Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tapping Screws: Ductility Testing of
Hochgeladen von
Ravindra ErabattiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tapping Screws: Ductility Testing of
Hochgeladen von
Ravindra ErabattiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
112 TECHNOLOGY
Ductility Testing of
Tapping Screws
by Larry Borowski
Brittle tapping screws can be problematic for
end users. Brittle is describing the heat treat/
material condition as unyielding, and has no So how do we test for ductility on
relationship to Hydrogen Embrittlement. Imagine tapping screws?
using your nut driver to install a cover onto a
casting, and as soon as you seat the screw, the 1. Determine what specification the tapping screw must
head snaps off. Now you have to figure out how conform to, as well as what kind of tapping screw it is. This will
to get that screw out when it is broken off flush provide you with the angle of head to shank deformation that
with the surface of the casting. Luckily, industry must be achieved. Most tapping screw types are required to have
experts developed tests years ago through various the heads bent to a 10 degree angle with the shank. Most Thread
consensus standards that give us guidance on Rolling screws require a 7 degree angle, and most Self Drilling
how to test tapping screws before such a problem screws require a 5 degree angle. There are also requirements of
occurs. Ductility testing is listed as one of 6 degree, and even up to 30 degrees stated in some standards.
the performance tests in most tapping screw Additional requirements for the testing apparatus are:
standards from ASME to DIN. a. The block shall be made of hardened steel.
Ductility can be generically defined as a b. The block shall have a hole(s) that are between .020” and
solid material’s ability to deform under tensile .040” (for Inch sizes), and .50mm to 1.0mm (for metric
stress. When seating a screw head onto an sizes) larger than the given nominal major diameter of the
uneven surface, the head will have a tendency to screw.
conform to that surface. As the head to shank
junction deviates from perpendicular, one side of c. The given wedge angle of the block face should be relative
the shank is under compression, while the other to the axis of the hole in the block.
side is in tension. It is the side in tension that will
crack and cause separation if the material is not d. The block can contain a single hole or any number of
ductile enough or is found to be too brittle. holes, and it can also have a common hole used for both
inch series and metric series screws. Below is one such
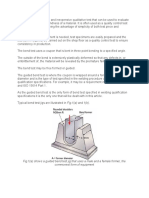
It is interesting to note that while many of block created by Greenslade & Company, Inc., which
the standards utilize the same language, some contains most of the common sizes of tapping screws
standards embellish more details than others. combining inch and metric into a single block. (Fig.1)
For instance ASME B18.6.3 states that Head
separation shall be cause for rejection. One 2. Insert the screw into the proper sized hole of the Ductility
might wonder if “head separation” means a Testing Block. (Fig.2)
significant crack or complete separation from
the shank. DIN 7500 goes on to better qualify Fig. 1 Fig. 2
the requirement by stating The test shall be
regarded as satisfactory even if a crack appears
in the first thread, provided the head does not
snap off. As in all requirements of standards, it
would be helpful to the users of those standards
if the same language was always used. What
we should take away is that separation means
complete separation or breaking into two pieces.
TECHNOLOGY 113
Fig. 3 Fig. 4 Fig. 5
3. Strike the head of the screw with a hammer
or other suitable device until it conforms to the
angled surface. That is until the bearing surface
of the head is flat against the angled surface. It
may take more than one blow with a hammer to
bend the screw head. (Fig.3 & 4)
4. Remove the screw from the Ductility
Testing Block and observe the condition of the
head. Note that it has been bent, and that it is
not completely separated from the shank. Even
if there is a significant crack at the head to shank
junction, but the head remains attached to the shank, the test for ductility was successful. (Fig.5)
Besides Ductility Testing being a required performance test, it is also a relatively easy and inexpensive test to perform in order
to ensure that the tapping screws being sold or used are good. Ductility test failures can also indicate other problems besides the
core hardness being too high or the case hardness being too deep. A failure can also be a result of the recess in the head being
too deep leaving very little material at the head to shank junction, or the under head fillet radius could be too small creating
a high stress point at the head to shank junction. It is always important to perform all required dimensional and mechanical
tests on a screw before passing it onto to the end user. A single test or check is not sufficient to provide enough information
regarding the quality of the fastener.
Besides the standards referenced above, the following standards also provide details of this test along with other dimensional
and performance related requirements. Some of which are FIP1000, ISO 898-1, ISO 7085, SAE J1237, SAE J78, etc. Again, be
sure you are working to the correct specification before assuming all self-tapping screws have the same angular deformation
requirement.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Machinery Vibration Related To Poor Bolting PracticesDokument24 SeitenMachinery Vibration Related To Poor Bolting PracticesBitbitterNoch keine Bewertungen
- O-Ringing The Block or Cylinder HeadDokument3 SeitenO-Ringing The Block or Cylinder Headgreg monroeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1.14 - Shackles: 1.1 Body and Pin Forging 1.2 Heat Treatment 1.3 FinishDokument8 SeitenUnit 1.14 - Shackles: 1.1 Body and Pin Forging 1.2 Heat Treatment 1.3 Finisheetua100% (2)
- Bolts and TighteningDokument4 SeitenBolts and TighteningArassen RunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-BCIS High Strength Bolts 2018Dokument55 Seiten13-BCIS High Strength Bolts 2018balamuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Assembly Technology: Shenyang Aerospace UniversityDokument21 SeitenAircraft Assembly Technology: Shenyang Aerospace Universityalokmotivation99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Testing of Bolts and NutsDokument2 SeitenTesting of Bolts and Nutsabc_8989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Roller Chain GuideDokument5 SeitenRoller Chain GuidechikoopandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Interchange: Modern Steel's Monthly Steel Interchange Is For You!Dokument2 SeitenSteel Interchange: Modern Steel's Monthly Steel Interchange Is For You!hector diazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bend Test SummaryDokument4 SeitenBend Test SummaryManish MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Embrittlement - What It Looks Like PDFDokument2 SeitenHydrogen Embrittlement - What It Looks Like PDFAdnan SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 04 13Dokument55 Seiten10 04 13Edu HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great RollFormedPartEbookDokument15 SeitenGreat RollFormedPartEbookPankajKumarSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- U3l1s FastenersDokument46 SeitenU3l1s FastenerspmcisissengueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding TWIDokument16 SeitenWelding TWIEngr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DesignDokument15 SeitenDesignMuhammed Sulfeek100% (1)
- HSFG Bolts RNGDokument34 SeitenHSFG Bolts RNGSANDEEP DANGDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Home About Us Software Services Training Download Pricing Bolting InfoDokument9 SeitenHome About Us Software Services Training Download Pricing Bolting Infopaeg6512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Material Engineer's Handbook: BoltingDokument5 SeitenPiping Material Engineer's Handbook: BoltingJitendra SurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft FastenerDokument91 SeitenAircraft FastenerPrasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torque and Aviation FastenersDokument9 SeitenTorque and Aviation FastenersMani Rathinam RajamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 4145 - 83 R96 - RdqxndutodnsotzfmqDokument3 SeitenD 4145 - 83 R96 - RdqxndutodnsotzfmqEmre DalgicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual INSPECTION OF WELDSDokument49 SeitenVisual INSPECTION OF WELDSpraveentienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bend TestDokument2 SeitenBend TestFsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Interchange: Modern Steel's Monthly Steel Interchange Is For You!Dokument2 SeitenSteel Interchange: Modern Steel's Monthly Steel Interchange Is For You!Andres CasadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 4145 - 83 R02 - RdqxnduDokument3 SeitenD 4145 - 83 R02 - RdqxnduEmre DalgicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Material FastenersDokument26 SeitenReading Material FastenersAbhinav SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm c1513Dokument4 SeitenAstm c1513Ramón RocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Watch 02Dokument7 SeitenAnchor Watch 02Janaka KarunarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welders Visual Inspection Handbook-2013 WEB PDFDokument77 SeitenWelders Visual Inspection Handbook-2013 WEB PDFketanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bend Testing: Job Knowledge 73Dokument3 SeitenBend Testing: Job Knowledge 73kevin herryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Focus: Welding Done WellDokument2 SeitenProduct Focus: Welding Done WellYami YugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design - Part 4 - Job Knowledge 93Dokument4 SeitenDesign - Part 4 - Job Knowledge 93Billy TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Burton R. Leathley: Oliver of Adrian, IncDokument8 SeitenBy Burton R. Leathley: Oliver of Adrian, IncOliver AlfaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajax Rivets HandbookDokument15 SeitenAjax Rivets HandbooknextreaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Ring Gaskets 2Dokument12 SeitenWeld Ring Gaskets 2bruteforce2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing Anchors (Steelwise Article On Anchor Bolt Fixes)Dokument3 SeitenAddressing Anchors (Steelwise Article On Anchor Bolt Fixes)Justin UyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Fillet WeldingDokument7 SeitenGuide To Fillet WeldingPeter KyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.nuts and Bolts PDFDokument9 Seiten5.nuts and Bolts PDFAnonymous sbOPJbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Tube ExpandingDokument22 SeitenBasic Principles of Tube ExpandingsvvsnrajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omni-X Tube Bending GuideDokument15 SeitenOmni-X Tube Bending GuidemsppmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 Omni X Tube Bending GuideDokument15 Seiten25 Omni X Tube Bending GuideMartin SilisqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTOD TestingDokument4 SeitenCTOD TestingkvijaymurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6-5 Fasteners Pt3 PresentationDokument44 SeitenModule 6-5 Fasteners Pt3 Presentationabdullahqureshi789456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bend Testing - TWIDokument8 SeitenBend Testing - TWIFarid Ahmed KhwajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 5 Vs Grade 8 Fasteners - TineLokDokument5 SeitenGrade 5 Vs Grade 8 Fasteners - TineLokTodd AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTOD Testing: Job Knowledge 76Dokument3 SeitenCTOD Testing: Job Knowledge 76kevin herryNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoltsDokument6 SeitenBoltsblackhawkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolts CatalogueDokument88 SeitenBolts CatalogueAnandh PsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan SmawDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan SmawJOHN-REY MANZANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah 4 Pengencangan SambunganDokument24 SeitenKuliah 4 Pengencangan SambunganAlifiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTOD Testing: Job Knowledge 71Dokument3 SeitenCTOD Testing: Job Knowledge 71pardissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah 4 Pengencangan SambunganDokument24 SeitenKuliah 4 Pengencangan SambunganAlifiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsVon EverandMetalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Off-Road Welding: Advanced Techniques on How to Become a True Off-Road WelderVon EverandOff-Road Welding: Advanced Techniques on How to Become a True Off-Road WelderBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataVon EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- Ye Nvcegbyef& Ceneveiejheeefuekeàe: Os Ekeà Efveefce&Leer Efoveebkeàeme Peeoe Pecee JkeìkeàceDokument1 SeiteYe Nvcegbyef& Ceneveiejheeefuekeàe: Os Ekeà Efveefce&Leer Efoveebkeàeme Peeoe Pecee JkeìkeàceRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Spring Wire With Bleed 3mmDokument2 SeitenStainless Steel Spring Wire With Bleed 3mmRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDokument1 SeiteCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VersionDokument2 SeitenVersionRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Indications Are Basically Founded On Our Actual Know-How. This Technical Data Sheet Is Without Commitment and Not ContractedDokument1 SeiteThe Indications Are Basically Founded On Our Actual Know-How. This Technical Data Sheet Is Without Commitment and Not ContractedRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 09 2017Dokument4 Seiten16 09 2017Ravindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Din en Iso 7089Dokument3 SeitenDin en Iso 7089Ravindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO Methodology PDFDokument132 SeitenISO Methodology PDFRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delta FerriteDokument4 SeitenDelta FerriteRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Systems Analysis: Repeatability & ReproducibilityDokument4 SeitenMeasurement Systems Analysis: Repeatability & ReproducibilityRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Standardization Practices: Iso Publication OnDokument175 SeitenGood Standardization Practices: Iso Publication OnRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIN 1.0722 AISI 11L08 SAE 11L08 EN 1.0722 GB Y12PbDokument1 SeiteDIN 1.0722 AISI 11L08 SAE 11L08 EN 1.0722 GB Y12PbRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical CompositionDokument2 SeitenChemical CompositionRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloying Elements ExcelDokument18 SeitenAlloying Elements ExcelRavindra ErabattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbas Ali Mandviwala 200640147: Ba1530: Information Systems and Organization StudiesDokument11 SeitenAbbas Ali Mandviwala 200640147: Ba1530: Information Systems and Organization Studiesshayan sohailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report-Smaw Group 12,13,14Dokument115 SeitenReport-Smaw Group 12,13,14Yingying MimayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zambia National FormularlyDokument188 SeitenZambia National FormularlyAngetile Kasanga100% (1)
- Functions PW DPPDokument4 SeitenFunctions PW DPPDebmalyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation Law 1Dokument7 SeitenTaxation Law 1jalefaye abapoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing The Marks and Spencers Retail ChainDokument10 SeitenAssessing The Marks and Spencers Retail ChainHND Assignment Help100% (1)
- Advanced Physiotherapeutic SyllabusDokument1 SeiteAdvanced Physiotherapeutic SyllabusAnup SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nyamango Site Meeting 9 ReportDokument18 SeitenNyamango Site Meeting 9 ReportMbayo David GodfreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument5 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSukanya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stochastic ProcessesDokument264 SeitenStochastic Processesmanosmill100% (1)
- P66 M10 CAT B Forms and Docs 04 10Dokument68 SeitenP66 M10 CAT B Forms and Docs 04 10VinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check e Bae PDFDokument28 SeitenCheck e Bae PDFjogoram219Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 24 - The Solar SystemDokument36 SeitenChapter 24 - The Solar SystemHeather Blackwell100% (1)
- Waswere Going To Waswere Supposed ToDokument2 SeitenWaswere Going To Waswere Supposed ToMilena MilacicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies in Work SitesDokument49 SeitenRisk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies in Work SitesNhut NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Be A Better StudentDokument2 SeitenHow To Be A Better Studentct fatima100% (1)
- Evolis SDK Use Latest IomemDokument10 SeitenEvolis SDK Use Latest IomempatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- SXV RXV ChassisDokument239 SeitenSXV RXV Chassischili_s16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Stressful Jobs 1 4Dokument4 SeitenReading Stressful Jobs 1 4Ivana C. AgudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Some of The Best Books On Computer ScienceDokument9 SeitenWhat Are Some of The Best Books On Computer ScienceSarthak ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows Intrusion Detection ChecklistDokument10 SeitenWindows Intrusion Detection ChecklistJosé Tomás García CáceresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bathinda - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument4 SeitenBathinda - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBhuwan GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- XU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Dokument5 SeitenXU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Harold John LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAED90DR Rev1 2 21.01.2011Dokument24 SeitenSAED90DR Rev1 2 21.01.2011Cherry AbhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSL Education Center Final Exam 30 Minutes Full Name - Phone NumberDokument2 SeitenLSL Education Center Final Exam 30 Minutes Full Name - Phone NumberDilzoda Boytumanova.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Datos Adjuntos Sin Título 00013Dokument3 SeitenDatos Adjuntos Sin Título 00013coyana9652Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment 4 PDFDokument10 SeitenAssessment 4 PDFAboud Hawrechz MacalilayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom SDDokument5 SeitenAtom SDatomsa shiferaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beamng DxdiagDokument22 SeitenBeamng Dxdiagsilvioluismoraes1Noch keine Bewertungen
- AAR Shell ProgrammingDokument13 SeitenAAR Shell ProgrammingMarimuthu MuthaiyanNoch keine Bewertungen