Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Percussion 2. Vibration 3. Shaking
Hochgeladen von
Mokibul0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
132 Ansichten2 SeitenPostural drainage is a technique that uses gravity and body positioning to drain secretions from the bronchial airways. It involves having the patient lay in different positions while deep breathing and coughing to clear mucus. Manual techniques like percussion, vibration, and shaking are applied to the chest wall to help mobilize secretions during exhalation. The sequence of positions is maintained for 5-10 minutes to effectively drain the lungs. Postural drainage is indicated for patients who are bedridden or have conditions involving increased mucus production.
Originalbeschreibung:
postural drainage
Originaltitel
postural drainage
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenPostural drainage is a technique that uses gravity and body positioning to drain secretions from the bronchial airways. It involves having the patient lay in different positions while deep breathing and coughing to clear mucus. Manual techniques like percussion, vibration, and shaking are applied to the chest wall to help mobilize secretions during exhalation. The sequence of positions is maintained for 5-10 minutes to effectively drain the lungs. Postural drainage is indicated for patients who are bedridden or have conditions involving increased mucus production.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
132 Ansichten2 SeitenPercussion 2. Vibration 3. Shaking
Hochgeladen von
MokibulPostural drainage is a technique that uses gravity and body positioning to drain secretions from the bronchial airways. It involves having the patient lay in different positions while deep breathing and coughing to clear mucus. Manual techniques like percussion, vibration, and shaking are applied to the chest wall to help mobilize secretions during exhalation. The sequence of positions is maintained for 5-10 minutes to effectively drain the lungs. Postural drainage is indicated for patients who are bedridden or have conditions involving increased mucus production.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
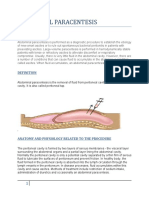
INTRODUCTION
It is a technique in which different positions are assumed to facilate the drainage of secretions
from the bronchial airways. Gravity helps to move the secretions to the tracheae to be coughed
up easily.
PREPARATION OF POSTURAL DRAINAGE
Loose and tight or bulky clothes.
Sputum cup or tissue paper.
Explain the treatment procedure to the patient.
Teach the patient to deep breathe prior to postural drainage.
Make any adjustment tube and wires such as test tubes, electrocardiography wire.
MANUAL TECHNIQUES
1. Percussion
2. Vibration
3. Shaking
Percussion: Percussion is an assessment technique which produces sounds by the examiner
tapping on the patient's chest wall. Just as lightly tapping on a container with your hands
produces various sounds, so tapping on the chest wall produces sounds based on the amount of
air in the lungs. Percussion sets the chest wall and underlying tissues into motion, producing
audible sounds and palpable vibrations. Percussion helps to determine whether the underlying
tissues are filled with air, fluid, or solid material.
Vibration:
It is also used to mobilize secretion to larger airways.
It is applied during the expiratory phase.
Vibration is applied by placing both hands directly on the skin over the chest wall and
gently compressing and rapidly vibrating the chest wall as the patient breaths out.
Shaking:
Shaking is a more vigorous form of vibration applied during exhalation.
The therapist thumbs are locked together.
Then the open hands are placed directly on the patient skin and fingers are wrapped on
the chest wall.
POSTURAL DRAINAGE SEQUENCE
Check the patient vital signs and breathe signs.
Correct positions should be given to the patient.
Maintain its positions for 5-10 minutes. If the patient can tolerate it or as long as the
position is productive.
Have the patient breathe deeply during postural drainage.
Encourage the patient to take a deep, sharp double cough whenever necessary.
INDICATIONS
Bed ridden patient
Those who have received general anesthesia
Painful incision causing restricted deep breathing and coughing
Diseases with increased production or viscosity of mucous
Pneumonia
Acute lung disease
Lung abscess
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Over fracture
Osteoporotic bone
Over tremor area
Trauma
Post thoracic surgery
Chest wall pain
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ThoracentesisDokument4 SeitenThoracentesisCyntia Theresia Lumintang100% (1)
- Seminar On ETDokument10 SeitenSeminar On ETISLAMIC KNOWLEDGE BASED ON TRULY HADISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On AtelectasisDokument14 SeitenCase Study On AtelectasisSanhati Ghosh BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Assignmnet 4Dokument4 SeitenAdvance Assignmnet 4CharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration On ParacentesisDokument10 SeitenDemonstration On ParacentesisDeepika PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETT IntubationDokument10 SeitenETT IntubationPoova RagavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL NO Content NODokument12 SeitenSL NO Content NOPdianghunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Writing Styles: Mrs. Monika Sharma Lecturer, DMCH, CON, Ludhiana. PunjabDokument82 SeitenReference Writing Styles: Mrs. Monika Sharma Lecturer, DMCH, CON, Ludhiana. PunjabNavpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On: Oxygen Administrration (Nasal Catheter, Mask, Oxygen Hood& Cpap)Dokument10 SeitenAssignment On: Oxygen Administrration (Nasal Catheter, Mask, Oxygen Hood& Cpap)Suganthi ParthibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PERITONITSDokument3 SeitenPERITONITSjyoti kundu100% (1)
- Assignment ON: TOPIC: PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminous Coronary Angioplasty)Dokument7 SeitenAssignment ON: TOPIC: PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminous Coronary Angioplasty)soniya josephNoch keine Bewertungen
- MENINGITIS Lesson PlanDokument12 SeitenMENINGITIS Lesson PlannidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assesment For Burns and Fluid Calculation PDFDokument10 SeitenAssesment For Burns and Fluid Calculation PDFRagaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cardiac ProcedureDokument9 SeitenAdvanced Cardiac ProcedureSachin DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung AbscessDokument46 SeitenLung AbscessJeevitha VanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endotracheal IntubationDokument11 SeitenEndotracheal Intubationanon_784834955100% (1)
- Central Venous Line CareDokument13 SeitenCentral Venous Line CarePaul Henry RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan BMA&BDokument14 SeitenLesson Plan BMA&BLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endotracheal IntubationDokument1 SeiteEndotracheal IntubationAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tracheostomy: S.No: Time Specific Objective Content Teachin G Activity Learning Activity Av Aids EvaluationDokument13 SeitenTracheostomy: S.No: Time Specific Objective Content Teachin G Activity Learning Activity Av Aids EvaluationaparnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANGIOGRAPHYDokument8 SeitenANGIOGRAPHYAkazukin AineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Function TestsDokument2 SeitenPulmonary Function TestsSafuan Sudin100% (1)
- Abg AnalysisDokument9 SeitenAbg AnalysisLakshmi RjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Nursing Practice: KMC College of Nursing, MeerutDokument29 SeitenAdvance Nursing Practice: KMC College of Nursing, MeerutJyoti Prem UttamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDokument4 SeitenHemodynamic Monitoringgurneet kourNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUBMITTED TO - Resp. Mr. Somorjit SinghDokument8 SeitenSUBMITTED TO - Resp. Mr. Somorjit SinghSimran JosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arterial Blood Gas (Abg) Analysis: Submitted ToDokument5 SeitenArterial Blood Gas (Abg) Analysis: Submitted ToRumela ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse OximetryDokument3 SeitenPulse OximetryJanna Favila100% (3)
- Lung Abscess: BackgroundDokument12 SeitenLung Abscess: BackgroundTaufik TiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Coronary Angiogram Is A Procedure That Uses XDokument5 SeitenA Coronary Angiogram Is A Procedure That Uses XSathya PatcheappinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculin Skin TestDokument5 SeitenTuberculin Skin TestAmit MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Clinical TeachingDokument21 SeitenECG Clinical TeachingSumi SajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDokument6 SeitenLab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDaisy MellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suture RemovalDokument42 SeitenSuture RemovalVishnu PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Dokument9 SeitenCardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Prince Rener Velasco PeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christian College of Nursing AsirDokument60 SeitenChristian College of Nursing AsirAnonymous aqeaNUn100% (1)
- MT Vitals Signs - RespirationDokument11 SeitenMT Vitals Signs - RespirationpriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burns DressingDokument4 SeitenBurns DressingBalaMuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT Plan Charu Final Ana 1Dokument7 SeitenUNIT Plan Charu Final Ana 1Manisha SamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisting With Arterial Puncture For Blood Gas Analysis EquipmentDokument7 SeitenAssisting With Arterial Puncture For Blood Gas Analysis EquipmentPoova RagavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Oximetry IDokument4 SeitenPulse Oximetry IFriends Forever100% (1)
- Jabalpur (M.P.) : Subject - Management Nursing Assignment ONDokument9 SeitenJabalpur (M.P.) : Subject - Management Nursing Assignment ONNikkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP42 Thoracentesis (Adult)Dokument7 SeitenSP42 Thoracentesis (Adult)Adam HuzaibyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suctioning Et SuctioningDokument7 SeitenSuctioning Et SuctioningKoochi PoojithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuctioningDokument13 SeitenSuctioningAmanda ScarletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Rhuematic Heart DiseaseDokument16 SeitenSeminar On Rhuematic Heart Diseasenaga maniNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Assignment ON: Bronchial HygieneDokument12 SeitenAn Assignment ON: Bronchial Hygienesoniya joseph100% (1)
- Administration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyDokument8 SeitenAdministration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyRonald ThakorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of AortaDokument25 SeitenDisorders of Aortavani reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal ParacentesisDokument14 SeitenAbdominal ParacentesisManisha Thakur100% (1)
- Case Presentation On Chronic Osteomyelitis: Prepared By: Sital Gautam MN1 Year, 2012Dokument55 SeitenCase Presentation On Chronic Osteomyelitis: Prepared By: Sital Gautam MN1 Year, 2012Rabina RajbanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure On Abdominal ParacentsisDokument22 SeitenProcedure On Abdominal ParacentsisBhawna JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiomyopathy SeminarDokument17 SeitenCardiomyopathy SeminarJyoti SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen TherapyDokument3 SeitenOxygen TherapyKristina PingolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Burns 2Dokument15 SeitenAssignment On Burns 2Suby Beigh100% (2)
- Course Plan ON Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing Education: Submittedto: Submitted byDokument10 SeitenCourse Plan ON Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing Education: Submittedto: Submitted byRanjana SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On ICU EquipmentDokument11 SeitenReport On ICU EquipmentZobaeir AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equipment EditedDokument6 SeitenEquipment EditedCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINANoch keine Bewertungen
- Percussion:: o o o o oDokument2 SeitenPercussion:: o o o o oAnonymous b4P7PDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 Respi. Percussion VibrationDokument8 Seiten4.3 Respi. Percussion VibrationRiza Angela BarazanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Communicable Diseases PDFDokument30 SeitenChapter 18 Communicable Diseases PDFcelloguy8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meningoencephalitis Caused by Mycoplasma EdwardiiDokument6 SeitenMeningoencephalitis Caused by Mycoplasma EdwardiiLatifa Putri FajrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 PDFDokument3 SeitenCFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 PDFChristian Garcia RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument3 SeitenPa Tho PhysiologyApril Dianne ParungaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infectious Diseases Oral RevalidaDokument22 SeitenInfectious Diseases Oral RevalidaShella Mae UsquisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Reagent SansureDokument3 SeitenDatasheet Reagent Sansuredanang setiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1Dokument87 SeitenQuestion 1hemihemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan - PCAPDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan - PCAPvonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCI Sep, 10 QnsDokument27 SeitenMCI Sep, 10 QnsdrmeenupNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS LecDokument15 SeitenMS LecAngel YN Patricio FlorentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 @radproflib Richard LindsayDokument313 Seiten2012 @radproflib Richard Lindsaysherief maroufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chandy C. John - Advances in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Infectious Diseases - 2013Dokument212 SeitenChandy C. John - Advances in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Infectious Diseases - 2013Alla AlkateebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thatchiayani Case 1Dokument7 SeitenThatchiayani Case 1Thatchiayani Sweneson100% (1)
- Salam Et Al-2015-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDokument34 SeitenSalam Et Al-2015-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsAna-Mihaela BalanuțaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Manifestation:: Medical ManagementDokument5 SeitenClinical Manifestation:: Medical ManagementChristina BarrogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 OB-Pulmonary Disorders in Pregnancy (Dr. Bautista)Dokument10 Seiten5.1 OB-Pulmonary Disorders in Pregnancy (Dr. Bautista)Monique BorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part I Answer KeyDokument6 SeitenCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part I Answer KeyMitch GatelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionDokument6 SeitenLower Respiratory Tract InfectionFlorence De ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community-Acquired Bacterial Meningitis in Adults: Review ArticleDokument10 SeitenCommunity-Acquired Bacterial Meningitis in Adults: Review ArticleÁlvaro NBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine MCQDokument34 SeitenMedicine MCQRuturaj JadejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal ComfortDokument12 SeitenJurnal ComfortrizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child With Respiratory DisorderDokument48 SeitenChild With Respiratory DisorderEmjay JapitanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (Vap) Sop: V1 February 2018 VAP-02-2018-SK-V1Dokument6 SeitenVentilator Associated Pneumonia (Vap) Sop: V1 February 2018 VAP-02-2018-SK-V1Devi Humairah IrawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Hygiene What Is ItDokument5 SeitenNatural Hygiene What Is ItJonas Sunshine Callewaert100% (1)
- PneumoniaDokument102 SeitenPneumoniaJay Kumar100% (1)
- BRS GS Compilation HIGHLIGHTEDDokument108 SeitenBRS GS Compilation HIGHLIGHTEDJaney T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Community Aquired Pneumonia (: Diagnosis CAP) and Current Management Yunita ArliniDokument12 SeitenCommunity Aquired Pneumonia (: Diagnosis CAP) and Current Management Yunita ArliniSundas EjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- NP3 RatioDokument17 SeitenNP3 RatioArnie Jude CaridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Osteomyelitis in Children - JurdingDokument25 SeitenAcute Osteomyelitis in Children - JurdingTimoty MarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines On Management of Covid-19 Icu PatientDokument32 SeitenGuidelines On Management of Covid-19 Icu PatientBrainy LumineusNoch keine Bewertungen