Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bearing Capacity of Layered Soilsstronger Soil Underlain by Weaker Soil
Hochgeladen von
bunheng lonCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bearing Capacity of Layered Soilsstronger Soil Underlain by Weaker Soil
Hochgeladen von
bunheng lonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Engineering Skills Training Center E.S.T.
Chapter VI BEARING CAPACITY OF LAYERED SOILS
STRONGER SOIL UNDERLAIN BY WEAKER SOIL
VI.1. Ultimate Bearing Capacity-Meyerhof and Hanna
Ultimate bearing capacity-Meyerhof and Hanna (1978) and Meyerhof (1974)
Figure: Bearing Capacity of a Continuous Foundation on Layered Soil
VI.1.1. In Case HB
2 Ca Pp sin ( δ')
qu qb γ1 H
B
B = Width of the Foundation
Ca = Adhesive Force = c'a H
c'a = Adhesion
Pp = Passive Force per Unit Length of the Faces aa' and bb'
qb = Bearing Capacity of the Bottom Soil Layer
Simplify Form
2 c'a H 2 Df KpH tan ( δ')
2
qu qb γ1 H 1 γ1 H
B H B
δ' = Inclination of the Passive Force Pp with the horizontal
KpH = Horizontal Component of Passive Earth Pressure Coefficient
KpH tan ( δ') Ks tan ϕ'1
Shallow Foundation 42 Prepared by: Hang Sopheak
Engineering Skills Training Center E.S.T.C
2 c'a H 2
2 Df Ks tan ϕ'1
qu qb γ1 H 1 γ1 H
B H B
q2
Ks = Punching Shear Coefficient = f ϕ'1
q1
1
q1 c'1 Nc(1) γ1 B Nγ(1)
2
1
q2 c'2 Nc(2) γ2 B Nγ(2)
2
Kc(1) Nγ(1) = Bearing Capacity Factors for Friction Angle ϕ'1
Kc(2) Nγ(2) = Bearing Capacity Factors for Friction Angle ϕ'2
Table: Bearing Capacity Factors
Shallow Foundation 43 Prepared by: Hang Sopheak
Engineering Skills Training Center E.S.T.C
Figure: Meyerhof and Hanna's Punching Shear Coefficient Ks
Figure: Variation of with based on the theory of Meyerhof and Hanna (1978)
Shallow Foundation 44 Prepared by: Hang Sopheak
Engineering Skills Training Center E.S.T.C
VI.1.2. In Case HB
1
qu qt c'1 Nc(1) q Nq(1) γ1 B Nγ(1)
2
to calculate Bearing Capacity Factors for ϕ' = ϕ'1
Combining Equation above
c'a H 2
2 Df Ks tan ϕ'1
qu qb 2 γ1 H 1 γ1 H qt
B H B
For Rectangular Foundation
B 2 c'a H B 2 Df Ks tan ϕ'1
qu qb 1 γ1 H2 1 1 γ1 H qt
L B L H B
1
qb c'2 Nc(2) Fcs(2) γ1 Df H Nq(2) Fqs(2) γ2 B Nγ(2) Fγs(2)
2
1
qt c'1 Nc(1) Fcs(1) γ1 Df Nq(1) Fqs(1) γ1 B Nγ(1) Fγs(1)
2
Fcs(1) Fqs(1) Fγs(1) = Shape Factors with Respect to Top Soil Layer
Fcs(2) Fqs(2) Fγs(2) = Shape Factors with Respect to Bottom Soil Layer
VI.2. Special Cases
VI.2.1. Top layer is strong sand and bottom layer is saturated soft clay
In Case: ϕ2 0
qb 1 0.2 5.14 cu(2) γ1 Df H
B
L
1
qt γ1 Df Nq(1) Fqs(1) γ1 B Nγ(1) Fγs(1)
2
B
2 Df Ks tan ϕ'1
qu 1 0.2 5.14 cu(2) γ1 H 1 1
B 2
γ1 Df
L L H B
1
qu γ1 Df Nq(1) Fqs(1) γ1 B Nγ(1) Fγs(1)
2
cu(2) = Undrained Cohesion
q2 cu(2) Nc(2) 5.14 cu(2)
q1 1 0.5 γ1 B Nγ(1)
γ B Nγ(1)
2 1
Shallow Foundation 45 Prepared by: Hang Sopheak
Engineering Skills Training Center E.S.T.C
VI.2.2. Top layer is stronger sand and bottom layer is weaker sand
In Case: c'1 0 c'2 0
1
qu γ1 Df H Nq(2) Fqs(2) γ2 B Nγ(2) Fγs(2)
2
2 B 2 Df Ks
tan ϕ'1
γ1 H 1 1 γ1 H
L H B
qu qt
1
qt γ1 Df Nq(1) Fqs(1) γ1 B Nγ(1) Fγs(1)
2
1
γ B Nγ(2) γ2 Nγ(2)
q1 2 2
q2 1 γ1 Nγ(1)
γ1 B Nγ(1)
2
VI.2.3. Top layer is stronger saturated clay and bottom layer is weaker saturated clay
In Case: ϕ1 0 ϕ2 0
B B 2 ca H γ D q
qu 1 0.2 5.14 cu(2) 1
L L B 1 f t
B
qt 1 0.2 5.14 cu(1) γ1 Df
L
cu(1) cu(2) = Undrained Cohesion
q2 5.14 cu(2) cu(2)
q1 5.14 cu(1) cu(1)
c1 H1 c2 H2 c3 H3 .... cn Hn
cav
ΣHi
1
ϕav
H1 tan ϕ1 H2 tan ϕ2 H3 tan ϕ3 .... Hn tan ϕn
tan
ΣHi
Shallow Foundation 46 Prepared by: Hang Sopheak
Engineering Skills Training Center E.S.T.C
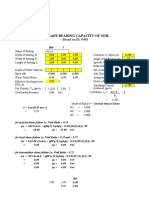
Problem
Heigh of Second Soil Layer to Bottom of the Footing H 1.2m
Inclination of the Load with Respect to the Vertical α 0.deg
Provided Width of Footing B 2m
Provided Length of Footing L 2.5 m
Depth of Footing Df 1.5m
Safety Factor FS 3
- First Soil Layer
kN
Unit Weight of Soil γs1 17
3
m
kN
Cohesion of Soil c'1 110
2
m
Friction Angle of Soil ϕ'1 0deg
- Second Soil Layer
kN
Unit Weight of Soil γs2 16.5
3
m
kN
Cohesion of Soil c'2 40
2
m
Friction Angle of Soil ϕ'2 0deg
Calculate the Allowable Bearing Capacity of Soil.
Shallow Foundation 47 Prepared by: Hang Sopheak
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDokument15 SeitenUltimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsMaria VencentciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity of Layered Soilsweaker Soil Underlain by Stronger SoilDokument4 SeitenBearing Capacity of Layered Soilsweaker Soil Underlain by Stronger Soilbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity of Mat FoundationsDokument7 SeitenBearing Capacity of Mat FoundationsConstructora Ingenieria AlemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardening Soil ModelDokument42 SeitenHardening Soil ModelClaudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enabling Works Design Calculation ReportDokument9 SeitenEnabling Works Design Calculation Reportbryan8eric-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plaxis ValidationDokument5 SeitenPlaxis Validationعصام السامرائيNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1116-GI REport PDFDokument31 Seiten1116-GI REport PDFNilay Gandhi100% (1)
- Shallow Foundations - Settlement and EC7Dokument18 SeitenShallow Foundations - Settlement and EC7Ashik Rehmath ParambilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3.1 Retaining WallDokument31 Seiten3.3.1 Retaining WallNeil SonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Safe Bearing Capacity of Soil: - Based On IS: 6403Dokument31 SeitenCalculation of Safe Bearing Capacity of Soil: - Based On IS: 6403sourabh_gupta_54100% (1)
- Chapter 6: Vertical Stress Increase in SoilDokument10 SeitenChapter 6: Vertical Stress Increase in SoilAlaa TelfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Foundation - RVNLDokument9 SeitenWell Foundation - RVNLVenkateswarlu DanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW2 - Sheet Pile Wall DesignDokument4 SeitenHW2 - Sheet Pile Wall DesignRubenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MN RUB 69 - SBC - Minor RUB - 60-79 KM (Part 1) - Rev IDokument70 SeitenMN RUB 69 - SBC - Minor RUB - 60-79 KM (Part 1) - Rev IKishore KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo-Technical Design of Deep FoundationsDokument16 SeitenGeo-Technical Design of Deep FoundationskKhalid YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 481 Compressibility of Soil 3Dokument43 SeitenCe 481 Compressibility of Soil 3DumasBellidoFloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Driving ChartDokument3 SeitenPile Driving ChartRio HandokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HS Model PresentationDokument58 SeitenHS Model Presentationgeologist84100% (2)
- PPTDokument21 SeitenPPTKunwarKhaliqeAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- KA35603+Foundation+Design CO2 TutorialDokument87 SeitenKA35603+Foundation+Design CO2 TutorialISMANOORIFAH BINTI ISMAIL -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Pile DesignDokument3 SeitenMicro Pile DesignPreethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations-7-Diaphragm WallsDokument69 SeitenFoundations-7-Diaphragm WallsElizhabet Flores PaucarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity - Sand Overlying ClayDokument1 SeiteBearing Capacity - Sand Overlying ClayMehdi.Most100% (1)
- Raft FoundationsDokument5 SeitenRaft FoundationsbotchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bored CIP Piles - Capacity Calculation - International Practice - Updated-1Dokument13 SeitenBored CIP Piles - Capacity Calculation - International Practice - Updated-1dineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SoilMech Ch5 Settlement CalculationDokument15 SeitenSoilMech Ch5 Settlement Calculationtolgadurmaz100% (1)
- Cantilever Retaining Wall DesignDokument58 SeitenCantilever Retaining Wall DesignNawanjana MaheepalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design For RR Stone Masonary Retaining Wall: General DataDokument2 SeitenDesign For RR Stone Masonary Retaining Wall: General DataRajesh GangwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Shear Failure Local Shear Failure: Net Ulimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDokument2 SeitenGeneral Shear Failure Local Shear Failure: Net Ulimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundationaditya gairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad - Trinity Bearing Capacity - MDKDokument5 SeitenMathcad - Trinity Bearing Capacity - MDKjcazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Chapter 5 - Shallow Foundations-Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement-MDokument68 Seiten04 Chapter 5 - Shallow Foundations-Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement-MWaqas Sadiq100% (2)
- Irc 58 2002Dokument40 SeitenIrc 58 2002Hari Prasad Paruchuri100% (1)
- MeyerhofDokument7 SeitenMeyerhofan diNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANCHORED Sheet Pile WallDokument11 SeitenANCHORED Sheet Pile WallFranklyn GenoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing CapacityDokument2 SeitenBearing CapacitypkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uplift CheckDokument2 SeitenUplift CheckKTMONoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral Pressure CoefficientDokument1 SeiteLateral Pressure CoefficientRoda CadizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Exercise (Solution)Dokument6 SeitenAdditional Exercise (Solution)abdul al muhaiminNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 441 - Lec02 - Bearing Capacity Theories and Eqns V2Dokument117 SeitenCE 441 - Lec02 - Bearing Capacity Theories and Eqns V2Md. Nahin Al ZakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral Capacities As Per Is 2911 Part 2 - Building AreaDokument1 SeiteLateral Capacities As Per Is 2911 Part 2 - Building AreaSripara KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity EquationsDokument23 SeitenBearing Capacity EquationsTonmoy Bhattacharjee50% (2)
- ch7 Deep Foundation Piles PDFDokument24 Seitench7 Deep Foundation Piles PDFJonathan SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piled Raft FoundationsDokument79 SeitenPiled Raft FoundationsVinod KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity Calculation (Is 6403:1981) : d c c c c q q q q γ γ γ γDokument1 SeiteBearing Capacity Calculation (Is 6403:1981) : d c c c c q q q q γ γ γ γAnand RaghuwanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6: Stresses Around Underground Openings: 6.6 Excavation Shape and Boundary StressDokument10 SeitenModule 6: Stresses Around Underground Openings: 6.6 Excavation Shape and Boundary Stressفردوس سليمانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Linear Hyperbolic Model & Parameter SelectionDokument24 SeitenNon-Linear Hyperbolic Model & Parameter SelectionNestor Bellido AñancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Bore Hole No. 2) : Calculation Spec.: NO. Soil Bearing & Pile Capacity REV. No.: 0Dokument26 Seiten(Bore Hole No. 2) : Calculation Spec.: NO. Soil Bearing & Pile Capacity REV. No.: 0mayureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation TutorialDokument6 SeitenConsolidation TutorialJavidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure of An Embankment Treated With Vacuum Preloading MethodDokument4 SeitenFailure of An Embankment Treated With Vacuum Preloading MethodtangkokhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Test Report KhagariaDokument28 SeitenSoil Test Report KhagariaSajan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Investigation Kargil ProposalDokument71 SeitenGeotechnical Investigation Kargil ProposalJack DoverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tunnelling in Bukit Timah Granite Formation - Challenges in Tunnelling From Newton To Stevens StationDokument14 SeitenTunnelling in Bukit Timah Granite Formation - Challenges in Tunnelling From Newton To Stevens StationfreezefreezeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBC For B1a FillDokument11 SeitenSBC For B1a FillAnonymous CQ4rbzLVENoch keine Bewertungen
- DGCS Volume 2C Annex GDokument12 SeitenDGCS Volume 2C Annex GRomel DecenillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument98 SeitenChapter 4Wai Yann ZawNoch keine Bewertungen
- ترزاكي - الجزء النظريDokument23 Seitenترزاكي - الجزء النظريمحمد شاويNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument39 SeitenChapter 2Zsoloa adamNoch keine Bewertungen
- B C OFS F: Earing Apacity Hallow OundationsDokument4 SeitenB C OFS F: Earing Apacity Hallow OundationsAleksiey PellicciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity of Shallow FootingsDokument17 SeitenBearing Capacity of Shallow FootingsSurya ChejerlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Design (Shallow Foundation)Dokument24 SeitenGeotechnical Design (Shallow Foundation)jianhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad - Maximum Deflection Analysis of Building PDFDokument8 SeitenMathcad - Maximum Deflection Analysis of Building PDFbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC54 Circular Column ChartingDokument13 SeitenRCC54 Circular Column Chartingbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocab UseDokument1 SeiteVocab Usebunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressed Materials and PropertiesDokument1 SeitePrestressed Materials and Propertiesbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad - Maximum Deflection Analysis of Building PDFDokument8 SeitenMathcad - Maximum Deflection Analysis of Building PDFbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14.10 Theory of Elastic FailureDokument6 Seiten14.10 Theory of Elastic Failurebunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rain LoadsDokument1 SeiteRain Loadsbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 32 Office Building PDFDokument1 Seite32 Office Building PDFbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Pactice For Dead and Imposed Loads 2011Dokument30 SeitenCode of Pactice For Dead and Imposed Loads 2011iyhkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad Users GuideDokument164 SeitenMathcad Users Guidebunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Surinder Singh PHD, MSC, Dipce, Dipqs, Fie, FisDokument196 Seiten(Surinder Singh PHD, MSC, Dipce, Dipqs, Fie, FisAulia MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Grade Beam or Grade Beam Is A Component of A BuildingDokument1 SeiteA Grade Beam or Grade Beam Is A Component of A Buildingbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad Users GuideDokument164 SeitenMathcad Users Guidebunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCC2014 Z Dolacek AldukDokument7 SeitenCCC2014 Z Dolacek Aldukbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Bridge Conference Pittsburgh, PA June 8, 2010Dokument117 SeitenInternational Bridge Conference Pittsburgh, PA June 8, 2010bunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- COM212 20181087 Page 200Dokument48 SeitenCOM212 20181087 Page 200bunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying TechnicDokument151 SeitenSurveying Technicbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coupling of Prestressing Tendons in Segmental ConstructionDokument10 SeitenCoupling of Prestressing Tendons in Segmental Constructionbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure For ProcurementDokument19 SeitenProcedure For Procurementbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution: Name: Lon Bunheng ID: 3279150168Dokument2 SeitenSolution: Name: Lon Bunheng ID: 3279150168bunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Construction Cost Analysis PDFDokument103 SeitenConstruction Cost Analysis PDFbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sketchup Modeling and Rendering: Phnom Penh Engineer CenterDokument33 SeitenSketchup Modeling and Rendering: Phnom Penh Engineer CentermensambathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Contracts PDFDokument3 SeitenBasics of Contracts PDFbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Way Solid Concrete Slab Design To Bs 81101997 Table 3.12Dokument7 Seiten1-Way Solid Concrete Slab Design To Bs 81101997 Table 3.12bunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Project Manager Competency 1 PDFDokument18 SeitenConstruction Project Manager Competency 1 PDFbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis S CurveDokument76 SeitenThesis S Curvebunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice and Theory of Schedule & Cost ControlDokument42 SeitenPractice and Theory of Schedule & Cost Controlbunheng lonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adwea Addc Approved Vendors ListDokument315 SeitenAdwea Addc Approved Vendors ListMohammed AnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Compressibility and Failure As Reservoir Mechanisms..Dokument3 SeitenRock Compressibility and Failure As Reservoir Mechanisms..German RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1617 FYP Project Titles - 20160318Dokument11 Seiten1617 FYP Project Titles - 20160318Anonymous 37PvyXCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9 Topographic Survey SentDokument30 SeitenLesson 9 Topographic Survey SentHunter Bravo100% (1)
- Swimming Pool DesignDokument8 SeitenSwimming Pool DesignHemn Rafiq TofiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation-Skylight StructureDokument5 SeitenDesign Calculation-Skylight Structuremsiddiq150% (4)
- Lecture 4 Splice Sleeves Report-G&WDokument9 SeitenLecture 4 Splice Sleeves Report-G&Wkai kaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compaction Seminar ReportDokument32 SeitenCompaction Seminar ReportKhalid Bin Walid100% (1)
- Approximate Analysis Methods of ACI: Beam SlabDokument30 SeitenApproximate Analysis Methods of ACI: Beam SlabDilon TkhomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohammad Albaji - Introduction To Water Engineering, Hydrology, and Irrigation-CRC Press (2022)Dokument273 SeitenMohammad Albaji - Introduction To Water Engineering, Hydrology, and Irrigation-CRC Press (2022)Marco Santiago GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elective - I - Advanced Hydraulics (Old)Dokument2 SeitenElective - I - Advanced Hydraulics (Old)Rhishikesh IngoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guniting MethodologyDokument3 SeitenGuniting MethodologykishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMDS0281Dokument67 SeitenFMDS0281Sandeep YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behaviour of Cold Formed Steel Single and Compound Plain Angles in CompressionDokument13 SeitenBehaviour of Cold Formed Steel Single and Compound Plain Angles in Compressionthiya123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cap. 4Dokument104 SeitenCap. 4OMAR ROLANDO CORREA FELIPENoch keine Bewertungen
- Blue Book: Fire Resisting DuctworkDokument20 SeitenBlue Book: Fire Resisting DuctworkMadan TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe ScheduleDokument2 SeitenPipe Scheduleriz2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic FormulaeDokument4 SeitenBasic FormulaeRiki AsmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrating Plate 2D Viscous Flow 53Dokument7 SeitenVibrating Plate 2D Viscous Flow 53Dr-Ateeq Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Hydrostatic Pressure and BouyancyDokument20 SeitenChapter 6 Hydrostatic Pressure and BouyancyAbba MuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting DefectsDokument5 SeitenCasting DefectsGurjinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model 50 (TS) Series Soda Post-Mix Refrigeration Unit Parts List For ModelsDokument8 SeitenModel 50 (TS) Series Soda Post-Mix Refrigeration Unit Parts List For ModelsAmauri RogérioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pub (WSN) Advisory Note-Prevention of Damage To WatermainsDokument17 SeitenPub (WSN) Advisory Note-Prevention of Damage To WatermainssimplyvenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eternal GU145 (S) Installation Operation Manual 2010-06-17Dokument54 SeitenEternal GU145 (S) Installation Operation Manual 2010-06-17NewbyJENoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 09 MSCRDokument5 Seiten2005 09 MSCRSri RamyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Structural and Fatigue Analysis of SpannerDokument17 SeitenStatic Structural and Fatigue Analysis of Spannerprashant kottalagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University (Established Under Gujarat Act No. 20 of 2007)Dokument28 SeitenGujarat Technological University (Established Under Gujarat Act No. 20 of 2007)Tarunkumar LadNoch keine Bewertungen
- QW-483 (Yellow) PQR No.: Tme 355Dokument1 SeiteQW-483 (Yellow) PQR No.: Tme 355Sudhir KotkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Civil EngineeringDokument98 SeitenIntroduction To Civil Engineeringsumanthcivil142100% (2)
- 1Dokument3 Seiten1Jose Fernando GemperleNoch keine Bewertungen