-355
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 0 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Construction Management: Significance, objectives and functions of construction management
types of constructions, resources for construction industry, stages for construction, construction
team, engineering drawings.
Construction Contracts & Specifications: Introduction, types of contracts, contract document,
specifications important conditions of contract, arbitration.
UNIT-II
Construction Planning: Introduction, work breakdown structure, stages in planning-pre-tender
stages, contract stage, scheduling by bar charts, preparations of material, equipment, labour and
finance schedule, limitation of bar charts, milestone charts.
Construction Organization: Principles of Organization, communication, leadership and human
relations, types of Organizations, Organization for construction firm, site organization, temporary
services, job layout.
UNIT-III
Network Techniques in Construction Management-I-CPM: Introduction, network techniques,
work break down, classification of activities, rules for developing networks, network development-
logic of network, allocation of time to various activities, Fulkerson‟s rule for numbering events,
network analysis, determination of project schedules, critical path, ladder construction, float in
activities, shared float, updating, resources allocation, resources smoothing and resources levelling.
Network Techniques in Construction Management-II-PERT: Probability concept in network,
optimistic time, pessimistic time, most likely time, lapsed time, deviation, variance, standard
deviation, slack critical path, probability of achieving completion time, central limit theorem.
UNIT-IV
Cost-Time Analysis: Cost versus time, direct cost, indirect cost, total project cost and optimum
duration, contracting the network for cost optimization, steps in time cost optimization, illustrative
examples.
Inspection & Quality Control: Introduction, principles of inspection, enforcement of
specifications, stages in inspection and quality control, testing of structures, statistical analysis.
Books:
1. Construction planning & Management by P.S. Gehlot & B.M.Dhir, Wiley Eastern Ltd.
2. PERT & CPM – Principles & Applications by L.S.Srinath. Affiliated East-west Press (P)
Ltd.
3. Project Planning & Control with PERT & CPM by B.C. Punmia & K.K. Khandelwal,
Lakshmi Pub. Delhi
4. Construction Management & Planning by B.Sengupta & H.Guha, Tata McGraw-Hills.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 9
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY
NC-CE-356
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Introduction: Definition, object, scope and sub division of geology, geology around us. The
interior of the earth. Importance of geology in Civil Engineering projects.
Physical Geology: The external and internal geological forced causing changes weathering and
erosion of the surface of the earth. Geological work of ice, water and winds. Soil profile and its
importance. Earthquakes and volcanoes.
UNIT-II
Mineralogy and Petrology: Definition and mineral and rocks. Classification of important rock
forming minerals, simple description based on physical properties of minerals. Rocks of earth
surface, classification of rocks. Mineral composition, Texture, structure and origin of ligneous,
Sedimentary and Metamorphic rocks. Aims and principles of stratigraphy. Standard geological /
stratigraphical time scale with its sub-division and a short description based on engineering uses of
formation of India.
Structural Geology:
Forms and structures of rocks. Bedding plane and outcrops Dip and Strike. Elementary ideas about
fold, fault, joint and unconformity and recognition on outcrops. Importance of geological structures
in Civil Engineering projects.
UNIT-III
Applied Geology: Hydrogeology, water table, springs and Artesian well, aquifers, ground water in
engineering projects. Artificial recharge of ground water, Elementary ideas of geological
investigations. Remote sensing techniques for geological and hydrological survey and
investigation. Uses of geological maps and interpretation of data, geological reports.
Suitability and Stability of foundation Sites and Abutments: Geological condition and their
influence on the selection, location, type and design of dams, reservoirs, tunnels, highways, bridges
etc. Landslides and Hill-slope stability.
UNIT-IV
Improvement of Foundation Rocks: Precaution and treatment against faults, joints and ground
water, retaining walls and other precautions. Geology and Environment of Earth.
Note: The physical study of rock samples and minerals may be performed in the tutorials.
Books:
1. A Text Book of Geology by P.K. Mukherjee
2. Physical and General Geology by S.K. Garg
3. Engineering and General Geology by Prabin Singh
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 10
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
STRUCTURAL MECHANICS-II LAB
CE-35P1
P On Semester Evaluation: 120 Marks
2 End Semester Evaluation: 80 Marks
1) Experiment on a two-hinged arch for horizontal thrust & influence line for Horizontal thrust.
2) Experimental and analytical study of a 3-bar pin-jointed Truss.
3) Experimental and analytical study of deflections for unsymmetrical bending of a Cantilever
beam.
4) Begg‟s deformeter-verification of Muller Breslau principle.
5) Experimental and analytical study of an elastically coupled beam.
6) Sway in portal frames-demonstration.
7) To study the cable geometry and statics for different loading conditions.
8) To plot stress-strain curve for concrete.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 11
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
CONCRETE LAB
CE-35P2
P On Semester Evaluation: 120 Marks
2 End Semester Evaluation: 80 Marks
Tests on Cement:
1) Standard consistency of cement using Vicat‟s apparatus.
2) Fineness of cement by Sieve analysis and Blaine‟s air permeability method.
3) Soundness of cement by Le-Chatelier‟s apparatus.
4) Setting time of cement, initial and final.
5) Compressive strength of cement.
6) Measurement of specific gravity of cement.
7) Measurement of Heat of Hydration of cement.
Tests on Aggregate:
1) Moisture content and bulking of fine aggregate.
2) Fineness modulus of coarse and fine aggregates.
Tests on Concrete:
1) Workability of cement concrete by (a) Slump Test, (b) Compaction factor test, (c) Flow
table test.
2) Compressive strength of concrete by (a) Cube test, (b) Cylinder test
3) Indirect tensile strength of concrete – split cylinder test.
4) Modulus of rupture of Concrete by flexure test
5) Bond strength between steel bar and concrete by pull-out test
6) Non-destructive testing of concrete
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 12
5th Semester (Civil Engineering)
GEOTECHNOLOGY LAB
CE-35P3
P On Semester Evaluation: 120 Marks
2 End Semester Evaluation: 80 Marks
1) Grain Size Analysis-Hydrometer method.
2) Shrinkage Limit Determination.
3) Relative Density of Granular Soils.
4) Consolidated Drained (CD) Triaxial Test.
5) Consolidated Undrained (CU) Triaxial Test with Pore Water Pressure measurement.
6) Consolidation Test.
7) Undisturbed Sampling.
8) Standard Penetration Test.
9) Dynamic Cone Penetration Test.
10) Model Plate Load Test.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 13
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES-II
CE-361
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Elementary Plastic Analysis and Design: Introduction, Scope of plastic analysis, ultimate load
carrying capacity of tension members and compression members, flexural members, shape factor,
mechanisms, plastic collapse, analysis, plastic analysis applied to steel beams and simple portal
frames and design.
UNIT-II
Design of Water Tanks: Introduction, permissible stresses, design of circular, rectangular and
pressed steel tanks including staging.
Design of Steel Stacks: Introduction, various loads to be considered for the design of steel stacks,
design of steel stacks including foundation.
UNIT-III
Towers: Transmission line towers, microwave towers, Design loads, classification, design
procedure and specification.
Cold Formed Sections: Introduction and brief description of various types of cold formed
sections, local buckling, concepts of effective width and effective sections, elements with stiffeners,
design of compression and bending elements.
UNIT-IV
Industrial Buildings:
Loads, general arrangement and stability, design considerations, design of purloins, design of roof
trusses, industrial building frames, bracing and stepped columns.
Books:
1. Design of Steel Structures, A.S. Arya & J.L.Ajmani, Nem Chand & Bros. Roorkee.
2. Design of Steel Structures, P.Dayaratnam, Wheeler Pub. Allahabad.
3. Design of Steel Structures, Gaylord & Gaylord, McGraw-Hill, New York / International
Students Edn., Toyo Kogakusha, Tokyo.
4. IS:800-2000, Indian Standard Code of Practice for General Construction in Steel.
5. Design Of steel structures By N. Subramanyan, Oxford University Press.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 14
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
IRRIGATION ENGINEERING
CE-362
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT –I
Water Requirement of Crops: Types and Methods of irrigation, duty and Delta relationship,
Factors affecting duty, Irrigation efficient, Consumptive use and its determination, Soil moisture –
irrigation relationship , Depth and frequency of irrigation.Canal Irrigation: Canal alignment, canal
losses, Estimation of design discharge of a canal Hydraulics of alluvial channels, Types and
economics of lining, Water logging – effects, cause, remedial measure, land drainage, Design of
title drains.
UNIT – II
Design of Hydraulic Structure: Types, consideration in design, Causes of failure of hydraulic
structure founded on previous foundation, Bligh creep theory and khosla seepage theory. Dams and
Spillways : Types, design
UNIT – III
Canal Head works : Layout and parts of diversion head works, location, Design of weir and
barrage , canal head regulator, River training for canal head works, sediment control in canals.
Canal Regulation Works: Canal falls necessity, location types and classification of falls,
Roughening measures for energy dissipation, cistern element, Design of glacis fall. Cross regulators
and distributor‟s head regulator; Canal escape, Meeting flumes
UNIT – IV
Outlets: Canal outlets requirement of a good outlet, Types, Criteria for judging the performance of
outlets, Design principle of open flume outlet and A.P.M outlet.
Cross Drainage Works: Need, Types, Selection of suitable CD work , design of transitions for
canal waterways, uplifts pressure on bottom floor CD works.
Text/Reference Books:
1. Irrigation, Water Resources and Water Power Engg. by P.N.Modi.
2. Fundamentals on Irrigation Engg. by Bharat Singh.
3. Irrigation Engg. & Hydraulic Structures by S.K. Garg.
4. Irrigation Engg. by S.K. Sharma.
5. Irrigation – Theory & Practice by A.M. Michael.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 15
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
GEOTECHNOLOGY-II
CE-363
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Earth Dams:Introduction, types of sections, earth dam foundations, causes of failure and criteria
for safe design, control of seepage through the embankment, control of seepage through the
foundation, drainage of foundations, criterion for filter design. Introduction to rock fill dams.
Stability of Slopes:Causes of failure, factors of safety, stability analysis of slopes-total stress
analysis, effective stress analysis, stability of infinite slopes types of failures of finite slopes,
analysis of finite slopes-mass procedure, method of slices, effect of pore pressure, Fellinius method
to locate center of most critical slip circle, friction circle method, Tayler‟s stability number, slope
stability of earth dam during steady seepage, during sudden draw down and during and at the end of
construction.
UNIT-II
Braced Cuts: Depth of unsupported vertical cut, sheeting and bracing for deep excavation,
movements associated with sheeting and bracing, modes of failure of braced cuts, pressure
distribution behind sheeting.
Cofferdams: Introduction, types of cofferdams, design and lateral stability of braced cofferdams,
design data for Cellular cofferdams, stability analysis of cellular cofferdams on soil and rock, inter-
lock stresses.
UNIT-III
Cantilever Sheet Piles:Purpose of sheet piles, cantilever sheet piles, depth of embedment in
granular soils-rigorous method, simplified procedure, cantilever sheet pile, penetrating clay and
limiting height of wall.
Anchored Bulkheads:Methods of design, free earth support method in cohesionless and cohesive
soils, fixed earth support method in cohesionless soils-Blum‟s equivalent beam method.
UNIT-IV
Soil stabilization:Soil improvement, shallow compaction, mechanical treatment, use of
admixtures, lime stabilization, cement stabilization, lime fly ash stabilization, dynamic compaction
and consolidation, Bituminous stabilization, chemical stabilization, pre-compression, lime pile and
column, stone column, grouting, reinforced earth.
Basics of Machine Foundations:Terminology, characteristics elements of a vibratory systems,
analysis of vibratory motions of a single degree freedom system-undamped free vibrations,
undamped forced vibrations, criteria for satisfactory action of a machine foundation, degrees of a
freedom of a block foundation, Barken‟s soils spring constant, Barken‟s method of a determining
natural frequency of a block foundation subjected to vertical oscillations.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 16
Books:
1. Analysis and Design of Foundation and Retaining Structures by S.Prakash, Gopal Rajan &
S.Saran,Sarita Prakashan.
2. Analysis and Design of Sub-Structures by Swami Saran, IBH Oxford.
3. Basic and ASpplied Soil Mechanics by Gopal Rajan and ASR Rao, Newage Int. Pub.
4. Soil dynamic by Shamsher Prakash, McGraw-Hill.
5. Foundaiton Design by Teng, Prentice Hall.
6. Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering by Bharat Singh, Shamsher Prakash, Nem
Chand & Bros., Roorkee.
7. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering by Alam Singh.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 17
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING-I
CE-364
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Introduction: Transportation and its importance. Different modes of transportation. Brief review
of history of road development in India and abroad: Roman, Tresagne, Telford and Macadam
constructions. Road patterns. Classification of roads, Objectives of highway planning, planning
surveys. Saturation system of planning.
Highway Plans, Highway Alignment and Surveys: Main features of 20 years road development
plans in India. Requirements of an ideal highway alignment. Factors affecting alignment. Surveys
for highway alignment.
UNIT-II
Cross Section Elements and Sight Distance Considerations: Cross section elements: friction,
carriageway, formation width land width, camber, IRC recommended values. Types of terrain
Design speed. Sight distance, stopping sight distance, overtaking sight distance, overtaking zones,
intermediate sight distance, sight distance at intersections, head light sight distance, set back
distance. Critical locations for sight distance.
Design of Horizontal and Vertical Alignment: Effects of centrifugal force. Design of
superelevation. Providing superelevation in the field. Radius of circular curves. Extra-Widening.
Type and length of transition curves. Gradient, types, values. Summit curves and valley curves,
their design criterion. Grade compensation on curves.
UNIT-III
Traffic Characteristics and Traffic Surveys: Road user and vehicular characteristics. Traffic
studies such as volume, speed and O & D study. Parking and accident studies. Fundamental
diagram of traffic flow. Level of service. PCU. Capacity for non-urban roads. Causes and
preventive measures for road accidents.
Traffic control Devices: Traffic control devices: signs, signals, markings and islands. Types of
signs. Types of signals. Design of an isolated fixed time signal by IRC method. Intersections at
grade and grade separated intersections. Design of a rotary. Types of grade separated intersections.
UNIT-IV
Highway Materials: Soil and Aggregates: Subgrade soil evaluation: CBR test, plate bearing test.
Desirable properties of aggregates. Various tests, testing procedures and IRC/IS specification for
suitability of aggregates. Proportioning of aggregates for road construction by trial and error and
Routhfuch method.
Bituminous Materials and Bituminous Mixes: Types of bituminous materials: bitumen, tar,
cutback and emulsions, Various test, testing procedures and IRS/IS specifications for suitability of
bituminous materials in road construction. Bituminous mix, desirable properties. Marshall‟ method
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 18
of mix design. Basic concept of use of polymers and rubber modified bitumen in bituminous mixes.
Books:
1. Highway Engg. by S.K. Khanna & C.E.G. Justo, Nem Chand & Bros., Roorkee.
2. Principles of Transportation and Highway Engg. by G.V.Rao, Tata McGraw Hill Pub.,
N.Delhi.
3. Traffic Engg. And Transport Planning by L.R.Kadiyali, Khanna Pub. Delhi.
4. Traffic Engg.by Matson, T.M., Smiith, W.S. and Hurd, P.W. McGraw Hill Book Co., New
York.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 19
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
WATER SUPPLY AND TREATMENT
CE-365
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Water Quantity: Importance and necessity of water supply scheme. Water demands and its
variations. Estimation of total quantity of water requirement. Population forecasting. Quality and
quantity of surface and ground water sources. Selection of a source of water supply. Types of
intakes.
UNIT-II
Water Quality: Impurities in water and their sanitary significance. Physical, chemical and
bacteriological analysis of water. Water quality standards.
UNIT-III
Water Treatment: Objectives, treatment processes and their sequence in conventional treatment
plant, sedimentation – plain and aided with coagulation. Types, features and design aspects. Mixing
basins and Flocculation units. Filtration-mechanism involved, types of filters, slow and rapid sand
filtration units (features and design aspects). Disinfection principles and aeration.
UNIT-IV
Water Distribution: Distribution system – Gravity system, Pumping System, Dual System, Layout
Distribution system – Dead End System, Grid Iron System, Ring System, Radial System, merits
and demerits. Distribution Reservoir-functions & determination of storage capacity.
Modern Methods of disinfection in water treatment / application of Jar Test in WTP
Books:
1. Water Supply and Sewerage: E.W.Steel.
2. Water Supply Engineering: S.R.Kshirsagar.
3. Water Supply Engineering: S.K. Garg.
4. Water Supply Engineering: B.C. Punmia.
5. Manual on Water Supply and Treatment: Ministry of Urban Dev., New Delhi.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 20
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
GENERAL PROFICIENCY & FITNESS
CE-366
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 21
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
TRASPORTATION ENGINEERING -I LAB
CE-36P1
P On Semester Evaluation: 120 Marks
2 End Semester Evaluation: 80 Marks
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS:
1. Aggregate Impact Test.
2. Los-Angeles Abrasion Test on Aggregates.
3. Dorry‟s Abrasion Test on Aggregates.
4. Devel Attrition Test on Aggregates.
5. Crushing Strength Test on Aggregates.
6. Penetration Test on Bitumen.
7. Ductility Test on Bituminous Material.
8. Viscosity Test on Bituminous Material.
9. Softening Point Test on Bitumen.
10. Flash and Fire Point Test on Bitumen.
11. Standard Penetration Test.
12. California Bearing Ration Test (CBR)
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 22
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING-I LAB
CE-36P2
P On Semester Evaluation: 120 Marks
2 End Semester Evaluation: 80 Marks
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS:
1. To determine the pH value of a given sample of water.
2. To determine the turbidity in given water sample.
3. To determine the acidity of given sample of water.
4. To determine the alkalinity of given sample of water.
5. To determine temporary and permanent hardness in a given water sample.
6. To determine the chlorine dose required for a given water sample.
7. To determine total suspended dissolved settable solids in a water sample.
8. To determine Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of given water Sample.
9. To determine Chemical Oxygen Demand COD of given water Sample.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 23
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
APPLICATION OF NUMERICAL METHODS LAB
CE-36P3
P On Semester Evaluation: 120 Marks
3 End Semester Evaluation: 80 Marks
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS:
1. Computation of roots of a polynomial using Bisection method.
2. Computation of roots of a polynomial using Newton-Raphson method
3. Solution of linear simultaneous equation using Gauss Elimination / Gauss Jordan /
Triangulation factorization method.
4. Solution of system of non-linear equation using fixed point / Newton Raphson / modified
Newton-Raphson method.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 24
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
SOFT SKILLS AND ANALYTICAL ABILITY
SSAA-360
L T P On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
1 0 2 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
UNIT I 5 Weeks (5L+0T+10P)
QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE
Arithmetic/ Algebraic/ Trigonometry
1. Numbers, Divisibility Test, HCF and LCM
2. Logarithms, Surds and Indices
3. Functions
4. Sequences and Series
5. Set Theory
6. Permutation and Combination
7. Probability
8. Mensuration
9. Trigonometry
Word Problems
1. Averages
2. Percentages
3. Profit and Loss
4. Simple and Compound Interest
5. Ratio, Proportion and Variation
6. Time, Speed and Distance/ Upstream and Downstream / Train
7. Time and Work
8. Mixtures and Alligation
9. Clocks, Pipes and Cisterns
10. Calendar
UNIT II 5 weeks (5L+0T+10P)
QUALITATIVE APTITUDE AND DATA INTERPRETATION
Data Interpretation and Logical Reasoning
1. Tabular Presentation
2. Bar Charts
3. X - Y Charts
4. Pie Charts
5. Mixed diagrams
Logical reasoning
1. Family Tree
2. Conditional ties and Grouping
3. Codes
4. Data Sufficiency
Text Books
1. Quantitative Aptitude R.S Aggarwal
2. Verbal and Non Verbal Reasoning by R.S Aggarwal
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 25
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
SOFT SKILLS AND ANALYTICAL ABILITY
SSAA-360
Syllabus „ English for Professional Purposes (EPP) for 6th Semester Students‟
UNIT III 5 Weeks (5L+0T+10P)
1. Antonyms: It tests the extent of vocabulary. Among the four/five choices offered, the word
that means the opposite of the given word is to be chosen.
2. Analogies: It tests the ability to see a relationship in a pair of words, to understand the ideas
expressed in the relationship, and to recognize a similar or parallel relationship. Each
analogy question begins with a pair of capitalized stem words. The task is to determine the
relationship between the stem words and to choose the pair of words with the same
relationship from the answer choices.
3. Sentence completion: It tests the ability to recognize relationships among parts of a
sentence. These problems present an incomplete sentence. In some problems there is one
word missing, in others, two words. In both cases, the word or words that best complete the
sentence must be chosen from the answer choices.
4. Reading comprehension: It tests the ability to read and understand a passage. Passages can
be about any subject (the most common themes are politics, history, science, business and
the humanities), followed by a series of questions.
5. Spotting the errors: It tests the command over the structure of English language by finding
error in the structure of a given sentence.
Antonyms and Analogies test the vocabulary. Sentence Completion and Reading
Comprehension test the reading skills.
Reference Books:
1. Sharon Weiner Green and Ira K. Wolf (latest edn.): Barron‟s How to Prepare for the GRE,
Graduate Record Examination, New York.
2. David Kaplan (2011): Kaplan New GRE 2011-2012 Premier (English), New York.
3. David Kaplan (2008): Kaplan GMAT Verbal Workbook (2nd edn.), New York.
4. Doug French (2nd edn.): Verbal Workout for the GMAT, (Graduate School Test Preparation),
Princeton Review.
5. P.C. Wren and H. Martin (1995): High School English Grammar and Composition, N.D.V.
Prasada Rao (ed.), S. Chand and Company, New Delhi.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 26
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
ROCK MECHANICS
CE-36E1
(Departmental Elective)
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 1 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Introduction:
Importance of rock mechanics, composition of rocks, geological and lithological classification of
rocks, classification of rocks for engineering purposes, R.Q.D. method of classification of rocks.
Theories of Brittle failure.
Laboratory Testing of Rocks:
Various methods of obtaining rock cores, methods of sample preparation, methods of removing end
friction of the rock samples. Compression testing machine, Uniaxial compression strength of rock
samples, methods of finding tensile strength-direct and indirect methods, Brazilian test, shear box
test, triaxial shear test, punch shear test.
UNIT-II
In-situ Testing of Rocks:
Field direct shear test on rock blocks, field triaxial strength, use of flat jacks, chamber test, plate
load test, cable jacking test.
Stress Evaluation in Field:
Stress-relief technique (over coring), use of strain gauges, bore hole, deformation cell, photo-elastic
stress meter, stress measurement with flat jack. Hydraulics Fracturing Techniques.
UNIT-III
Stabilization of Rocks:
Rock bolting, principle of rock bolting, various types of rocks bolts, application of rock bolting.
Field testing of rock bolts and cable anchors.
Elastic and Dynamic Properties of Rocks:
Stress-strain behavior dynamic properties, resonance method and ultra-sonic pulse method.
UNIT-IV
Pressure on Roof of Tunnels:
Trap door experiment, Terzaghi‟s theory, Bieraumer, kommerel, Protodyakanov theory.
Stress Around the Tunnels:
Basic design and Principles of tunnels in rocks, design of pressure tunnels in rocks.
Books:
1. Rock Mechanics, Vol. I, II, III, IV by Lama, et.al.
2. Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics by Jaeger and Cook
3. Rock Mechanics by Stagg & Zienkiewiez
4. Rock Mechanics & Design of Structures in Rocks by Obert & Duvell
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 27
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
WATER RESOURCES & SYSTEMS ENGINEERING
CE-36E2
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 0 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Water Resources Planning:
Role of water in national development, assessment of water resources, planning process,
environmental consideration in planning, system analysis in water planning, some common
problems in project planning, functional requirements in multipurpose projects, Reservoir planning-
dependable yield, sedimentation in reservoir, reservoir capacity, empirical-area reduction method.
UNIT-II
Economic and Financial Analysis:
Meaning and nature of economic theory, micro and macro economics the concept of equilibrium,
equivalence of kind, equivalence of time and value, cost benefit, discounting factors and
techniques, conditions for project optimality, cost benefit analysis, cost allocation, separable and
non-separable cost, alternate justifiable and remaining benefit methods, profitability analysis.
UNIT-III
Water Resources Systems Engineering:
Concept of system‟s engineering, optimal policy analysis, simulation and simulation modeling,
nature of water resources system, analog simulation, limitations of simulation, objective function,
production function, optimality condition, linear, non-linear and dynamic programming,
applications to real time operations of existing system, hydrologic modeling and applications of
basic concepts.
UNIT-IV
Applications of System Approach in Water Resources:
Applications of system engineering in practical problems like hydrology, irrigation and drainage
engineering, distribution network mathematical models for forecasting and other water resources
related problems.
Books:
1. Water Resources Engineering by Linseley and Franzini.
2. Economics of Water Resources Engineering by James and Lee.
3. Optimisation Theory and Applications by S.S.Roy.
4. Water Resources Systems Planning & Economics by R.S.Varshney.
5. Operational Research-An Introduction by Hamdy A.Taha.
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 28
6th Semester (Civil Engineering)
REMOTE SENSING & GIS
CE-36E3
L T On Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
3 0 End Semester Evaluation: 100 Marks
Note: - 1. There are NINE questions in a set of question-paper. All questions carry equal
marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. FIRST question is compulsory which covers the
whole syllabus. Attempt ONE question from each of the other four Units.
UNIT-I
Introduction to Remote Sensing:
Basic concepts of remote sensing: Airborne and space borne sensors; Data acquisition; Digital
image Processing; Restoration; Enhancement; Segmentation feature extraction; Clustering edge
detection;
UNIT-II
GIS:
Geographic Information System; Introduction to Microwave remote sensing and Global Positioning
System;
UNIT-III
Applications of RS & GIS:
Applications to Water resources; Land use and erosion; Forestry; Environment and ecology;
UNIT-IV
Software Applications:
Use of relevant software for Remote sensing and GIS applications
Books:
1. GPS and Surveying using GPS by Gopi S, Tata McGraw-Hill
2. Introduction to GIS by Chang, Tata Mc Graw – Hill
3. An Introduction to Geographical information Systems by Heywood, Cornelius and Carver,
Pearson Edu., N. Delhi
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 29
6th Semester Civil Engineering
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
CE-36E4
L T On Sem. Evaluation 100
3 - End Sem. Evaluation 100
Note 1. There are nine questions in a set of paper. All questions carry equal marks.
2. Attempt five questions in all. First question is compulsory which carry whole syllabus. Attempt One question from
each of the other four units.
UNIT – I
Introduction to Disaster Management: Natural and Man made Disasters- International Year of
Disaster Reduction.
Hydro-meteorological based disasters I: Tropical Cyclones, Floods, droughts.
Unit-II
Hydro-meteorological based disasters II: Desertification Zones and Forest Fires.
Geological based disasters: Earthquake, Tsunamis, Landslides, and Avalanches.
Unit-III
Manmade Disasters I: Chemical Industrial hazards, major power break downs, traffic accidents,
Fire hazards etc.
Manmade Disasters II: Chemical Industrial hazards, major power break downs, traffic accidents,
Fire hazards etc.
Unit-IV
Use of remote sensing and GIS in disaster mitigation and management.
Text Books
1. Thomas D. Schneid., Disaster Management and Preparedness, CRC Publication, USA, 2001
2. Patrick Leon Abbott, Natural Disasters, Amazon Publications, 2002
Ref. Books
1. Ben Wisner., At Risk: Natural Hazards, People vulnerability and Disaster, Amazon
Publications, 2001
2. Oosterom, Petervan, Zlatanova, Siyka, Fendel, Elfriede M., “Geo-information for Disaster
Management”, Springer Publications, 2005
B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) 5th & 6th Semester, Syllabus 2016-17 30
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Design of Concrete StrcturesDokument3 SeitenDesign of Concrete Strcturesapi-3696315Noch keine Bewertungen
- 70r Loading - PDFXHRXHRDokument14 Seiten70r Loading - PDFXHRXHRbalwant_negi7520Noch keine Bewertungen
- Environment and Hydrology Objective QuestionsDokument5 SeitenEnvironment and Hydrology Objective QuestionsICE Group of Education BhopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRC Live Load Design SpecificationsDokument1 SeiteIRC Live Load Design SpecificationsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compendium On Silting of Reservoirs in India - CWC (2015)Dokument219 SeitenCompendium On Silting of Reservoirs in India - CWC (2015)saradhi26Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 B-002 - Master Template With MedianDokument6 Seiten1.3 B-002 - Master Template With MediankanagarajodishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial-Structures - Question BankDokument14 SeitenIndustrial-Structures - Question BankSherlin SibithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well FoundationDokument10 SeitenWell FoundationGopal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRC 5 Amendment Silt Factor May 2021Dokument1 SeiteIRC 5 Amendment Silt Factor May 2021Biswaprakash DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tee Beam ProbDokument14 SeitenTee Beam ProbSai GowthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMPROVEMENT OF ALIPINGAL-KHAIRA ROADDokument15 SeitenIMPROVEMENT OF ALIPINGAL-KHAIRA ROADPradeepta PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Concept RCC SuperstructureDokument5 SeitenDesign Concept RCC SuperstructureSaroj BhattaraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimns. & Reinf. of Pier CapDokument1 SeiteDimns. & Reinf. of Pier Capsantosh yevvariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Design Sandhi KholaDokument15 SeitenSlab Design Sandhi Kholasakar shresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.C. Girder Bridge DesignDokument28 SeitenR.C. Girder Bridge DesignSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of 75Kl Zinc Alume (Znal) Elevated Water Storage TankDokument26 SeitenDesign of 75Kl Zinc Alume (Znal) Elevated Water Storage TankSmit PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Halaba Bridge PierDokument79 Seiten6 Halaba Bridge PierReader of Down HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST7006-Design of Bridges PDFDokument9 SeitenST7006-Design of Bridges PDFmiestyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Developers LTD.: Design of Retaining Walls @bridge Approach KM 368+385Dokument13 SeitenRCC Developers LTD.: Design of Retaining Walls @bridge Approach KM 368+385Shivendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Load Testing of Bridges PDFDokument6 SeitenDynamic Load Testing of Bridges PDFankurshah1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- A A AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDokument19 SeitenA A AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaSolmon SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geoploymer Mix DesignDokument13 SeitenGeoploymer Mix DesignShahid PerwezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Socket Piles at Coventry Point, Market Way, CoventryDokument16 SeitenRock Socket Piles at Coventry Point, Market Way, Coventrynagas440% (1)
- Timber dome structures for salt storageDokument6 SeitenTimber dome structures for salt storageLidhia Fairuz HarlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 37.500 in The State of Arunachal Pradesh Under SARDP-NE"Dokument3 Seiten37.500 in The State of Arunachal Pradesh Under SARDP-NE"Rayees AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical and Numerical Methods in Structural EngineeringDokument4 SeitenAnalytical and Numerical Methods in Structural EngineeringJasper AgbakwuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Design of Box Girder and T-Beam Bridge Superstructure - A Comparative StudyDokument13 SeitenAnalysis and Design of Box Girder and T-Beam Bridge Superstructure - A Comparative StudyParth TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix L - Information of Steel Reinforcement - BNBC 2020 CommentaryDokument4 SeitenAppendix L - Information of Steel Reinforcement - BNBC 2020 CommentaryTarif Aziz MarufNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Tech Project Presentation (Stage I) : College of Engineering Pune (COEP)Dokument31 SeitenM.Tech Project Presentation (Stage I) : College of Engineering Pune (COEP)kajal jadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stay CablesDokument22 SeitenStay Cablesalex_g00dyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Section 2 Example Bridge (E)Dokument11 Seiten03 Section 2 Example Bridge (E)Diego Benavides KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On Comparative Analysis of PSC Box Girder Bridge and PSC Precast I Girder Bridge StructureDokument11 SeitenReview On Comparative Analysis of PSC Box Girder Bridge and PSC Precast I Girder Bridge StructureIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge LoadingDokument7 SeitenBridge LoadingVarma Amit0% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Road Bridges: Prof. Nirjhar DhangDokument110 SeitenReinforced Concrete Road Bridges: Prof. Nirjhar DhangAnonymous oVmxT9KzrbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Booklet PPC Jan19Dokument25 SeitenBooklet PPC Jan19MAYURESH PATILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loading On Road Bridges (As Per IRC 6) - Excl. LLDokument76 SeitenLoading On Road Bridges (As Per IRC 6) - Excl. LLarunkumar.mgsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Based SHMDokument20 SeitenVibration Based SHMSri N100% (1)
- Optimum Design of Cable-Stayed BridgesDokument219 SeitenOptimum Design of Cable-Stayed Bridgesakhilesh kumar100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Prestressed ConcreteDokument1 SeiteAdvantages and Disadvantages of Prestressed ConcreteMarlou Salazar SabanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Stayed Bridge Over Vistula River in Plock. Dynamic Analysis and Site Test-ZoltowskiDokument8 SeitenCable Stayed Bridge Over Vistula River in Plock. Dynamic Analysis and Site Test-ZoltowskiparamsandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class A Loads Govt. of West Pakistan - Code of Practice Highway BridgesDokument1 SeiteClass A Loads Govt. of West Pakistan - Code of Practice Highway BridgesBunkun150% (1)
- Vulnerability Study For Roads and Bridges in KathmanduDokument49 SeitenVulnerability Study For Roads and Bridges in KathmanduAshish ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Foundation Design FactorsDokument23 SeitenBridge Foundation Design FactorsNisarga KeshavmurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative Forms of Two Lane T-Beam Bridge Superstructure - Study by Grillage AnalogyDokument9 SeitenAlternative Forms of Two Lane T-Beam Bridge Superstructure - Study by Grillage AnalogyAnkur SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Culvert Irc 21 Irc 112Dokument5 SeitenSlab Culvert Irc 21 Irc 112Rupendra palNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Final Report Group 7Dokument86 SeitenTraffic Final Report Group 7erlyn alagonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Underground Works in VietNam-B.DDokument42 SeitenUnderground Works in VietNam-B.Dapi-3714473Noch keine Bewertungen
- DRC Two MarksDokument26 SeitenDRC Two MarksVenkatesh GRmNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Plug-Ins of Arc BdsDokument48 SeitenAll Plug-Ins of Arc BdsAshish LoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link and Internal HingeDokument10 SeitenLink and Internal Hingesagar kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of a 16th Century Historic Brick Masonry DomeDokument9 SeitenSeismic Evaluation and Retrofit of a 16th Century Historic Brick Masonry DomeHabib Ur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Substructure & Foundation (As Per IRC 78)Dokument49 SeitenDesign of Substructure & Foundation (As Per IRC 78)arunkumar.mgs100% (1)
- Bridge CantileverDokument9 SeitenBridge CantileverPriyal vasaiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grillage Voided BoxculvertsDokument32 SeitenGrillage Voided BoxculvertsNaga Manikanta TatikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irc Ih June 2018Dokument76 SeitenIrc Ih June 2018Subhransu Sekhar Swain100% (1)
- Flood Estimation Report for Lower Godavari Subzone 3(fDokument90 SeitenFlood Estimation Report for Lower Godavari Subzone 3(fRas RamanujamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 78th PDFDokument35 Seiten78th PDFsushantNoch keine Bewertungen
- PG Political Science 2018Dokument28 SeitenPG Political Science 2018ANJANI KUMAR SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be Civil CBCGS 2019 Syllabus (Mumbai University)Dokument69 SeitenBe Civil CBCGS 2019 Syllabus (Mumbai University)Atiq SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- OU Faculty of Engineering Scheme of Instruction & Examination for B.E. III and IV Semesters (2019-2020Dokument37 SeitenOU Faculty of Engineering Scheme of Instruction & Examination for B.E. III and IV Semesters (2019-2020سيد القادريNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Architecture Ebook) Building Design and Construction HandbookDokument1.721 Seiten(Architecture Ebook) Building Design and Construction Handbookvivek100% (1)
- Data DesignDokument38 SeitenData DesignvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environment Chapter 6Dokument38 SeitenEnvironment Chapter 6vivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Web Developer ResumeDokument1 SeiteSenior Web Developer ResumePredrag GlisicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive House Planning PDFDokument77 SeitenPassive House Planning PDFAna RebeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil V Structural Analysis II (10cv53) NotesDokument90 SeitenCivil V Structural Analysis II (10cv53) NotesGagan NagpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Guide to Hydro-Electric Engineering PracticeDokument2 SeitenComprehensive Guide to Hydro-Electric Engineering Practicevivek100% (2)
- CROSS REGU (Final) PDFDokument8 SeitenCROSS REGU (Final) PDFvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering Lab Lab Manual-10Cvl67: Department of Civil EngineeringDokument76 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering Lab Lab Manual-10Cvl67: Department of Civil EngineeringNitic VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To FMDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To FMvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- CROSS REGU (Final) PDFDokument8 SeitenCROSS REGU (Final) PDFvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 09 Be Civil Engineering PDFDokument33 Seiten2008 09 Be Civil Engineering PDFvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv102019.hryssc - in AdmitCard Written Online 102019 Cat1To35 PrintAdmitCard - Aspx Pid 1 PDFDokument4 SeitenAdv102019.hryssc - in AdmitCard Written Online 102019 Cat1To35 PrintAdmitCard - Aspx Pid 1 PDFvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 PDFDokument5 Seiten10 PDFvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Tech. (3 Semester) Civil Engineering BS-204A Mathematics-III Tutorial Practical Credits Major Test Minor Test Total Time (HRS.)Dokument1 SeiteB. Tech. (3 Semester) Civil Engineering BS-204A Mathematics-III Tutorial Practical Credits Major Test Minor Test Total Time (HRS.)vivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure - J1 B - Tech - (Civil Engg - )Dokument28 SeitenAnnexure - J1 B - Tech - (Civil Engg - )vivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer-Aided Civil Engineering DrawingDokument1 SeiteComputer-Aided Civil Engineering DrawingvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time TableDokument3 SeitenTime TablevivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defender 110 en INTDokument56 SeitenDefender 110 en INTNed Villarama100% (1)
- Map Sea and HeightsDokument2 SeitenMap Sea and HeightsVictoria PulidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Applications - Track - Switches and Crossings - : Part 1: DefinitionsDokument56 SeitenRailway Applications - Track - Switches and Crossings - : Part 1: DefinitionsTC Ercan Asude AlpNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTT-180 Wheel AlignmentDokument5 SeitenTTT-180 Wheel Alignmentbilly000123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arizona Drivers Handbook - Arizona Drivers ManualDokument60 SeitenArizona Drivers Handbook - Arizona Drivers Manualpermittest100% (2)
- A Proposed New Mabuhay Maritime Express Jetty Port ReminalDokument21 SeitenA Proposed New Mabuhay Maritime Express Jetty Port ReminalJester Montalbo GallanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPM 4 - Construction EquipmentsDokument52 SeitenCPM 4 - Construction Equipmentsveeveegarcia_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis for Monorail Hoist InstallationDokument27 SeitenJob Safety Analysis for Monorail Hoist InstallationZvezdan SitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bliss Installation BookletDokument66 SeitenBliss Installation BookletbigjohnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument31 SeitenUntitledJoshua Te�osoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3485a Service ProgrammeDokument11 Seiten3485a Service ProgrammeHuincaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alaska Fabtech Pvt. LTDDokument5 SeitenAlaska Fabtech Pvt. LTDVIKAS DALMIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Loyalty Program in Strans LogisticsDokument29 SeitenCustomer Loyalty Program in Strans LogisticsRajan AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Errata 112Dokument81 SeitenErrata 112kom1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chicago Grid SystemDokument1 SeiteChicago Grid SystemArvind MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Town Planning in Washington D.C & ParisDokument38 SeitenHistory of Town Planning in Washington D.C & ParisIoana SpirescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yale 3000Dokument2 SeitenYale 3000VitorMelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Ignacio/Santa Elena Municipal Development Plan: Chapters 1, 2 and 3Dokument51 SeitenSan Ignacio/Santa Elena Municipal Development Plan: Chapters 1, 2 and 3Dorian Enriquez100% (1)
- NBC NormsDokument32 SeitenNBC NormsArathi KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chennai Metro Rail LimitedDokument8 SeitenChennai Metro Rail LimitedNirmal RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiet Pavements PresentationDokument15 SeitenQuiet Pavements PresentationMiran FlegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journey Management Plan (QHSE Manual)Dokument6 SeitenJourney Management Plan (QHSE Manual)Yahya DarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering SystemDokument29 SeitenSteering SystemJiju Joseph M100% (1)
- Fork Lift Truck Daily ChecklistDokument4 SeitenFork Lift Truck Daily ChecklistRameeSahibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSB - Lexus Transmission Serial LocationsDokument6 SeitenTSB - Lexus Transmission Serial Locationsgemni7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Okinawa Guidemap enDokument2 SeitenOkinawa Guidemap enochsrtNoch keine Bewertungen
- India's Extensive Road Network and its Importance to the EconomyDokument19 SeitenIndia's Extensive Road Network and its Importance to the EconomyAakash PuttigeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Campanile (Vol 90, Ed 1) Published Oct 1, 2008Dokument24 SeitenThe Campanile (Vol 90, Ed 1) Published Oct 1, 2008The CampanileNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGRD06-20 Guide To Road Design Part 6 Roadside Design Safety and BarriersEd3.1Dokument248 SeitenAGRD06-20 Guide To Road Design Part 6 Roadside Design Safety and BarriersEd3.1Marcos Vinicios MagalhaesNoch keine Bewertungen