Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case 4 Anatomic Defect On Pelvic Floor & Urogynecology
Hochgeladen von
cbac19900 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten1 SeiteCase 4 Anatomic Defect on Pelvic Floor & Urogynecology
Originaltitel
Case 4 Anatomic Defect on Pelvic Floor & Urogynecology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCase 4 Anatomic Defect on Pelvic Floor & Urogynecology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten1 SeiteCase 4 Anatomic Defect On Pelvic Floor & Urogynecology
Hochgeladen von
cbac1990Case 4 Anatomic Defect on Pelvic Floor & Urogynecology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
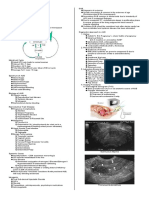
CASE 04: ANATOMIC DEFECT ON PELVIC FLOOR & UROGYNECOLOGY
CASE 4
65 year old G7P7 (7007) consulted because of an introital mass, which she noted 3 years. Lately she feels the need to reduce
the mass inside the vagina to be able to urinate. PMH: COPD on pulmonary rehabilitation since 2008. She has been menopausic
since age 52 with no episodes of postmenopausal bleeding. OB history: 7 NSD, biggest baby: 8 lbs. PPE: external genitalia –
\ anterior and posterior vaginal walls protrude 3 cms beyond the hymen, cervix is smooth and descends 3 cms below the level of
the hymen; uterus is small; adnexa – no masses & tenderness; RVE: (+); Stress test (+); Bonney test (+).
CC: Introital Mass: POP Q numbers:
Is it a mass within the vagina or protruding out the vulva?
For the case, the mass is already out of the vulva because
she has to push the mass inside the vagina for the past 3
years
ADDITIONAL DATA NEEDED:
Gen Data: Occupation - heavy lifting, prolonged standing
NSD
Where were these deliveries done?
Hospital: performed Episiotomy In the past, there are no numbers. The products of anterior
Home delivery: unlicensed to perform Episiotomy vaginal wall correspond to what used to be called a Cystocoele.
Menopause
Still important that after she have menopause, did
she had any symptoms? Did she receive any
hormonal treatment? (Symptomatic: 50% Women)
ROS: Urinary System (very important)
Frequency of urination
How often do you urinate during the day?
Presence of urinary incontinence:
Can you still control urination? Is there involuntary
voiding when you laugh, cough or strain?
What descends? BLADDER
To know kind of UI (stress, overflow, detrusor
Prolapse of anterior vaginal wall is represented by Aa & Ba
muscle), Do URODYNAMIC STUDIES
Symptoms of Anterior Vaginal Wall Prolapse:
Risk Factor for the weakening of the pelvic masses or
Urinary frequency
supporting structures for the uterus:
Introital mass (felt when washing)
65 years old, menopausic since age 52
Residual urine (when the residual urine does not come
PE: (Lithotomy position) out, some place their finger in the vagina then push
Inspection: bladder up)
Grand multiparous - see the beginning of the vaginal Stagnant urine makes the patient prone to frequent
canal, the labia are already apart from one another attacks of urinary infection
Nulliparous – only the labia minora & majora
Cystocoele represented by the new term: Aa & Ba
When you ask the patient to strain, you will see the If C prolapses, uterus will start to go down held by several
gradual appearance of the cervix, recognized by external ligaments
os Strongest ligament: Cardinal or Mackenrodt's ligament
As you strain further, you will be able to observe the: What happens? The ligaments that hold the uterus in
o Prolapse of the anterior vaginal wall, posterior place becomes lax as an effect of pregnancy, delivery,
vaginal wall & uterus. occupation, menaupasal state…
o Involuntary loss of urine
Uterine prolapse: "Buwa"
PREPARATION FOR PELVIC EXAM: Uterus going down to the vagina, to the vulva
Normally: Empty Bladder Most likely accompanied by the prolapse of both anterior
Case, Presence of Urinary Incontinence: Full bladder & posterior vaginal wall
(+) Stress Test Recommended treatment:
(+) = Incontinence Principle:
Urinary Stress Incontinence – due to weakness of the o Take off the uterus that prolapses,
urethra-vesical angle o Strengthen the pubocervical fascia,
o Strengthen the posterior pararectal fascia.
(+) Bonney test Vaginal hysterectomy (not abdominal) with anterior and
(+) = No loss of urine, can be corrected surgically posterior repair + suspension operation for the stress
incontinence
2 fingers placed in below the urethral orifice to make the
urethra-vesical angle smaller make the patient strain
IF patient just had MI, she cannot be operated. You can push it
back inside the pelvis & block the prolapse by means of a
DIAGNOSIS:
PESSARY.
POP AaBaApBp,C + 3
Anterior (Aa,Ba) & posterior vaginal walls (Ap,Bp)
protrude 3 cms beyond the hymen, cervix (C) is smooth
and descends 3 cms below the level of the hymen
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Gynecology - Case 14 - Benign Lesions For Ovaries (Gonzalez)Dokument2 SeitenGynecology - Case 14 - Benign Lesions For Ovaries (Gonzalez)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFDokument3 SeitenGyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Dokument2 SeitenGynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Dokument2 SeitenGynecology - Case 13 - Benign Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Lec 03 CytologyDokument3 SeitenGyne - Lec 03 Cytologycbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne Notes Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - Dra TrinidadDokument3 SeitenGyne Notes Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - Dra Trinidadcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFDokument3 SeitenGyne - Case 18 - Neoplastic Lesions of The Ovaries (Gonzalez) PDFcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Dokument1 SeiteGyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 14 Benign Lesions of The OvariesDokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 14 Benign Lesions of The Ovariescbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 16 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of Cervix (Gonzalez)Dokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 16 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of Cervix (Gonzalez)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 16 Neoplastic Lesions of The CevixDokument1 SeiteGyne - Case 16 Neoplastic Lesions of The Cevixcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)Dokument1 SeiteGyne - Case 17 - Intraepithelial & Neoplastic Lesions of The Uterus (Gonzalez)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 12 Upper Genital UTIDokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 12 Upper Genital UTIcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & VaginaDokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & Vaginacbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 08 Dysmenorrhea & Endometriosis PDFDokument3 SeitenGyne - Case 08 Dysmenorrhea & Endometriosis PDFcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)Dokument1 SeiteGyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 10 MenopauseDokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 10 Menopausecbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 13 Benign Lesions of The UterusDokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 13 Benign Lesions of The Uteruscbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 11 Lower Genital UTI PDFDokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 11 Lower Genital UTI PDFcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)Dokument1 SeiteGyne - Case 07 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperprolactinemia)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 9 Infertility PDFDokument4 SeitenCase 9 Infertility PDFcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 06 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperandrogenism)Dokument2 SeitenGyne - Case 06 Secondary Amenorrhea (Hyperandrogenism)cbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Case 05 Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokument3 SeitenGyne - Case 05 Abnormal Uterine Bleedingcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary AmenorrheaDokument3 SeitenCase 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary Amenorrheacbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1 History & PEDokument3 SeitenCase 1 History & PEcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary AmenorrheaDokument3 SeitenCase 3 Congenital Anomalies, Primary Amenorrheacbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 2 Pre-Op & Post-Op CareDokument1 SeiteCase 2 Pre-Op & Post-Op Carecbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- PTAL Residency CaliforniaDokument24 SeitenPTAL Residency Californiacbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- AMC-Residency CV Worksheet-III PDFDokument1 SeiteAMC-Residency CV Worksheet-III PDFcbac1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Quiz 9 Human Reproduction Pregnancy Menstruation GraphsDokument4 SeitenQuiz 9 Human Reproduction Pregnancy Menstruation Graphsrafiqah nasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animation ListDokument10 SeitenAnimation ListFranchelys marie Reyes de la cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Reproductive SystemDokument4 SeitenThe Female Reproductive SystemIvygrace Ampodia-SanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asuhan Keperawatan Kegawatdaruratan Maternal Pada Kasus Ket: Maria Lupita Nena MeoDokument20 SeitenAsuhan Keperawatan Kegawatdaruratan Maternal Pada Kasus Ket: Maria Lupita Nena MeoCathleen GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDO - TARLAC CITY - MABALACAT - CSE MODULE - HUMAN AND BODY DEVELOPMENT For 4th 2Dokument28 SeitenSDO - TARLAC CITY - MABALACAT - CSE MODULE - HUMAN AND BODY DEVELOPMENT For 4th 2Ma Concepcion Adriano GuansingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Clinical Reference Chart For Visual Inspection With Acetic Acid (VIA)Dokument1 SeiteQuick Clinical Reference Chart For Visual Inspection With Acetic Acid (VIA)Alie MourtezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Cee Model ExaminationDokument72 SeitenOnline Cee Model ExaminationPrepladder ChayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & TypesDokument1 SeiteCervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & Typesramit singlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Genitalia and RectumDokument3 SeitenFemale Genitalia and Rectumadrian lozanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 4.1 AFS Classifi Cation System (: The Embryological-Clinical Classifi CationDokument111 SeitenTable 4.1 AFS Classifi Cation System (: The Embryological-Clinical Classifi CationArya Syafaromania RachmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Female AnatomyDokument1 SeiteExternal Female AnatomybabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejaculation: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokument14 SeitenEjaculation: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searchmarlenrez perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetri: Uswatul Khoirot, S. KedDokument19 SeitenObstetri: Uswatul Khoirot, S. KedNovia RizqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- !special Cunnilingus Techniques and SecretsDokument7 Seiten!special Cunnilingus Techniques and Secretsanon-71392793% (41)
- Yeny Elfiyanti - 1910070100082 - Tugas Praktikum Anatomi 2Dokument5 SeitenYeny Elfiyanti - 1910070100082 - Tugas Praktikum Anatomi 2Yeny ElfiyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Dokument6 SeitenSession #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Complete Vaginal Discharge Color GuideDokument3 SeitenA Complete Vaginal Discharge Color GuideAmna SerafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDokument11 SeitenAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemLenovo Legion Y520Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anomaly Genital in Children - RandyDokument47 SeitenAnomaly Genital in Children - RandyAdhyatpNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Genital Organ: - Internal Female Genital Organs - External Female Genital OrgansDokument14 SeitenThe Female Genital Organ: - Internal Female Genital Organs - External Female Genital OrgansAgus Hendra JayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive OrgansDokument42 SeitenFemale Reproductive Organsaliyah nerz83% (6)
- Science5 q2 Mod1 ThePartsOfTheReproductiveSystemAndTheirFunctions v2Dokument24 SeitenScience5 q2 Mod1 ThePartsOfTheReproductiveSystemAndTheirFunctions v2Shiela AsiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28-01 - The Reproductive SystemDokument18 Seiten28-01 - The Reproductive SystemMelinda AprilyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skenario A Blok 17 L3 FixDokument35 SeitenSkenario A Blok 17 L3 FixSelli Novita BelindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penis Enlargement Pump in Pakistan - Handsome Up Penis Enlargement Pump For MenDokument4 SeitenPenis Enlargement Pump in Pakistan - Handsome Up Penis Enlargement Pump For MenSana KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDokument32 SeitenScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive SystemDokument56 SeitenReproductive SystemRochelle Ann CunananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The PenisDokument16 SeitenAnatomy of The PenisKKK777100% (1)
- S5LT-IIa-1.1.1.2.b-Male and Female Reproductive SystemDokument5 SeitenS5LT-IIa-1.1.1.2.b-Male and Female Reproductive SystemRhona Liza CanobasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminal FluidDokument24 SeitenSeminal FluidNicole Edelweiss LizaNoch keine Bewertungen