Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Domperidone Motilium
Hochgeladen von
Kenneth Mark B. Teves0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten2 SeitenDOMPE
Originaltitel
60783730 Domperidone Motilium
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDOMPE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten2 SeitenDomperidone Motilium
Hochgeladen von
Kenneth Mark B. TevesDOMPE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
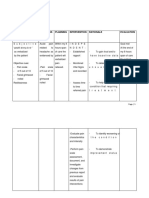
PHARMACOLOGIC SHEET
DRUG ACTION INDICATION/S CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFECTS NURSING
RESPONSIBILITIES
Domperidone Antidopaminergic Symptomatic Contraindicated in Serum prolactin level Teaching points:
(Motillium) Antiemetic management of patients with known may increase resulting in Proper dosing:
1 tab TID upper sensitivity or intolerance galactorrhoea in females Missed dose: Take
gastrointestinal to the drug. (increasing of milk as soon as possible;
motility disorders Domperidone should not production, probably by not taking if almost
associated with be used whenever increasing prolactin time for next
chronic and gastrointestinal production by the pituitary scheduled dose; not
subacute gastritis stimulation might be gland) & less frequently doubling doses.
and diabetic dangerous, i.e., gynaecomastia in males. Obtaining medical
gastroparesis. gastrointestinal CNS: dry mouth (1.9%), attention if fainting,
May also be used hemorrhage, mechanical headache/migraine dizziness, irregular
to prevent obstruction or (1.2%), insomnia, heartbeat or pulse,
gastrointestinal perforation. nervousness, dizziness, or other unusual
symptoms Also contraindicated in thirst, lethargy, irritability symptoms occur.
associated with the patients with a prolactin- (all<1%).
use of dopamine releasing pituitary tumor Gastrointestinal (2.4%):
agonist (prolactinoma). abdominal cramps,
antiparkinsonian diarrhea, regurgitation,
agents. changes in appetite,
nausea, heartburn,
constipation (all<1%).
Endocrinological (1.3%):
hot flushes, mastalgia,
galactorrhea,
gynecomastia, menstrual
irregularities.
Mucocutaneous (1.1%):
rash, pruritus, urticaria,
stomatitis, conjunctivitis.
Urinary (0.8%): urinary
frequency, dysuria.
Cardiovascular (0.5%):
edema, palpitations.
Musculoskeletal (0.1%):
leg cramps, asthenia.
Miscellaneous (0.1%):
drug intolerance.
Laboratory parameters:
elevated serum prolactin,
elevation of AST, ALT and
cholesterol (all<1%).
Extrapyramidal
phenomena are rare in
adults; they reverse
spontaneously as soon
as treatment is stopped.
When the blood-brain
barrier is immature (as in
infants) or impaired, the
possible occurrence of
neurological side effects
cannot be excluded.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- I. General InformationDokument9 SeitenI. General InformationIlda Lekka RequizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domperidone MotiliumDokument2 SeitenDomperidone MotiliumKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- As An Innocent ChildDokument6 SeitenAs An Innocent ChildKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baldder Cancer By: Teves Kenneth Teves B. BSN IIIDokument7 SeitenBaldder Cancer By: Teves Kenneth Teves B. BSN IIIKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuhra Region12 and Armm Agenda PDFDokument17 SeitenNuhra Region12 and Armm Agenda PDFKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Data Base For Family Nursing PracticeDokument18 SeitenInitial Data Base For Family Nursing PracticeKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac-Tamponade With HighlightsDokument4 SeitenCardiac-Tamponade With HighlightsKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument3 SeitenCase StudyKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 NUR1021 Calculation of Basic IV Drip Rates - InstructorDokument39 Seiten2016 NUR1021 Calculation of Basic IV Drip Rates - InstructorMikhaelEarlSantosTacorda100% (1)
- Actual Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument11 SeitenActual Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationNoli Galope IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Acknowledgement Sample 02Dokument2 SeitenAcknowledgement Sample 02Shania ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReflectionDokument2 SeitenReflectionNoli Galope IINoch keine Bewertungen
- NiceDokument45 SeitenNiceKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Blood PressureDokument10 SeitenHigh Blood PressureKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Urinary Pathogens Isolated From Two Tertiary Hospitals in Southwestern NigeriaDokument11 SeitenAntimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Urinary Pathogens Isolated From Two Tertiary Hospitals in Southwestern NigeriaKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referral PhilippinesDokument42 SeitenReferral Philippinesemed vsmmcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium Chloride - Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsDokument4 SeitenPotassium Chloride - Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDokument5 SeitenDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOHStat Health Status-MortalityDokument25 SeitenDOHStat Health Status-MortalityKenn yahweexNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOHStat Health Status-MortalityDokument25 SeitenDOHStat Health Status-MortalityKenn yahweexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych406-5 3 2Dokument8 SeitenPsych406-5 3 2api-287406663Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Urinary Pathogens Isolated From Two Tertiary Hospitals in Southwestern NigeriaDokument11 SeitenAntimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Urinary Pathogens Isolated From Two Tertiary Hospitals in Southwestern NigeriaKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument9 SeitenNursing Care PlanKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute PyelonephritisDokument6 SeitenAcute PyelonephritisKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute PyelonephritisDokument6 SeitenAcute PyelonephritisKenneth Mark B. TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Comparitive Study of Pile Foundations With Foundations On Stone Column Treated Ground 170704090313Dokument23 SeitenComparitive Study of Pile Foundations With Foundations On Stone Column Treated Ground 170704090313anurag hazarikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEB Korba THERMAL POWER PLANT Mechanical Training ReportDokument20 SeitenCSEB Korba THERMAL POWER PLANT Mechanical Training Reporthaxxo24Noch keine Bewertungen
- SinusitisDokument402 SeitenSinusitisIsidro Roberto Santana Gonzalez100% (1)
- Manualevu VheDokument60 SeitenManualevu VheThariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hilti AnchorsDokument202 SeitenHilti AnchorsmwendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying Operation: Meika Syahbana RusliDokument69 SeitenDrying Operation: Meika Syahbana RusliFrida GinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antithesis Essay Joseph JaroszDokument3 SeitenAntithesis Essay Joseph JaroszJoseph JaroszNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEQUERED PLATE - Engineer DiaryDokument9 SeitenCHEQUERED PLATE - Engineer DiaryAnonymous imkwF8N7TeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hide and DrinkDokument562 SeitenHide and DrinkMao Lee100% (1)
- Lean Six Sigma Green BeltDokument7 SeitenLean Six Sigma Green Beltmulpuru sai snehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusDokument4 Seiten4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusZia Ammarah SaripNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8Dokument2 SeitenGeared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8seetharaman K SNoch keine Bewertungen
- SWT Nedelka Cartagena enDokument2 SeitenSWT Nedelka Cartagena enChristian Lazo FerreyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Reproduction Practice ExamDokument5 SeitenCell Reproduction Practice Examjacky qianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)Dokument5 SeitenEnzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)Mrs Rehan100% (1)
- 1402AHS Prac Manual - 2023 - FINALDokument200 Seiten1402AHS Prac Manual - 2023 - FINALRuan BritsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AscindiaDokument16 SeitenAscindiaHeeman TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT VT Basics SonnenbergDokument71 SeitenCT VT Basics SonnenbergAnonymous OCDJg17Z67% (3)
- Annual Report - TakedaDokument50 SeitenAnnual Report - TakedaAbdullah221790Noch keine Bewertungen
- EO MNC 10 June 2022Dokument4 SeitenEO MNC 10 June 2022LeulaDianneCantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSE Issues Tracker - DAFDokument28 SeitenHSE Issues Tracker - DAFMohd Abdul MujeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Psychology (2022)Dokument642 SeitenIntroduction To Psychology (2022)hongnhung.tgdd2018Noch keine Bewertungen
- Icu2 Vol22 Sepsisincriticalcare 29marchDokument52 SeitenIcu2 Vol22 Sepsisincriticalcare 29marchricardoatejassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contextual Marketing Based On Customer Buying Pattern In: Nesya Vanessa and Arnold JaputraDokument12 SeitenContextual Marketing Based On Customer Buying Pattern In: Nesya Vanessa and Arnold Japutraakshay kushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Rhodamine B (C.I.45170) For MicrosDokument9 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Rhodamine B (C.I.45170) For MicrosSeshagiri KalyanasundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Installation - AfbcDokument2 SeitenBoiler Installation - AfbcSarah FrazierNoch keine Bewertungen
- M 17Dokument5 SeitenM 17amhm2000100% (1)
- 9 F 957375 B 361250 FB 704Dokument15 Seiten9 F 957375 B 361250 FB 704api-498018677Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyDokument2 SeitenBergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyGeetha Anjali0% (1)
- Physical, Chemical and Biological HazardsDokument32 SeitenPhysical, Chemical and Biological HazardsDaisy ObisoNoch keine Bewertungen