Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
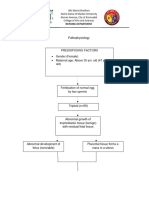
Modifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Iv. Schematic Diagram
Hochgeladen von
AIMOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Modifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Iv. Schematic Diagram
Hochgeladen von
AIMCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
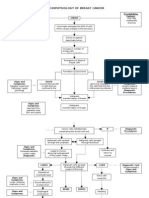
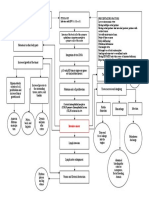
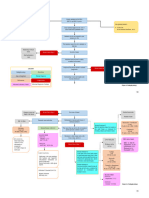
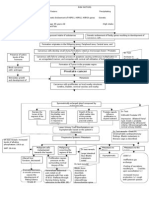
IV.
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
Modifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Obesity Age
Physical Inactivity Age of First Live Birth
Alcohol Consumption Hormonal Factors
Hormone Therapy after Breast Density
Menopause Sex (Female)
Genetics
Family History
Exposure to Ionizing Radiation
DNA Damage
Failure of DNA Repair
Mutations in the
Genome of the Cells
(INITIATION)
Activation of growth- Inactivation of tumor Alterations in genes
promoting oncogenes suppressor genes (BRCA1, that regulate apoptosis
BRCA2, TP53) (P53 gene)
Unregulated cell Decreased
proliferation apoptosis
Affected cells (epithelial
cells) grow and replicate PROMOTION (Proliferation at the mitotic rate of tissue of origin)
out of control
STAGE I
Tumor progression along the
lactiferous ducts
Hard lump or swelling
Malignant neoplasm (Angiogenesis
and Escape from immunity)
STAGE II
Primary tumor grows into Releases "mobility factor"
surrounding tissue and
interstitial spaces
Tumor crosses
basement membrane
PROGRESSION
STAGE III
Tumor breaks through
Inflammation
squamous epithelial cells;
migrates along lactiferous Pain
ducts
Invasion to nearby
Tumor spreads through
tissue
body cavities
Extracellular fluid escapes
Malignant cells break through breaks in the skin
Damage to Suspensory
off from primary tumor
Nipple discharges Ligaments and
cells and spread
Tumor enters and blocks Lactiferous Ducts
through circulation
lymphatic vessels
Swelling under armpit
Cancer cells migrate Fluid dries and forms
Build-up of lymph in the onto skin crust FIbrosis of lactiferous
interstitial space ducts and suspensory
Paget's disease
ligaments
Skin Dimpling
Retraction
Breast skin unable to Skin Dimpling
stretch due to
suspensonry ligaments
Swelling; dimpling
and retraction
Peau d'orange Release of cytokines
Activation of inflammatory
mediator interleukin 6
Invades nearby tissues Affectation of appetite
(Pectoral muscles, skin; (certain cytokines ↑hepatic hepcidin
STAGE IV spreads through blood to affect centers for production
spine, brain and bone) then hunger in the brain)
continues to distant sites
Reduces transfer of iron to
develop erythroid
precursors in bone marrow
Decrease in food intake
s/s: anorexia and
weight loss Precursor starved for iron
Low RBC production
Anemia
Frailty
Generalized weakness
Weight loss
Decreased mobility
Hematocrit at least 25%
Hemoglobin at least 9g/dL
Decreased oxygen
carrying capacity of the
blood Decreased blood
flow/oxygen to the brain
Difficulty of breathing
Generalized weakness Dizziness
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Unkno Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Unkno Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsKevin Ercia100% (1)
- 08 Entertaining On A Shoestring - Betty Crocker Recipe Card LibraryDokument60 Seiten08 Entertaining On A Shoestring - Betty Crocker Recipe Card LibraryKenneth100% (6)
- Cervical Cancer PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCervical Cancer PathophysiologyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- TAHBSO PathophysiologyDokument5 SeitenTAHBSO Pathophysiologybregette50% (2)
- Case Study (Asthma)Dokument3 SeitenCase Study (Asthma)AIM50% (4)
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerDokument2 SeitenPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerJie BandelariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Endometrial HyperplasiaDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Endometrial Hyperplasiatinatin989100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Book Based Myoma UteriDokument1 SeitePathophysiology Book Based Myoma UteriChristina Barroga0% (1)
- Jareds BoyDokument31 SeitenJareds BoyAnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forgotten Realms Archetypes Savagery & Shadow (11293249) PDFDokument55 SeitenForgotten Realms Archetypes Savagery & Shadow (11293249) PDFMark Avrit100% (12)
- Modifiedpatho ToyodaDokument4 SeitenModifiedpatho ToyodaCaneEscabarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Dokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Moses Gabriel ValledorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular AberrationDokument6 SeitenCellular AberrationNeslie Lagare SamonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagram2 PDFDokument1 SeiteDiagram2 PDFjanna mae patriarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 106 Cellular-AberrationDokument6 SeitenNCM 106 Cellular-AberrationJoanne TolopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CancerDokument16 SeitenCancerRobert َMirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Print 3Dokument2 SeitenPrint 32080500Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument8 SeitenModule 4Pauline GamlangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaDokument3 SeitenPatho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaBESA JERIC FLORESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer Hallmark 1 (From Jargonwall - Com)Dokument9 SeitenCancer Hallmark 1 (From Jargonwall - Com)eihimekpen02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Malignant: Malignant Transformation: Retrovirus (RNA Virus)Dokument3 SeitenBenign Malignant: Malignant Transformation: Retrovirus (RNA Virus)ChiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncology Pathology Tanuvas NotesDokument17 SeitenOncology Pathology Tanuvas NotesNagesh NNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPP of The Malignant Process: Oncology: Nursing Management in Nursing CancerDokument3 SeitenPPP of The Malignant Process: Oncology: Nursing Management in Nursing Cancer알파Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slides Carcinogenesis Basic PrinciplesDokument62 SeitenSlides Carcinogenesis Basic PrinciplesOnder AydogmusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNDokument20 SeitenEsophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNAnn SalvatierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Intro OpathDokument5 Seiten1 - Intro Opathcath.rada17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Uterine FibroidsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Uterine FibroidsNathaniel SupanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEOPLASIA ExpDokument17 SeitenNEOPLASIA ExpYuris AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis of Neoplasm PDFDokument3 SeitenPathogenesis of Neoplasm PDFTasya Citra KiranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Malignant 2023Dokument62 Seiten4 - Malignant 2023drsafwatismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- UterusDokument8 SeitenUterusyaraabdulkaderaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumor Markers Week 8 Reviewer TypeDokument5 SeitenTumor Markers Week 8 Reviewer TypeROSALINA MALAIKA III PARARUANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostate Cancer Patho (Patient Based) by Francis OliverosDokument2 SeitenProstate Cancer Patho (Patient Based) by Francis Oliverosfrancis00090100% (3)
- 4 ConceptDokument1 Seite4 ConceptStacey GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi. Pathophysiology Benign Tumors of The UterusDokument1 SeiteXi. Pathophysiology Benign Tumors of The UterusWengel RedkissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi. Pathophysiology Benign Tumors of The UterusDokument1 SeiteXi. Pathophysiology Benign Tumors of The UterusWengel RedkissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of Neoplasia Cancer Malignant Benign Carcinoma Lecture PDFDokument8 SeitenPathology of Neoplasia Cancer Malignant Benign Carcinoma Lecture PDFjax111Noch keine Bewertungen
- II. Schematic Pathophysiology Diagram: Risk FactorsDokument1 SeiteII. Schematic Pathophysiology Diagram: Risk FactorsEarl MarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiologyofbreastcancer2 121124072801 Phpapp01Dokument4 SeitenPathophysiologyofbreastcancer2 121124072801 Phpapp01Gerome ManantanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finals ReviewerDokument35 SeitenFinals Reviewerimlookingforyou.03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neoplasia: Neo+ PlasiaDokument4 SeitenNeoplasia: Neo+ PlasiaKieran LeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Abberration Transes Lesson 1-3Dokument10 SeitenCellular Abberration Transes Lesson 1-3RHEA ROSE GACHONoch keine Bewertungen
- Eca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalDokument29 SeitenEca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalFrancis Alfred EscaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageDokument1 SeitePathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageMoses Gabriel ValledorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of H MoleDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of H MoleHenzbely JudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netic Cancer Sem Jan 2022Dokument66 SeitenNetic Cancer Sem Jan 2022AIMAN MUHAIMMIN HASNANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho Breast CancerDokument2 SeitenPatho Breast CancerMaythresha GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho of CA & Breast CaDokument3 SeitenPatho of CA & Breast CaAngeline EspinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Dokument3 SeitenEctopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Alexe Nicole BiscanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Prof - Barmawi H - Carcinoma, Efusi PleuraDokument48 Seiten09 Prof - Barmawi H - Carcinoma, Efusi PleuraRama BiomantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of SarcoidosisDokument1 SeiteCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of SarcoidosisCleobebs AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDokument1 SeiteBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- Genetics Finals 1Dokument19 SeitenGenetics Finals 1EDLENE JOY ALBANIELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marjolin Ulcer POSTER (RSCM)Dokument1 SeiteMarjolin Ulcer POSTER (RSCM)Juli Jamnasi100% (1)
- BookDokument11 SeitenBookNeeru GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Aberrations Cancer, Malignant Neoplasm, Oncologic DisorderDokument5 SeitenCellular Aberrations Cancer, Malignant Neoplasm, Oncologic DisorderIrish Eunice Felix100% (1)
- Book Based Risk Factor Tall For Age Repeated Trauma Hereditary Exposure To RadiationDokument2 SeitenBook Based Risk Factor Tall For Age Repeated Trauma Hereditary Exposure To RadiationJenievieve MerzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PELVIC TUMOR PATHO - DrawioDokument7 SeitenPELVIC TUMOR PATHO - DrawioMarvie TorralbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding CancerDokument5 SeitenUnderstanding CancerEunice Villa CuñadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemotherapy AgentsDokument12 SeitenChemotherapy Agentsaaliyah frances habawelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedsteffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical and Molecular Aspects of Selected CancersVon EverandBiochemical and Molecular Aspects of Selected CancersThomas G. PretlowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathobiology of the Endothelial CellVon EverandPathobiology of the Endothelial CellHymie L. NosselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study (Asthma)Dokument3 SeitenCase Study (Asthma)AIM100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument62 SeitenNursing Care PlanAIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Patterns of Functioning and Levels of Competencies: AnalysisDokument5 SeitenI. Patterns of Functioning and Levels of Competencies: AnalysisAIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac MonitoringDokument6 SeitenCardiac MonitoringAIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med MNGTDokument7 SeitenMed MNGTAIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) ?: Other Symptoms IncludeDokument3 SeitenWhat Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) ?: Other Symptoms IncludeAIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Which Is A Gram-Positive, Acid-Fast Aerobic Bacillus and CanDokument15 SeitenPulmonary Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Which Is A Gram-Positive, Acid-Fast Aerobic Bacillus and CanAIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leo GoatDokument5 SeitenLeo GoatIndre IndraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- THBT Animal Testing Should Be BannedDokument3 SeitenTHBT Animal Testing Should Be BannedFabio RizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branchial Cleft CystsDokument8 SeitenBranchial Cleft CystsHere LeafsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level H - Animals AnimalsDokument16 SeitenLevel H - Animals AnimalsPhạm Thị Hồng ThuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 030722the Physiology of MicturitionDokument3 Seiten030722the Physiology of MicturitionAnnizah Paramitha100% (1)
- The Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryDokument20 SeitenThe Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryBertran RousseauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 - Second Period - Set BookDokument5 SeitenGrade 10 - Second Period - Set BookMoh ArtkwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Final Exam - Glory 2017 PDFDokument14 SeitenPhysiology Final Exam - Glory 2017 PDFMohammad BarakatNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Deforestation On Wildlife Along The Transamazon HighwayDokument8 SeitenThe Effects of Deforestation On Wildlife Along The Transamazon HighwayCleber Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Lab1 TerminologyDokument4 SeitenAnswers Lab1 TerminologyColleen Mae MaciasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.2 MovementDokument24 Seiten11.2 MovementAndyChoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 Read MeDokument56 SeitenCH 3 Read MeelzianhawkwindNoch keine Bewertungen
- 103 CÂU TỪ VỰNG TỪ ĐỀ CÔ VŨ MAI PHƯƠNGDokument31 Seiten103 CÂU TỪ VỰNG TỪ ĐỀ CÔ VŨ MAI PHƯƠNGDuong Hong AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal SacrificeDokument1 SeiteAnimal SacrificeArab BloodNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Use Case Study For - A Cat-Food Product's Launch Strategy in US MarketDokument11 SeitenA Use Case Study For - A Cat-Food Product's Launch Strategy in US MarketNatasha IlievskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isopod BehaviorDokument4 SeitenIsopod BehaviorCody Griffin100% (1)
- Joyway Std-3-19Dokument40 SeitenJoyway Std-3-19Vharry Watson33% (3)
- How To Analyze People Uncover Sherlock Ho - Patrick LightmanDokument69 SeitenHow To Analyze People Uncover Sherlock Ho - Patrick LightmanRuney DuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prohibited & Restricted Item For IndonesiaDokument13 SeitenProhibited & Restricted Item For IndonesiaAhmad AmirudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dragon Magazine #422Dokument39 SeitenDragon Magazine #422Tristan Takson100% (5)
- Morphology Lecture 1Dokument38 SeitenMorphology Lecture 1Rishabh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Leo WahyuDokument3 SeitenTugas Leo WahyuChowa RemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describing How Muscles Work Activity SheetDokument3 SeitenDescribing How Muscles Work Activity SheetTasnim MbarkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bird Imagery in Portrait of The Artist As A Young ManDokument2 SeitenBird Imagery in Portrait of The Artist As A Young ManProfadeengleza8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Highlights November 2015Dokument44 SeitenHighlights November 2015Milena100% (2)
- Glow PDFDokument6 SeitenGlow PDFDanica MalazarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Sensesquiz 1Dokument2 SeitenQuiz Sensesquiz 1api-396156360100% (2)