Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Prostate Cancer
Hochgeladen von
Michael ChauCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Prostate Cancer
Hochgeladen von
Michael ChauCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
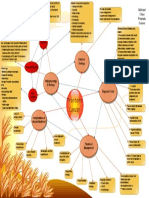
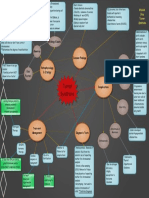
-95% of prostatic neoplasms are -Germ line mutation in the BRCA2 & BRCA1 -Bladder obstruction symptoms
adenocarcinomas gene~ related to breast cancer gene >Urinary retention
-Occurs outside in the periphery of the -1st degree relatives have a 2x increased >Dysuria -Rectal obstruction Michael
prostate risk >Slow stream -Liver enlargement
-Heterogeneous tumor -Having a genetic predisposition is not 100 >Hesitency -Lymph node enlargement Chau
-Alterations to size and shape of prostate penetrance >Hematuria -Bone pain at side if metastasizes Prostate
glandular cells (prostate intraepithelial cells >Incomplete emptying Cancer
(PIA)) >Painful urination
-Androgen (testosterone) and estrogen >Painful ejaculation -Gleason Score (Grading size,
imbalance -Bladder obstruction symptoms do shape)
-Chronic inflammation has been not remit with prostate cancer 1) Resembles normal cells small
associated with prostatic adenocarcinomas 2) Well-differentiated, loosely
due to damage from repeated inflammatory Genetics irregular, invades neighbor cells
response that results in injury and cell death 3) Most common, less-well
>Inflammation causes: infection, hormones, differentiated, variable shape
trauma, urine reflux, and diet 4) Poorly differentiated, highly
>Focal atrophy of PIA and PIA becomes irregular, invasion of neighbor cell
progressed
precursor to cancer cells Common
5) Undifferentiated, large masses,
Findings no longer normal, extensive
-Older Age Etiology/Causes invasion of neighbor cells
-Ethnicity (African American)
-Cigarette Smoking -Prostate Specific
-Vasectomy Antigen positive
-Benign Prostate Hyperplasia Pathophysiology testing:
BPH & Etiology >4 ng/ml
-Genetics **Can cause false
-Obesity/High BMI Diagnostic Tests positives and over
-Dietary:
Risk
diagnosis and
Factors
>high fats (Alpha-linolenic
acids)
>high sugar
Prostate treatment
-Tumor Nodes Metastasis
>Low vegetable/fiber intake
-Loss of
Cancer (TMN) staging
urinary control Complications of -Digital Rectal
disease/treatment Examination (DRE)
-Sexual
dysfunction -TransRectalUltra
Sound (TRUS)
-Over diagnosis
& Over
treatment -Tissue biopsy for
-Stress/Urge Treatment cancer confirmation
incontinence Management
-Loss of bowel -Metastasis to other
organ/tissue -Combination of
function -MRI, CT, Bone Scan to
any of the other
therapies check for metastasis to
other tissue
-Supportive
therapy -Observation of tumor size
-Surgical treatment -Watch and wait
-Chemotherapy
-Radiation >Prostectomy (Surveillance)
therapy >TURP -No treatment due to
>Cryotherapy ****risks vs benefits
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Prostate Cancer PDFDokument1 SeiteProstate Cancer PDFMichael ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostate Cancer PDFDokument1 SeiteProstate Cancer PDFMichael ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostate Cancer PDFDokument1 SeiteProstate Cancer PDFMichael ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turner Syndrome PDFDokument1 SeiteTurner Syndrome PDFMichael ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrating Advanced Practice ConceptMap PDFDokument1 SeiteIntegrating Advanced Practice ConceptMap PDFMichael ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turner Syndrome PDFDokument1 SeiteTurner Syndrome PDFMichael ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- RDPL Royal Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd.Dokument6 SeitenRDPL Royal Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd.Royal Diagnostic Centre in Vaishali Nagar JaipurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health Law RA 11036 - TIRADORDokument17 SeitenMental Health Law RA 11036 - TIRADORLuis Miguel TiradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indicadores ICMM PDFDokument16 SeitenIndicadores ICMM PDFJesús Omar Solís100% (1)
- Vaccine Cold Chain in General Practices: A Prospective Study in 75 Refrigerators (Keep Cool Study)Dokument13 SeitenVaccine Cold Chain in General Practices: A Prospective Study in 75 Refrigerators (Keep Cool Study)Cherry LwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented by Amir Sadaula BVSC & Ah, 8 Sem Rampur Campus Roll No: 01Dokument19 SeitenPresented by Amir Sadaula BVSC & Ah, 8 Sem Rampur Campus Roll No: 01naturalamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB PrimerDokument1 SeiteTB PrimerEdwin AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Last ProposalDokument30 SeitenLast ProposalRahmet AbdulfetahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovarian CystDokument1 SeiteOvarian CystLoriene LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Polio Eradication: History, Achievements & ChallengesDokument59 SeitenGlobal Polio Eradication: History, Achievements & ChallengesfahimalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middle and Late Adulthood StageDokument2 SeitenMiddle and Late Adulthood StageSATOR DOMINICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke Topic DiscussionDokument19 SeitenStroke Topic Discussionapi-648714317Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatomycosis 18th July 2021Dokument120 SeitenDermatomycosis 18th July 2021Sekar OktaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care - Comprehensive Health Insurance PlanDokument39 SeitenCare - Comprehensive Health Insurance PlanKirat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2017 QP - Paper 2 AQA Biology A-LevelDokument32 SeitenJune 2017 QP - Paper 2 AQA Biology A-LevelreneehandsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AK Term 1 SET A 2023-24Dokument15 SeitenAK Term 1 SET A 2023-24pro.atharv.patilNoch keine Bewertungen
- GuidelinesDokument62 SeitenGuidelinesAli Aborges Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gallstone Ileus: An Unusual Cause of Intestinal ObstructionDokument7 SeitenGallstone Ileus: An Unusual Cause of Intestinal ObstructionSiska Eni WijayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endoscopy: DR Rubeena Ali SR Radiology Deptt Amth/RlmcDokument58 SeitenEndoscopy: DR Rubeena Ali SR Radiology Deptt Amth/RlmcMuhammad WasifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nihms 695755 PDFDokument29 SeitenNihms 695755 PDFGabriel Gaspar Bike FitNoch keine Bewertungen
- PedsCases CF Note (SP Edit)Dokument1 SeitePedsCases CF Note (SP Edit)Mehtab AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex B - Health Declaration FormNov2020Dokument4 SeitenAnnex B - Health Declaration FormNov2020Raul Jr. BlasabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buttler, Irene Dr. Thornton, Karen 17851920Dokument1 SeiteButtler, Irene Dr. Thornton, Karen 17851920ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating The Impact of Field Epidemiology Training ProgramsDokument21 SeitenEvaluating The Impact of Field Epidemiology Training ProgramsNishtha BhawalpuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Roles and Responsibilities of MLHPDokument25 Seiten1) Roles and Responsibilities of MLHPShankar MurariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Effect of High Intensity Interval Training On Luecocytes BoutsDokument5 SeitenAcute Effect of High Intensity Interval Training On Luecocytes BoutsAhmad AlfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal SystemDokument92 SeitenMusculoskeletal SystemMohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rehabilitation EngineeringDokument33 SeitenRehabilitation EngineeringMuhammad MoazzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Case StudyDokument24 SeitenFamily Case Studycamel100% (1)
- Short Course (Tevaki Cohort 4C)Dokument19 SeitenShort Course (Tevaki Cohort 4C)Tevaki MathavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (03241750 - Acta Medica Bulgarica) Antiretroviral Therapy and Bone HealthDokument6 Seiten(03241750 - Acta Medica Bulgarica) Antiretroviral Therapy and Bone HealthTeodorNoch keine Bewertungen