Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electoral Politics Direct Democracy: Entire Population Participate in Decision Making Process Why Election
Hochgeladen von
AdtOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electoral Politics Direct Democracy: Entire Population Participate in Decision Making Process Why Election
Hochgeladen von
AdtCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
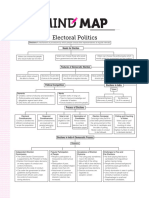
Electoral Politics
Direct Democracy: Entire population participate in decision making process
Why election:
1987- Election in Haryana
- Ruled by Congress since 1982
- Chaudhary Davi Lal (opposition leader) led movement “Nyaya Yudh’
o Formed new party Lok Dal
Promises
Waive loans of farmers and small businessmen
- Election
o Lok Dal fought election with allies – against Congress
76/90 seats- Lok Dal- 60, Congress 5
1991- Election in Haryana
- Congress won election and formed government
Election:
- Mechanism to choose our representatives at regular intervals and change them if
we wish to do so.
o Choose who will make laws for us
o Choose who will form govt. and take major decisions
o Choose the party whose policies will guide the govt.
Why do we need Election?
- Democracy without election is possible
o If all people sit together every day and take all decisions
Not possible in large community
Not everyone have the time/knowledge to take decision
Therefore most democracy rule through representatives
- Is there a democratic way to select representative without election
o If selected on basis of age and experience
o If selected on basis of education and knowledge
Difficult to decide who is more experienced or knowledgeable
- How can we find that people like their representative or not
- How to ensure that these representative rule as per the wishes of people
What makes election democratic?
- Everyone should be able to choose
o One vote one value
- Something to choose from
o Parties and candidates should be free to contest election
- Choice should be made at regular intervals
- Candidates preferred by the people should get elected
- Election should be conducted in free and fair manner
What is Political Competition? Is it good to have political competition?
Merits and Demerits of Political Competition?
- Election is all about political competition
o Competition among political parties
o At constituency level among candidates
Merits Demerits
Political leaders are motivated by the desire to advance their political career Political parties and candidates level allegation against each other
Want to remain in power Parties and candidates use dirty tricks to win election
Provides incentives to political parties and leaders Does not allow sensible long term policy to be formulated
Some good people does not enter into political
System of Election in India:
1. Electoral Constituencies
- Area from where representatives are elected by the people
- Reserved Constituency
- Some group does not have the required resources, education and contest election
- Lok Sabha (84 SC, 47 ST)
- OBC and Women in Local Bodies
2. Electoral Roll/ Voter List
- All citizen above 18 years of age
- Some criminals and persons with unsound mind can be denied
- Revised every five years
-EPIC (Electronic Photo Identity Card)
- card not yet necessary for voting
3. Nomination of Candidate:
- Any one above 25 years can contest election
- Some restriction on criminals
- Those who want to contest election – need to fill nomination form- give security deposit and make declaration:
- Serious criminal case pending
- Details of assets and liabilities
- Educational qualification
4. Election Campaign:
- Free and open discussion about who is better representative, - which party will make better government
- Focus public attention
- Garibi Hatao – Congress – 1971
- Save Democracy – Janta Party – 1977
- Land for Tiller – West Bengal – 1977
- Protect the Self-respect of Telugus – Andhra Pradesh- 1983, Telugu Desam Party
- Follow Regulations: (Fair and Equal chance to compete)
- Bribe or threaten voters
- Appeal in the name of caste or religion
- Use govt. resources for election campaign
- Expenditure- 25 lakh (Lok Sabha), 10 lakh (State Assembly)
- Model Code of Conduct – No party or Candidate
- Use place of worship for election propaganda
- Use govt. vehicles, aircrafts and officials for elections
- Once election is announced- ministers shall not lay foundation stone- take big policy decisions
5. Polling and Counting of Votes:
Election Outcome:
Some negative features of Indian Election System:
o Inclusion of false name in voter list
o Misuse of govt. facilities
o Excessive use of money- party/candidates
o Intimidating voters- rigging on polling day
1. Independent Election Commission
- Appointed by President- work independently- difficult to remove
- take decision on every aspect of election
- Conduct and control
- Implement Code of Conduct
- Punish violators
- During election- can order govt. to follow certain guidelines
- On election duty govt. officials work under EC
2. Popular Participation
- If election in not free and fair- people’s participation will be less
- India:
- Voter’s turnout stable or gone up- Europe and America turnout is down
- Poor, illiterate and unprivileged vote in large number compared to rich- reverse in US and Europe
- Common people attach lot of importance to election
- can bring pressure on political parties to adopt policies and programmes favourable to them
- Interest of voters in election related activities has increased
3. Acceptance of election outcome:
- If election is not free and fair outcome will always in favour of powerful
- Ruling party will not lose elections
- In India
- Ruling party routinely lose election
- About half of sitting MPs and MLAs lose election
- Candidate with money power and criminal connections often lose election
Challenges to Free and Fair election:
- Candidate and Parties with lot of money enjoy advantage over smaller parties and independents
- Candidates with criminal connection able to secure ticket from major parties
- Some families tend to dominate political parties
- Election offer little choice to ordinary citizen
- Smaller Parties and Independent candidates suffer a huge disadvantage
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Elections and RepresentationDokument36 SeitenElections and RepresentationAmey BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral PoliticsDokument1 SeiteElectoral PoliticsNikhat SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics 2 SynopsisDokument7 SeitenElectoral Politics 2 SynopsisArnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pol. Sci. Ch-3 Electoral Politics WorksheetDokument3 SeitenPol. Sci. Ch-3 Electoral Politics WorksheetSiddhant NarayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics Final Notes-1Dokument10 SeitenElectoral Politics Final Notes-1Bhavya PantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th STD Democratic Politics Notes L 4 Electoral Politics 1643555741Dokument11 Seiten9th STD Democratic Politics Notes L 4 Electoral Politics 1643555741hi byeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral PoliticsDokument8 SeitenElectoral PoliticsBaibhab BhattacharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electorial PoliticsDokument16 SeitenElectorial PoliticsVempala SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Election System in IndiaDokument33 SeitenElection System in IndiaShyam Sunder BudhwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hum Notes 2Dokument4 SeitenHum Notes 2sudasinghesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES - Electoral POLITICSDokument12 SeitenNOTES - Electoral POLITICSIshaan GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral PoliticsDokument39 SeitenElectoral PoliticsNeeyati BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics Part IDokument2 SeitenElectoral Politics Part ID-47 Saswata PattanaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Class Ix Electoral Politics 2022-2023Dokument9 SeitenDelhi Public School Bangalore North Class Ix Electoral Politics 2022-2023dailybeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics PPT - Class 9Dokument31 SeitenElectoral Politics PPT - Class 9aannoosandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electoral ProcessDokument8 SeitenThe Electoral ProcessCasandra HyltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral PoliticsDokument9 SeitenElectoral Politicspayashjha29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral PoliticsDokument38 SeitenElectoral Politicswildestdreams163Noch keine Bewertungen
- Election and Political PartiesDokument48 SeitenElection and Political PartiesRahim AhilonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation (1) 2Dokument24 SeitenPresentation (1) 2gaurikasaxena29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civics Chapter 3Dokument6 SeitenCivics Chapter 3vijaykumarmahli12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics NotesDokument4 SeitenElectoral Politics NotesshambhaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Electoral PoliticsDokument38 SeitenClass 9 Electoral PoliticsAnita Pant100% (1)
- Election and Political PartiesDokument17 SeitenElection and Political PartiesKylie VoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Voting and Elections PPDokument25 SeitenChapter 10 Voting and Elections PPNgoc AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - Election SystemDokument68 SeitenChapter 7 - Election SystemHasdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Election and Electoral SystemDokument16 Seiten14 Election and Electoral SystemFyna BobNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Past The PostDokument3 SeitenFirst Past The PostBhavya ChandragiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elections & Voting BehaviorDokument45 SeitenElections & Voting BehaviorJulie CrabbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral PoliticsDokument8 SeitenElectoral PoliticsAnna AjithNoch keine Bewertungen
- L2 - Electoral PoliticsDokument52 SeitenL2 - Electoral PoliticsGunika JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Electoral PoliticsDokument4 SeitenChapter 4 Electoral PoliticsguruavibroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Need For Elections in A DemocracyDokument9 SeitenNeed For Elections in A Democracymission.iist.1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral MalpracticesDokument24 SeitenElectoral MalpracticesRaushan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right To SuffrageDokument46 SeitenRight To SuffrageRian Hanz AlbercaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPG NotesDokument4 SeitenPPG NotesmariaantonnettegologilosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1 Am GovDokument26 SeitenPresentation 1 Am GovLeousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics - Part IvDokument2 SeitenElectoral Politics - Part IvD-47 Saswata PattanaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectoralPolitics NotesDokument6 SeitenElectoralPolitics Notesgurdeepsarora8738Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics NOTESDokument6 SeitenElectoral Politics NOTESeeren41789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 13 Electoral Politics in DemocracyDokument4 SeitenLesson 13 Electoral Politics in DemocracyRakoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q. 32. What Makes Election in India Democratic? Q.30.The Outcome of India's Elections Speaks For Itself. ExplainDokument2 SeitenQ. 32. What Makes Election in India Democratic? Q.30.The Outcome of India's Elections Speaks For Itself. ExplainYash GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Civics LN 3Dokument3 Seiten9 Civics LN 3kanagaragavan1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elections & Voting BehaviorDokument59 SeitenElections & Voting BehaviorJulie CrabbNoch keine Bewertungen
- OVERVIEWDokument7 SeitenOVERVIEWhandk456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Right To Suffrage 2022 FinalDokument46 SeitenRight To Suffrage 2022 FinalCyrus ArmamentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectionDokument17 SeitenElectionBethel DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics - 09.11.2020Dokument6 SeitenElectoral Politics - 09.11.2020Armaan PruthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL 10 Political Parties CivicsDokument12 SeitenCL 10 Political Parties Civicsnonupuri453Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics Full Chapter ExplanationDokument32 SeitenElectoral Politics Full Chapter Explanationviratvamika180Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS 9 Civics CH 2 (PDF - Io)Dokument7 SeitenCLASS 9 Civics CH 2 (PDF - Io)SimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pad240 t7 The Election System 240123 232553Dokument43 SeitenPad240 t7 The Election System 240123 232553arabellaniaroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electoral Politics One ShotDokument22 SeitenElectoral Politics One ShotkashvikayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suffrage, Election, & Political PartiesDokument29 SeitenSuffrage, Election, & Political PartiesDexter Balisi BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC Ch4 Electoral PoliticsDokument1 Seite09 Social Science Key Notes Pol SC Ch4 Electoral PoliticsPrem KukrejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civics and Government Electoral SystemDokument22 SeitenCivics and Government Electoral SystemWillem ViljoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electroal Malpractice EthicsDokument17 SeitenElectroal Malpractice EthicsR B SHARANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Do We Need Elections?: Electoral PoliticsDokument3 SeitenWhy Do We Need Elections?: Electoral Politicsvishvendra pratap singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemocarcyDokument2 SeitenDemocarcyShah FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Power of Your Vote: Look past theatrics, Assess your priorities, and Make educated choicesVon EverandThe Power of Your Vote: Look past theatrics, Assess your priorities, and Make educated choicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLM 09 03Dokument2 SeitenNLM 09 03AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diwali Worksheet 1Dokument4 SeitenDiwali Worksheet 1AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGDEMADokument4 SeitenPGDEMAAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tapping The Inner Teacher: Delivering High-Impact Learning Through Leader-Led DevelopmentDokument6 SeitenTapping The Inner Teacher: Delivering High-Impact Learning Through Leader-Led DevelopmentAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Science Mixed Bag 2 (The Answer Key Will Be Shared by The End of This Week) 1. (1) 2.Dokument2 SeitenGrade 10 Science Mixed Bag 2 (The Answer Key Will Be Shared by The End of This Week) 1. (1) 2.AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS 15 Grade 10 ComprehensionDokument4 SeitenWS 15 Grade 10 ComprehensionAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Science PRE BOARD II 2018 19Dokument21 SeitenAnswer Key Science PRE BOARD II 2018 19AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 646853052math Quiz For Classes Vi To XDokument19 Seiten646853052math Quiz For Classes Vi To XAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Periodic Test-03 Exam Sample Paper 01 (2018-19)Dokument5 SeitenKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Periodic Test-03 Exam Sample Paper 01 (2018-19)AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1365445901maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 01Dokument5 Seiten1365445901maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 01AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1745806749maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 02Dokument5 Seiten1745806749maths Class Ix Periodic Test II Exam Sample Paper 02AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 WS 20 DeterminersDokument2 SeitenG8 WS 20 DeterminersAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Introduction Worksheet: Phase Change Name Endo-Or ExoDokument3 SeitenThermochemistry Introduction Worksheet: Phase Change Name Endo-Or ExoAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Adaptation SAT Answers 3-6: Greenwich Bulk LEA 1Dokument5 SeitenClassification and Adaptation SAT Answers 3-6: Greenwich Bulk LEA 1AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTSE Class 7 Solved Paper 2012 PDFDokument21 SeitenNSTSE Class 7 Solved Paper 2012 PDFAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity SAT Answers 5-7Dokument3 SeitenElectricity SAT Answers 5-7AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03Dokument5 SeitenMaths Class Vii Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System SAT Answers 3-6Dokument4 SeitenRespiratory System SAT Answers 3-6AdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- G-L5:Water: ITL Public School Social Science Hand Out (2016-17) Class VII Subject: GEOGRAPHYDokument7 SeitenG-L5:Water: ITL Public School Social Science Hand Out (2016-17) Class VII Subject: GEOGRAPHYAdtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions For Comprehensive Exams NovemberDokument2 SeitenInstructions For Comprehensive Exams Novembermanoj reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 202309040934Dokument5 SeitenResume 202309040934dubai eyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsDokument2 SeitenNitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsmilanbrasinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forecasting and Demand Management PDFDokument39 SeitenForecasting and Demand Management PDFKazi Ajwad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 269-2022-014 Rotary Table NDT Cat IV - Rev1Dokument1 SeiteIso 269-2022-014 Rotary Table NDT Cat IV - Rev1Durgham Adel EscanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- David Sm15 Inppt 06Dokument57 SeitenDavid Sm15 Inppt 06Halima SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rule 63Dokument43 SeitenRule 63Lady Paul SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branch CodeDokument3 SeitenBranch CodeAhir MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of SpeakerDokument11 SeitenRole of SpeakerSnehil AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boeing 247 NotesDokument5 SeitenBoeing 247 Notesalbloi100% (1)
- Comparison of The Gasification Performance in The Downdraftfixed-Bedgasifier Fed by Different Feedstocks Rice Husk, Sawdust, and Their MixtureDokument8 SeitenComparison of The Gasification Performance in The Downdraftfixed-Bedgasifier Fed by Different Feedstocks Rice Husk, Sawdust, and Their MixturechaniefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meeting Protocol and Negotiation Techniques in India and AustraliaDokument3 SeitenMeeting Protocol and Negotiation Techniques in India and AustraliaRose4182Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maturity AssessmentDokument228 SeitenMaturity AssessmentAli ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquamaster 3 Flow Measurement: Saving Every Drop of Energy and Cost Naturally!Dokument7 SeitenAquamaster 3 Flow Measurement: Saving Every Drop of Energy and Cost Naturally!FIRMANSYAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS 671Dokument9 SeitenSS 671OwNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVDokument1 SeiteCVotieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Server Operating SystemDokument20 Seiten1.2 Server Operating SystemAzhar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bromate Prove Ulr en 2016-01-06 HintDokument3 SeitenBromate Prove Ulr en 2016-01-06 Hinttata_77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Katalog Bonnier BooksDokument45 SeitenKatalog Bonnier BooksghitahirataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Research ProjectDokument37 SeitenMarketing Research ProjectVijay100% (15)
- 99990353-Wsi4-2 C1D2-7940022562 7950022563 7940022564Dokument2 Seiten99990353-Wsi4-2 C1D2-7940022562 7950022563 7940022564alltheloveintheworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Developer Shed Network) Server Side - PHP - Database Abstraction With PHPDokument29 Seiten(Developer Shed Network) Server Side - PHP - Database Abstraction With PHPSeher KurtayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Conduct Policy StpsoDokument57 SeitenEmployee Conduct Policy StpsoWWLTVWebteamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline ReviewerDokument12 SeitenCourse Outline Reviewerjmd.besanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIP & CouponsDokument5 SeitenFIP & CouponsKosme DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAYA1010 EnglishDokument30 SeitenMAYA1010 EnglishjailsondelimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DefinitionDokument6 SeitenDefinitionRatul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Framework For Durable ConcreteDokument8 SeitenFramework For Durable ConcreteDai ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Bulletin: Service Bulletin NUMBER: 8.8/134A Caterpillar: Confidential Green Page 1 of 8Dokument8 SeitenService Bulletin: Service Bulletin NUMBER: 8.8/134A Caterpillar: Confidential Green Page 1 of 8GutsavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Participation 9 E7-18: Last Name - First Name - IDDokument2 SeitenClass Participation 9 E7-18: Last Name - First Name - IDaj singhNoch keine Bewertungen